Digestive System: Structure and Function of Exchange Surfaces in Multicellular Organisms
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Heterotrophs
Organisms that obtain energy by using the organic molecules present in food.
Ingestion
Intake of food.
Digestion
Breakdown of molecules.
Absorption
Uptake of nutrients into blood or lymph.
Defecation/Egestion
Elimination of undigested material.
Mechanical Digestion
Breaking down food into smaller pieces when force is applied.
Chemical Digestion
Enzymes are involved to break down food into small, water-soluble molecules.
Amylase
Enzyme that breaks down starch (polysaccharide) to maltose (disaccharide).
Peristalsis
An involuntary muscle contraction that moves food along the oesophagus.
Pepsin
Enzyme produced in the stomach that breaks down proteins to polypeptides.
Hydrochloric Acid
Substance produced in the stomach to maintain an optimum pH of 2 for pepsin to work.
Maltase
Enzyme that converts maltose to glucose.
Peptidase
Enzyme that converts polypeptides to amino acids.
Lipase
Enzyme that converts lipids to fatty acids and glycerol.
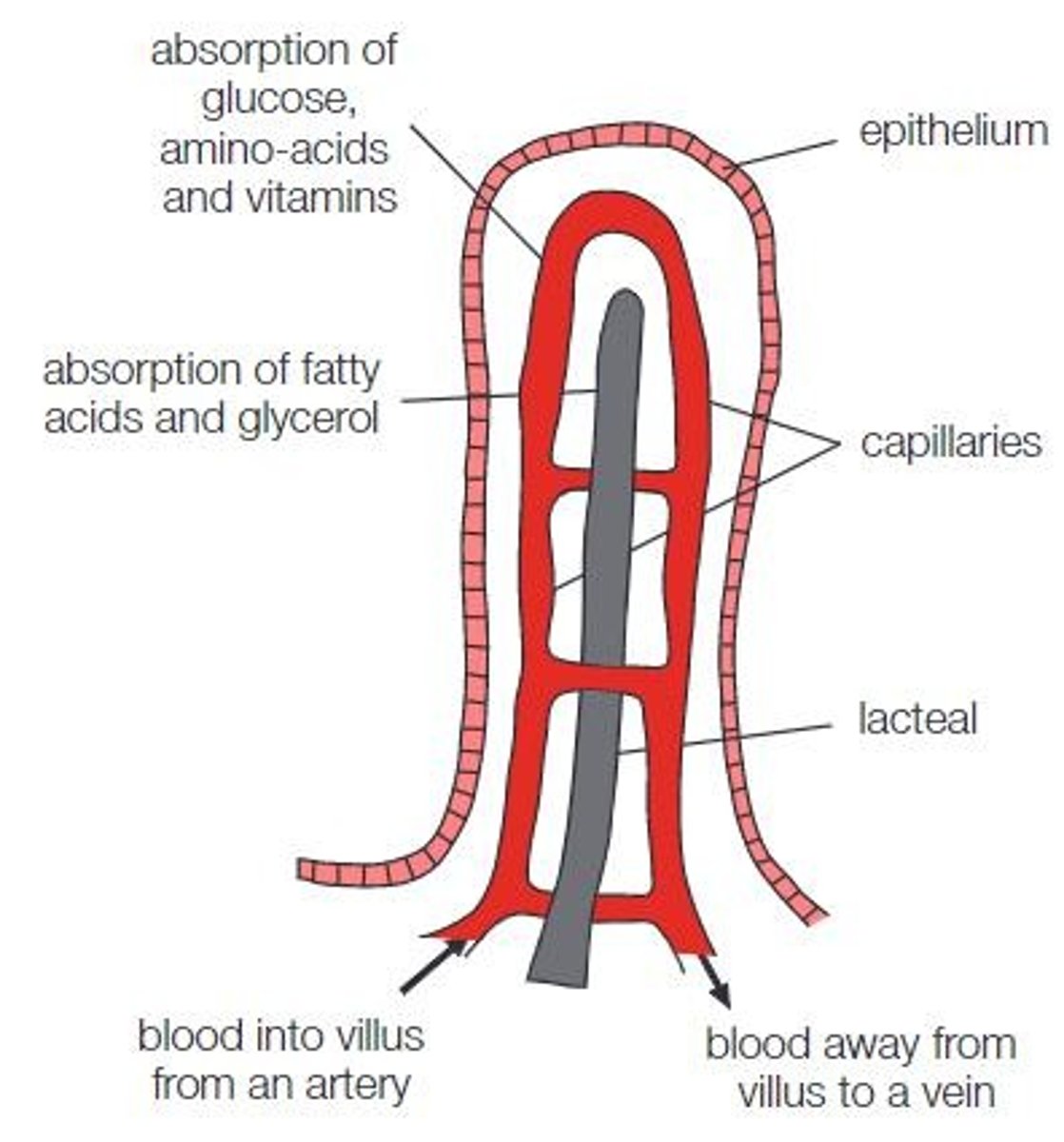
Villi
Exchange surface in the digestive system located in the small intestine.
Gall Bladder
Stores bile produced in the liver, which breaks down lipids.
Pancreas
Produces enzymes and bicarbonate solution which restores the pH to 7.
Small Intestine
Receives fluids from the gall bladder and pancreas and is involved in nutrient absorption.
Incisors
Teeth used to cut food.
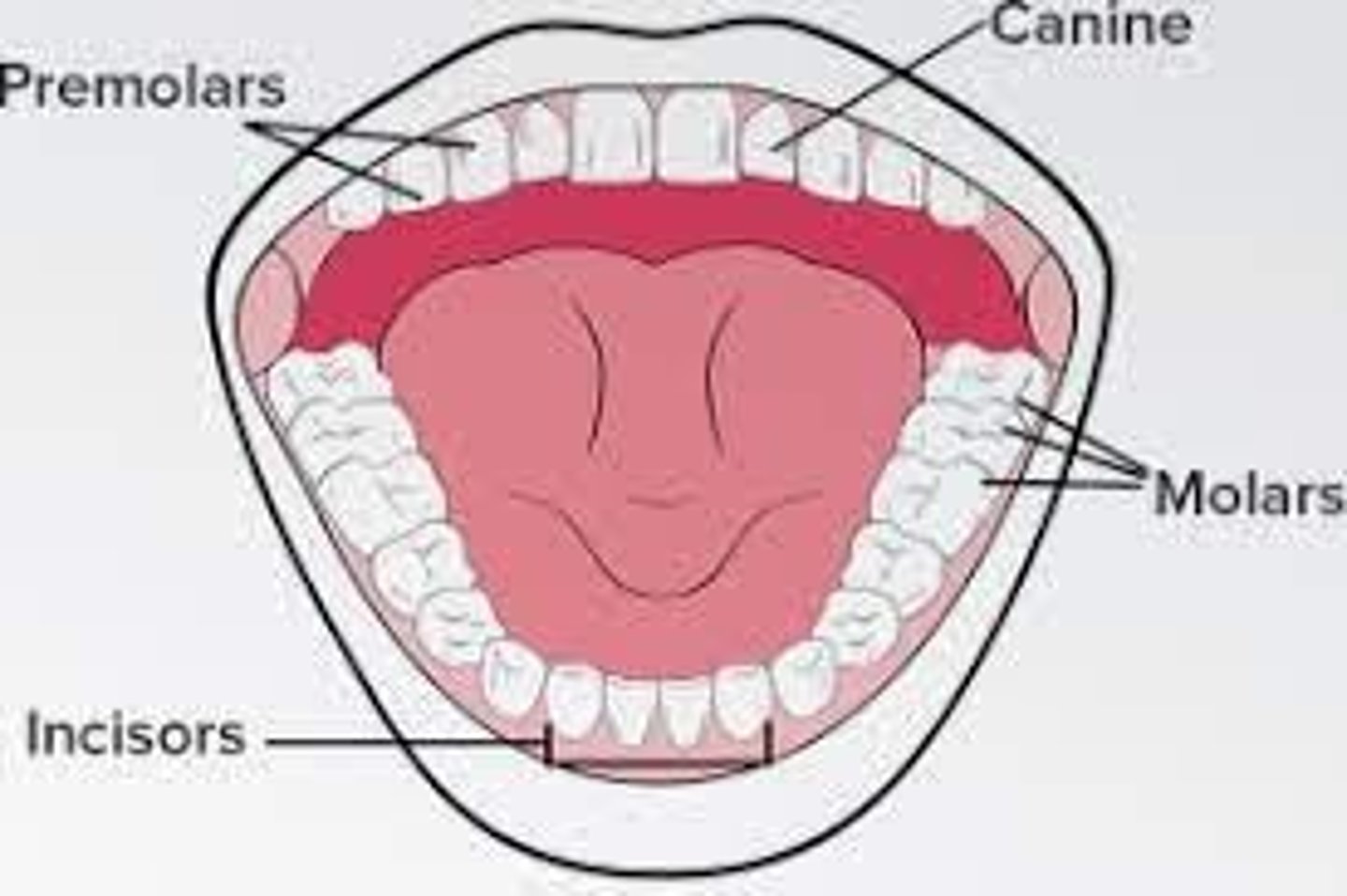
Canines
Teeth used to tear food.
Molars
Teeth used to grind food.
Pre-molars
Teeth used to grind food.
Amino acids
Organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins.
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important energy source in living organisms.
Microvilli
Tiny projections on the surface of villi that further increase the surface area for absorption.
Large Intestine
Part of the digestive system where water is absorbed from cellulose, making remains solid.
Fibre
Indigestible material, such as cellulose, that humans cannot break down.
Caecum
An offshoot from the large intestine with no function in humans.
Appendix
An offshoot from the large intestine with no function in humans.
Salivary gland
Gland that secretes saliva containing enzymes to begin the digestion of starch.
Oesophagus
Tube that transports partly digested food from the mouth to the stomach.
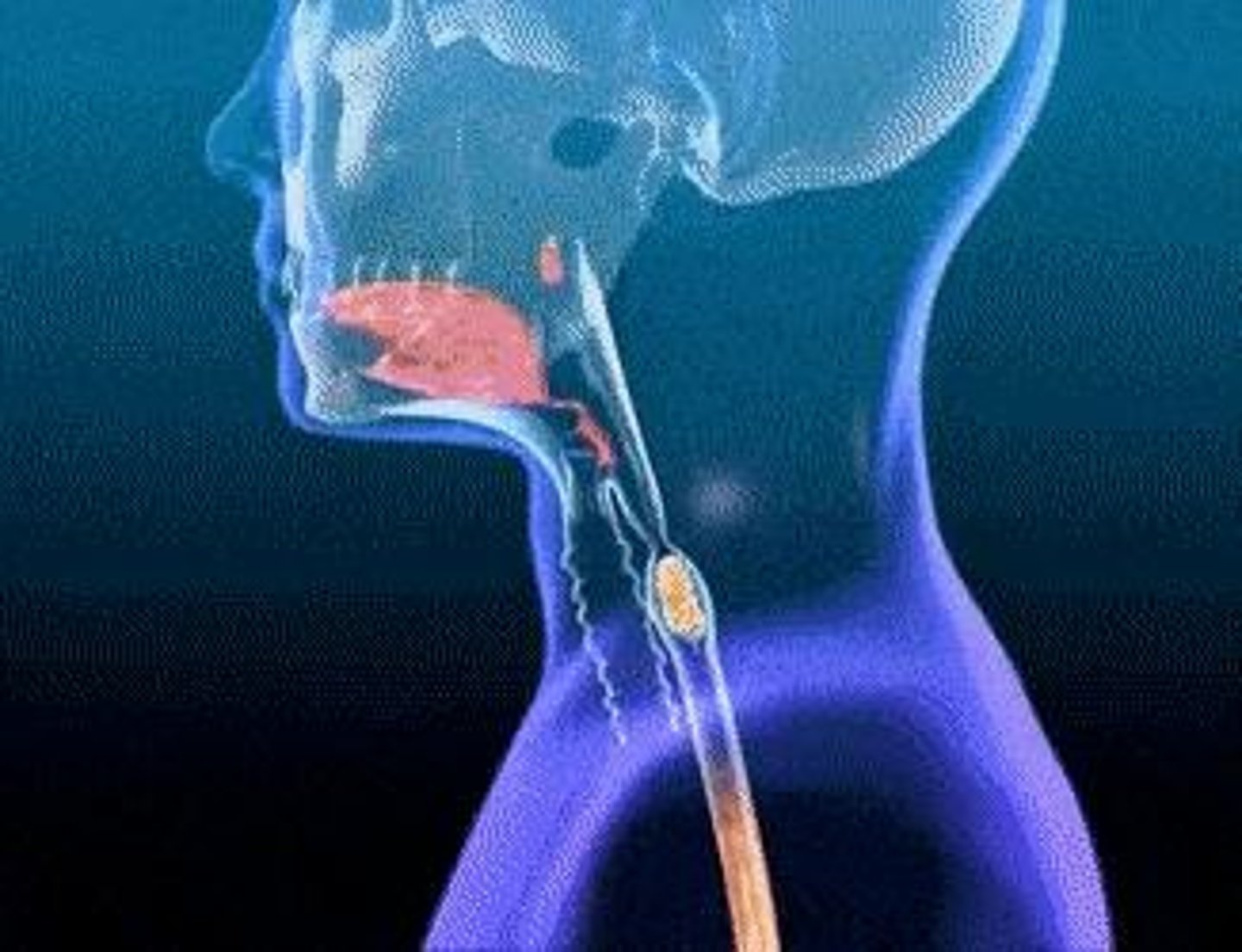
Stomach
Organ that secretes gastric juice containing hydrochloric acid and enzymes for protein digestion.
Liver
Organ that produces bile, which is stored in the gall bladder.
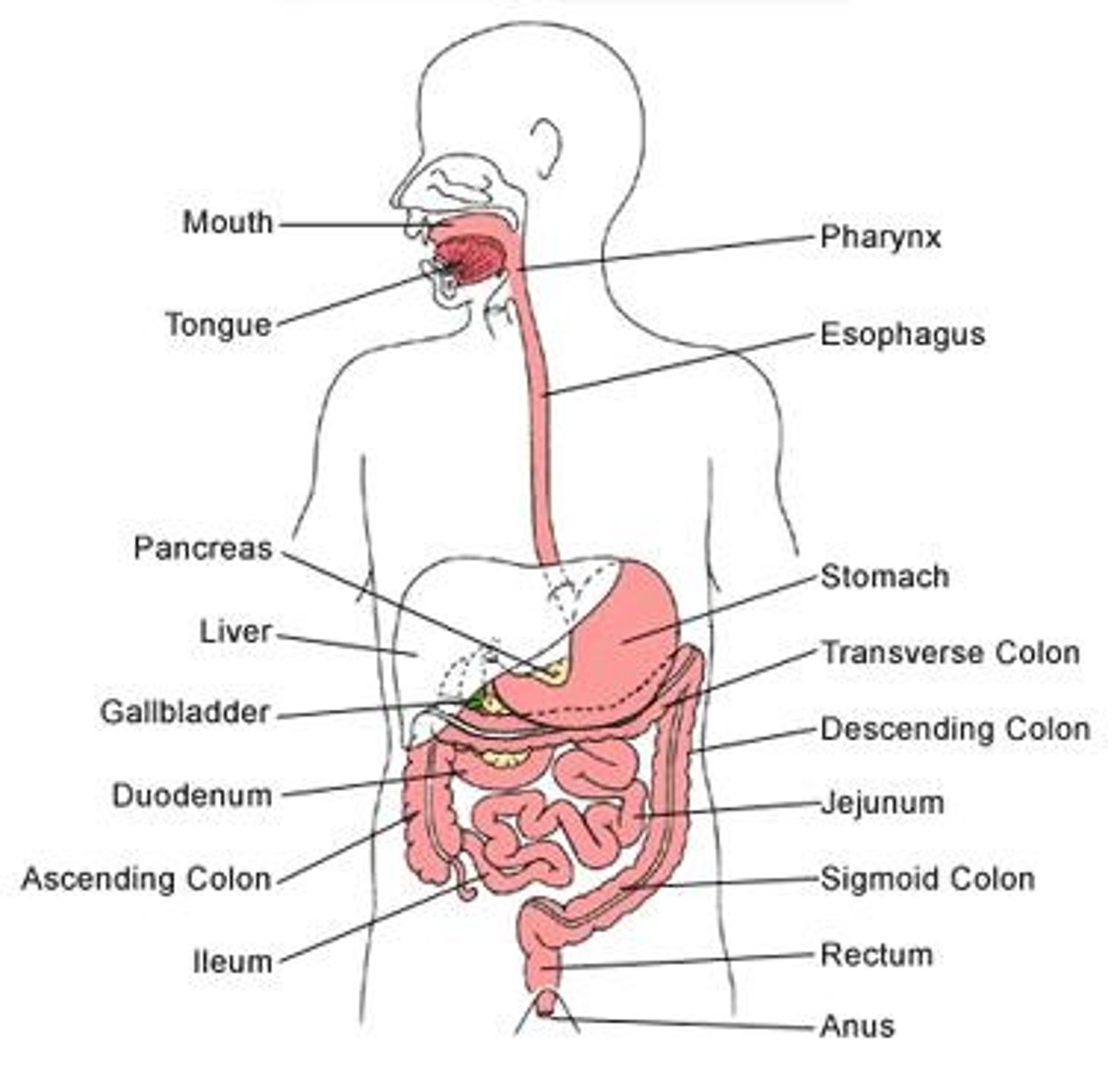
Duodenum
First part of the small intestine that secretes enzymes to complete digestion.
Ileum
Last part of the small intestine that absorbs most small, water-soluble products of digestion.
Colon
Part of the large intestine that absorbs water, minerals, and some vitamins.
Rectum
Part of the large intestine that stores indigestible food material before elimination.
Gastric juice
Liquid secreted by the stomach containing hydrochloric acid and enzymes.
Pancreatic juice
Liquid secreted by the pancreas containing enzymes for digestion.
Bile
Liquid produced by the liver that aids in the digestion of fats.