Housing Design and Considerations
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Animal Housing
Structures designed to meet species-specific needs.
Livestock Housing
Essential for optimal animal production and welfare.
Stockmanship
Caregiver behaviors ensuring animal health and performance.
Disease Minimization
Housing reduces disease spread among livestock.
Cattle Housing Options
Includes cubicles, straw yards, and pasture.
Comfortable Lying Areas
Clean, dry spaces for rumination and rest.
Weather Shelter
Protection from adverse conditions with air circulation.
Space Requirements
Animals need room to move and access resources.
Calving Pens
Designated areas for calving and sick animals.
Isolation Provision
Separate areas for sick or quarantined animals.
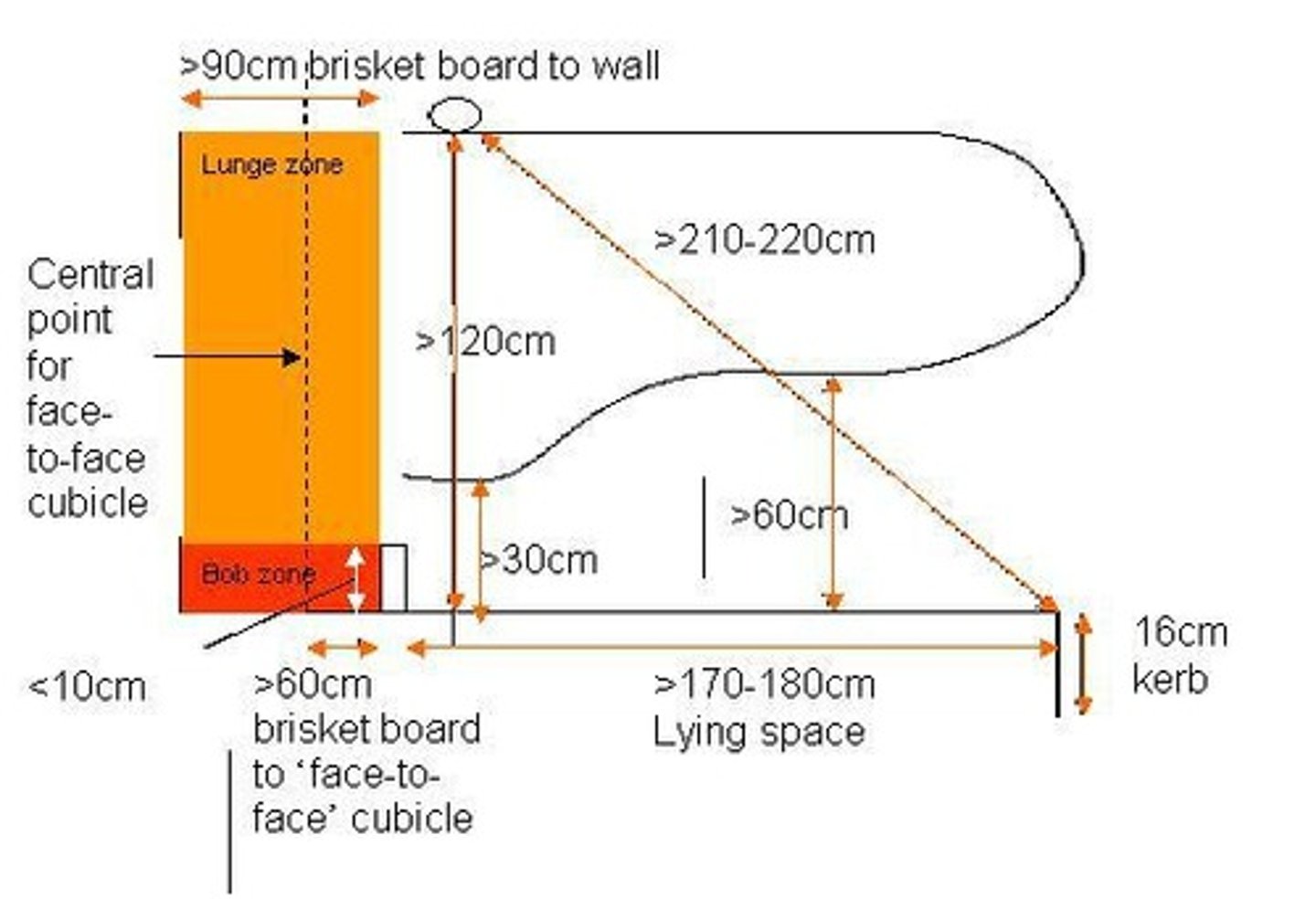
Cubicle Length
Must allow lunging space and prevent soiling.
Cubicle Width
Should be 1.8 times cow hip width.
Occupancy Rates
Higher stocking reduces milk yield per cow.
Social Hierarchy Effects
Lower-ranked cows spend more time standing.
Comfort Enhancements
Extra feed and space improve animal welfare.
Brisket Board
Helps position cows correctly in cubicles.
Hock Sores
Indicate abrasive bedding material in cubicles.
Cubicle Preferences
Cows prefer wider cubicles and high neck rails.
Lying Time Influence
Design affects rumination and overall comfort.
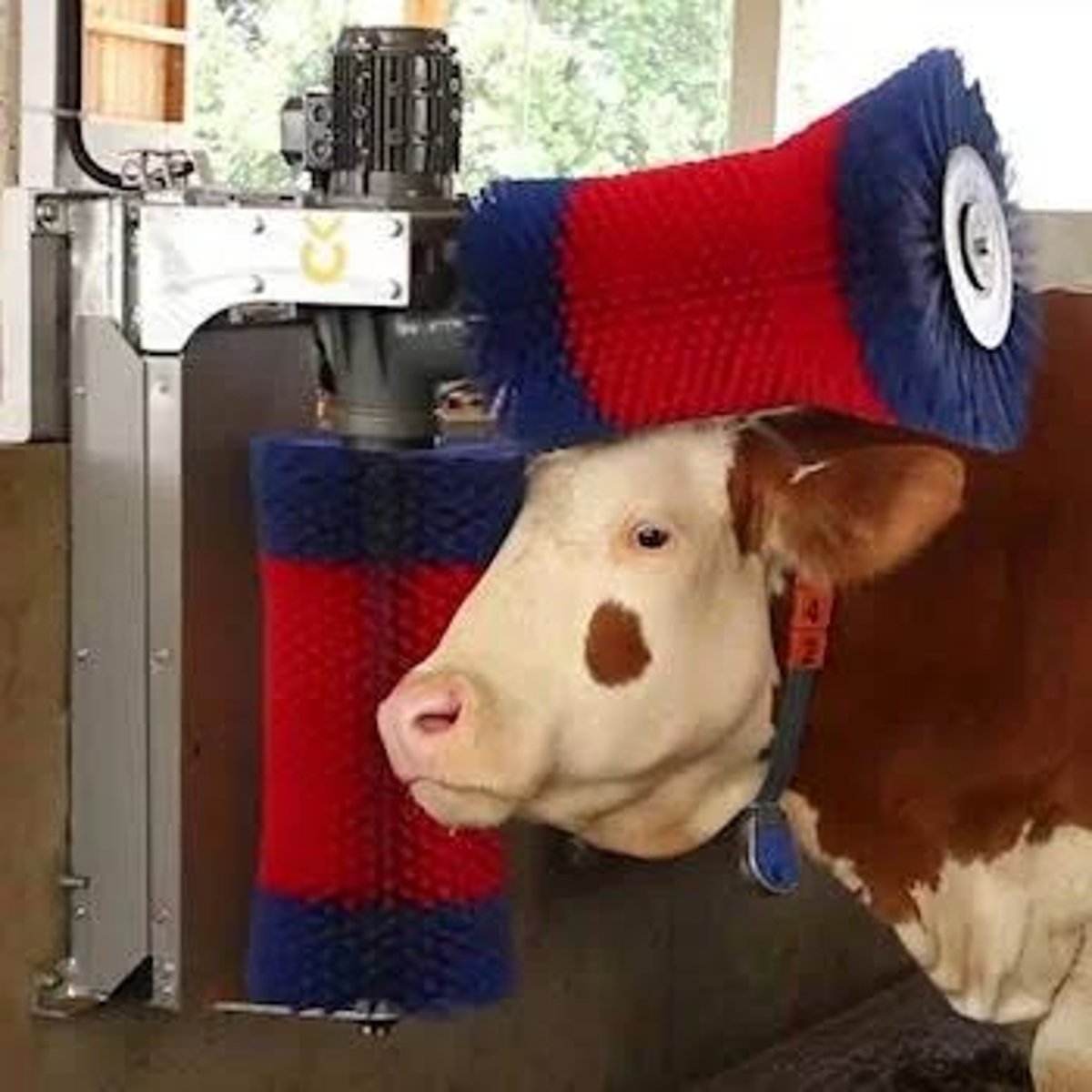
Cow Comfort Brushes
Grooming aids improve welfare and milk yield.

Loose Housing Issues
Mastitis risk higher than in cubicle housing.
Bedding Requirements
Depends on cattle type and housing conditions.
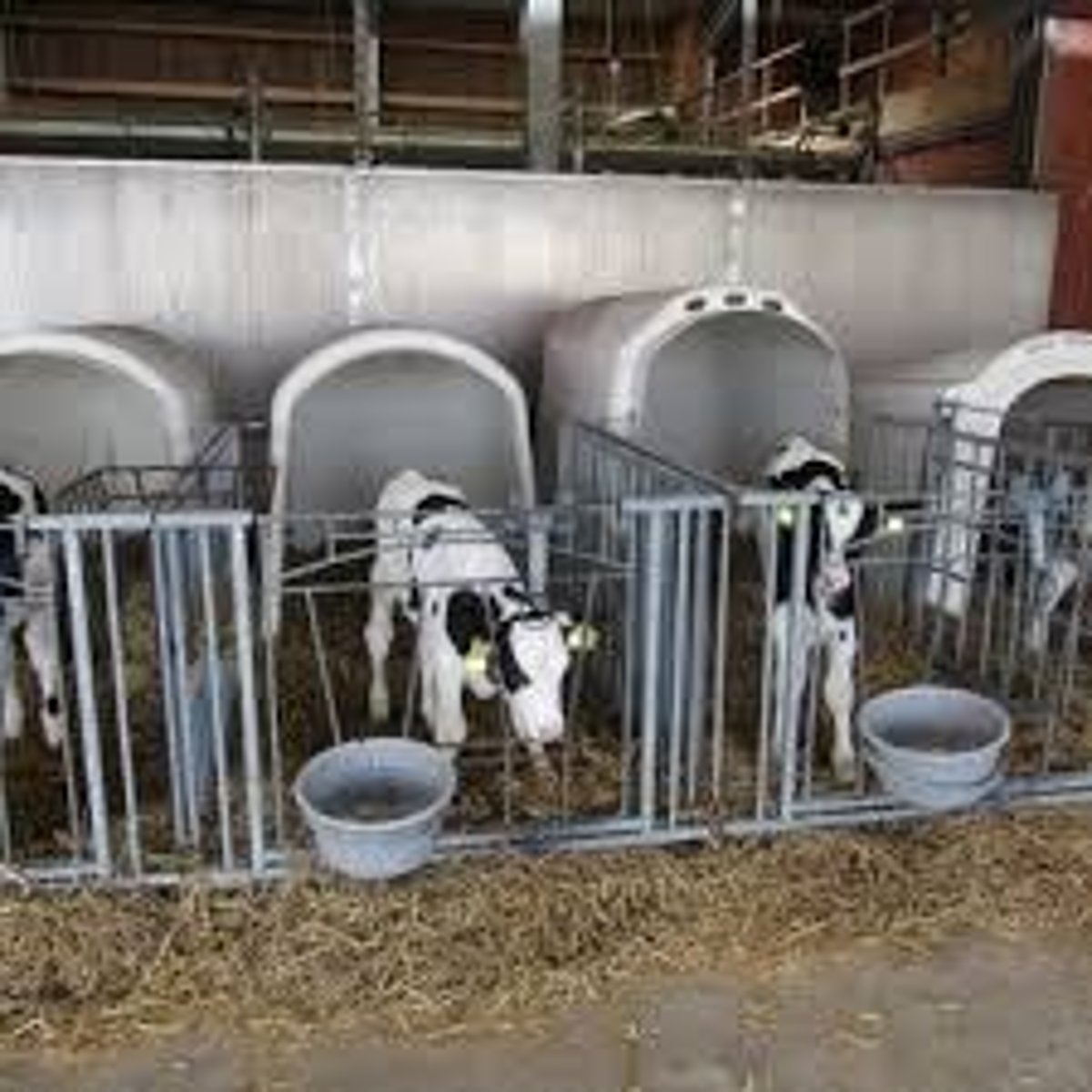
Calf Housing Types
Includes loose housing, igloos, and individual pens.

Ventilation Importance
Adequate airflow prevents heat loss and dust.
Flooring Types
Influence cattle comfort and moisture management.
Grooved Flooring
Parallel grooves aid drainage and prevent slipping.
Slatted Flooring
Allows waste removal but may affect comfort.
Rough Finished Floors
Increase wear on hooves; smooth increases slip risk.