A&P - 12.1 Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
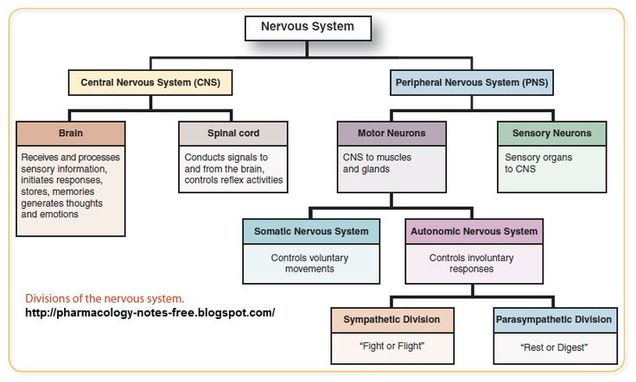
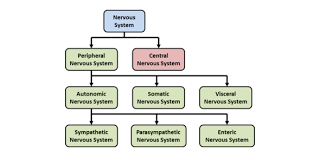
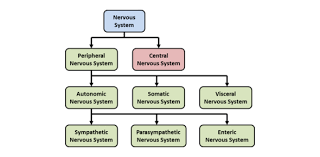
divisions of the nervous system
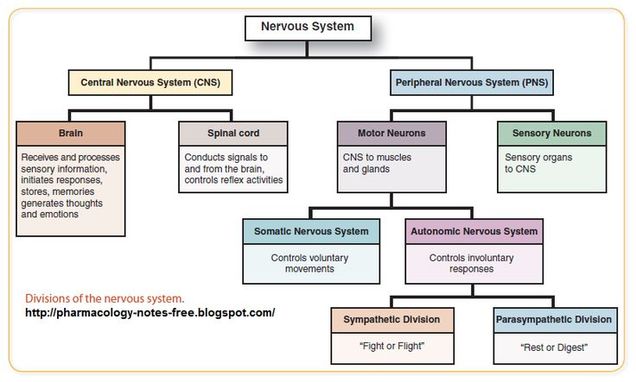
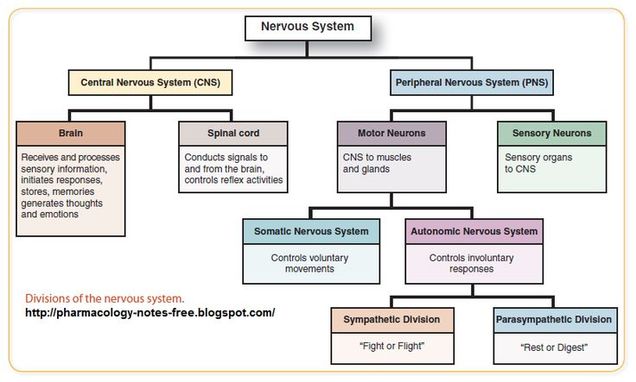
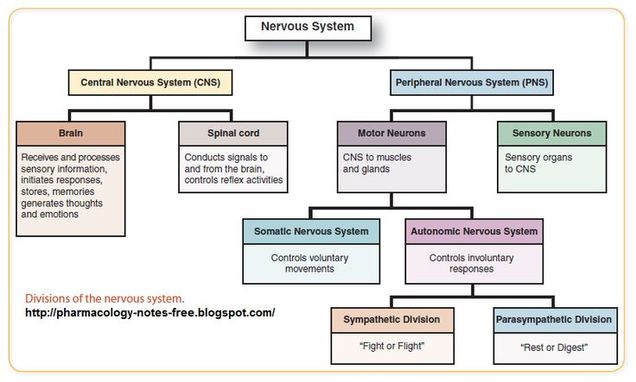
central nervous system (CNS)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
central nervous system (CNS)
interprets sensory input and dictates motor responses based on past experiences, reflexes, and current conditions
“seat of all mental activity”
main structures of central nervous system (CNS)
brain
spinal cord
brain
receives and processes sensory information, initiates responses, stores memories, generates thoughts and emotions
the large organ of the central nervous system composed of white and gray matter, contained within the cranium and continuous with the spinal cord
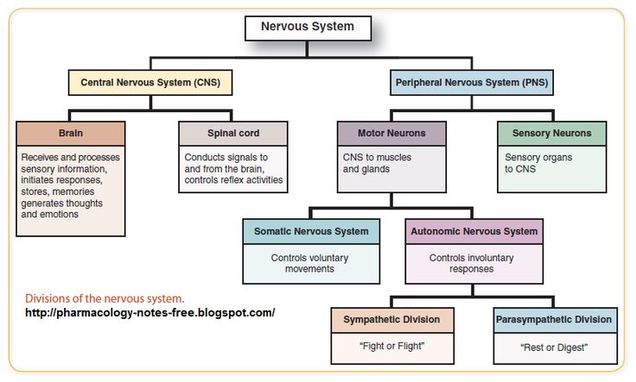
spinal cord
conducts signals to and from the brain, controls reflex activities
organ of the central nervous system found within the vertebral cavity and connected with the periphery through spinal nerves; mediates reflex behaviors
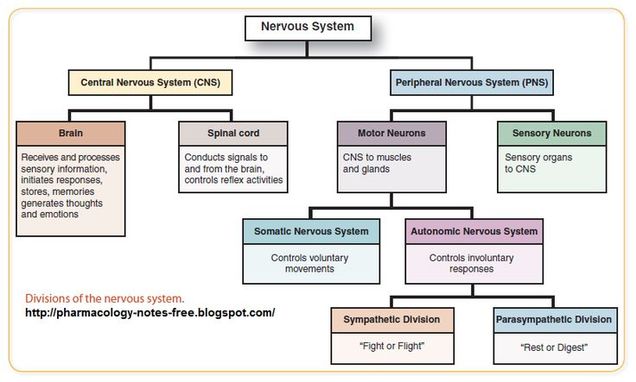
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
cranial & spinal nerves are the communication lines between the CNS and the rest of the body
functional divisions of the peripheral nervous system:
sensory division (somatic and visceral subdivisions)
motor division (somatic and visceral subdivisions)
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
enteric nervous system
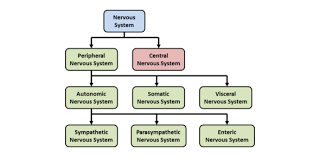
main structures of peripheral nervous system (PNS)
cranial nerves
spinal nerves
specialized receptors
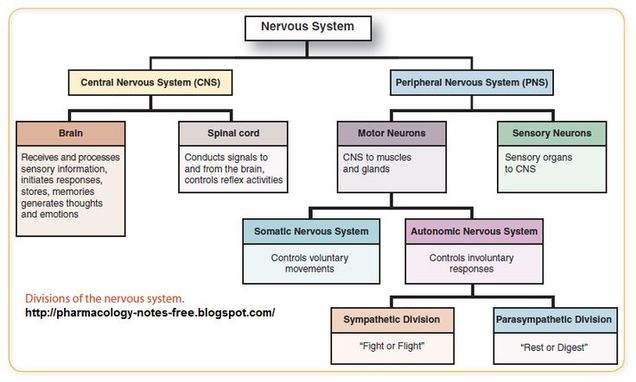
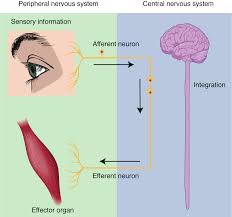
sensory (afferent) division
sensory organs to CNS
conducts impulses of the body into the CNS (carries signals from receptors to CNS)
considered the “input” region
somatic sensory division
carries signals from receptors in the skin, muscles, bones, and joints - and then transmits the stimulus to the brain and spinal cord for interpretation
visceral sensory division
carries signals from the viscera (heart, lungs, stomach, and urinary bladder) - and then transmits the stimulus to the brain and spinal cord for interpretation
motor (efferent) division
CNS to muscles and glands
carries signals (motor neurons conduct impulses) from CNS to effectors (glands and muscles that carry out the body’s response) to produce a response to a stimulus
considered the “output” region
further subdivided functionally into:
somatic nervous system (SNS)
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
enteric nervous system (ENS)
somatic nervous system (SNS) - somatic motor division
controls voluntary movements
carries signals to skeletal muscles
a voluntary system that conducts impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
output produces muscular contraction as well as somatic reflexes (involuntary muscle contractions)
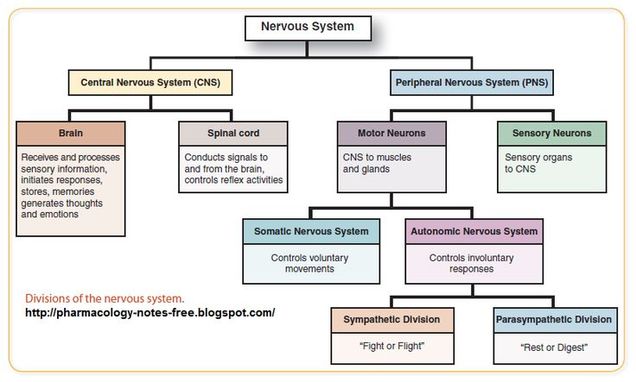
autonomic nervous system - visceral motor division
controls involuntary responses
carries signals to glands, cardiac and smooth muscle
involuntary because it conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac muscles, smooth muscle, and glands
its involuntary responses are visceral reflexes
further subdivided functionally into:
parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
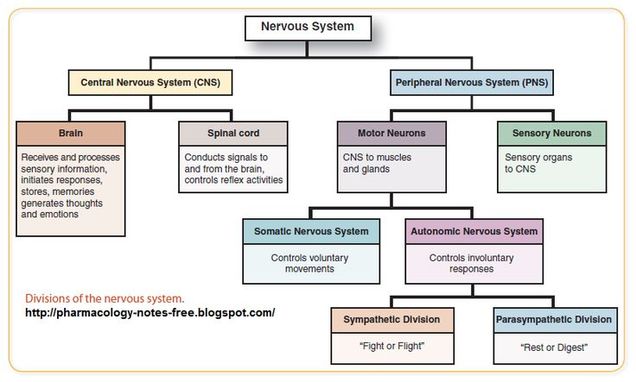
parasympathetic nervous system
“rest or digest”
conserves energy and maintains homeostasis
tends to have calming effect
slows heart rate and breathing
stimulates digestive and urinary systems
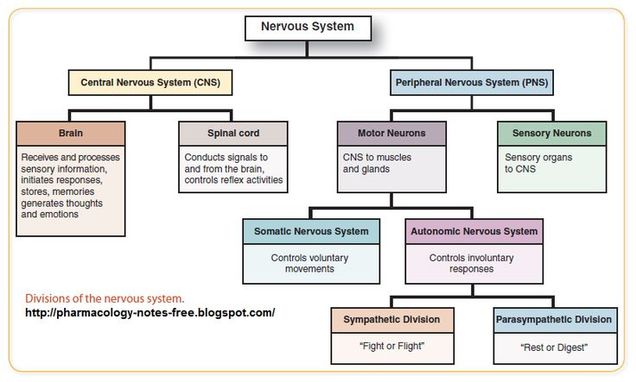
sympathetic nervous system
“fight or flight”
mobilizes the body to respond to “emergency” situations or when the body has moved outside of homeostasis
tends to arouse body for action
accelerating heart beat and respiration, while inhibiting digestive and urinary systems
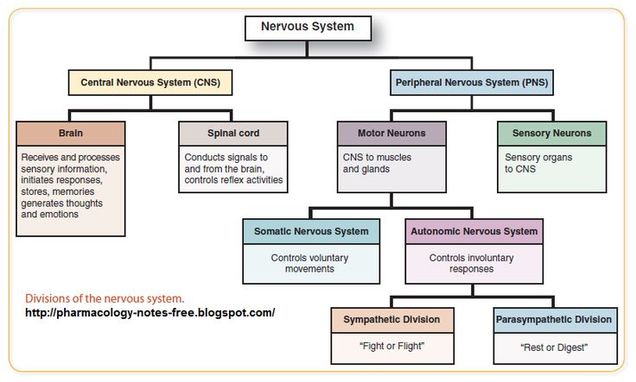
enteric nervous system (ENS)
frequently considered a part of the ANS but is specifically responsible for controlling the smooth muscle and glands of the digestive tract
involved with digestive system (neural tissue associated with the digestive system)
it is a large part of the PNS, and is not dependent on the CNS
functions of the nervous system
sensory input
integration
motor output
homeostasis
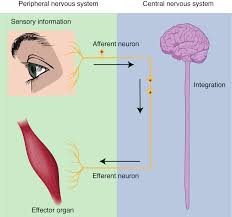
stimulus
an event in the external or internal environment that registers as activity in a sensory neuron
sensory input
sensation = use of sensory receptor to detect stimuli both inside and outside the body and then transmit those stimuli to the central nervous system
receives information from the environment and translates it into the electrical signals of nervous tissue
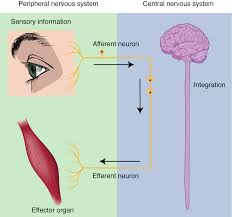
integration
process and interpret sensory stimuli and then determine and/or trigger and appropriate motor response to those stimuli
combines sensory perceptions and higher cognitive functions (memories, learning, emotion, etc.) to produce a response
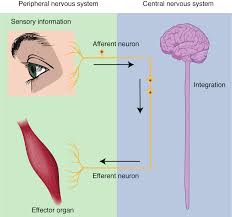
motor output
response = effects a response appropriate to the stimulus by sending an impulse from the central nervous system to the effector organs of the body such as the muscles and glands
causes a target tissue (muscle or gland) to produce an event as a consequence to stimuli
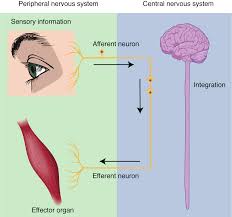
homeostasis
maintain homeostasis by acting as a regulatory or control center through sensory input, motor output, and integration functions