Topic 2: Solubility
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are the 4 KEY rules for a substance to dissolve?

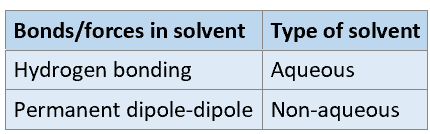
When using polar solvents, depending on whether hydrogen bonds or permanent dipole-dipole interactions are present, what type of solvent do you have?
What do ionic compounds usually dissolve in?
Water
When can ionic compounds not dissolve in water?
When the ionic bonds are too strong
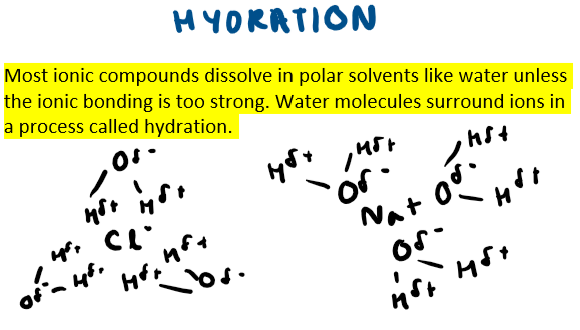
What is the process called when water molecules surround ions and please draw an example of this using NaCl
What solvents do polar substances dissolve in?
Polar solvents
When can non-ionic substances dissolve in water?
When they can hydrogen bond with water (keep in mind the non-polar part of the molecule would not dissolve in water)
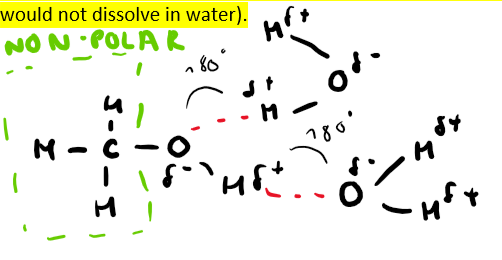
What do non-polar substances dissolve best in? And why
Non-polar solvents as they can form London forces between the molecules
Why can non-polar substances not dissolve in water?
Non-polar molecules tend not to dissolve in water as water forms stronger hydrogen bonds with each other than when interacting with non-polar molecules.
Are ions soluble in water, explain why?
Soluble-> ions are hydrated when dissolved -> enthalpy change in hydration greater than energy needed to break apart the ionic lattice
Are ions soluble in hexane, explain why?
Insoluble -> any London forces that form between ion and hexane would be smaller in magnitude than forces in ion
Are non-polar molecules soluble in water?
Insoluble -> Cannot form hydrogen bonds with water
Are non-polar molecules soluble in hexane?
Soluble -> London forces in both compounds are similar in strength -> so resultant forces in mixture are of similar magnitude