thermoregulation, obesity and pulmonary glossary
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Body composition
quantification of different body tissue compartments (fat free (lean) vs. fat)
Body fat percentage
ratio of body tissue comprised of fat, healthy range for young adult males (10-20%) and females (20-30%)
Obesity
excess fat accumulation that poses an adverse health risk, commonly qualified as BMI>30 kg/m3
Body Mass Index (BMI)
ratio of mass in kilograms to squared height in meters, used to broadly categorize weight status
Waist Circumference
measurement around waist used to assess disease risk, proxy for visceral fat, often compared with hip
Visceral fat
intra-abdominal fat that when in excess poses an increased risk for metabolic syndrome and CVD
Computed tomography scan (CT)
medical imaging technique that details internal body structures
Dual Energy Xray Absorptiometry
a procedure used to assess body composition and bone mineral density using Xrays
Body Density (densitometry)
ratio of mass to volume, correlated to body fat % as more dense —> less fat
Hydrostatic (underwater) weighing
body composition assessment technique that uses Archimedes’ principle to determine body volume
Archimedes’ Principle
the difference in weight of an object above and below water is equal to the weight of displaced water
BOD POD
body composition assessment tool that uses air displacement to determine body volume
Skinfold Measurement
body composition assessment technique that uses skinfold thicknesses of various sites
Bioelectrical impedance analysis
body composition assessment technique that uses an electrical current speed measurement
Thermoregulation
control of core body temperature via heating and cooling mechanisms
Hemotherm
animal that maintains constant core body temperature by virtue of its own heating and cooling mechanisms
Core Body Temperature (Tc)
temperature of metabolically active/critical organs (brain/heart, etc.)
-normally 37± 0.5degC (~98.6 F)
Skin (shell) temperature
variable temperature due to the environment of which a small % of the thermoregulatory response is based
Heat Balance Equation
thermal equilibrium between heat added to and removed from a system
Metabolic Heat
heat liberated during metabolic reactions, scales with exercise intensity, reliable source of heat gain
Radiation
heat transfer of thermal energy by means of electromagnetic (infrared) waves
Conduction
heat transfer between molecules in direct contact with each other
Convection
heat transfer to or away from molecules via a fluid (liquid or gas), can be natural or forced (via fan)
Evaporation
heat loss mechanism involving conversion of a liquid to a vapor, requires ~580 kcal of heat/L of water
humidity
concentration of water vapor in air, inhibits evaporation thus threatens temperature regulation in the heat
Thermoneutral zone
ambient temperature range in which a nude individual need only use vasomotor tone to thermoregulate
Sudomotor control
regulation of sweat gland activity, involves varying sympathetic cholinergic impulses
Vasomotor control
blood vessel tone regulation, involves varying sympathetic adrenergic impulses
Sweat gland myoepithelium
specialized epithelium around sweat glands that have a contractile function and sympathetic innervation
Dehydration
excessive water loss from the body, often expressed as a % of body weight loss
Dysthermia
poor temperature regulation
Hyperthermia
elevated core body temperature
Heat Exhaustion
heat illness stage due to excessive heat, sweating, dehydration, and competition for blood (Tc= 99-102F)
Heat Stroke
most severe (life threatening) heat illness stage in which thermoregulation is impaired (Tc can be >106F)
Hypothermia
Low core body temperature (Tc below 35C/ 95F)
Central Blood Volume
Blood within major vessels of the thorax, lower in hot conditions with blood in vasodilated skin
Acclimation
process of getting accustomed to a new condition via adaptations
Ventilation
Movement of gases in and out of the lungs
Respiration
Biological process involving gas diffusion
External respiration
Diffusion of gases between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood
Internal respiration
Diffusion of gases between systemic capillary blood and body tissues
Cellular respiration
Metabolic (aerobic) processes in which O2 is used and CO2 is produced within mitochondria
Respiratory tree
Name given to progressively branched airways from trachea to alveoli due to tree form resemblance
Conducting zone
Airway space where gas diffusion cannot take place, airways dedicated to conducting air
Dead space
Air volume of the conducting zone
Respiratory zone
Airway space where gas diffusion takes place, primarily composed of alveoli
Alveolar cells
Primarily simple squamous cells optimized for diffusion, 3% are specialized to produce surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant
Phospholipid-protein product of specialized alveolar cells that acts to reduce alveolar surface tension
Pulmonary surface area
Total gas diffusion area, in a healthy lung equivalent to square footage of half a tennis court
Respiratory muscles
Muscles causing and/or aiding breathing (e.g. diaphragm), more aptly termed "muscles of ventilation"
Boyle's Law
The pressure of a gas, at constant temperature, varies inversely with its volume (P1V1 = P2V2 )
Atmospheric (barometric) pressure
Gas pressure exerted by air, ~745 and ~760 mmHg in Milwaukee and at sea level, respectively
Intra-alveolar pressure
Pressure within the alveolar space, is negative relative to atmospheric pressure during inspiration
Valsalva maneuver
A forced expiration against a closed glottis (think "straining")
Thorax
Thoracic cavity
Pleural membranes
Friction-reducing serous membranes that cover the lungs (visceral) and adjacent thorax surface (parietal)
Lung elastic recoil (elastance)
Resistance to deformation, property of structural elastic fibers and intra-alveolar liquid surface tension
Surface tension
Force acting across a liquid surface as a result of intermolecular attraction that minimizes surface area
Pneumothorax
Presence of air in the pleural cavity, results in a collapsed lung as pleural membranes lose fluid bond
Pulmonary fibrosis
Condition characterized by deposition of fibrous tissue in the lung, lowers compliance, restricts volume
Spirometry
Lung function test measuring lung volumes as a function of time, can also indicate maximal flow rates
Tidal volume (VT)
Amount of air inspired in a single breathe, ~500 ml/br at rest, increases with exercise
Functional residual capacity (FRC)
Lung volume after normal expiration, balance between inward lung recoil and outward thorax recoil
Total lung capacity (TLC)
Lung volume following maximal inspiration (maximal volume of air held by lungs)
Residual volume (VR)
Volume of air remaining in lungs following a complete expiration
Vital capacity (VC)
Maximal volume of air that's expired from a full inspiration, difference between TLC and RV
Forced vital capacity (FVC)
Maximal volume of air that's expired from a full inspiration when performed with maximal speed
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
FEV1 is the volume of air expired during the first second of an FVC maneuver
Obstructive lung disease
Condition characterized by an increase in airflow resistance, diagnosed by low FEV1 /FVC ratio, difficulty exhaling air
Restrictive lung disease
Condition characterized by a low (restricted) lung volume, diagnosed by low FVC compared to predicted, difficulty inhaling
Respiratory membrane
External respiration diffusion barrier comprised of alveolar epithelium, interstitium, capillary endothelium
Dalton’s Law
Each gas in a mixture of gases exerts a pressure proportional to its concentration in the mixture
Partial pressure
Pressure exerted by a gas in a mixture of gases, the product of total pressure and gas concentration
Atmospheric O2 partial pressure
PO2 is ~160 mmHg at sea-level (760 mmHg x 21%)
Alveolar O2 partial pressure
PAO2 is ~105 mmHg during normal sea-level breathing and hyperpnea, varies by ratio of VA/VO2
Water vapor pressure (PH2O)
Partial pressure of water when in gas form, inspiration becomes fully saturated (humid) lowering PAO2
Arterial O2 partial pressure
PaO2 is ~100 mmHg during normal sea-level breathing and hyperpnea, varies based on PAO2
Venous O2 partial pressure
PvO2 is ~40 mmHg at rest, decreases during exercise as muscle PO2 decreases
Hypoventilation
A level of ventilation rate that's less than what's appropriate for the metabolic rate
Hyperpnea
Increase in ventilation during exercise that's proportional to the increase in metabolic rate
Hyperventilation
A level of ventilation that's out of proportion to (above) the level of metabolism
Henry's Law
Gas amount dissolved in a liquid is the product of the gas partial pressure and its solubility in the liquid
Solubility constant for O2 in blood
Volume of O2 dissolved in deciliter of blood per mmHg PO2 is 0.003 ml O2 , this alone won't sustain life
Fick's law of diffusion
Describes gas diffusion rate as being related to surface area and pressure gradient over surface thickness
Emphysema
Condition resulting in loss of alveolar walls, increases compliance and lowers respiratory surface area
Pulmonary edema
Condition characterized by fluid accumulation in the alveoli, often resulting from high pulmonary BP
Pulmonary transit time
Duration an RBC spends in a pulmonary capillary, is ~0.75 sec at rest and decreases during exercise
Hemoglobin saturation
Average level of O2 binding by hemoglobin, ranges from 0 - 100%
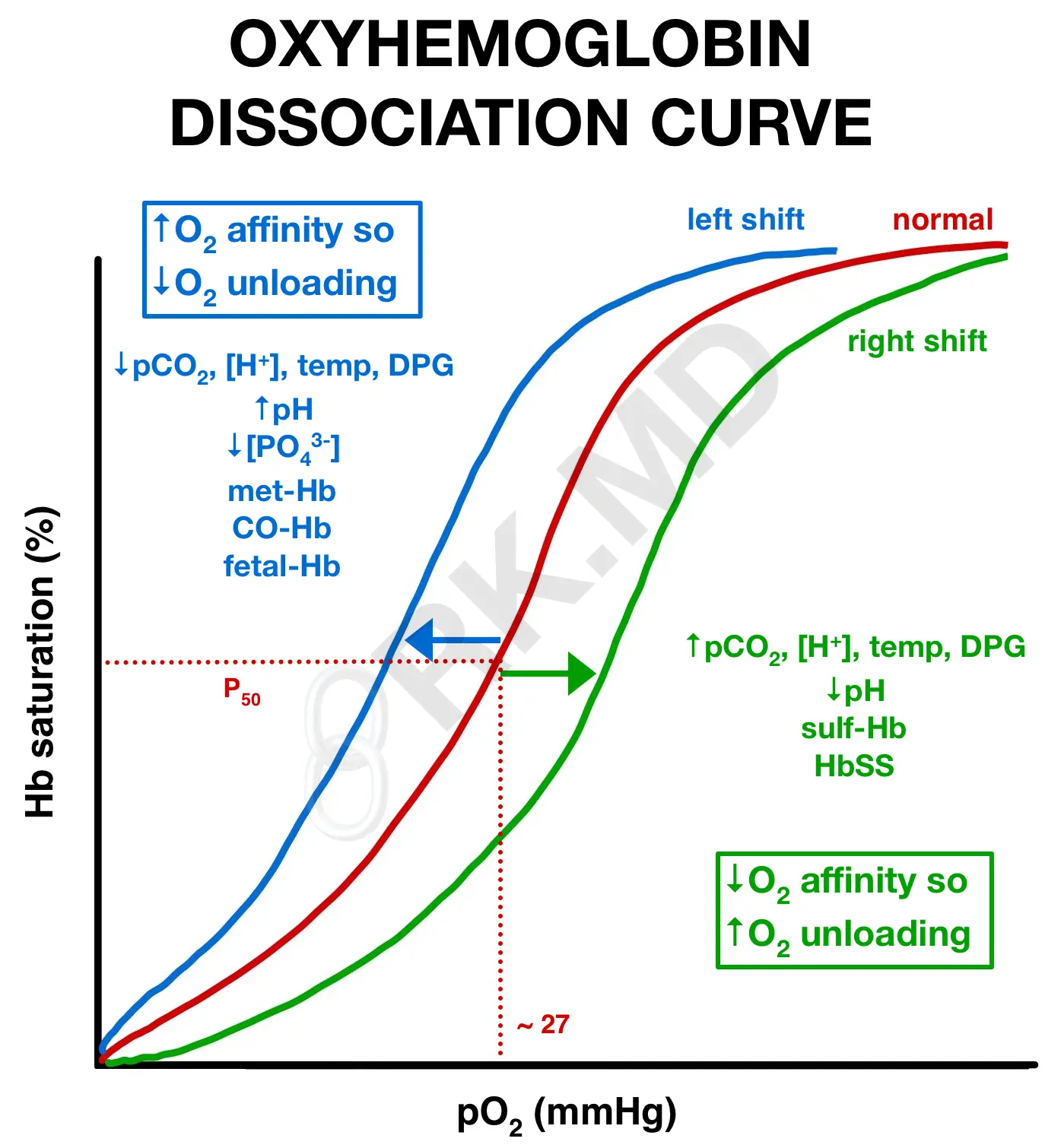
Oxy-hemoglobin dissociation curve
Figure describing hemoglobin saturation with O2 as a function of PO2 , is affected by H+ , temp, PCO2
Pulse oximeter
Medical device that sends light beams through a finger tip to assess HR and level of Hb saturation
Hemoglobin concentration
Amount of hemoglobin per blood sample, ~15 g/dl in a healthy individual
Anemia
Condition of low O2 carrying capacity by blood as a result of a depressed hemoglobin concentration
Venous CO2 partial pressure
PvCO2 is ~45 mmHg at rest, increases during exercise as muscle PCO2 increases
Alveolar CO2 partial pressure
PACO2 is ~40 mmHg during normal sea-level breathing and hyperpnea, varies by ratio of VCO2 /VA
Arterial CO2 partial pressure
PaCO2 is ~40 mmHg during normal sea-level breathing and hyperpnea, varies based on PACO2
Total CO2 content in blood
Combined CO2 total from dissolved, protein bound, and HCO3 - forms, a function of PCO2 and Hb sat
Carbonic acid reaction
Reaction in RBC with an equilibrium of dissolved CO2 and carbonic acid (CO2 + H20 ↔ H+ + HCO3 - )
Carbonic anhydrase
RBC enzyme that catalyzes the equilibration of: CO2 + H20 ↔ H+ + HCO3 -
Arterial O2 content
CaO2 is normally ~20 ml O2 / dl, which includes both the dissolved and hemoglobin bound components
Mixed venous O2 content
CvO2 is normally ~15 ml O2 / dl at rest and decreases during exercise due to tissue extraction