A-Level Chemistry - Topic 6 - Organic Chemistry I (PART 1 - "The Basics" - "Fuels")
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:39 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
1
New cards
What does a general formula show and what is an example?
an algebraic formula that can describe any member of a family of compounds
\
e.g. Cn H2n+1 = alkanes
\
e.g. Cn H2n+1 = alkanes
2
New cards
What does a empirical formula show and what is an example?
the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
\
e.g. C4H10O
\
e.g. C4H10O
3
New cards
What does a molecular formula show and what is an example?
the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule
\
e.g. C4H10O
\
e.g. C4H10O
4
New cards
What does a structural formula show and what is an example?
shows the arrangement of atoms CARBON BY CARBON
\
with the attached hydrogens and functional groups
\
e.g. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
\
with the attached hydrogens and functional groups
\
e.g. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
5
New cards
What does a skeletal formula show and what is an example?
shows the bonds of the carbon skeleton only
\
(with any functional groups)
\
H and C aren’t shown
\
(with any functional groups)
\
H and C aren’t shown
6
New cards
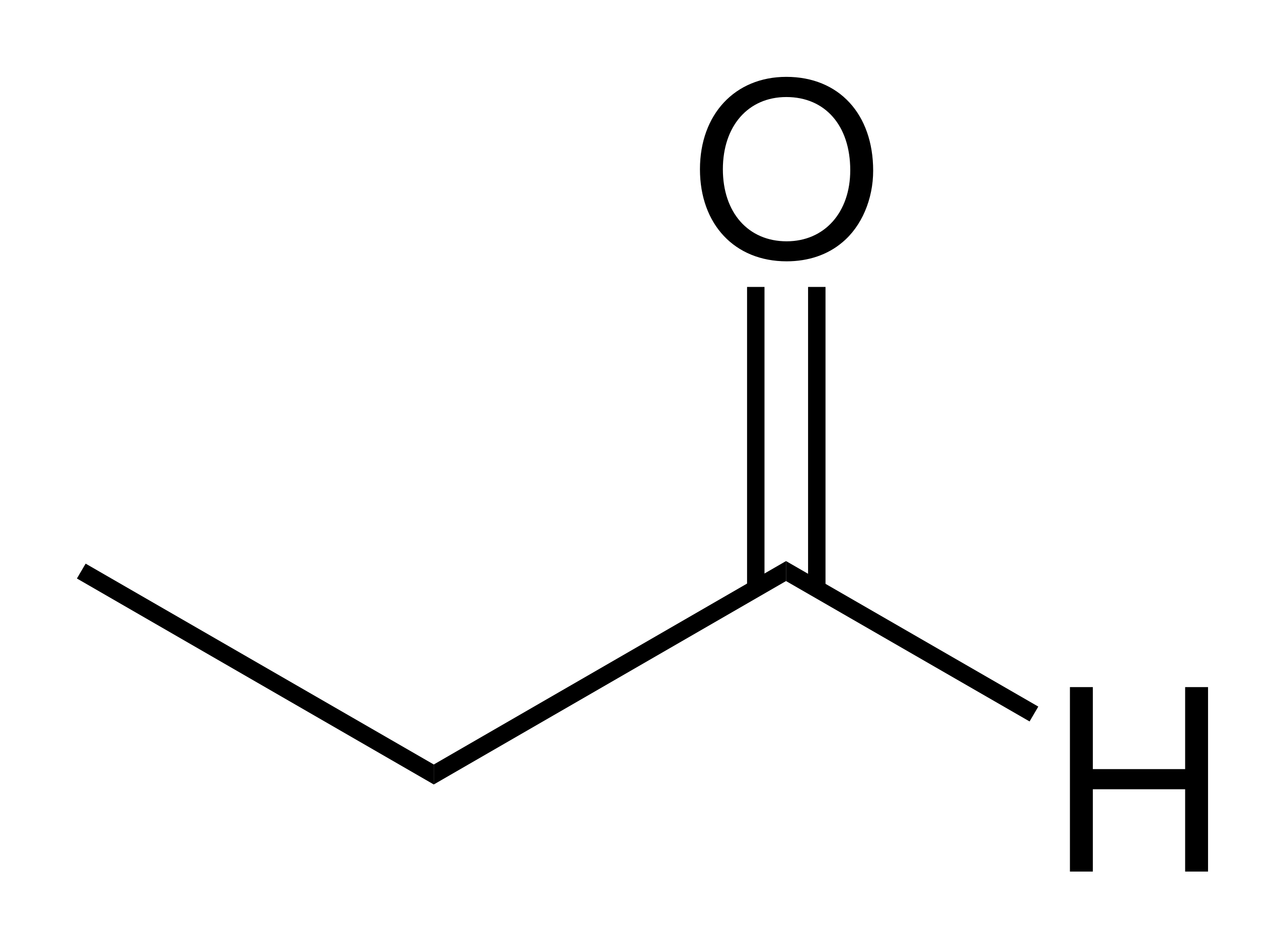
What does a displayed formula show and what is an example?
shows how all the atoms are ARRANGED
\
and shows the bonds between them
\
and shows the bonds between them
7
New cards
What system is used for naming organic compounds
IUPAC
8
New cards
What are members of a homologous series?
a bunch of organic compounds that have the same functional group and general formula
\
consecutive members of a homologous series differ by -CH2-
\
consecutive members of a homologous series differ by -CH2-
9
New cards
What is the prefix/suffix for alkane , branched alkanes, alkenes and halogenoalkanes?
alkane = ane
\
branched alkanes = alkyl (-yl)
\
alkenes = ene
\
halogenoalkanes = -chloro/bromo-/iodo-
\
branched alkanes = alkyl (-yl)
\
alkenes = ene
\
halogenoalkanes = -chloro/bromo-/iodo-
10
New cards
What is the prefix/suffix for alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, cycloalkanes and carboxylic acids?
alcohol = -ol
\
aldehydes = -al
\
ketones = -one
\
cycloalkanes = cyclo-…-ane
\
carboxylic acids = -oic acid
\
aldehydes = -al
\
ketones = -one
\
cycloalkanes = cyclo-…-ane
\
carboxylic acids = -oic acid
11
New cards
What is an addition reaction?
the joining of two+ molecules together to form a larger molecule
12
New cards
What is a polymerisation reaction?
joining together lots of simple molecules to form a giant molecule
13
New cards
What is an elimination reaction?
when a small group of atoms breaks away from a larger molecule
14
New cards
What is a substitution reaction?
when one species is replaced by another
15
New cards
what is a hydrolysis reaction?
splitting a molecule into two new molecules by adding H+ and OH- derived from water
16
New cards
what is an oxidation/reduction reaction?
oxidation = any reaction in which a species loses electrons
\
reduction = any reaction in which a species gains electrons
\
reduction = any reaction in which a species gains electrons
17
New cards
what is a “mechanism”?
diagrams that break reactions down into individual stages to show how substances react together
18
New cards
how do curly arrows work in a mechanism?
starts at the bond/lone pair where the electrons are at the beginning of the reaction
\
points to where the new bond is formed at the end of the reaction/to the atom where the electrons go
\
points to where the new bond is formed at the end of the reaction/to the atom where the electrons go
19
New cards
what is a nucleophile?
electron pair donors
\
often negatively charged ions/species that contain a lone pair of electrons
\
electron rich, so attracted to places that are electron poor
\
\
\
often negatively charged ions/species that contain a lone pair of electrons
\
electron rich, so attracted to places that are electron poor
\
\
20
New cards
what else are nucleophiles attacked by?
molecules with polar bonds
\
since they have 𝛿+ areas
\
since they have 𝛿+ areas
21
New cards
what are electrophiles?
electron pair acceptors
\
often positively charged ions or w/ 𝛿+ areas
\
electron poor, so attracted to places that are electron rich
\
often positively charged ions or w/ 𝛿+ areas
\
electron poor, so attracted to places that are electron rich
22
New cards
what do electrophiles “like” to react with?
negative ions
\
atoms w/ lone pairs
\
the electron-rich areas around a C=C bond
\
atoms w/ lone pairs
\
the electron-rich areas around a C=C bond
23
New cards
What are radicals?
species with an unpaired electron
\
= v. reaction
\
= will react with ANYTHING: positive, negative or neutral
\
= v. reaction
\
= will react with ANYTHING: positive, negative or neutral
24
New cards
what is a problem with radical’s reacting with anything in sight?
probably end up with a mixture of products
\
= radical reactions aren’t useful if after a PURE product
\
\
\
could also take place anywhere along the carbon chain
\
= a mixture of structural isomers can be formed
\
= radical reactions aren’t useful if after a PURE product
\
\
\
could also take place anywhere along the carbon chain
\
= a mixture of structural isomers can be formed
25
New cards
what do isomers have in common (and not)?
the same molecular formula (the actual number of atoms in each element in a molecule)
\
but the atoms are arranged differently
\
\
but the atoms are arranged differently
\
26
New cards
what are structural isomers?
isomers that have different STRUCTURAL ARRANGEMENTS of atoms
\
but the same molecular formula despite having a different structural formula
\
but the same molecular formula despite having a different structural formula
27
New cards
what are the 3 types of structural isomer?
chain isomers
\
positional isomers
\
functional group isomers
\
positional isomers
\
functional group isomers
28
New cards
what is a chain isomer?
the carbon skeleton can be arranged differently
\
= a straight chain OR branched in different ways
\
= a straight chain OR branched in different ways
29
New cards
what similarities/differences to chain isomers have with each other?
similar chemical properties
\
but physical properties (e.g. b.p.) will change due to the shape change
\
but physical properties (e.g. b.p.) will change due to the shape change
30
New cards
what is a positional isomer?
the skeleton and the functional group could be the same
\
only with the functional group attached to a different carbon atom
\
only with the functional group attached to a different carbon atom
31
New cards
what differences do positional isomers have with each other?
different physical + chemical properties
32
New cards
what are functional group isomers?
the same atoms can be arranged into different functional groups
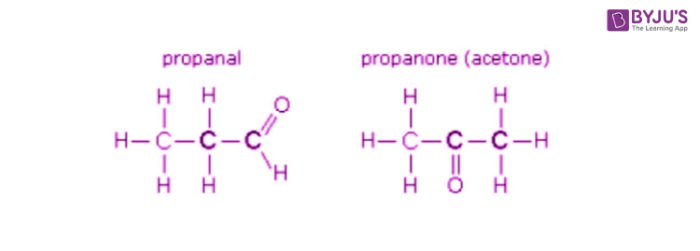
33
New cards
what differences do functional group isomers have with each other?
very different physical + chemical properties
34
New cards
what can atoms do as much as they like around single C-C bonds?
rotate as much as they like
\
= what looks like an isomer may not be one
\
= what looks like an isomer may not be one
35
New cards
What are the two types of bond fission?
heterolytic
\
homolytic
\
homolytic
36
New cards
what is bond fission?
the breaking of a covalent bond
37
New cards
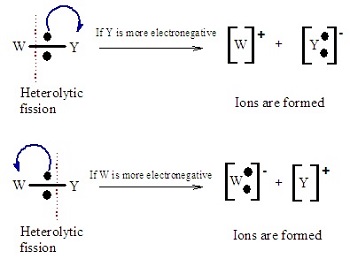
what is heterolytic fission?
when the bond breaks unevenly
\
with one of the bonded atoms receiving both electrons from the bonded pair
\
forms a positively charged cation and a negatively charged anion
\
\
with one of the bonded atoms receiving both electrons from the bonded pair
\
forms a positively charged cation and a negatively charged anion
\
38
New cards
what is homolytic fission?
the bond breaks evenly
\
each bonding atoms receive one electron from the bonded pair
\
2 electrically charged radicals formed (with an unpaired electron)
\
= both v. reactive
\
each bonding atoms receive one electron from the bonded pair
\
2 electrically charged radicals formed (with an unpaired electron)
\
= both v. reactive
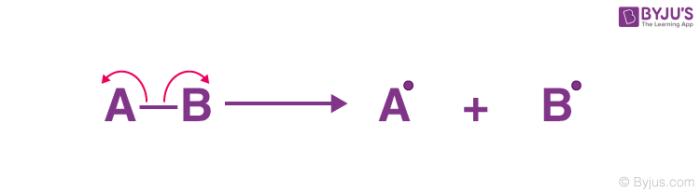
39
New cards
in what type of reaction do halogens react with alkanes?
photochemical reactions
40
New cards
what is a photochemical reaction?
a reaction that required uv light to get going
\
(an example of a radical substitution reaction)
\
(an example of a radical substitution reaction)
41
New cards
what happens during a photochemical reaction?
a hydrogen atom is substituted
\
by chlorine/bromine
\
by chlorine/bromine
42
New cards
what are the three steps in a radical substitution reaction?
initiation
\
propagation
\
termination
\
propagation
\
termination
43
New cards
what does the mechanism look like for the radical substitution reaction between chlorine and methane?
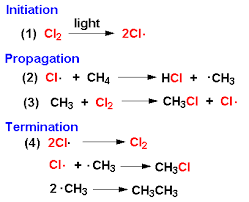
44
New cards
what is the problem with radical substitution reactions?
you end up with a mixture of products
45
New cards
when does a substitution reaction have to stop?
where there are no more H atoms to replace
46
New cards
what is petroleum a.k.a?
crude oil
47
New cards
what is crude oil?
a mixture of hydrocarbons
\
mostly made up of alkanes
\
massive range of hydrocarbons
\
mostly made up of alkanes
\
massive range of hydrocarbons
48
New cards
what are the steps in fractional distillation?
1. crude oil is vaporized (about 350 degrees C)
\
2. vapor goes into a fractionating column
\
3. due to temperature gradient, the hydrocarbons cool and condense in different fractions
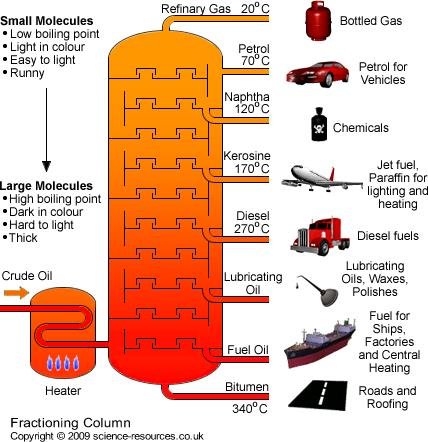
49
New cards
where do the longest chain hydrocarbons end up in the fractionating column?
bottom of the column
\
due to having the highest boiling point of them all
\
(could also be drawn away if the boiling point is too high to even evaporate)
\
due to having the highest boiling point of them all
\
(could also be drawn away if the boiling point is too high to even evaporate)
50
New cards
what is the highest desired length of hydrocarbon?
shorter ones
\
e.g. petrol + naphtha
\
e.g. petrol + naphtha
51
New cards
what is cracking?
the breaking of long-chain alkanes into smaller hydrocarbons
\
(which include alkenes)
\
involving the breaking of the C-C bonds
\
(which include alkenes)
\
involving the breaking of the C-C bonds
52
New cards
what is the use for a 1-4 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
LPG
\
camping gas
\
camping gas
53
New cards
what is the use for a 5-12 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
petrol
54
New cards
what is the use for a 7-14 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
processed to make petrochemicals
55
New cards
what is the use for a 11-15 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
jet fuel
\
petrochemicals
\
central heating fuel
\
petrochemicals
\
central heating fuel
56
New cards
what is the use for a 15-19 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
diesel fuel
\
central heating fuel
\
central heating fuel
57
New cards
what is the use for a 20-30 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
lubricating oil
58
New cards
what is the use for a 30-40 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
ships
\
power stations
\
power stations
59
New cards
what is the use for a 40-50 carbon chain hydrocarbon?
candles
\
lubrication
\
lubrication
60
New cards
what is the use for a 50+ carbon chain hydrocarbon?
roofing
\
road surfacing
\
road surfacing
61
New cards
what are the 2 types of cracking
thermal
\
catalytic
\
catalytic
62
New cards
what happens in thermal cracking?
1. high temperature (around 100 degrees c)
\
2. high pressure (up to 70atm)
\
3. produces a lot of alkene
63
New cards
what are alkenes good for?
making polymers
\
e.g. poly(ethene)
\
e.g. poly(ethene)
64
New cards
what catalyst is usually used in catalytic cracking?
zeolite catalyst = hydrated aluminosilicate
65
New cards
what are the conditions for catalytic cracking?
slight pressure
\
high temperature (around 450 degrees c)
\
zeolite catalyst
\
high temperature (around 450 degrees c)
\
zeolite catalyst
66
New cards
what is a zeolite catalyst in terms of aluminosilicate?
hydrated aluminosilicate
67
New cards
what do aromatic compounds contain?
benzene rings
68
New cards
what is a benzene ring?
contain a ring of 6 carbon atoms
\
with a delocalised ring of electrons
\
with a delocalised ring of electrons
69
New cards
what is knocking?
where alkanes expload oftheir own accord
\
when the fuel/air mixture in the engine is compressed
\
when the fuel/air mixture in the engine is compressed
70
New cards
what are the most likely hydrocarbons to cause knocking?
straight chain alkanes
\
adding branched chains and cyclic hydrocarbons to the petrol makes knocking less likely to happen = more efficient too
\
adding branched chains and cyclic hydrocarbons to the petrol makes knocking less likely to happen = more efficient too
71
New cards
what is the name of the process where straight-chain alkanes are converted into branched chain alkanes and cyclic hydrocarbons?
reforming
72
New cards
what does reforming require?
a catalyst
\
e.g. platinum stuck on aluminum oxide
\
e.g. platinum stuck on aluminum oxide
73
New cards
what does the reforming of hexane into cyclohexane look like?
hexane reformed into cyclohexane (and H gas)
\
then: the H gas could be reformed into benzene (C6H6) and H gas
\
then: the H gas could be reformed into benzene (C6H6) and H gas
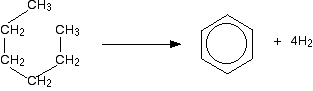
74
New cards
what could octane be reformed into?
2,5 - dimethylhexane
\
= now branched = lower b.p.
\
= now branched = lower b.p.
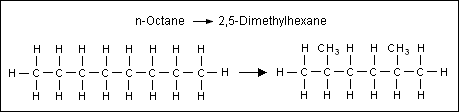
75
New cards
what do you get when you undergo complete combustion with an alkane?
carbon dioxide
\
water
\
water
76
New cards
what are the products of incomplete combustion?
carbon monoxide
\
carbon
\
water
\
carbon
\
water
77
New cards
where does combustion reactions happen?
between gases
\
(so liquid alkanes have to be vaporised first)
\
(so liquid alkanes have to be vaporised first)
78
New cards
are combustion reactions endo or exothermic?
exothermic
\
= release heat
\
= release heat
79
New cards
why do larger alkanes release more neergy per mol?
because they have more bonds to react
80
New cards
what are 2 examples of methane’s uses?
central heating
\
cooking
\
cooking
81
New cards
what are the 3 fossil fuels?
coal
\
oil
\
natural gas
\
oil
\
natural gas
82
New cards
when do we use fossil fuels most often?
power stations
\
transport
\
heating
\
transport
\
heating
83
New cards
what are the pollutants formed by burning fossil fuels?
carbon monoxide
\
unburnt hydrocarbons
\
carbon particulates
\
oxides of sulfur (NOx)
\
oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
\
unburnt hydrocarbons
\
carbon particulates
\
oxides of sulfur (NOx)
\
oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
84
New cards
why is carbon monoxide toxic?
oxygen in bloodstream carried around by haemoglobin
\
carbon monoxide binds better to haemoglobin than oxygen
\
so it bids to the haemoglobin in bloodstream before oxygen can
\
means that less oxygen can be carried around the body
\
= oxygen deprivation
\
= could be fatal (at v. high concentrations)
\
carbon monoxide binds better to haemoglobin than oxygen
\
so it bids to the haemoglobin in bloodstream before oxygen can
\
means that less oxygen can be carried around the body
\
= oxygen deprivation
\
= could be fatal (at v. high concentrations)
85
New cards
how does sulfur dioxide produce sulfuric acid that comes down in rain?
1. caused by burning fossil fuels that contain sulfur
2. sulfur burns to form sulfur dioxide gas
3. enters atmosphere + dissolves in the moisture
4. then converted into sulfuric ACID
86
New cards
how do oxides of nitrogen lead to acid rain?
1. oxides of nitrogen are produced when the high pressure and temperature in a car engine
2. = the nitrogen and oxygen in the air to react together
1. escapes into the atmosphere
3. dissolves in moisture and then converted into nitric acid = falls as acid rain
87
New cards
what are the problems with acid rain?
destroys trees + vegetation
\
corrodes buildings + statues
\
killing fish in lakes
\
corrodes buildings + statues
\
killing fish in lakes
88
New cards
what do catalytic converters do?
remove some pollutants from car emissions
89
New cards
what do catalytic converters prevent?
carbon monoxide
\
oxides of nitrogen
\
unburnt hydrocarbons
\
= prevented being spewing out
\
oxides of nitrogen
\
unburnt hydrocarbons
\
= prevented being spewing out
90
New cards
how does a catalytic converter work?
using a platinum catalyst to change then into harmless gases / less harmful ones
\
e.g. water vapor, nitrogen / carbon dioxide
\
\
\
e.g. water vapor, nitrogen / carbon dioxide
\
\
91
New cards
how does a catalytic converter convert nitrogen monoxide and carbon monoxide into nitrogen and carbon dioxide?
2NO(g) + CO(g) -→ N2(g) + CO2(g)
92
New cards
what will be the first hydrocarbon to go?
oil
\
gets really scarce = become more expensive
\
not sustainable to keep using fossil fuels unnecessarily
\
gets really scarce = become more expensive
\
not sustainable to keep using fossil fuels unnecessarily
93
New cards
what are biofuels?
fuels made from living matter over a short period of time
94
New cards
what is bioethanol and how is it formed?
ethanol = made by the fermentation of sugar from crops (e.g. maize)
\
AN EXAMPLE OF A BIOFUEL MADE FROM RENEWABLE RESOURCES
\
AN EXAMPLE OF A BIOFUEL MADE FROM RENEWABLE RESOURCES
95
New cards
what is biodiesel and how is it fomed?
fats +/ oils (e.g. vegetable oil) = made by refining renewable fats and oils
\
AN EXAMPLE OF A BIOFUEL MADE FROM RENEWABLE RESOURCES
\
AN EXAMPLE OF A BIOFUEL MADE FROM RENEWABLE RESOURCES
96
New cards
what is biogas and how is it formed?
organic waste matter = breaks down, producing biogas
\
AN EXAMPLE OF A BIOFUEL MADE FROM RENEWABLE RESOURCES
\
AN EXAMPLE OF A BIOFUEL MADE FROM RENEWABLE RESOURCES
97
New cards
What do biofuels form when burnt but why isn’t this as bad as burning hydrocarbons?
carbon dioxide
\
but it’s carbon dioxide that the plants absorbed while growing
\
= classed as carbon neutral
\
but it’s carbon dioxide that the plants absorbed while growing
\
= classed as carbon neutral
98
New cards
what are the negatives of using biofuels?
carbon dioxide still given out:
\
while refining = transporting the fuel
\
while making the fetilisers
\
while powering agricultural machinery used to grow and harvest the crops
\
while refining = transporting the fuel
\
while making the fetilisers
\
while powering agricultural machinery used to grow and harvest the crops
99
New cards
what else could biodiesel and biogas be made from?
waste that would otherwise go to landfill
100
New cards
what is the issue with switching from petrol to biofuels to transport?
petrol car engines would have to be modified to use fuels with high ethanol concentrations
\
(e.g. in bioethanol)
\
(e.g. in bioethanol)