14: trash and unfinished Interactions between cells in multicellular systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Tissues in the Body
The four major tissue types:
epithelial
connective
nervous
muscular
Epithelial Tissue
cover surfaces and line internal cavities
organised into sheets
sheets can be rolled up into tubes eg in kidney collecting duct
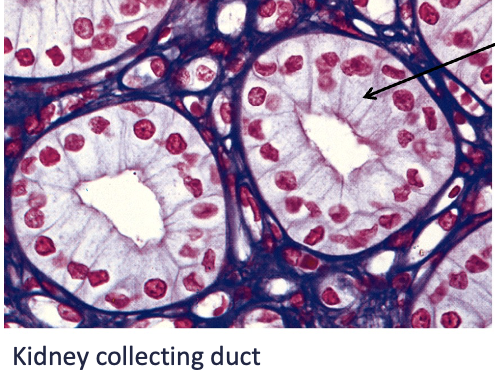
Functions of Epithelial Sheets
Act as barriers between the body and the environment.
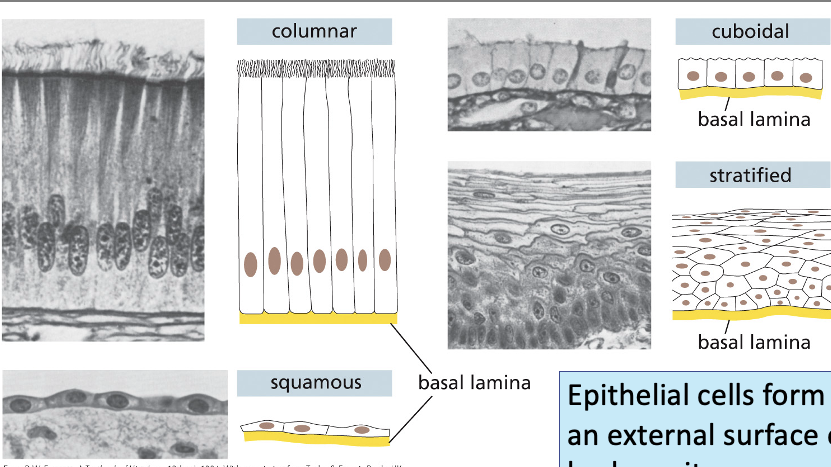
types of epithelia
columnar
cuboidal
squamous
stratified
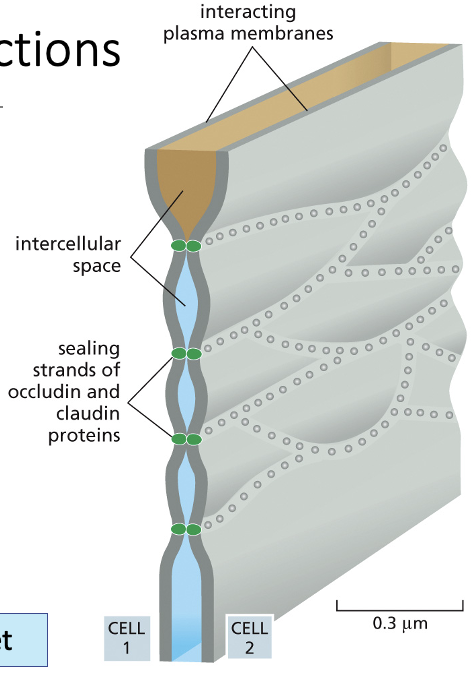
Tight Junctions
Form a seal between epithelial cells to prevent diffusion / leakage across the sheet.
allow the apical and basolateral membranes to be different in function and composition (meaning epithelia are functionally polarised)
Proteins in Tight Junctions
Occludin and claudin proteins
secretion from the apical surface in epithelia
airways
stomach
intestine
mammary gland
adherens junction
joins an actin bundle in one cell to a similar bundle in a neighbouring cell
desmosome
joins intermediate filaments in one cell to those in a neighbouring cell
gap junction
forms channels that allows small, water-soluble molecules to pass from cell to cell
hemidesmosome
anchors intermediate filaments in a cell to the basal lamina
Cytoskeleton-Linked Junctions
Provide mechanical strength and stability to epithelial sheets.
examples
adheren and desmosomes- link cytoskeleton of epithelial cells to their neighbours
use cadherins
hemidesmosomes - link cytoskeleton of epithelial cells to basal lamina
use integrins
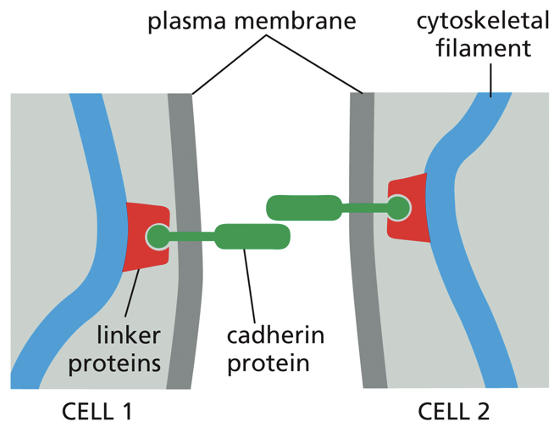
Cadherins
Transmembrane proteins that mediate attachment between epithelial cells.
interaction needs calcium
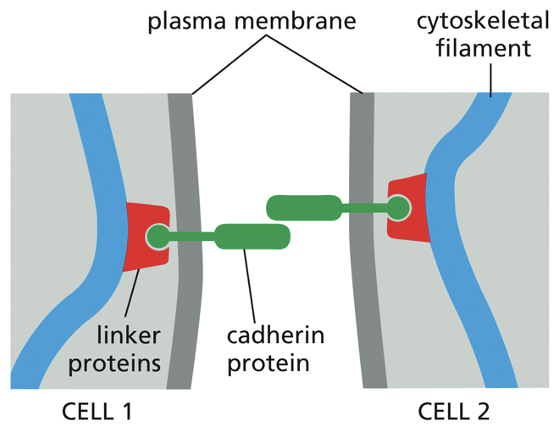
Adherens Junctions mode of action
Cadherins link to actin filaments to form adhesion belts.
Properties of Adherens Junctions
Contractile because of presence of myosin II - allows epithelial sheets to move
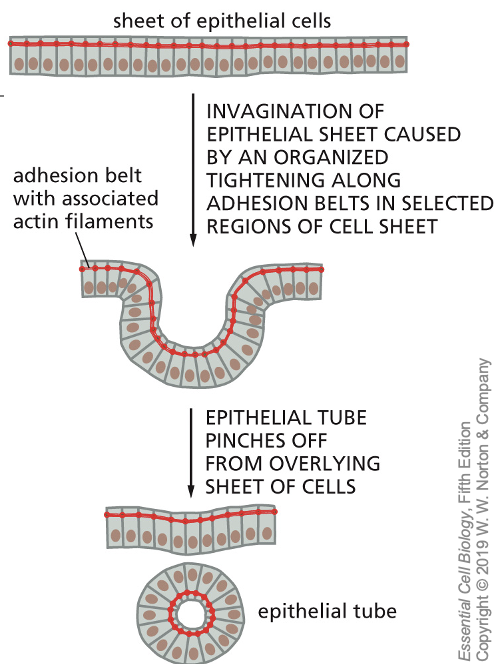
examples of where contractility is important
lens formation
neurulation
Examples of Desmosome-Rich Tissues
Found in heart muscle and exposed epithelia under stress.
properties of intermediate filaments (desmosomes)
great tensile strength
Gap Junctions
Allow direct communication between neighboring cells by transferring ions and small molecules.
Connexons
Channel proteins that form gap junctions.
Gap Junction Function in the Heart
Enables electrical coupling
Plasmodesmata
The plant equivalent of gap junctions
Cadherins in Tissue Organization
Specific cadherins define which cells can interact to form tissues.
E-Cadherin vs. N-Cadherin
Epithelial cells express E-cadherin
Cadherins and Cancer
Cancer cells often lose cadherin expression
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) and Connective Tissue
Provides structural support to tissues and helps with cell communication.