Organic Chemistry - Chapter 10: Alchohols
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Alchohol
molecule with hydroxyl (OH) functional group
Physical Properties of Alcohol
unusually high boiling points due to hydrogen bonding and miscibility for only small alcohols with water due to their polar nature
Acidity of Alcohols
generally weak acids, (from ability to donate a proton (H+) from the hydroxyl group) much lower than water’s; more halogens, more acidity; more alkyls, less acidity
Acidity of Phenols
100 million times more acidic than cyclohexanol due to resonance stability
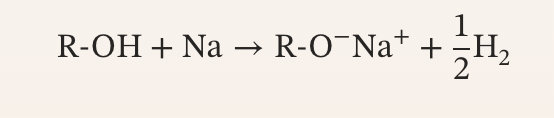
Formation of Sodium Alkoxides Reaction
an irreversible reaction where alcohols react with sodium to form alkoxides and hydrogen gas; used as nucleophile (Williamson ether synthesis), as a strong base in organic reactions (deprotonation), and in E2 elimination reactions to form alkenes
Formation of Sodium Alkoxides Reagents
alcohol (R-OH) + sodium metal (Na) or sodium hydride (NaH)
Formation of Sodium Alkoxides Products
primary alcohol (strong nucleophile - RONa+) + hydrogen gas
Formation of Potassium Alkoxides Reaction
an irreversible reaction where alcohols react with potassium to form alkoxides and hydrogen gas; used as nucleophile (Williamson ether synthesis), as a strong base in organic reactions (deprotonation), and in E2 elimination reactions to form alkenes
Formation of Potassium Alkoxides Reagents
alcohol (R-OH) + potassium metal (K) or potassium hydride (KH)
Formation of Potassium Alkoxides Products
secondary & tertiary alcohols (strong nucleophiles - ROK+) + hydrogen gas
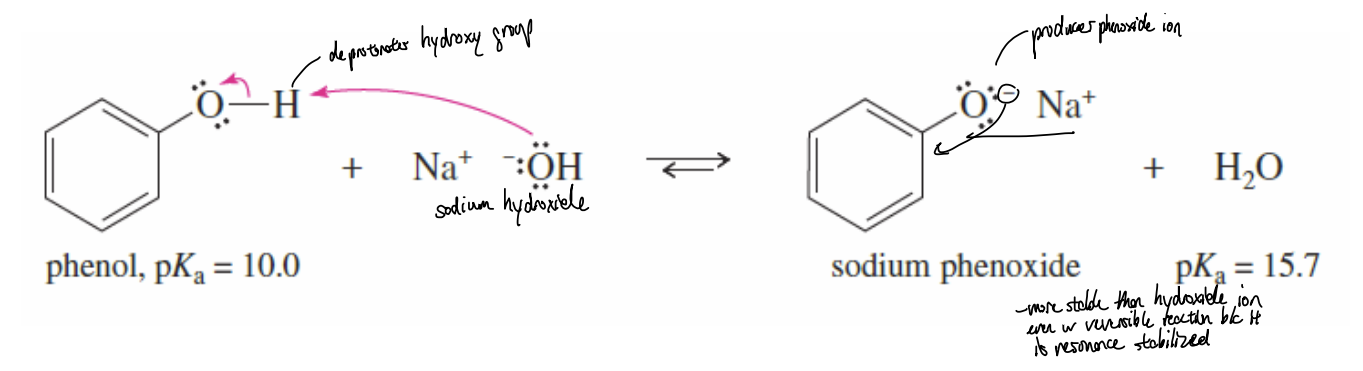
Formation of Phenoxide Ion Reaction
phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide to form phenoxide ions; used in the synthesis of ethers and esters (Williamson Synthesis, Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution)
Formation of Phenoxide Ion Reagents
phenol + strong base (sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH)) for deprotonation
Formation of Phenoxide Ion Products
phenoxide ion (C6H5O-) + water (H2O)
Organometallic Reagents
partial positive charge (metal) + partial negative charge (carbon) equals polarized C-M bond and electrophilic carbon
Limitations of Organometallic Reagents
no water or other acidic protons (to avoid protonation) and no other electrophilic multiple bonds (C=N, C—N, S=O, or N=O)
Grignard Reagents
made from reaction of alkyl halide + magnesium metal with ether solvent; heavier halide = greater reactivity
Organolithium Reagents
made from an alkyl halide with lithium with ether, alkanes, or non-protic solvents
Grignard + Organolithium reagents
can both produced from (1, 2, 3) alkyl, vinyl (−CH=CH2), or aryl (cyclic) halides
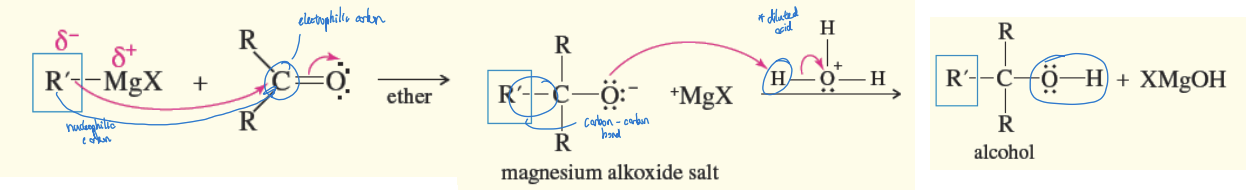
Carbonyl Nucleophilic Addition Reaction
a nucleophile (Grignard reagent) attacks the electrophilic (+) carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion intermediate
Carbonyl Nucleophilic Addition Reagents
ether (for intermediate) + diluted alcohol (H3O+ - protonates intermediate to product)
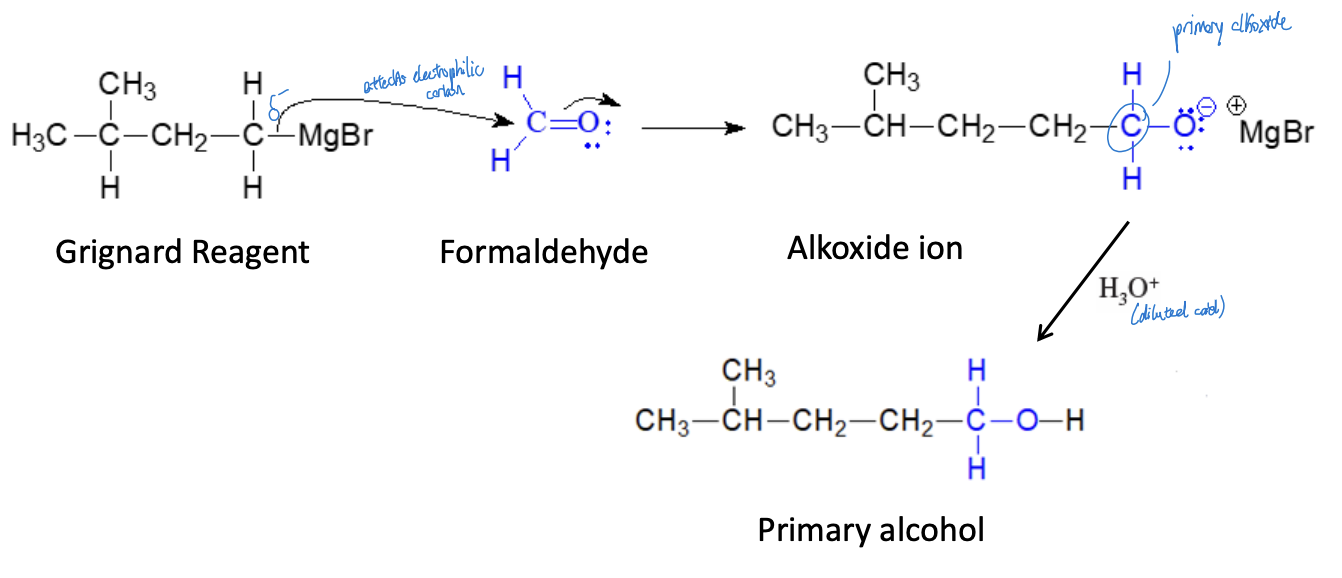
Synthesis of 1° Alcohols (Single Addition) Reaction
grignard reagent + formaldehyde & ether + diluted alcohol = primary alcohol with one additional carbon
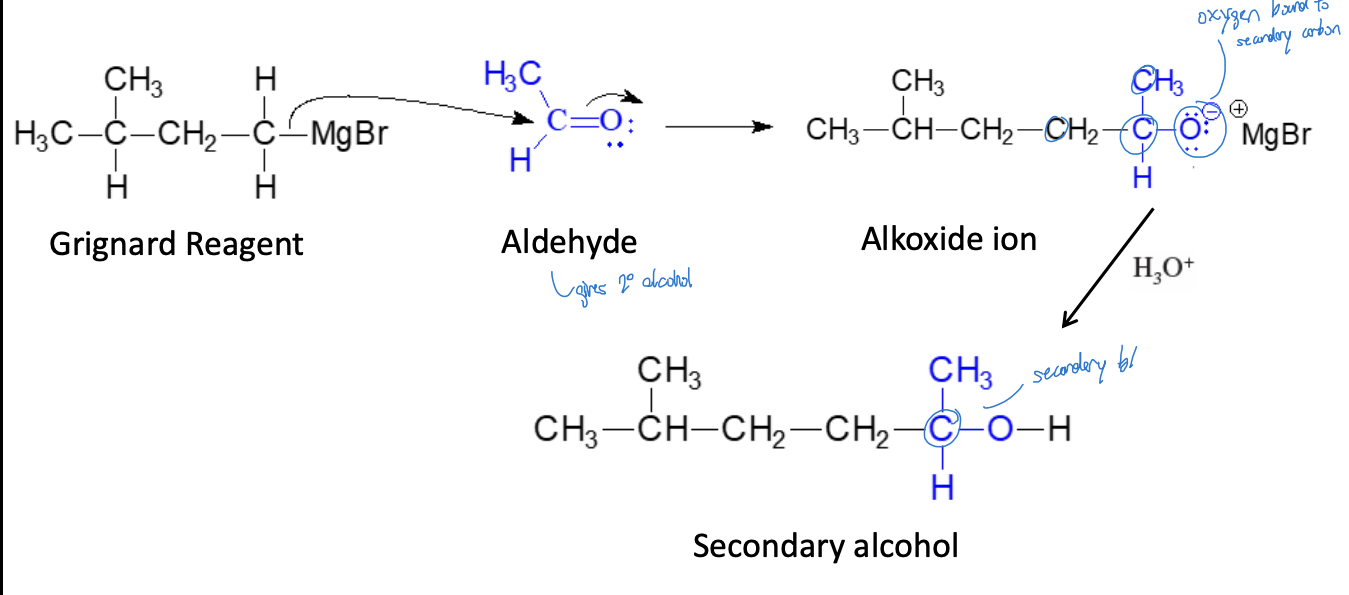
Synthesis of 2° Alcohols (Single Addition) Reaction
grignard reagent + aldehyde & ether + diluted alcohol = secondary alcohol
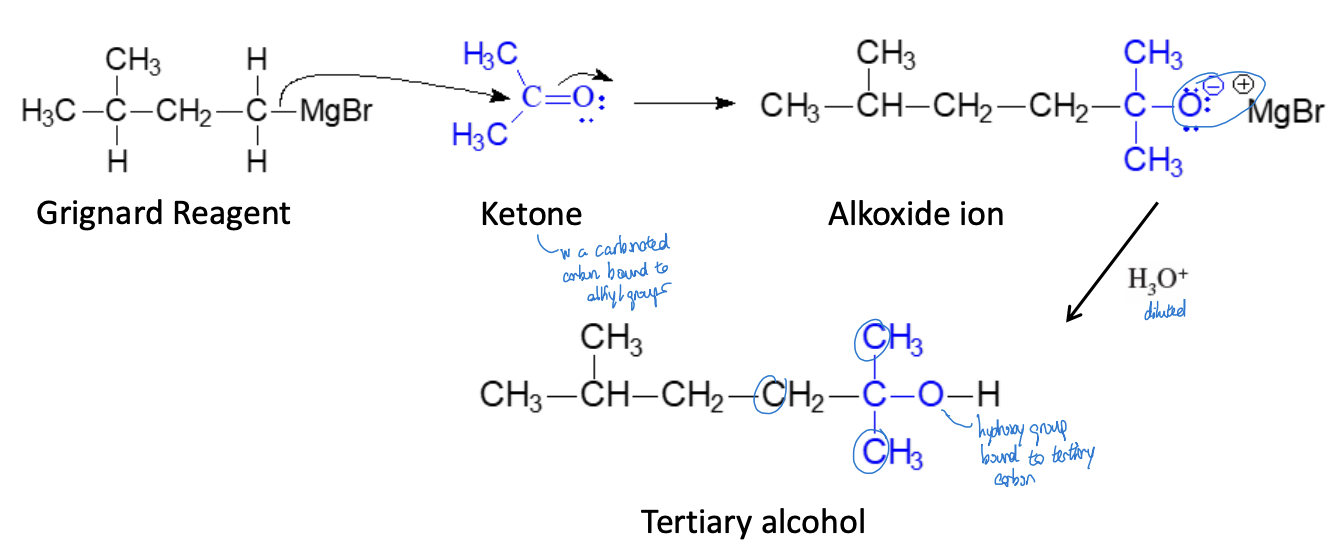
Synthesis of 3° Alcohols (Single Addition) Reaction
grignard reagent + ketone & ether + diluted alcohol = tertiary alcohol
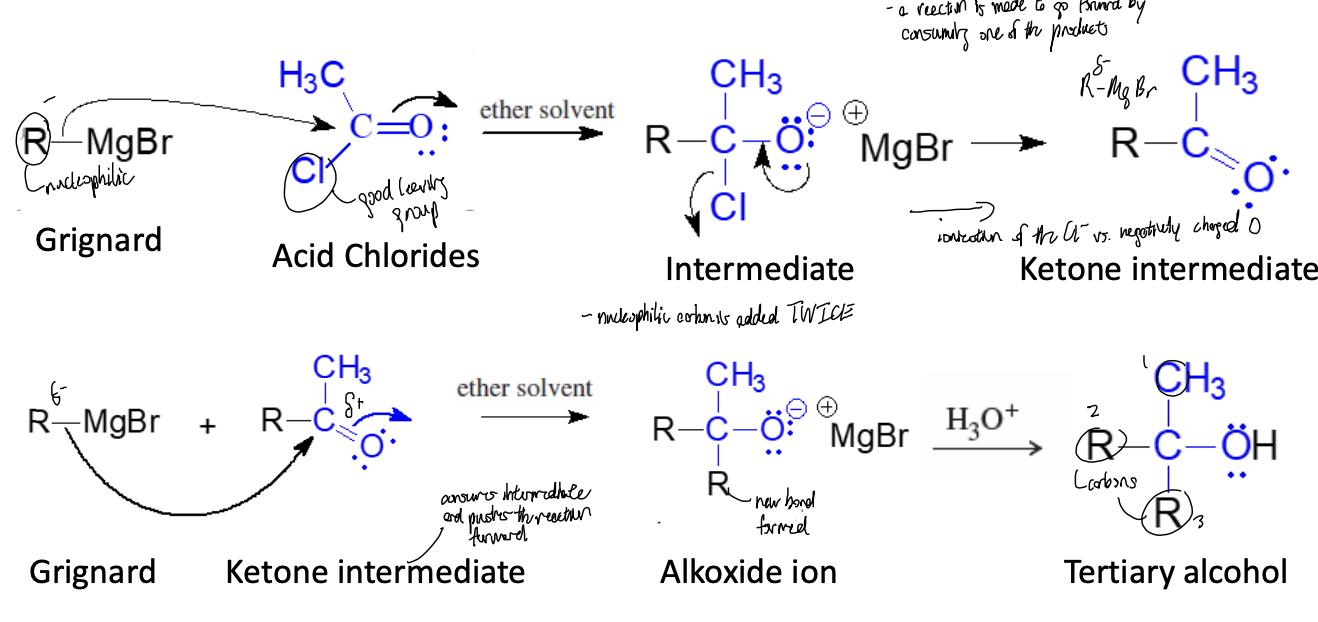
Acid Chloride (Multiple Addition) Reaction
grignard attacks the acid chloride, chloride ion leaves, second mole of Grignard reacts with the ketone intermediate to make alkoxide ion
Acid Chloride (Multiple Addition) Products
alkoxide ion protonated with diluted alcohol to produce tertiary alcohol
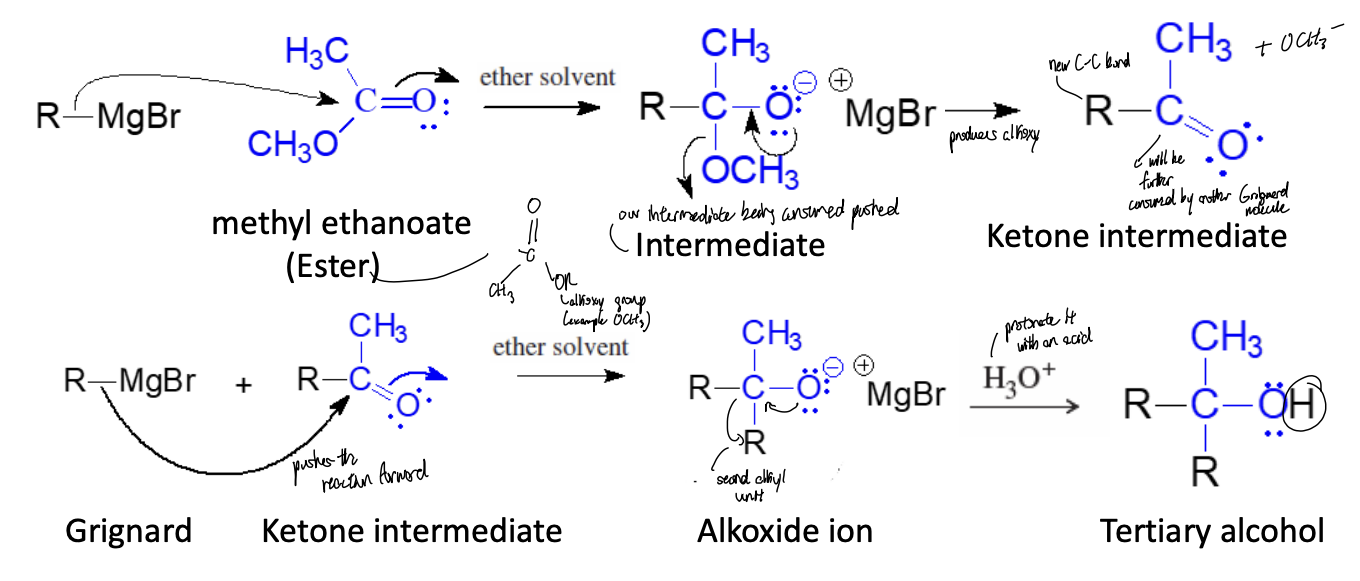
Ester Addition Reaction
grignard attacks carbonyl, alkoxide ion leaves, second mole of Grignard reacts with the ketone intermediate to make alkoxide ion
Ester Addition Product
tertiary alcohol
Ring-Opening with Ethylene Oxide Reaction
grignard (strong nucleophile) attacks ethylene oxide (weak electrophile) forming alkoxide ion, alkoxide ion is protonated by dilute acid to make alcohols
Ring-Opening with Ethylene Oxide Products
primary + secondary alcohols
Carbonyl Reduction Reaction
hydride ion from the reducing agent attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide intermediate which is protonated by a solvent or acid
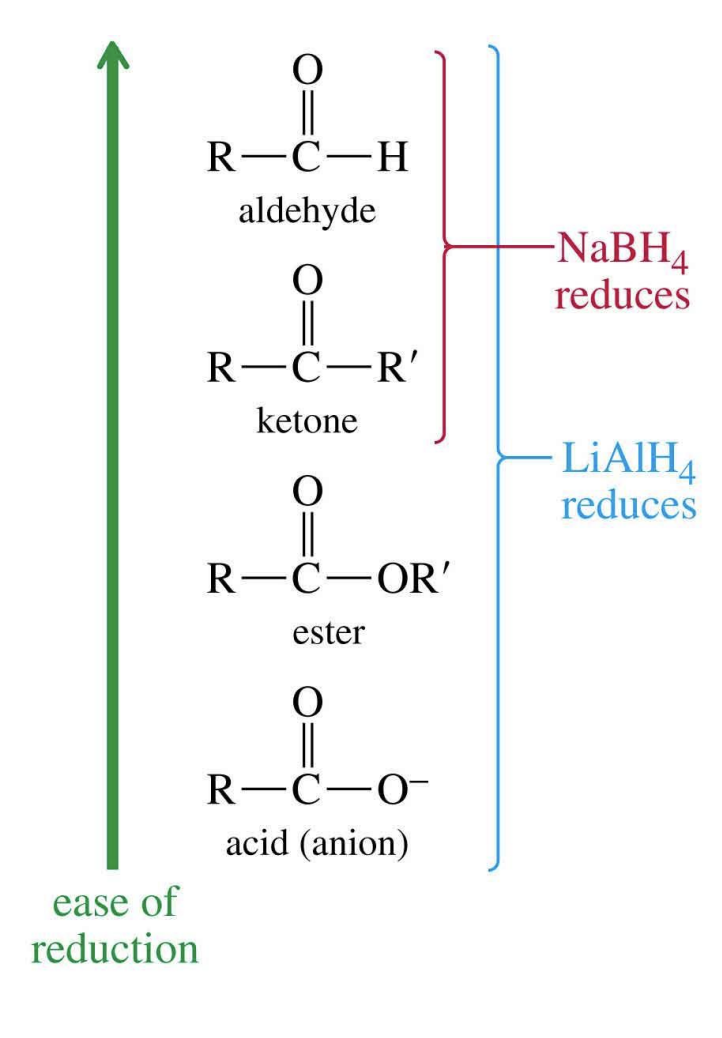
Carbonyl Reduction Reagents
hydride reagents: sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4)
Sodium Borohydride
only reacts with carbonyl of aldehyde or ketone (more selective)
Lithium Aluminum
stronger reducing agent – reacts with carbonyl of aldehyde, ester + carboxylic acids for primary alcohols and ketone for secondary alcohols
Carbonyl Reduction Products
primary + secondary alcohols
Catalytic Hydrogenation Reaction
reduces a ketone or an aldehyde to an alcohol by adding H2 with Raney nickel catalyst (Raney Ni) (also reduces C-C double bonds)
Thiols
sulfur analogues of alcohols (-SH) instead of (-OH); more acidic than alcohol; larger size helps sulfur withstand negative charges
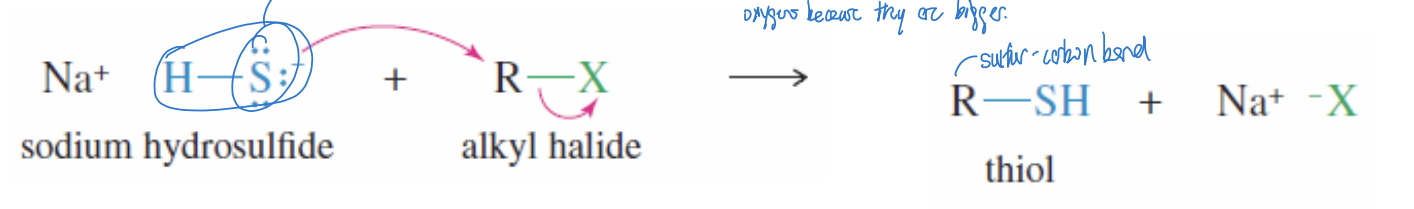
Thiol Synthesis Reaction
SN2 reactions of sodium hydrosulfide + unhindered alkyl halides producing a thiol (R-SH)
Thiol Oxidation Reaction
thiol groups (-SH) are converted to oxidized forms like disulfides (R-S-S-R') and sulfonic acids (R-SO3H)
Thiol Oxidation Reagents
disulfides: 2RSH (two thiol molecules) + oxidizing agent (Br2;Zn, HCl or O or peroxide)
sulfonic acids: KMnO4 or nitric acid (HNO3)
Thiol Oxidation Products
disulfides: R-S-S-R + Br or H2O
sulfonic acids: R-SO3H - expanded octet and charge separation