24 - Population Ecology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is population in ecology?
- Group of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time
- Interact and breed with each other
- Share a common gene pool
- Share resources and environmental factors
How does a population evolve?
It evolves as natural selection acts on variation in populations
What is population ecology?
- How biotic and abiotic factors affect populations
- How and why populations change over time
What are the features of populations?
- Site
- Density
What is a Site?
Number of individuals
What is the Density?
Number of individuals per unit area or volume
What is Dispersion?
Within a population range, local densities may vary
What are the types of dispersion?
- Clumped
- Uniform
- Random
What is clumped dispersion?
Individuals aggregate where conditions favorable
What is uniform dispersion?
Often results from direct interaction between individuals
What is random dispersion?
Position of each individual is independent of others
What is the formula for an overall change over time?
AN/At = B - D
Where...
N = Population size
t = time
B = # of births
D = # of deaths
What is per capita change?
Contribution of average individual to population size per unit of time
What is the per capita birth rate?
b and it stands for the # of offspring
How do you solve for the per capita birth rate?
b = # births/N
What is the per capita death rate?
d and it stands for the # of deaths
How do you solve for the per capita death rate?
m = # deaths/N
Example: 75 births and 50 deaths per year in a population of 1000 solve for b and d
b = 75/1000 = 0.075 births/year/indiv
m = 50/1000 = 0.05 deaths/year/indiv
What are the formulas for calculating per capita rates to calculate expected change in population size
# of births/unit time —> B = bN
# of deaths/unit time —> D =mN
Example: 400 individuals where b = 0.03 and m = 0.04. What is the expected change in population size per year?
B: 0.03(400) = 12 births
D: 0.04(400) = 16 deaths
AN/At = B - D so, 12-16 = -4
What is the formula for population change over time?
r = b-m
What are the possible outcomes for r?
If...
r < 0 then, population decreasing
r > 0 then, population increasing
r = 0 then, zero population growth (ZPG), births and deaths cancel out
Change in population size over time formulas
AN/At
dN - dt
B - D
bN - mN
N(b-m)
They all equal each other
Population Growth Model
- Exponential Growth Model
- Logistic Growth Model
What is the exponential growth model?
- Describes a population in which conditions are ideal
- Population density is low
- Every individual has access to abundant resources
- Free to reproduce until no longer able to
When does population growth occur?
At its intrinsic rate of increase
What is the max rate?
The max rate of a population could increase under ideal conditions
= r max
What type of organism has the highest r max?
Microorganisms
What is an example of a microorganism and an r max?
Bacteria reproducing by binary fission every 20 mins
(1 cell —> 10 billion cells in 10 hours)
How fast is the r max for larger organisms?
- Larger organisms tend to have a lower r max
(d = exponential shaped curve)
In exponential growth...
- Rate of increase is constant
- There are more new individuals that are being produced per unit time when population is large than when its small
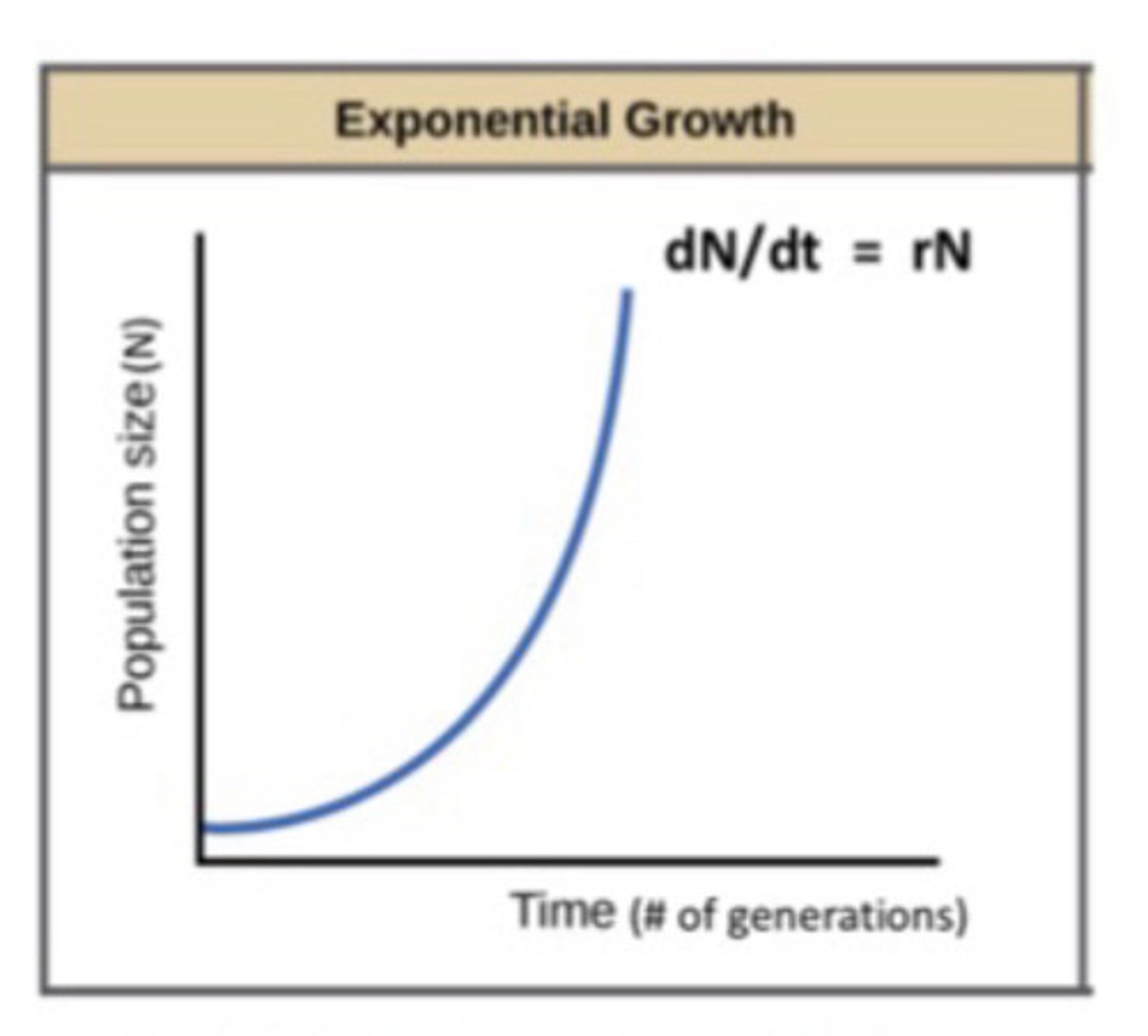
What does exponential growth characterize?
Some rebounding populations
Is exponential growth realistic in nature?
No, growth can NOT occur indefinitely because of environmental resistance
- Some populations may undergo exponential growth for a short period of time, BUT, over longer periods of time growth rate may decrease or even decrease to nearly 0
As population density increases...
- Less resources per individual
- Build up of toxic wastes
What is the logistic growth model?
- This model accounts for environmental resistance
- As a population reaches the limit of the environment's ability to support it, the population growth rate will approach 0
What is Carrying Capacity
- Max amount of organisms that can be sustained by their environment for an indefinite period
- Represented by K
- Assumes no changes in an environment
In logistic growth...
- S shaped curve (Sigmold)
- First part resembled exponential growth
- Levels out as K is approached
- Reflects decline in growth as population reaches K
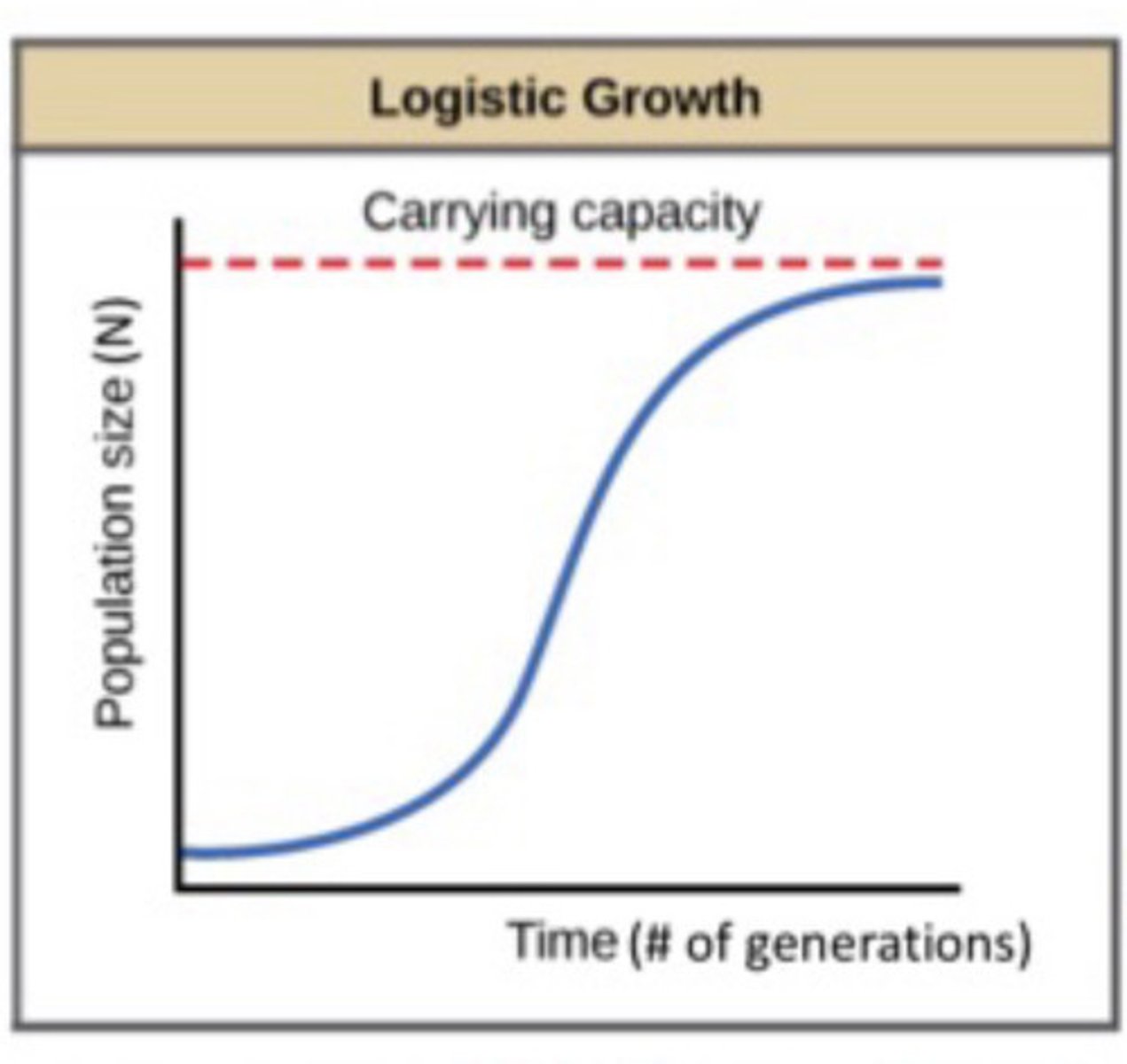
What is the equation of logistic growth?
dN/dt = rN (K-N)/K
where,
rN resembles exponential growth
What are the possible outcomes for K?
If...
N is small and not close to K, dN/dt is high
N is getting close to K, dN/dt is low
N=K, dN/dt=0 ans growth is stable
Are S-curves in nature logistic and why?
- They are usually not perfectly s-shaped (logistic)
- Populations tend to fluctuate around K
- Environment is never completely constant and subject to change
Which model is more realistic?
The logistic growth model is more realistic than the exponent growth model
What can be traded for what?
Trade-offs occur between Survival and Reproduction
Where is energy put towards in early life?
Energy is put towards own growth and survival
Where is energy put in late life?
Energy put towards own growth and survival, but less time for reproduction
What are the three main variables?
- Age at first reproduction
- How often organisms reproduce
- Number of offspring per reproductive episode
What are some different strategies of reproducing?
- Semelparous
- Iteroparous
What is semelparous reproduction?
- A single, immense reproductive effort
- Environment highly variable and unpredictable
What is a result of semelparous reproduction?
- Adults are less likely to survive (survival rate is low)
- Lots of offspring ensures that some will survive
Examples of organisms that are semelparous
- Insects
- Plants
- Fish
What is iteroparous reproduction?
- Reproduce many times during life cycle
- Advantageous when environment is less variable
What is a result of iteroparous reproduction?
- Adults more likely to survive to reproduce again
- Competition for resources may be intense
- A few well-suited offspring are more likely to survive
An example of an organism that is iteroparous
Most vertebrates
What are the two extremes
r-selected species
K-selected species
What are r-selected species?
- One formed in variable, temporary, or unpredictable environment
What happens to r-selected species?
- Probability of long term survival is low
- Rapid production of many offspring
- High growth rate
What do r-selected species have a tendency for?
- Small body size
- Mature early
- Large broods
- Little to no parental cave
- Short life span
What are K-selected species located?
Usually in relative stable environment with a population size close to K
What do K-selected species have a tendency for?
- Long life span with slow development
- Large body size
- High competitive ability
- Defenses against predators
- Relatively old at age of first
- Low reproductive rate of first reproduction
- Provide parental care for young
What are some factors that influence population size?
- Density-Independent factors
- Density-Dependent factors
What are density-independent factors?
- Operate without relation to population density
- Tend to be abiotic factors
- Density independent population
What is an example of density-independent factor that is an abiotic factor?
- A volcano destroys 1/2 the population of palm trees
- Drought -> Pond dries -> All fish die
What is a density-independent population?
Birth rate or death rate does NOT change with population density
What are density-dependent factors?
- Impact is affected by population density
- In general, it acts as a negative feedback system
As population density INCREASES...
Factors slow population growth
(decrease birth rate or increases death rate)
As population density DECREASES...
Factors increase population growth (either increases birth rate or decreases death rate)
Mechanisms of density-dependent regulation
- Competition for resources
- Disease
- Predators
- Territoriality
- Intrinsic factors
- Toxic wastes
Combinations of density-dependent and independent factors interact...
to determine population size in most species