1.1 coagulation pathways
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Coagulation consists of three pathways that interact together to form a stable blood clot:
the extrinsic pathway
the intrinsic pathway
The common pathway.
The extrinsic pathway
leads into the final common pathway by activating Factor X.
The intrinsic pathway -
also lead into the final common pathway by activating Factor X independently of the extrinsic pathway.
its called the extrinsic pathway because
it being initiated by tissue factor, which exists "outside" the blood
The extrinsic pathway is initiated by
injury to the endothelial tissue (i.e., skin tissue), exposing tissue factor (Factor III) to the blood.
Tissue factor then becomes bound with calcium + Factor VIIa to activate → Factor X.
Factor VII is present in the blood and requires Vitamin K to be activated.
its called the intrinsic pathway because
all required factors being present WITHIN the blood compartment.
The intrinsic pathway begins when Factor XII is exposed to
collagen,
kallikrein,
and high molecular weight kininogen (HMWK)
and is subsequently activated.
factor XII
hageman factor
Factor XIIa activates Factor XI into XIa.
In the presence of Ca2+, Factor XIa activates Factor IX.
Factor IXa,
Factor VIIIa,
and Ca2+
form a complex to activate Factor X.
Factor VIII is found in the blood
and is often activated by thrombin (Factor IIa).
The common pathway comes into play
following the activation of Factor X at the end of either pathway.
. The common pathway begins when Factors Xa + Va, bind together with Ca2+
, forming a prothrombinase complex.
The prothrombinase complex then activates prothrombin (Factor II) into thrombin (Factor IIa). Thrombin then:
Cleaves fibrinogen (Factor I) into fibrin (Factor Ia) and
Cleaves the stabilizing factor (Factor XIII) into XIIIa which binds with Ca2+ to then create fibrin crosslinks and stabilises the clot.
Activates Factors V, VIII, and IX.
Activates platelets.
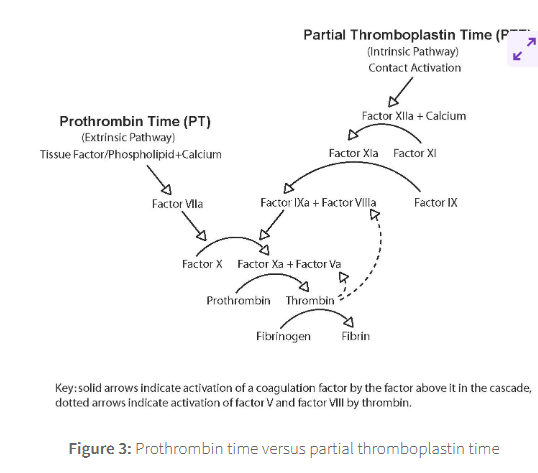
Blood tests can be used to measure the activity of the coagulation cascade.
Either of the intrinsic or the extrinsic pathway can be measure through Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) or Prothrombin Time (PT), respectively.