MCAT Biology Pt. 2
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Endocrine System
Organs; glands
Hormones: signaling molecules secreted by glands directly into bloodstream to target distant tissues
Peptide Hormones
made up of amino acids, from small to relatively large
must bind to extracellular receptor bc they are charged and cannot diffuse through plasma membrane
generally rapid response but short lived
water-soluble, can travel freely in bloodstream
Peptide Hormone Pathway
peptide hormone is first messenger (binds to receptor) → transmission of second messenger → signaling cascade
Amplification: binding to multiple receptors before it is degraded
common second messengers: cAMP, IP3, calcium
Peptide Hormone - GPCR Pathway
GPCR → activate/inhibit adenylate cyclase → raise or lower level of cAMP → bind to intracellular targets like protein kinase A → phosphorylates transcription factors like CREB to exert hormone’s ultimate effect
Steroid Hormones
derived from cholesterol
produced primarily by gonads and adrenal cortex
nonpolar → easily cross cell membrane so receptors usually intracellular or intranuclear
generally slower response but longer lived
not water-soluble, so carried in an inactive state by protein carriers that may be specific or nonspecific and must dissociate from carrier to be active
carrier affects levels of active hormone
Steroid Hormone Pathway
bind to intracellular/intranuclear receptor → undergo conformational change → bind directly to DNA → increased or decreased transcription of particular genes depending on identity for hormone
Steroid Hormone Dimerization Pathway
Pairing of two receptor-hormone complexes as conformational change
Amino-Acid Derivative Hormones
less common than peptide and steroid hormones
epinephrine, norepinephrine, triiodothyronine, thyroxine
derived from 1 or 2 amino acids
catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine): bind to G protein-coupled receptors
thyroid hormones: bind intracellularly
Direct Hormones
secreted then act directly on target tissue
ex. insulin from pancreas causes increased uptake of glucose by muscles
Tropic Hormones
require intermediary to act on target tissue
GnRH from hypothalamus stimulates release of LH and FSH to act on gonads
Usually originate from brain and anterior pituitary gland to allow for coordination of multiple processes in body
Hypothalamus
Bridge between nervous and endocrine systems
regulates pituitary gland through tropic hormones via paracrine release of hormones into blood portal system connecting two organs (hypophyseal portal system)
in forebrain, directly above pituitary gland and below thalamus
negative feedback regulation of pituitary/hypophysis gland → maintain homeostasis and conserve energy
Hypothalamus - Anterior Pituitary Interactions
Hypothalamus release Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) → pituitary release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
Hypothalamus releases Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) → pituitary releases growth hormone (GH)
Hypothalamus releases Thyroid-releasing hormone (TRH) → pituitary releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) → pituitary releases adenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin-inhibiting factor (PIF) / dopamine release in hypothalamus → INHIBITION secretion of prolactin
Hypothalamus - Anterior Pituitary Interactions Negative Feedback
Axes: three-organ systems that have negative feedback
ex. hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA)

Hypothalamus - Posterior Pituitary Interactions
neurons from hypothalamus directly send axons down pituitary stalk into posterior pituitry to release oxytocin and ADH
Oxytocin - stimulate uterine contraction and initial milk letdown during lactation, and bonding behavior
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)/Vasopressin: increase reabsorption of water in collecting ducts of kidneys in response to increased plasma osmolarity
Anterior Pituitary - Tropic Hormones
Tropic (FLAT)
FSH → gonads
LH → gonads
ACTH → adrenal cortex
TSH → thyroid
Anterior Pituitary - Direct Hormones
Direct (PEG)
Prolactin → milk production in mammary glands
Endorphins → decrease perception of pain
Growth hormone (GH) promote growth of bone and muscle → prevent glucose uptake and stimulate breakdown of fatty acids
Kids excess can cause gigantism and deficit results in dwarfism
adults have acromegaly and large hands, feet and head
Posterior Pituitary
contain nerve terminal of neurons with cell body in hypothalamus
ADH and oxytocin produced by hypothalamus stored here
Posterior Pituitary - ADH
low blood volume (baroreceptors) or increased blood osmolarity (osmoreceptors) → secrete ADH → increased reabsorption of water in kidney at collecting duct
Posterior Pituitary - Oxytocin
during childbirth and suckling of breast → positive feedback loop
Thyroid
Controlled by thyroid-stimulating hormone from anterior pituitary
Thyroid - Basal Metabolic Rate
sets basal metabolic rate (via triiodothyronine T3 & hydroxine T4)
increase cellular respiration → protein and fatty acid turnover
negative feedback loop to anterior pituitary and hypothalamic nuclei
both T3 & T4 produced by iodination of amino acid tyrosine in follicular cells of thyroid
hypothyroidism: deficiency of iodine or inflammation of iodine
cretinism: deficiency of thyroid hormones leading to intellectual disability and developmental delay
hyperthyroidism: excess hormone from tumor or thyroid overstimulation
Thyroid - Calcium homeostasis
promote calcium homeostasis (via calcitonin)
C-cells/parafollicular cells produce calcitonin
Decreases plasma calcium levels:
increasing calcium excretion from kidneys
decreasing calcium absorption from gut
increasing storage of calcium in bone
stronger bones and less bone breakdown
Parathyroid Glands
four glands posterior to thyroid
produces parathyroid hormone (PTH):
antagonistic hormone to calcitonin
subject to feedback inhibition
promotes phosphorus homeostasis by increasing resorption of phosphate from bone and reducing reabsorption of phosphate in kidney
activates vitamin D (absorption of calcium and phosphate in gut)
Adrenal Cortex
located at top of kidneys
secretes corticosteroids: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and cortical sex hormones
Adrenal Cortex - Glucocorticoids
steroid hormones that regulate glucose levels and protein metabolism
Cortisol and cortisone:
raise blood glucose by increasing gluconeogenesis and decreasing protein synthesis
decrease inflammation and immunologic responses
controlled by CRF → ACTH
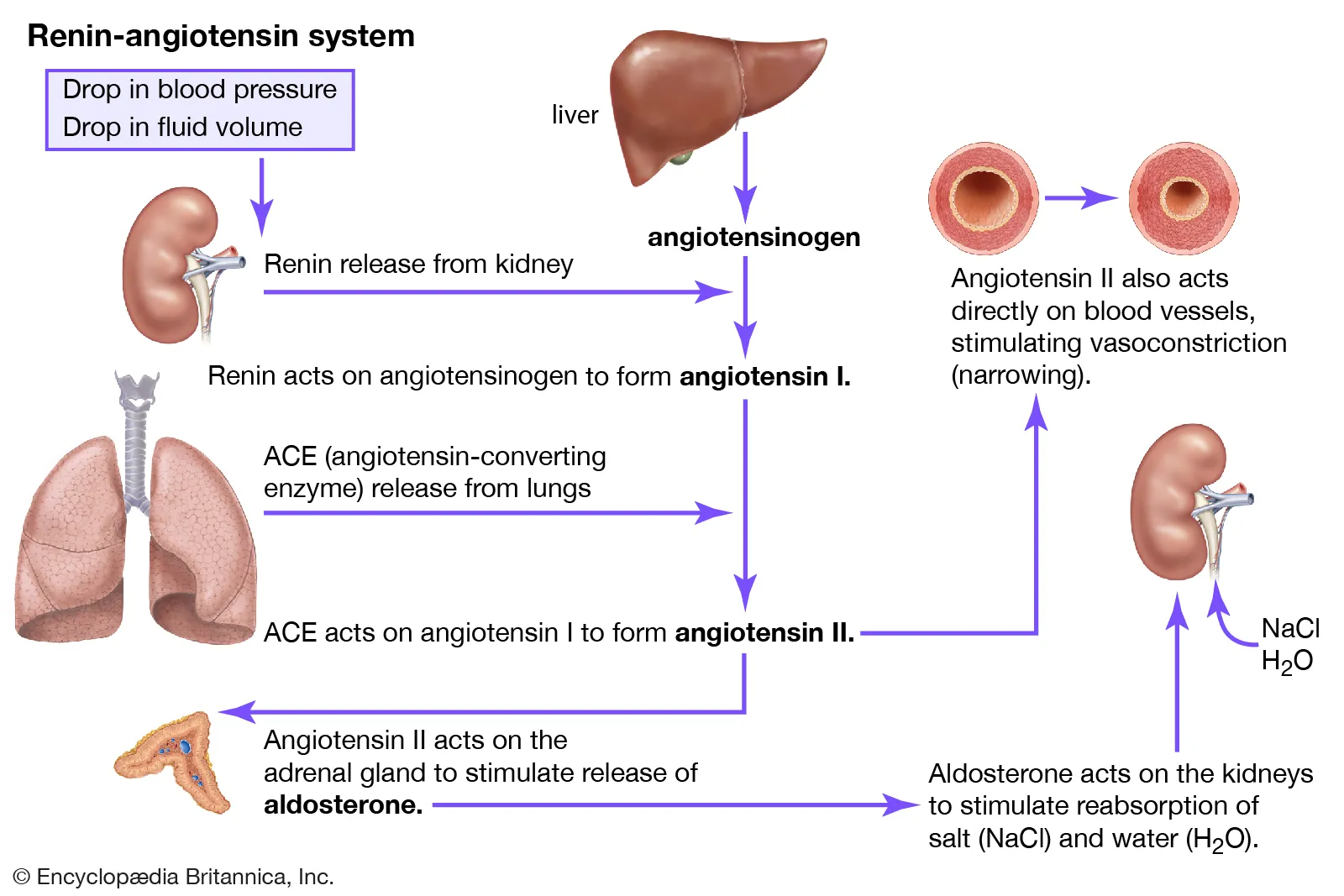
Adrenal Cortex - Mineralcorticoids
used in salt and water homeostasis
aldosterone
increase sodium reabsorption in distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of nephron
decrease reabsorption of potassium and hydrogen ions in nephron
under control of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Adrenal Cortex - Cortical Sex Hormones
androgens and estrogens
ovaries much more sensitive to disorders of cortical sex hormone production bc relies more on it than testes
Adrenal Medulla
production of catecholamine sympathetic hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine
short-term (fast) stress responses compare to cortisol
cortisol increases synthesis of catecholamines
Pancreas
exocrine and endocrine functions
exocrine: secrete substance directly into ducts
endocrine:
islets of Langerhans (small clusters of hormone-producing cells)
alpha cell: secrete glucagon
beta cell: secrete insulin
delat cell: secrete somatostatin
pancreas: produce large number of digestive enzymes
Pancreas - Glucagon
secrete during times of fasting
increase glucose production via glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and degradation of protein and fat
Pancreas - Insulin
antagonistic to glucagon
secrete when blood glucose levels are high
induce muscle and liver cells to take up glucose and store it as glycogen for later use
stimulate anabolic processes like fat and protein synthesis
Pancrease - Insulin Problems
Excess insulin:
hypoglycemia: low blood glucose concentration
Underproduction:
diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia: excess glucose in blood
glucose will be present in urine b/c kidney nephron cannot reabsorb - accompanied by excess excretion of water
polyuria (increased frequency of urination)
polydipsia (increased thirst)
Type I diabetes (insulin-dependent): autoimmune destruction of beta cells of pancreas → low or absent insulin production
Type II diabetes (non-insulin-dependent): receptor-level resistance to effects of insulin, partially inherited and partially due to environmental factors
Pancreas - Somatostatin
inhibitor of insulin and glucagon secretion
high blood glucose and amino acid concentration stimulate its secretion
produced by hypothalamus too → decrease growth hormone secretion
Gonads
Testes: secrete testosterone in response to stimulation by gonadotropins (LH and FSH)
Ovaries: secrete estrogen and progesterone in response to stimulation by gonadotropins (LH and FSH)
Pineal Gland
deep in brain
secrete melatonin: involved in circadian rhythms
receives projections from retina → release melatonin when decrease in light
blood levels of melatonin responsible for sleepiness
Kidney Hormones
ADH
erythropoietin: stimulate bone marrow to increase productions of red blood cells w/ low oxygen levels in blood
Heart Hormones
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP):
regulate salt and water balance if excess blood volume stretches atria cells
promote excretion of sodium and increase urine volume
no effect on blood osmolarity
Thymus Hormones
thymosin:
important for proper T-cell development and differentiation
atrophies by adulthood
Pathway of Respiratory System
nares (nose) → mucous membrane and nasal hairs (vibrissae) → pharynx behind nasal cavity and back of mouth (food + air) → epiglottis (covering of glottis) → glottis (opening of larynx) → larynx → two vocal cords → trachea → two bronchi → lungs → bronchioles → alveoli (tiny balloon like structure for gas exchange) coated with surfactant (detergent lower surface tension and prevent alveoli collapsing on itself)
Surrounding of Lung
lungs in thoracic cavity
pleurae: membranes that surround each lung
visceral pleura: surface adjacent to lung
parietal pleura: outer part surface along chest wall
intrapleural space: contain thin layer of fluid
How Lungs Fill
not passive
require diaphragm: skeletal muscle to generate negative pressure for expansion & divides thoracic cavity from abdominal cavity
diaphragm under somatic control, but breathing under autonomic control
Inhalation
active process
use diaphragm and external intercostal muscles (layer of muscles between ribs) to expand thoracic cavity
negative-pressure breathing:
diaphragm flattens and chest walls expand outward → intrathoracic volume increases → decrease in intrapleural pressure → lungs increase in volume bc higher pressure in lungs than intrapleural space → inhale air in
Exhalation
not active process
external intercostal muscles are relaxed → lungs decrease in volume bc lower pressure in lungs than intrapleural space → air pushed out
internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles: oppose external intercostals and pull rib cage down → decrease volume of thoracic cavity → speed up exhalation
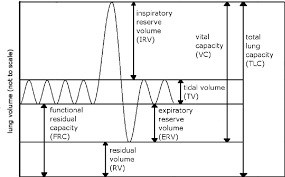
Lung Capacities and Volumes
spirometer: instrument that measures lung capacities and volumes
Total lung capacity (TLC)
max volume of air in lungs when one inhales completely
usually around 6-7 liters
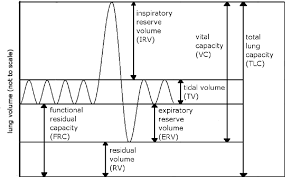
Residual Volume (RV)
volume of air remaining in lungs when one exhales completely
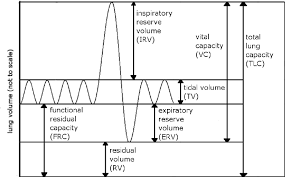
Vital Capacity VC)
difference between the minimum and maximum volume of air in the lungs (TLC - RV)
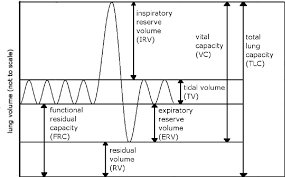
Tidal volume (TV)
Volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a normal breath
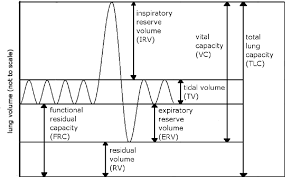
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Volume of additional air that can be forcibly exhaled after normal exhalation
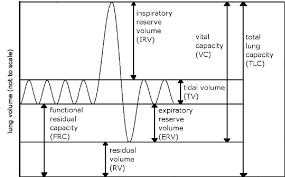
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Volume of additional air that can be forcibly inhale after a normal inhalation
Regulation of breathing
Ventilation center: collection of neurons in medulla oblongata that fire rhythmically to cause regular contraction of respiratory muscles
contain chemoreceptors sensitive to CO2 concentration
partial pressure of CO2 in blood increases (hypercarbia/hypercapnia) → respiratory rate increase → more CO2 exhaled
also respond to changes in oxygen concentration but only significant during periods of significant hypoxemia (low O2 concentration in blood)
Gas Exchange
primary function of lungs
deoxygenated blood from body → right ventricle of heart → pulmonary arteries → capillaries → alveoli for diffusion of CO2 from blood to lungs and oxygen to blood → oxygenated blood → pulmonary veins → oxygenated blood
driving force for gas exchange is pressure differential of oxygen down concentration gradient
Gas Exchange - higher altitudes
less oxygen available
breathe more rapidly to avoid hypoxia
binding dynamics of hemoglobin to oxygen be altered too → and more RBC and blood vessel formation
Respiratory Thermoregulation
regulation of body temperature
vasodilation: increase thermal energy dissipation
vasoconstriction: decrease thermal energy dissipation and conserve them
Immune Function
lysozyme (attack bacteria) and vibrissae present in nasal cavity
mucociliary escalator: underlying cilia in respiratory tract to oral cavity propel mucus with gunk
alveoli contain macrophages: digest pathogens
lungs also contain mast cells: preformed antibodies on surfaces (cause of allergic reactions though too!)
Respiratory Control of pH
pH balance via bicarbonate buffer system in blood
kidneys play a role in this too by modulating secretion and resorption of acid and base within nephron → but much slower response and long-term compensation
Respiratory Control of pH - Acidemia
acidemia: pH lower (H+ conc higher) than desired range
acid-sensing chemoreceptors outside BBB send signals to brain to increase respiratory rate & generate additional carbon dioxide to decrease (H+)
more carbon dioxide blown off and exhaled from the chemoreceptors in medulla too → shift to left as well to decrease (H+)
Respiratory Control of pH - Alkalemia
alkalemia: blood too basic, seek to increase acidity
in lungs if respiratory rate slowed → more CO2 retained → shift eqn to right and make more hydrogen and bicarbonate ions → lower pH
Anatomy of Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular system: consists of muscular four-chambered heart, blood vessels, and blood
vasculature: arteries, capillaries and veins
*Refer to anatomy lab drawings for details about valves, pulmonary circulation, etc.
Electrical Conduction in Heart
sinoatrial node (SA node): impulse initiation occurs, 60-100 signals per minute w/o neurological input → two atria contract (systole) simultaneously
atrial kick: additional volume of blood from atria contracting and pushing blood to ventricles (5-30% cardiac output)
atrioventricular node (AV node): at junction of atria and ventricles → signal delayed to wait to fill ventricles before they contract
bundle of His (in intraventricular septum - wall)
Purkinje fibers: distribute electrical signal through ventricular muscle
muscle cells connected by intercalated discs → contain many gap junctions directly connecting cytoplasm of adjacent cells → coordinated ventricular contraction
Contraction
systole: ventricular contraction and closure of AV valves → blood pumped out of ventricles
diastole: ventricles relaxed, semilunar valve are closed, blood from atria fills ventricles
arteries are elastic to accommodate these large changes in pressure as blood is pumped through them and also maintain pressure of blood overall
Cardiac Output
cardiac output: total blood volume pumped by ventricle in minute
CO = HR (beats per min) x SV (stroke volume, volume of blood pumped per beat)
humans = 5 liter per min
Vasculature
Arteries: leave heart
much more smooth muscle than veins / elastic (rounded shape compared to floppy veins)
Vein: go toward heart
have valves going up to keep blood from flowing back
contain up to ¾ of our blood at any given time
Blood vessels lined with endothelial cells maintain vessel by releasing chemicals aiding in vasodilation and vasoconstriction
Blood circulation order
inferior/superior vena cava → right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary artery → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → mitral valve → left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta → arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → vein → venae cavae → right atrium
Portal Systems
one capillary bed connect to another before going back to heart
hepatic portal system: blood leaving capillary beds in wall of gut pass hepatic portal vein before reaching capillary beds in liver
hypophyseal portal system: blood leaving capillary beds in hypothalamus travels to capillary beed in anterior pituitary
renal portal system: blood leaving glomerulus travels in efferent arteriole before surrounding the nephron in capillary network called vasa recta
Blood Composition - Erythrocyte/RBC
oxygen transport
contains 250 million molecules of hemoglobin which can carry 4 molecules of oxygen
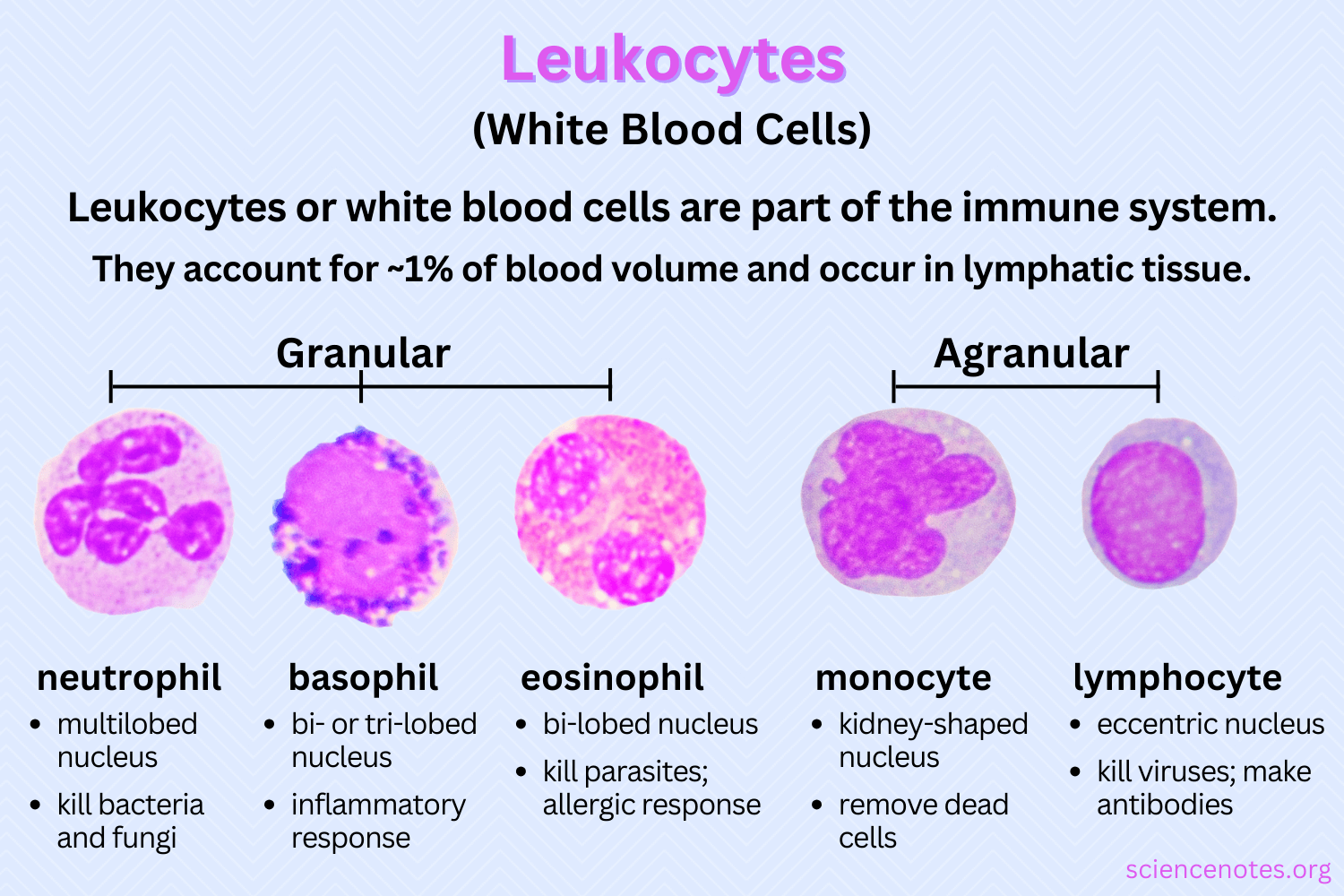
Blood Composition - Leukocytes/WBC
less than 1% total blood
granular leukocytes/granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
contain cytoplasmic granules toxic to invading microbes and released via exocytosis
agranulocytes: lymphocytes and monocytes
lymphocytes: specific immune response like viruses and bacteria via T-cells and B-cells
monocytes → macrophages when leave blood cell; microglia in CNS, Langerhans cells in skin, osteoclasts in bone
Blood Composition - Thrombocytes/Platelets
cell fragments or shards released from cells in bone marrow known as megakaryocytes
assist in blood clotting and present in high concentrations
Blood Composition - Hematopoiesis
hematopoiesis: production of blood cells and platelets, triggered by hormones, growth factors and cytokines
erythropoietin: secrete by kidney and stimulate RBC development
thrombopoietin: secreted by liver and kidney and stimulate platelet development

Blood Antigens
antigens: surface proteins expressed by RBC
any specific target (protein) to which immune system can react
Blood Antigens - ABO
A and B alleles are codominant
O allele is recessive
O blood: universal donors b/c blood will not cause ABO-related hemolysis in any recipient
AB blood: universal recipient can receive blood from all blood types
e Coli has proteins that match A and B alleles so body can make antibodies in response to that → ex. blood type A can make anti-B antibodies
Blood Antigens - Rh Factor
Rh-positive or Rh-negative refers to presence of specific allele called D
Rh positivity follows autosomal dominant inheritance
Erythroblastosis fetalis: fatal to fetus bc if second child Rh+ and mom Rh-, after first child Rh+, mom already made antibodies to attack baby
Blood Pressure
sphygmomanometer
normal is between 90/60 and 120/80
DeltaP (pressure differential across circulation) = CO (cardiac output) x TPR (total peripheral vascular resistance)
atrial natriuretic peptide - ANP - lowers blood pressure
Gas and Solute Exchange - Oxygen
carried by hemoglobin
normal partial pressure of O2 in blood is 70-100mmHg
oxygen saturation: percentage of hemoglobin molecules carrying oxygen - generally above 97%
cooperative binding: easy to bind if one oxygen bound and easy to unbind if one oxygen unbinds
Bohr effect: CO2 bicarbonate buffer make H+ with dissociation → bind to hemoglobin → lower hemoglobin affinity for oxygen → release more O2
Gas and Solute Exchange - Fluid Balance
Hydrostatic pressure: force per unit area that blood exerts against vessel walls, by contraction of heart and elasticity of arteries towards interstitium via capillary walls
Osmotic pressure/oncotic pressure: sucking pressure generated by solutes to draw water back into bloodstream via plasma proteins
Starling forces: balancing of these opposing pressures
Edema: too much excess fluid in interstitium (can be caused by blockage of lymph via thoracic duct)
Coagulation
Clots: composed of coagulation factors (proteins) and platelets
tissue factor: protein in underlying connective tissue at site of injury exposed
platelets see this exposed collagen and protein → release content and begin to aggregate + coagulation factors from liver sense tissue factor and initiate complex activation cascade → activation of prothrombin to form thrombin by thromboplastin → fibrinogen into fibrin → clot → plasminogen → plasmin to break down clot
Innate Immunity/Nonspecific Immunity
composed of defenses always active against infection by lack ability to target specific invaders
Adaptive/Specific Immunity
Defenses that target specific pathogen
slower to act but can maintain immunological memory of infection to mount faster attack on subsequent infections
Anatomy of Immune System
bone marrow → leukocytes (WBC)
Spleen → location of blood storage and activation of B cells → plasma cells to produce antibodies (act in blood = humoral immunity)
thymus → location of T-cells maturation in front of pericardium (cell-mediated immunity = act in cell directly killing viral cells)
lymph nodes → immune cells communicate and mount attack → B cells activated here too
gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT): tonsils & adenoids in head, Peyer’s patches in small intestine, lymphoid aggregates in appendix
Innate Immune System - Noncellular Nonspecific Defenses - Skin
Skin (integument):
physical barrier
defensins: antibacterial enzymes on skin
sweat: antimicrobial properties
Innate Immune System - Noncellular Nonspecific Defenses - Mucus
trap particulates like smoke and dirt
prevent bacteria and viruses from gaining access to lung tissue below
lysozyme: nonspecific bacterial enzyme around eye and oral cavity, secreted in tears and bacteria
Innate Immune System - Gastrointestinal Tract
stomach secrete acid that kills pathogens
gut flora in intestine → does not allow too many other bacteria to invade and grow
Innate Immune System - Complement
number of proteins in blood that act as nonspecific defense against bacteria
classical pathway: require binding of antibody to pathogen
alternative pathway: does not require antibodies
punch holes in cell walls of bacteria to make them osmotically unstable
Innate Immune System - Interferons
proteins that prevent viral replication and dispersion, produced by infected cells
responsible for many flu-like symptoms
upregulate MHC class I and class II easier to antigen presentation
decrease permeability of neighboring cells
decrease production of viral and cellular protein in neighboring cells
Innate Immune System - Macrophages
agranulocyte residing within tissues
from blood borne monocytes and can become resident population within tissue
Innate Immune System - Macrophages Pathway
phagocytizes the invader through endocytosis
digests invader using enzymes
presents little pieces of invader (mostly peptides) to other cells using protein called major histocompatibility complex (MHC) → bind to pathogenic peptide called antigen → carries it to cell surface → recognized by cells of adaptive immune system
macrophage also release cytokines: chemical substances stimulating inflammation and recruiting additional immune cells to the area
Innate Immune System - MHC Class I Molecules
loaded onto MHC-1 and presented on surface of cell
only infected cells would present unfamiliar (nonself) protein on surfaces
endogenous pathway: binds antigens that come from inside cell
can be killed then by T-Cells
Innate Immune System - MHC Class I Molecules
displayed by professional antigen-presenting cells like macrophages, dendritic cells in skin, some B-cells and certain activated epithelial cells
antigen: substance (pathogenic protein) that can be targeted by an antibody
exogenous pathway: antigens originated outside of cell
presentation of antigen by immune cell result in activation of both innate and adaptive immune systems
Innate Immune System - Pattern Recognition Receptors
macrophage and dendritic cell also have special receptors: pattern recognition receptors (PRR) / toll-like receptors (TLR): recognize category of invader and produce appropriate cytokines to recruit right type of immune cells
Innate Immune System - Natural Killer Cells (NK)
viruses can cause downregulation of MHC molecules → harder for T-cells to recognize presence of infection
NK cell: nonspecific lymphocyte detecting downregulation of MHC via these viruses and even some cancers and induce apoptosis in these virally infected or cancerous cells
Innate Immune System - Granulocytes - Neutrophils
most populous leukocyte in blood, very short lived
phagocytic
follow bacteria with chemotaxis (movement of organism via chemical stimuli)
detect bacteria once they have been opsonized (marked with antibody from B-cell)
dead neutrophil → pus
Innate Immune System - Granulocytes - Eosinophils
bright red-orange granules
involved in allergic reactions and invasive parasitic infection
release a lot of histamine: inflammatory mediator → vasodilation and leakiness of blood vessels → additional immune cells to move out of bloodstream and into tissue
Innate Immune System - Granulocytes - Basophils
large purple granules
allergic responses
least populous leukocyte
Mast cells: closely related to basophils but smaller granules and exist in tissues, mucosa and epithelium
release a large amount of histamine in response to allergens
Humoral Immunity
production of antibodies (immunoglobulins Ig)
take up to a week to become fully effective
antibodies specific to antigens of invading microbe
antibodies produced by B-cells, which are lymphocytes that originate and mature in bone marrow and activate in spleen and lymph nodes
Humoral Immunity - Function of antibodies
once antibodies bound to specific antigen, antibodies may attract other leukocytes to phagoytize antigens immediately (opsonization)
antibodies may cause pathogens to clump together (agglutinate), forming large insoluble complexes that can be phagocytized
antibodies can block ability of pathogen to invade tissues, essentially neutralizing it
when antigen binds to cell-surface antibodies on B-cell → proliferation of B-cells and formation of plasma and memory cells
when antigen binds to antibodies on surface of mast cell → degranulation (exocytosis of granule contents) → release histamine → inflammatory allergic reaction
Humoral Immunity - Structure of antibodies
two identical heavy chains inside and two identical light chains parallel to heavy chains, make a Y shape (V) domain and C domain
antigen binding region/variable region/domain: at end of Y
hypermutation: mutation of antigen-binding region for B-cell, trying to find best match for antigen
clonal selection: only best affinity antibody survive
constant region (C) domain: cells like NK cells, macrophages, monocytes and eosinophils have receptors for to initiate complement cascade
isotype switching: cells change which isotype of antibody they prduce when stimulated by specific cytokines
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE
Humoral Immunity - Types of B cells
naive B-cells (note yet exposed to antigen) wait in lymph nodes for particular antigen to come along → then produce two daughter cells
Plasma cells: produce large amount of antibodies
memory B cells: stay in lymoh node, awaiting reexposure to same antigen
primary response: initial activation of the two types of daughter cells, 7-10 days
secondary response: rapid and robust, re-exposed to previous antigen
Vaccination: development of lasting memory cells basis for efficacy of vaccines
Cytotoxic Immunity
positive selection: allowing only maturation of cells that can response to presentation of antigen on MHC, apoptosis of those that don’t react to MHC
Negative selection: causing apoptosis in cells that are self-reactive (activated by proteins produced by organism itself)
Cytotoxic Immunity: Types of T cells
helper T-cells (Th) CD4+ T-cells: coordinate immune response by secreting other immune cells (plasma cells, cytotoxic T-cells, macrophages)
loss of these cells = HIV / AIDS
cytotoxic T-cells (Tc) CTL or CD8+ T-cells: capable of directly killing virally infected cells by injecting toxic chemicals for apoptosis of infected cells
respond to antigen on MCH-I molecules
Suppressor or regulatory T-cells (Treg): express CD4 but differentiated bc also express Foxp3
tone down immune response once infection adequately contained
self-tolerance: turn off self-reactive lymphocytes to prevent autoimmune disease
memory T-cells: similar to memory B-cells, wait until next exposure to same antigen
Bacterial (Extracellular Pathogen) Infections
macrophage engulf bacteria and release inflammatory mediators → digest bacteria and present antigens in conjunction with MHC-II → cytokines → inflammatory cells (neutrophils and other macrophages and mast cells) → histamine release and leakiness of capillaries → dendritic cell goes to lymph node to present antigen to B-cells to make plasma cells and memory cells → tag bacteria for instruction + dendritic cells → antigen to T-cells to activate helper T cells