Historic Chem Lock-in
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
chemical formula
an expression that shows the elements in a
compound and the relative proportions of those elements.
Stoichiometry
The study of quantitative relations between amounts of reactants and products.
Stoichiometric Factor
A mole‑ratio factor relating moles of one compound to moles of another in a chemical equation.
Limiting Reagent
The reactant present in limited supply that determines the maximum product formed.
Excess Reagent
The reactant present in excess supply that remains after the reaction
Theoretical Yield
Maximum amount of product that can be produced from the limiting reagent.
Actual Yield
Experimentally measured amount of product obtained.
Percent Yield
Ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield × 100%.
Molarity (M)
Number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
Mole (mol) –
Amount of substance containing 6.022×1023 entities (Avogadro’s number)
Molecular Mass
Sum of atomic masses (amu) in a molecule.
Molar Mass –
Mass of 1 mole of a substance in grams.
Formula Mass –
Sum of atomic masses of all atoms in a compound’s formula.
Percent Composition by Mass –
Percent by mass of each element in a compound
Chemical Formula –
Expression showing elements in a compound and their proportions.
Empirical Formula –
Simplest whole‑number ratio of atoms in a compound.
Molecular Formula –
Actual number of atoms in a molecule
Chemical Equation –
Symbolic representation of a chemical reaction
Oxidation‑Reduction (Redox) Reaction –
Reaction involving electron transfer.
Oxidized Element
– Loses electrons.
Reduced Element –
Gains electrons.
combination run
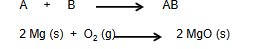
Decomposition Rxn
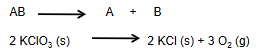
Single displacement Rxn
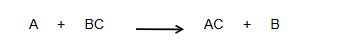
Double displacement
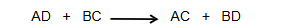
Precipitate
insoluble solid that separates from solution
Combustion
a fast reaction of a compound with molecular oxygen
Pressure
force per unit area
Partial pressure of a gas
the pressure exerted by a specific gas in a gas mixture at the temperature and volume of the mixture
Boyles Law
the pressure exerted by a fixed quantity of a gas at constant temperature is inversely proportional to its volume.
Charles’s Law
the volume occupied by a fixed quantity of a gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature
Ideal gas law (IGL)
the product of the pressure times volume of a gas is directly proportional to the product of the number of moles
of the gas times its absolute temperature. The constant of proportionality is known as the gas constant R = 0.08206 L∙ atm/mol ∙ K
Dalton’s law of partial pressures
the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of each gas in
the mixture