Lecture 1: Hematopoietic System Part 1 (Anemia)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
_osis
INCREASE in #
_penia
DECREASE in #
_emia
blood
bone marrow
specialized connective tissue + many capillaries
immature, intermediate, mature forms of blood cells
erythropoiesis
RBC production
stimulated by erythropoietin from KIDNEY
stem cell reproduction
yolk sac = embryonic life
fetal liver = 3-6mth gestation
bone marrow = 6+ mth gest (ONLY site of blood cell production after birth, stores RBC/WBC)
precursor cells to
RBC
Platelet
Granulocytes
lymphocytes
monocytes
Stem cell
Erythroblast
Myeloblast
Monoblast
Lymphoblast
Megakaryoblast
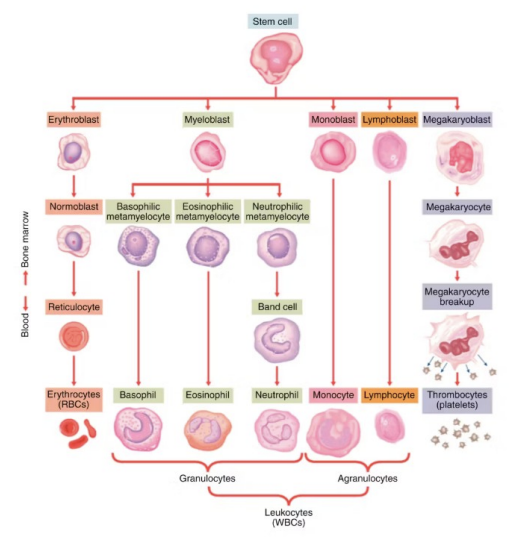
Erythroblast (immature)
Normoblast → reticulocyte → erythrocytes (RBC) (carry O2 via hemoglobin, CO2 back to lungs, acid-base balance)
Myeloblast (immature)
Basophilic → basophilic (allergy/inflammation = histamine)
Eosinophilic → eosinophil (parasite defense + asthma)
Neutrophilic → neutrophil (1st response to infection, kill bacteria via phagocytosis)
Granulocytes (immature)
Basophilic (WBC)
Eosinophil (WBC)
Neutrophil (WBC)
Monoblast (immature)
Monocyte (WBC) (long-term immune = macrophages + dendritic cells)
Lymphoblast (immature)
Lymphocyte (WBC) (B (antibodies) and T lymphocytes (helper/killer) = adaptive immunity)
Agranulocytes
Monocyte (WBC) (long-term immune = macrophages + dendritic cells)
Lymphocyte (WBC) (B (antibodies) and T lymphocytes (helper/killer) = adaptive immunity)
Megakaryoblast (immature)
Thrombocytes (platelets for clotting/coagulation)
Erythrocytes
RBC
Transport O2/CO2 + acid-base balance
Bioconcave shape = flexibility = pass through tiny capillaries
Thin cell membrane = diffusion of gases
Composed of hemoglobin
Leukocytes
granulocytes
Basophilic (WBC)
Eosinophil (WBC)
Neutrophil (WBC)
agranulocytes
Monocyte (WBC) (long-term immune = macrophages + dendritic cells)
Lymphocyte (WBC) (B (antibodies) and T lymphocytes (helper/killer) = adaptive immunity)
Blood
Connective tissue
3 major functions
Protection
Regulation
Transportation
2 components
Plasma
Blood cells
Plasma
55% of blood + serum (plasma withOUT water)
Water mostly
Proteins = Fibrinogen
Electrolytes
Gases
Nutrients
Waste
Plasma proteins
Albumin
Globuline
Clotting factors (fibrinogen)
Protection - Functions of the blood
Maintaining homeostasis of blood coagulation
Combating invasion of pathogens/foreign substances
Regulation - Functions of the blood
fluid/electrolyte balance
Acid-base balance (erythrocytes as a buffer)
Body temp
Maintain intravascular oncotic pressure
Transportation - Functions of the blood
O2 from lungs → cells
Nutrients from GI tract → cells
Hormones from endocrine glands → tissue/cells
Metabolic waste products (CO2, NH3 (ammonia), urea) from cells → lungs/liver/kidneys
Fe processing
digest (diet/supplement)
transports via transferrin
bone marrow, liver, spleen (transferrin binds to Fe)
Fe → RBC, store if RBC adequate in Hb
RBC breakdown every 120days → liver/spleen, release bili
Fe REMAINS (lost via blood loss or recycled when RBC dies)
recycling
macrophages in liver/spleen
Hemosiderin = Fe storage in tissue when RBC breakdown
RBC - Erythrocytes
NO nucleus
biconcave disk
transport O2
amount of O2 transported in RBC-Erythrocytes
# of RBC in circulation
amount of Hb within
WBC
granulocytes (neutrophil, esosinhil, basophil)
Inflammation rxn
lymphocytes
T and B lymphocytes
monocytes
various rxn
platelets (thrombocytes)
cytoplasmic fragments of megakaryocyte
NOT cells
no nucleus/limited metabolic machinery
granules of chemical mediators = clotting/inflammation
must be replaced con’t
Anemia
frequent and serious disease (1/3 of world population)
deficiency in 1+
erythrocytes
quantity of Hb
quality of Hb
volume of packed RBCs
3 morphological classifications
normocytic, normochromic (normal size/colour)
macrocytic, normochromic (large size, normal colour)
microcytic, hypochromic (small size, PALE colour)
Normocytic, normochromic
(normal size and colour)
malnutrition
acute blood loss
chronic renal diseases
cancers
hemolytic anemia
sickle cell anemia
aplastic anemia (bone marrow does not produce enough blood cells)
Macrocytic, normochromic
(large size, normal colour)
vitamin B12-deficiency anemia (defective DNA syn)
folic acid-deficiency anemia (defective DNA syn)
liver disease
Microcytic, hypochromic
(small size, pale colour)
iron-deficient anemia (decreased hema syn)
thalassemia (inherited hemoglobin synthesis disorder, chronic microcytic hemolytic anemia due to reduce/absent globin chain production) (decreased hema syn)
vitamin B6 deficient
lead poisoning
classification by etiology
decreased erythrocyte production
defective DNA synthesis
decreased hemoglobin synthesis
decrease number of erythrocyte precursors blood loss
increased erythrocyte destruction
intrinsic or extrinsic
defective DNA synthesis (etiology)
Cobalamin (vit B12) deficient
folic acid deficient
decreased hemoglobin synthesis (etiology)
Iron deficient
Thalassemias (decrease globin synthesis)
sideroblastic anemia (decreased porphyrin)
decrease number of erythrocyte precursors (etiology)
aplastic anemia + inherited disorders
fanconi syndrome
anemia of myeloproliferative disorders + myelodysplasia
chronic disease/disorders
medications (chemo)
radiation
blood loss (etiology)
acute
trauma
blood vessel rupture
splenic sequestration crisis
chronic
gastritis
menstrual flow
hemorrhoids
increased erythrocyte destruction
intrinsic
abnormal hemoglobin (sickle cell)
enzyme deficient (G6PD)
membrane abnormalities (paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria/hereditary spherocytosis)
extrinsic
physical trauma (prosthetic heart valves)
acquired antibodies against RBCs
infectious agents, meds, toxins
disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC)
HELLP syndrome
thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
cancer
mild anemia manifestations
Hb = 100-120 g/L
palpitations
exertional dyspnea
moderate anemia manifestations
Hb = 60-100 g/L
increased palpitations, bounding pulse
dyspnea (roaring in ears)
fatigue
severe anemia manifestations
hb = <60 g/L
pallor, jaundice, pruritus
icteric conjunctiva/scarla, retinal hemorrhage, blurred vision
glossitis (smooth tongue)
tachycardia, increase pulse pressure, systolic murmurs, agina, HF, MI
tachypnea, orthopnea, dyspnea at rest
headache, vertigo, irritable, depression, impaired thought
anorexia, hepatomegaly/splenomegaly (increase size), sore mouth, dif swallow
bone pain
sensitive to cold, weight loss, lethargy
inspection - assessment
gen appearance
pallor, fatigue, weight loss
skin/mucous mem
pale conjunctiva
pale oral muscosa
jaundice
petechia
delayed cap refill
VS
tachycardia
tachypnea
hypotension (blood loss)
orthostatic changes
palpation - assessment
skin/perfusion
cool skin
delayed cap refill
dry skin
turgor
pulse
tachy
weak or building
symmetry
lymph nodes
abdo
splenomegaly and hepatomegaly
RBC cell count lab test
# of RBCs in the blood
Female: 3.50–5.00 × 1012/L
Male: 4.00–5.50 × 1012/L
Hemoglobin HgB lab test
amount of Hb in RBC
Female: 115–155 g/L
Male: 125–170 g/L
mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) lab test
average amount of Hb in a single RBC
Female: 25–34 pg
Male: 27–34 pg
pg = picograms
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) lab test
average SIZE of RBC cells
80 - 100 fL
fL = femtoliters
hematocrit (HCT) lab test
% of RBC in the blood
36 - 50%
Anemia Drugs (4)
Ferrous Salts and Injectables Iron Supplements
Cyanocobalamin (B12) Water-soluble B-Complex
Folic Acid/Folate Water-soluble B-Complex
Epoetin Alpha (Eprex) Darbepoetin (Aranesp)
Ferrous Salts and Injectables
Ferrous Salts PO = ferrous gluconate, ferrous sulphate/sulphate, ferrous fumarate
injectables = iron dextran, iron sucrose, ferric gluconate, ferumoxytol
class = iron supplements
MOA = Fe as O2 carrier in HgB and myoglobin (O2 carrying molecule in muscle tissue)
Contra = drug allergy, hemochromatosis (Fe overload), hemolytic anemia, other anemia NOT associated with Fe deficiency
AE = N/V, diarrhea, constipation, dark stool, stomach cramps = TAKE WITH FOOD
Nursing = Fe absorption enhanced with Ascorbic Acid (Vit C), nut assessment (pt diet), energy level for ADLs, monitor constipation
Time Action
PO Ferrous Salts = reticulocyte 3-5 days, Hb rise 1-2wks, normal 6-8 wks, replenished 3-6mths
injectable (parenteral) Fe = reticulocyte 2-4days, Hg rise 1 wk, normal 2-4wks, replenished faster than PO
Cyanocobalamin (B12)
class = Water-soluble B-Complex
DEEP IM
MOA = coenzyme for metabolic pathways (fat/carbs) + protein syn. responsible for growth, cell replication, hematopoiesis, nucleoprotein, myeline syn
indications = pernicious anemia, deficiency via malabsorption
contra = drug allergy, COBALT sensitive, heredity optic nerve atrophy (Leber’s disease)
AE = heart failure, PVT, pulmonary edema, flushing, optic nerve atrophy, diarrhea, pruritus, rash, HYPOKALEMIA
Nursing = assess med order, route of admin, GI stat, decreased efficiency with anticonvulsants, aminoglycoside AB, long-acting potassium prep
Peak plasma Conc = 8-12hrs
half-life = 6 days
Folic Acid/Folate
Class = Water-soluble B-Complex
MOA = erythropoiesis and syn of nucleic acids (DNA/RNA)
Indications = folic acid deficient anemia, prevention of neural tube defects, tropical sprue (malabsorption syndrome)
conta = drug allergy, anemia not caused by folic acid deficient
AE = allergic rxn (rare), yellow discolouration of urine
Nursing = assess/monitor nutritional intake, blood work, interactions with PO contraceptives, corticosteroids, sulfonamides, dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors (methotrexate) and abx trimethoprim
peak plasma = 60-90 min
Epoetin Alpha (Eprex) Darbepoetin (Aranesp)
injectable only (IV/SC)
class = human recombinant hormone (erythropoietin) analogue
MOA = biosynthetic form of natural hormone erythropoietin (excreted from kidneys in response to decrease RBCs) stims RBC manufacturing/maturation of bone marrow
contra = drug allergy, uncontrolled HTN (hypertension), red cell aplasia, Hgb 100g/L + for cancer pt, Hgb 130g/L + for kidney disease pt
AE = HTN, fever, pruritus, rash, N/V, arthralgia (pain at joint), injection site rxn
nursing = check bloodwork (Hgb), VS, allergy rxn
onset = 7-10 days
half life = 4-13hr
peak plasma concentration = 5-24hr
hemolytic anemias
RBC prematurely destroyed by mononuclear phagocytes
hyperplastic marrow leads to reticulocytosis (elevated immature RBCs in blood)
pt are NOT depleted of Iron
hemolytic anemias may be caused by…
production of defective RBCs
events that affect normal cells
sickle cell anemia
altered sequence of a.a. in globin molecule
person with 2 hemoglobin S genes
RBC collapse into sickle shape
more susceptible to rupture/premature death
can sludge obstruct small blood vessels
manifestations of sickle cell anemia
most present healthy but are anemic
may have chronic conditions/pain due to organ/tissue hypoxia (not enough O2)/damage
± jaundice
sickling episode
pain = mild-excruicitating
impacting ANY area of the body
± fever
± swelling
± tenderness
± tachypnea
± hyPERtension
± N/V
complications of sickle cell anemia
brain = trhombosis/hemorrhage = paraylsis/sensory deficit/death
eye = hemorrhage/retinal detachment
lung = acute chest syndrome/pulmonary hypertension/pneumonia
heart = failure
liver/gallbladder = hepatomegaly/gallstone
kidney = hematuria/renal failure
spleen = atrophy
bones/joints = hand-foot syn/osteonecrosis
penis = priapism
skin = ulcers
collaborative care for sickle cell anemia
preventing dequalea from disease
alleviate manifestations from complication
minimize end-target organ damage
promptly treating serious sequelae
acute care for sickle cell anemia
O2
NB assess resp stat
fluids/electrolytes
collab care for pain management
rest
DVT prophylaxis
± antibiotics
pt education for sickle cell anemia
avoid triggers
high altitude
extreme temps
stress
adequate fluid intake
preventing/treating infections
screening
retinopathy (eye)
pharmacotherapeutic for sickle cell crisis
hydroxyurea (PO) - NOT in sealock
hydroxyurea (PO)
class = antineoplastic (myelosuppressive agent)
MOA = antimetabolite reduces vaso-occlusive pain crisis, needed for transfusion of sickle cell pt by reducing marrow production of neutrophils, reticulocytes, and platelets (all mediators of inflammation)
indications = vaso-occlusive sickle cell crisis, squamous cell carcinoma, chronic myeloid leukemia, acute chest syndrome, severe symptomatic anemia, hemolytic antibodies/anticoagulants
contra = preg, active liver disease (HBV/HCV)
AE = headache, GI, nausea, skin hyperpigmentation/darkening of nails
nursing = check VS, bloodwork, opreg test women of reproductive age
peak plasma concentration = 1-4hrs
76yr + anemia (no feel toes/tips fingers walking, tired, fatigue, SOB)
cause of s/s
adequate amounts of Hb needed to carry O2 for tissue metabolism
32yr female pt (fatigue, dizzy, SOB exertion 2mths, heavy menstrual, veg diet)
VS
BP = 110/70
HR = 104 bpm
RR 20/min
SpO2 = 98%
what diagnostic test nurse expect order?
Hgb = 90 g/L (normal 115-155 g/L)
Hematocrit (Hct): 26% (normal: 36–50%)
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): 72 fL (normal: 80–100 fL)
Ferritin: 10 ng/mL (normal: 15–150 ng/mL)
iron deficiency anemia consistent findings
low MCV
fatigue
tachycardia
heavy menstrual bleeding
NOT
elevated ferritin
hypotension
which intervention needed for 32yr female pt (fatigue, dizzy, SOB exertion 2mths, heavy menstrual, veg diet)
encourage intake of vit C
admin oral ferrous as prescribed
monitor Hg + hematocrit levels
NOT
Iron fortified milk
blood transfusion