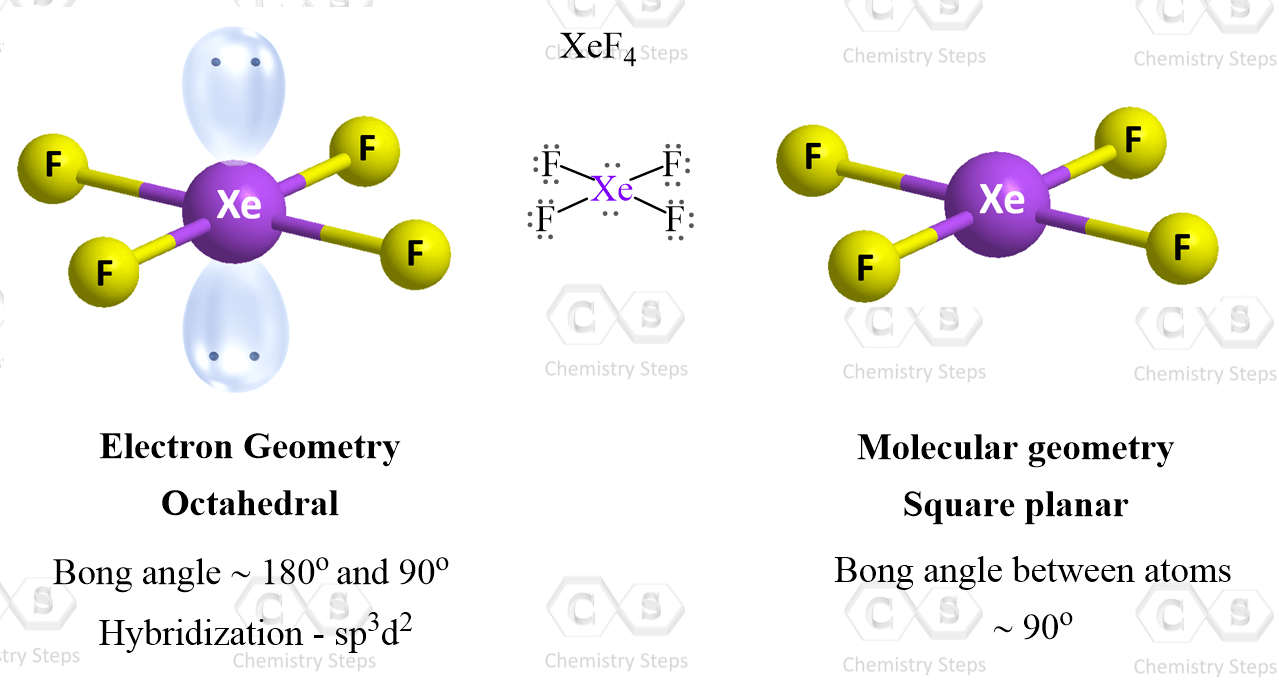Atomic and Molecular Structure
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are the four main points regarding Dalton’s atomic theory?
All matter is composed of atoms
Atoms of a specific element are identical in mass and properties
Compounds are formed by whole-number ratios of two or more different atoms
A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms
What is the atomic number of an atom?
It is the number of protons found in that atom
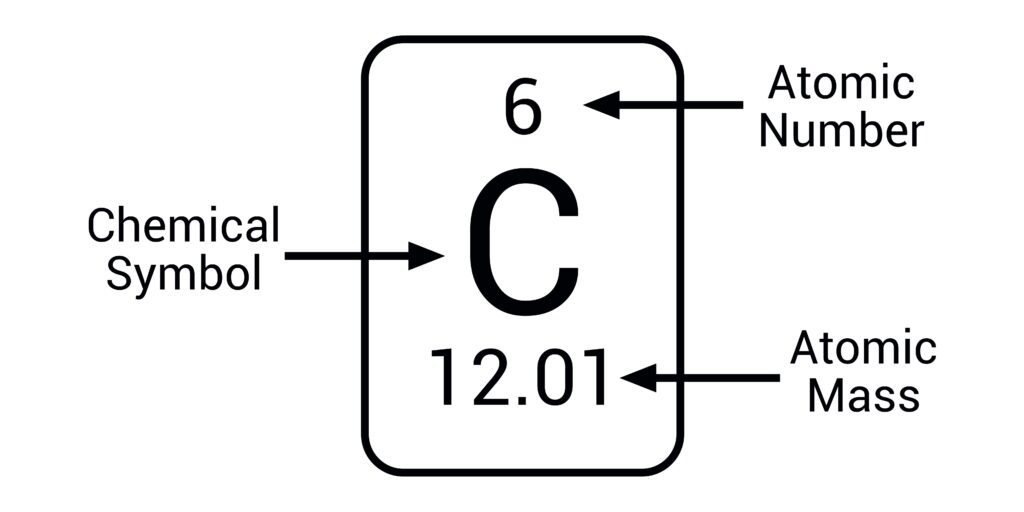
What is the mass number of an atom?
It is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an atom.
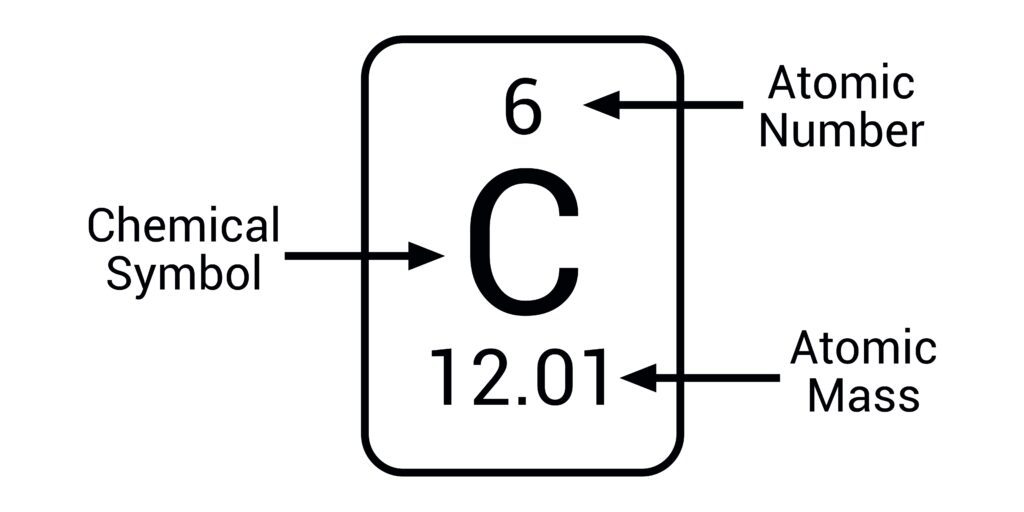
What is a neutral atom?
An atom with the same number of protons and electrons
What is the atomic notation of carbon
The mass number will be listed above the atomic number, and to the right will be the symbol that represents the chemical element..
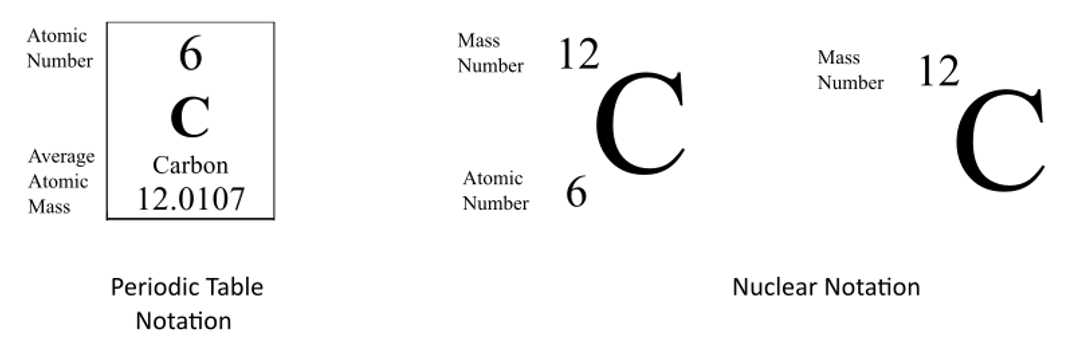
What are isotopes?
They are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
What is the core electron equation?
2(n)²
What is an element?
An element is a pure substance composed of ONE type of atom. Elements can not be broken down into other substances through physical or chemical reactions.
What is a compound?
A compound is formed when two or more atoms from different elements combine.
What is a physical reaction?
It is when a molecule undergoes rearrangement to produce a physical change. No new substances are created, and no new chemical bonds are formed or destroyed.
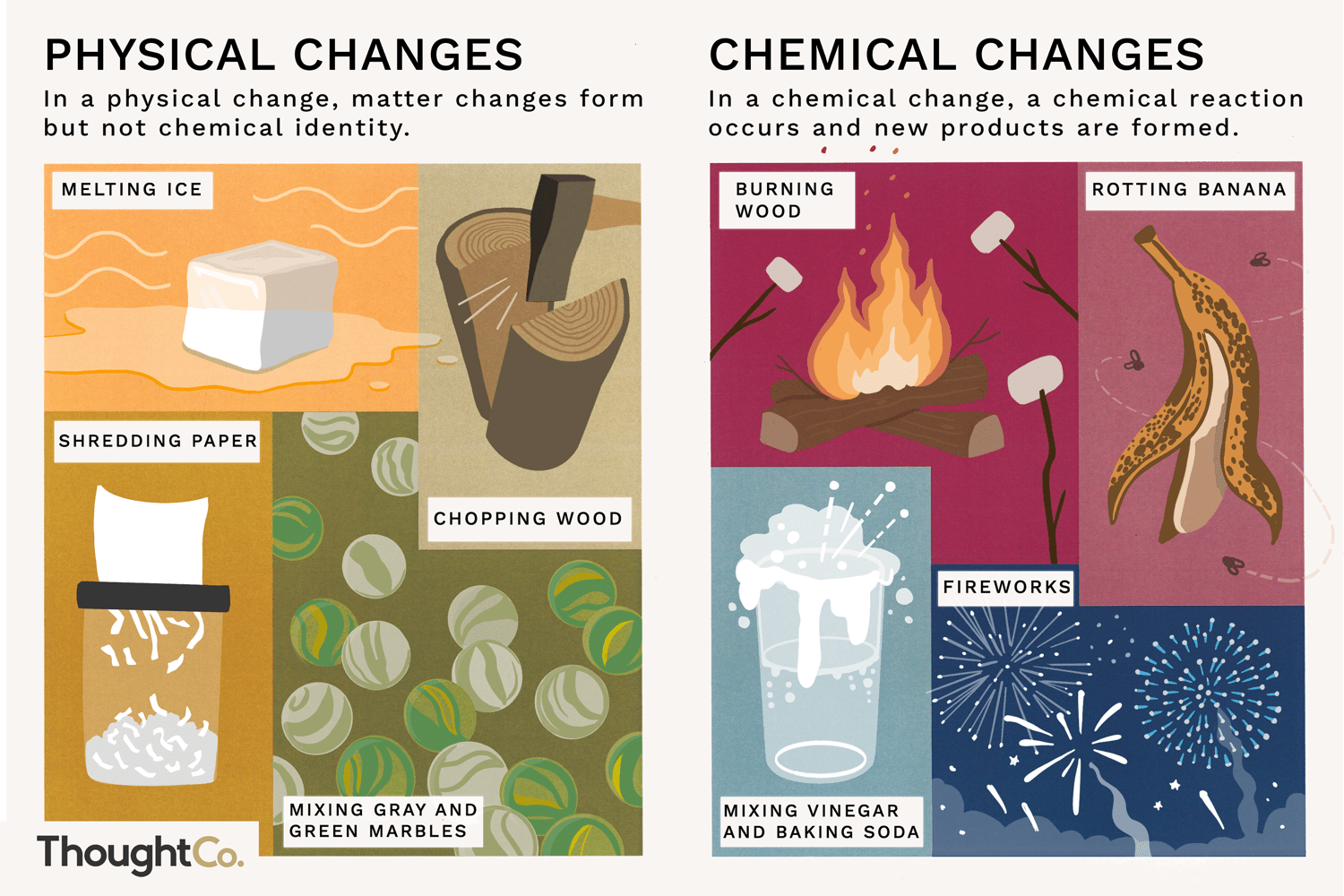
What is a chemical reaction?
It is where a new substance is created. Intermolecular bonds between atoms are created or destroyed.
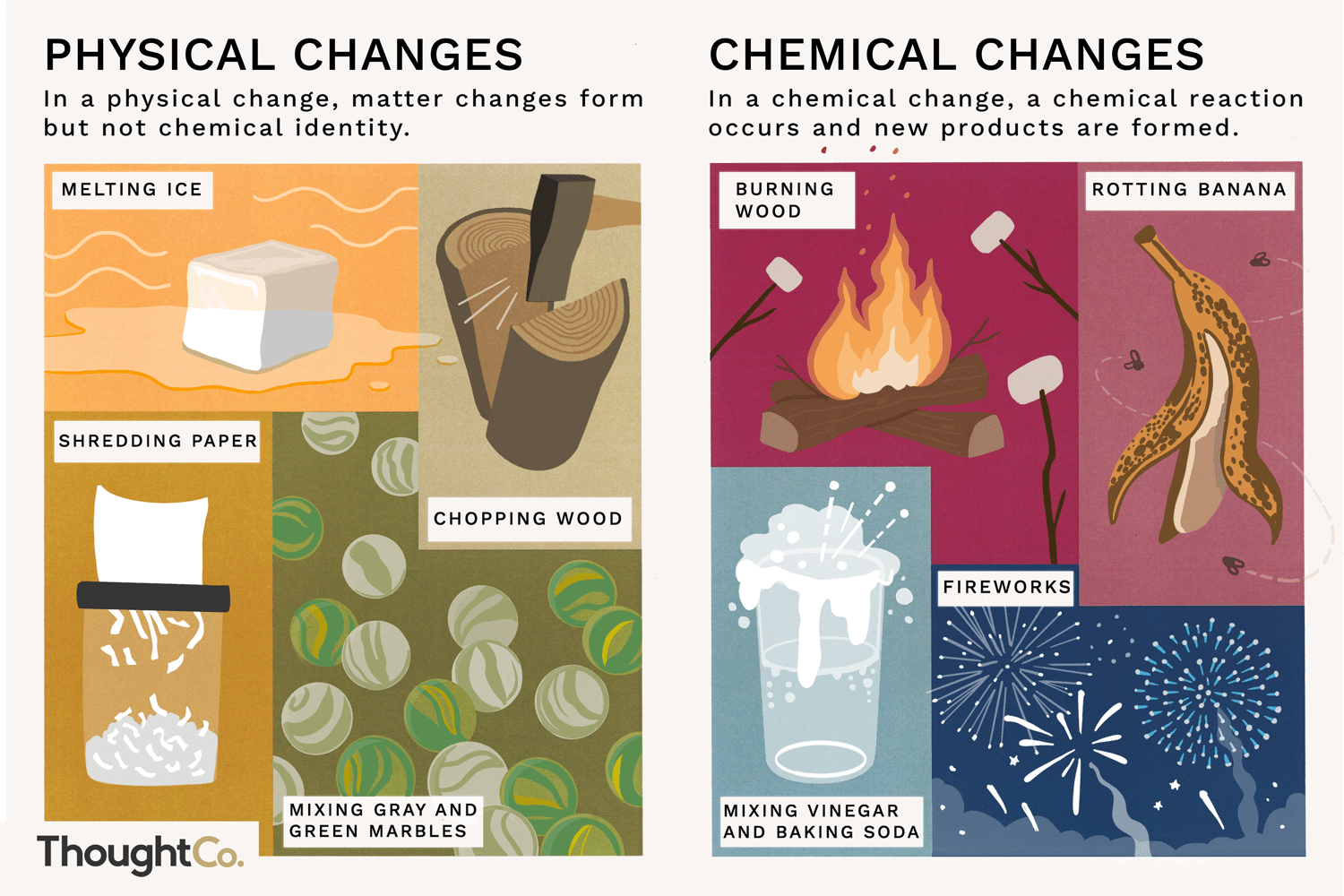
What are the five different chemical reactions? explain
Synthesis Reaction: When two or more atoms or molecules combine to form a single compound. This reaction usually involves the release of energy
Decomposition Reaction: When a compound breaks down into two or more products. This reaction usually requires the input of energy
Single Displacement Reaction: When another replaces one element in a compound
Double Displacement Reaction: The exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species → common types are neutralization and precipitation reactions
Combustion Reaction: When a substance reacts with O2 gas to produce light and heat. It must involve oxygen as a reactant
For hydrocarbon reactions, water and carbon dioxide are always the products.
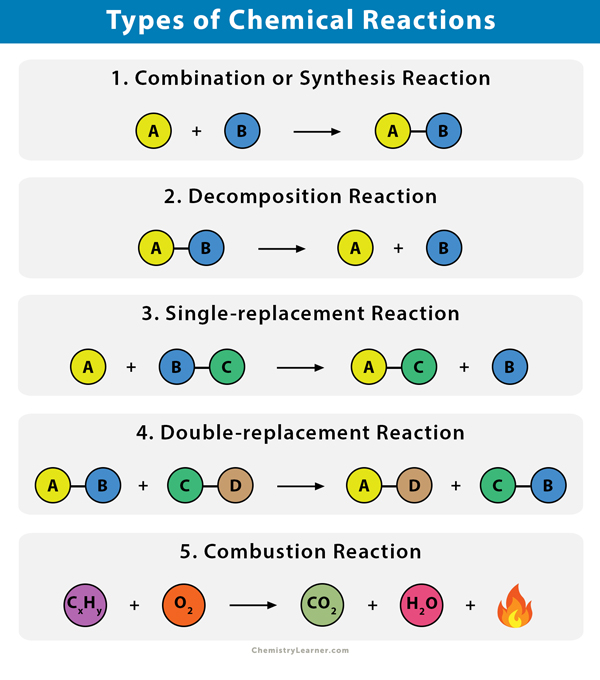
What does Bohr’s model state?
It is an outdated idea, where it was initially believed that electrons follow a fixed circular path around the nucleus.
What is the modern quantum theory?
Electrons are localized in a cloud of electrons
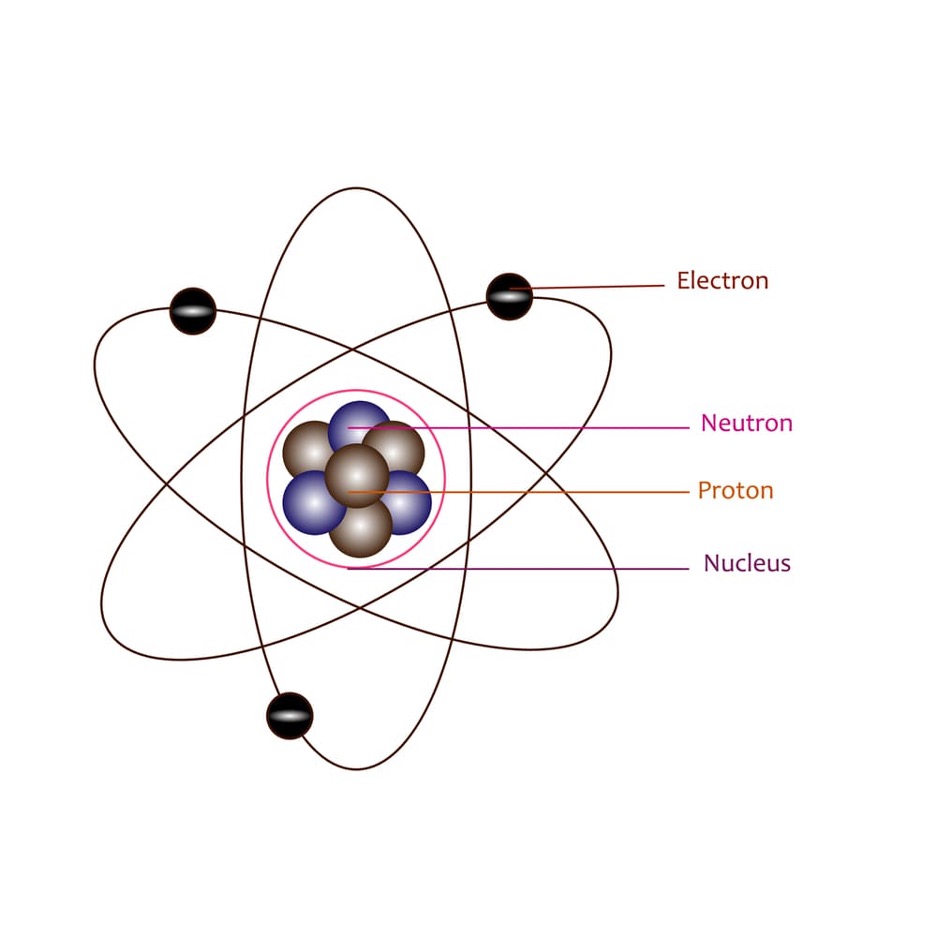
What is a quantum number?
It describes the probable location and energy of an atom’s electrons. It is unique to each electron in an atom.
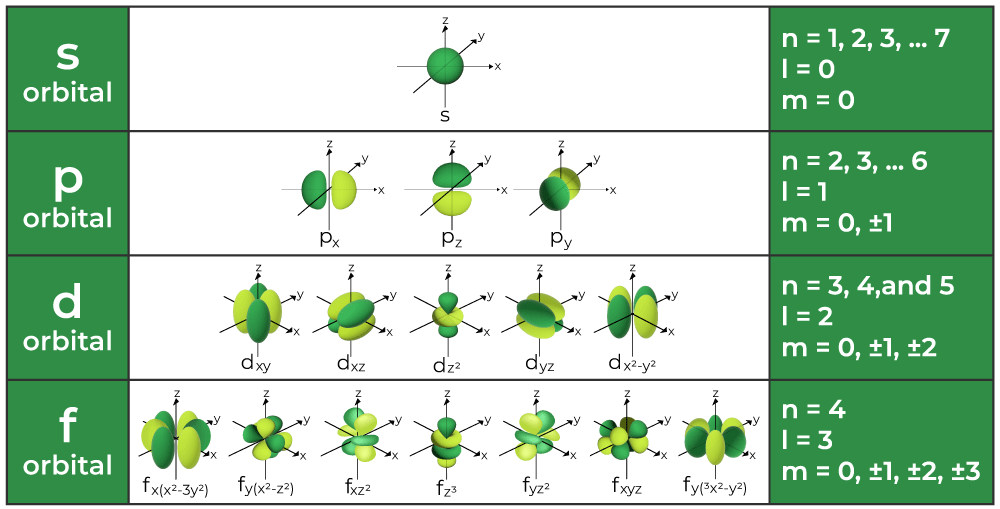
What are the four quantum numbers that help describe the electrons of an atom?
Principal Quantum Number (n): It represents the main energy level occupied by electrons.
It is a positive integer, greater than or equal to 1. At n=1, an electron is closest to the nucleus, and with each successive electron shell, electrons get farther.
→ A shortcut to deduce the energy level of a ground-state atom’s valence electron is by referring to the row it belongs to on the periodic table.
Azimuthal Quantum number (I): Describes the orbital shape within each principal energy level.
The possible values are all integers between zero and n-1.
The subshell is represented by a letter → I=0 is s, I=1 is p shell, I=2 is d, and I=3 is f.
The subshells can hold 2,6,10,and 14 electrons
Magnetic Quantum Number (mI): Describes the orientation of orbitals in space.
The magnetic quantum number ranges between the negative and positive magnitudes of the azimuthal quantum number.
Spin quantum Number (ms): Describes the angular momentum of an electron.
It is denoted as ±1/2. Electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins.
What does Pauli’s exclusion principle state?
It states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
What is electron configuration?
It is the number of electrons in each energy level and the order in which the subshells of an atom are filled.
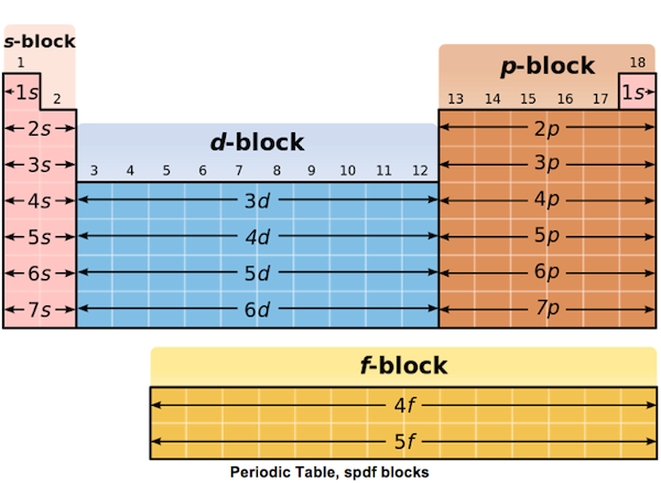
Using the periodic table, label the s-block, d-block, f-block, and p-block
Look at the image
What does the Aufbau principle state?
It states that subshells tend to get filled from lower to higher energy levels
What does the Hund’s rule state?
It states that all orbitals of a subshell must first receive an electron before pairing can occur
How many electrons do the s-orbital, p-orbital, d-orbital, and f-orbital hold?
s→ 2
p→ 6
d→10
f→14
The decision to share one’s electrons or give them away entirely depends on?
The electronegativity between the atoms involved
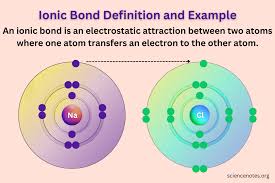
How is an Ionic bond formed?
It is formed when the more electronegative atom accepts the electron from the less electronegative atom.
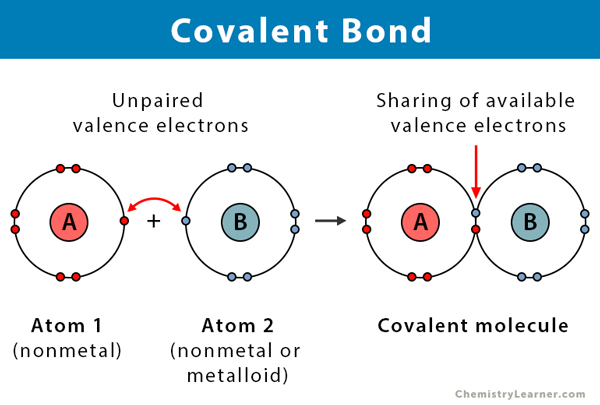
How is a covalent bond formed?
It is formed when a slight difference in electronegativity exists between atoms. Both atoms share the electron amongst themselves.
Why is forming bonds necessary for atoms?
It allows for an atom to achieve a full octet or full valence shell, making it more stable.
Ionic bonds occur between what two types of atoms?
Metal and non-metal. The non-metal will accept the electron from the metal atom.
Covalent bonds occur between?
non-metals
Which compounds are soluble in water?
Ionic compounds
What is ductile?
When a metallic compound can be drawn into thin wires

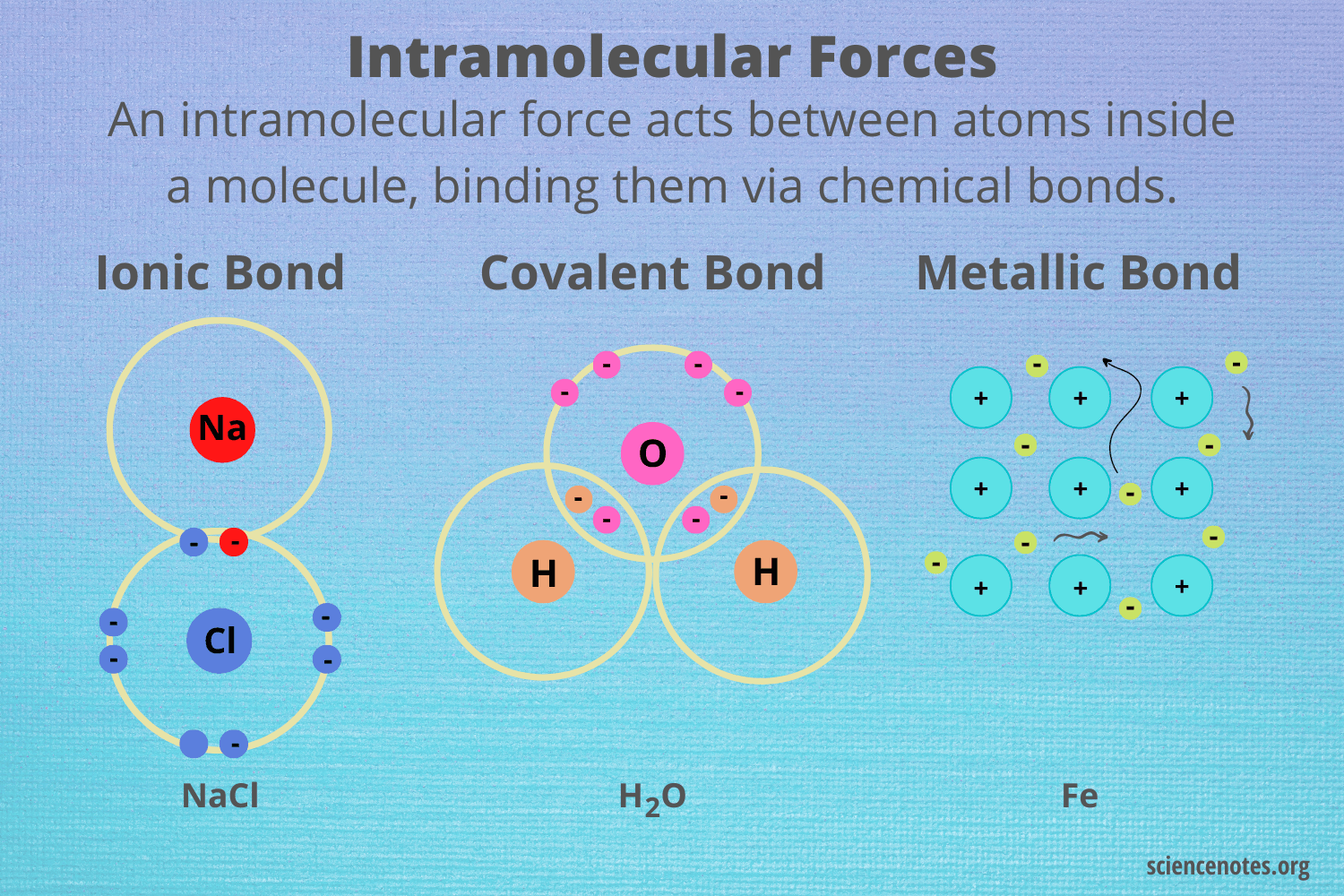
What are intramolecular forces?
The attractive forces holding atoms within a molecule together
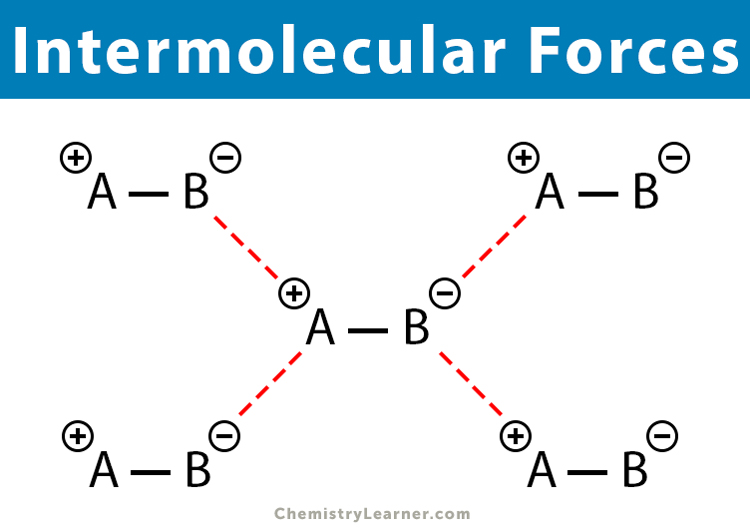
What are Intermolecular forces?
The attractive forces holding atoms between molecules.
What are dipole-dipole forces?
It is when a partially positive side of a molecule attracts the partially negative side of another molecule.
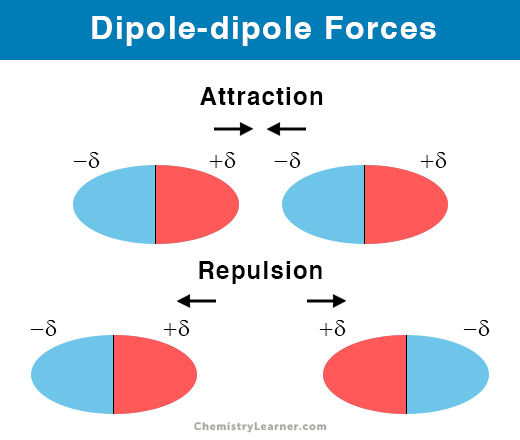
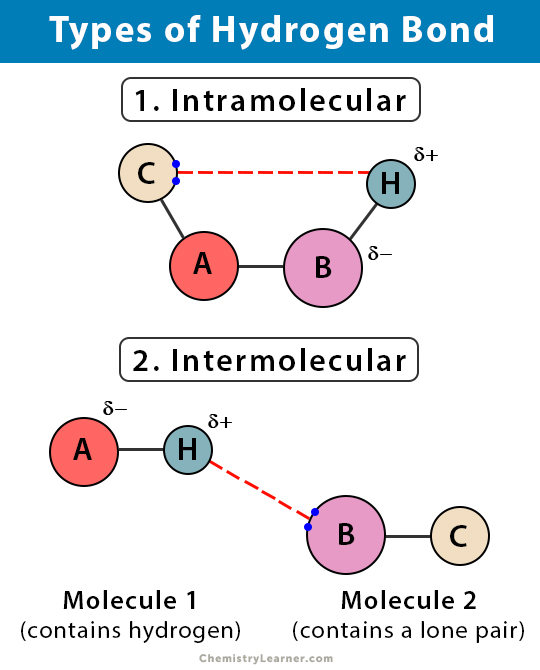
What are hydrogen bonds?
They are a strong dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is attached to highly electronegative nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atoms
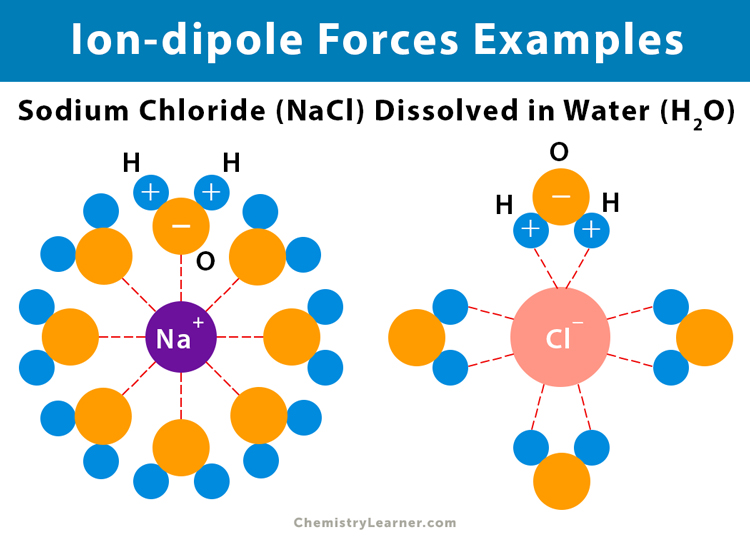
How are Ion-Dipole interactions formed?
It is the attraction between an ion and a polar molecule. Stronger than dipole-dipole interaction
What are the six elements that form a reduced octet?
H, HE, LI,BE,B, and AI
Which elements form an exceeding octet?
Elements within the 3rd row or more have d-subshell
What is the equation for formal charge?
Formal charge= (# of valence e-)- (# of nonbonding e-) - (# of bonds)
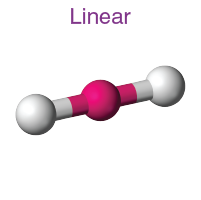
How many electron domains does a linear molecular geometry have?
2 electron domains and its 180 degrees
How many electron domains does a Trigonal planar molecular geometry have?
3 electron domain and its 120 degrees
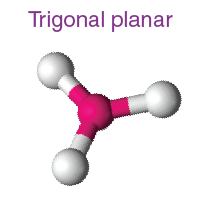
How many electron domains does a Tetrahedral molecular geometry have?
4 electron domain and its 109.5 degrees
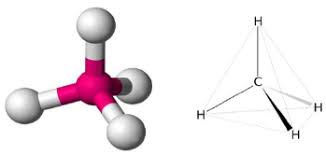
How many electron domains does a Trigonal Bipyramidal molecular geometry have?
5 electron domain and it has 180, 90, and 120 degrees

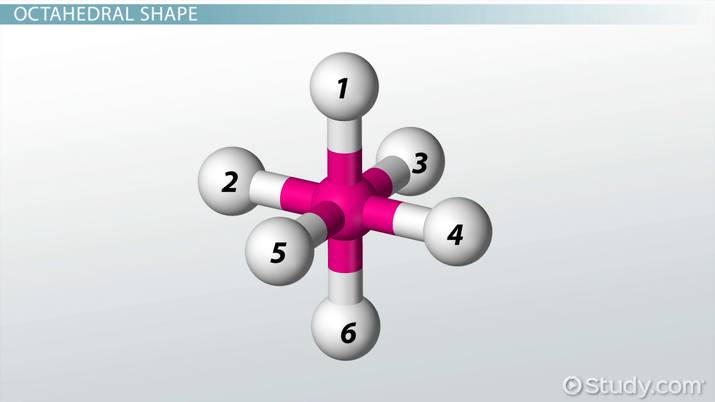
How many electron domains does an octahedral molecular geometry have?
6 electron domain
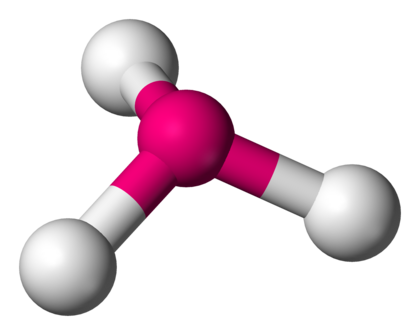
3 bonds and 1 lone pair with a bond angle of 107.5 degrees is called what? The molecular geometry
Trigonal pyramidal
4 bonds and one lone pair with a bond angle of 90 or 120 is called what? molecular geometry
Seesaw
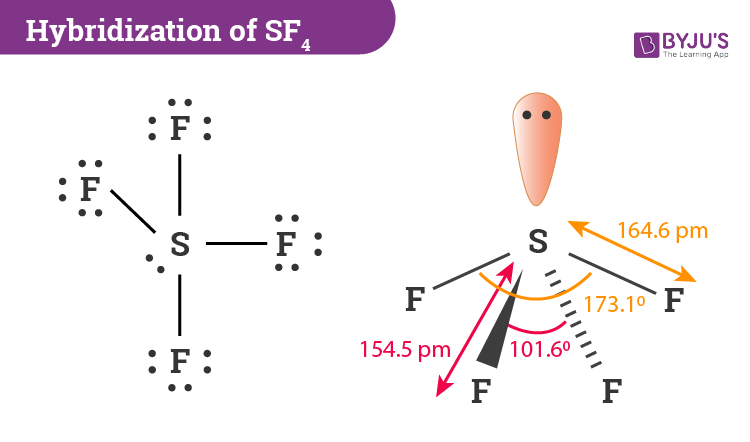
3 bonds and 2 lone pairs with a bond angle of 90 degrees is called what? molecular geometry
t shaped
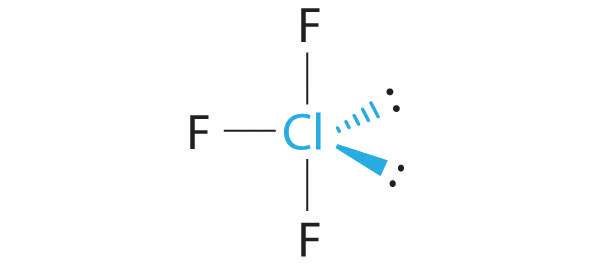
2 bonds, and 3 lone pairs with a bond angle of 180 degrees is called what? molecular geometry
Linear
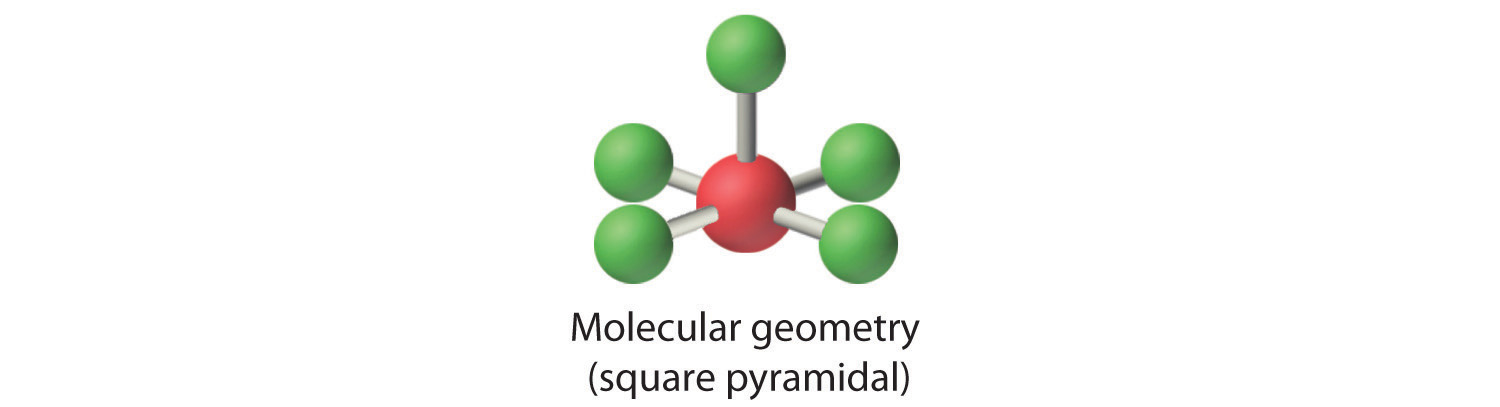
5 bonds and 1 lone pair with a bond angle of 90 degrees is called what? molecular geometry
square pyramidal
4 bonds and 2 lone pairs with a bond angle of 90 degrees is called what? molecular geometry
square planner