Genetics, Neurons, and Brain Structures in Physiology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the two types of chromosomes in humans?
23 pairs of chromosomes, one from mother and one from father.
What do the first 22 chromosomes in humans direct?
Development of the body and brain.
What does the 23rd chromosome determine?
Sex of the individual.
Define genotype.
Genetic inheritance.
Define phenotype.
Observable traits.
What is a dominant gene?
A gene that is always expressed (e.g., brown eye color).
What is a recessive gene?
A gene that must be paired with another recessive gene to be expressed.
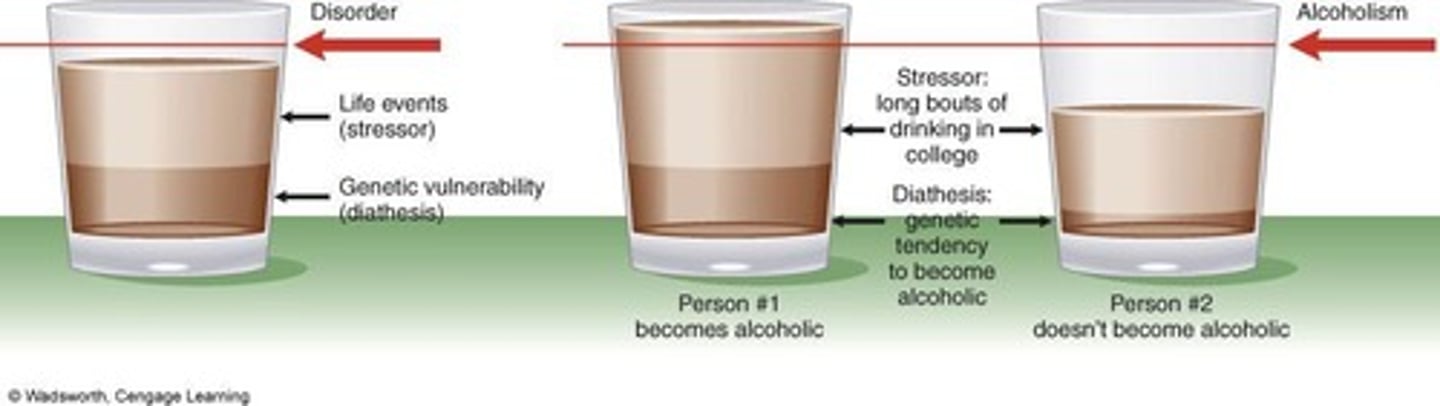
What is the Diathesis-Stress Model?
A model explaining how genetic predispositions and environmental stressors interact to influence behavior.
What are the main parts of a neuron?
Cell body, dendrites, axon, and terminal buttons.
What is a synapse?
The space between neurons.
What is the function of astrocytes?
Provide support to neurons, clean up debris, control the external environment, and provide nutrients.
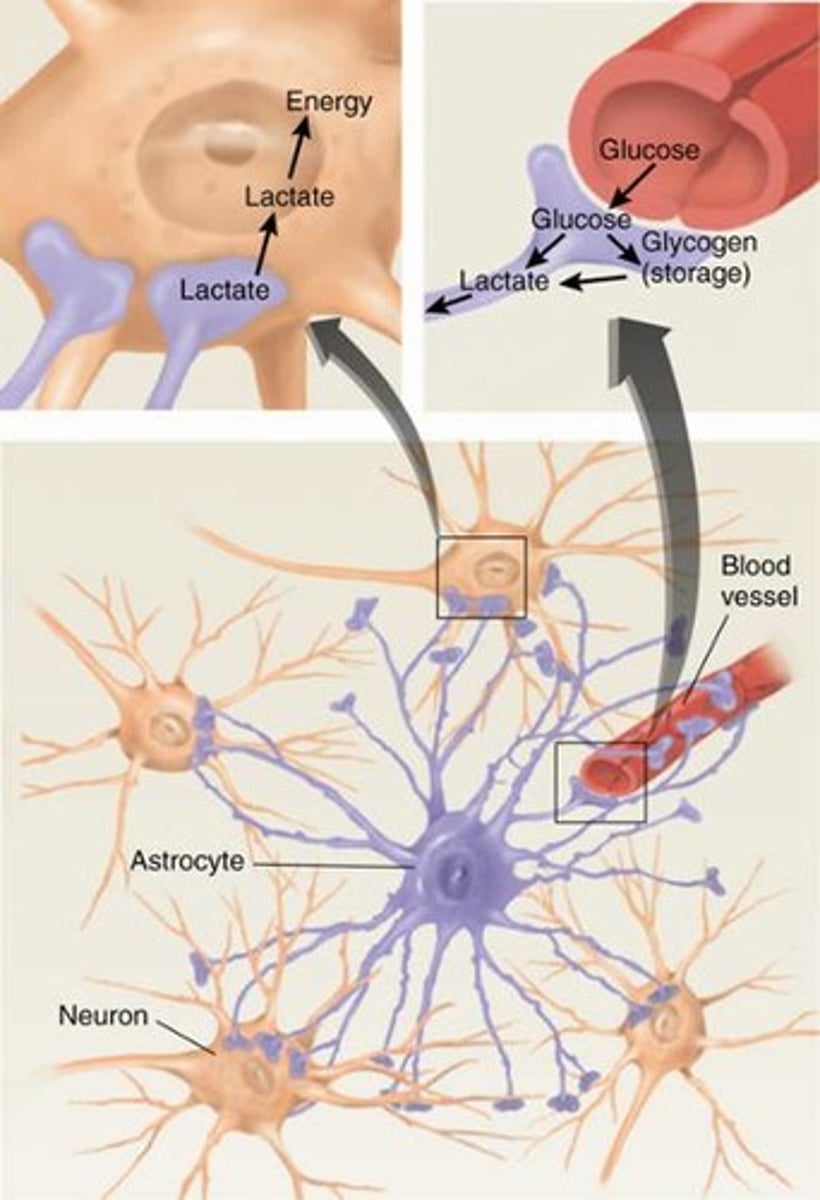
What do oligodendrocytes do?
Support axons and produce the myelin sheath.
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
Inside of neuron is negatively charged relative to outside (-70 mV).
What happens during depolarization?
A positive charge is added to the neuron.
What is action potential?
A change in charge from negative to positive past the threshold of excitation.
What does the All-or-None Law state?
Once the threshold of excitation is reached, the neuron fires completely.
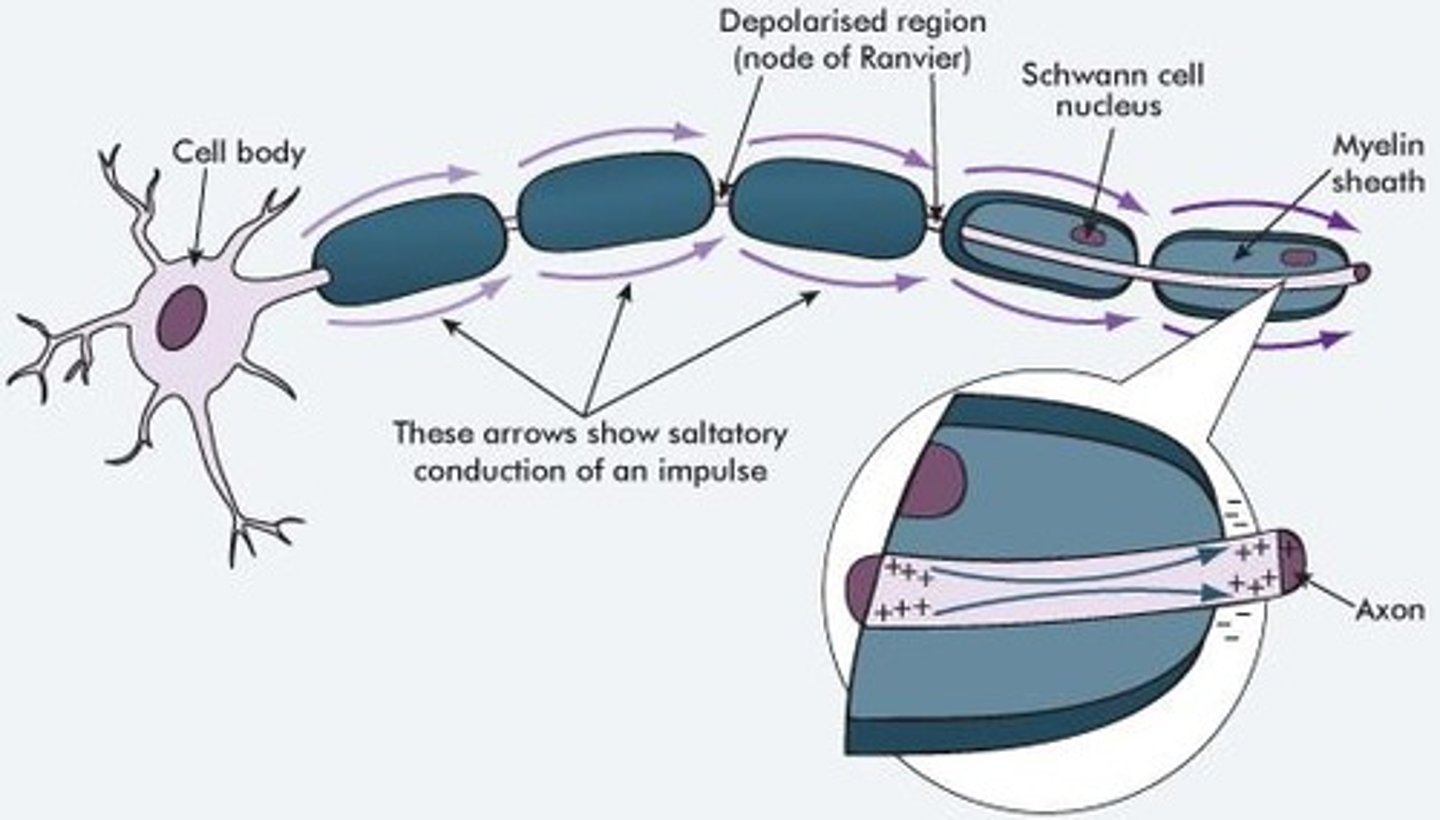
What is saltatory conduction?
Conduction through the axon that 'jumps' at the nodes of Ranvier.
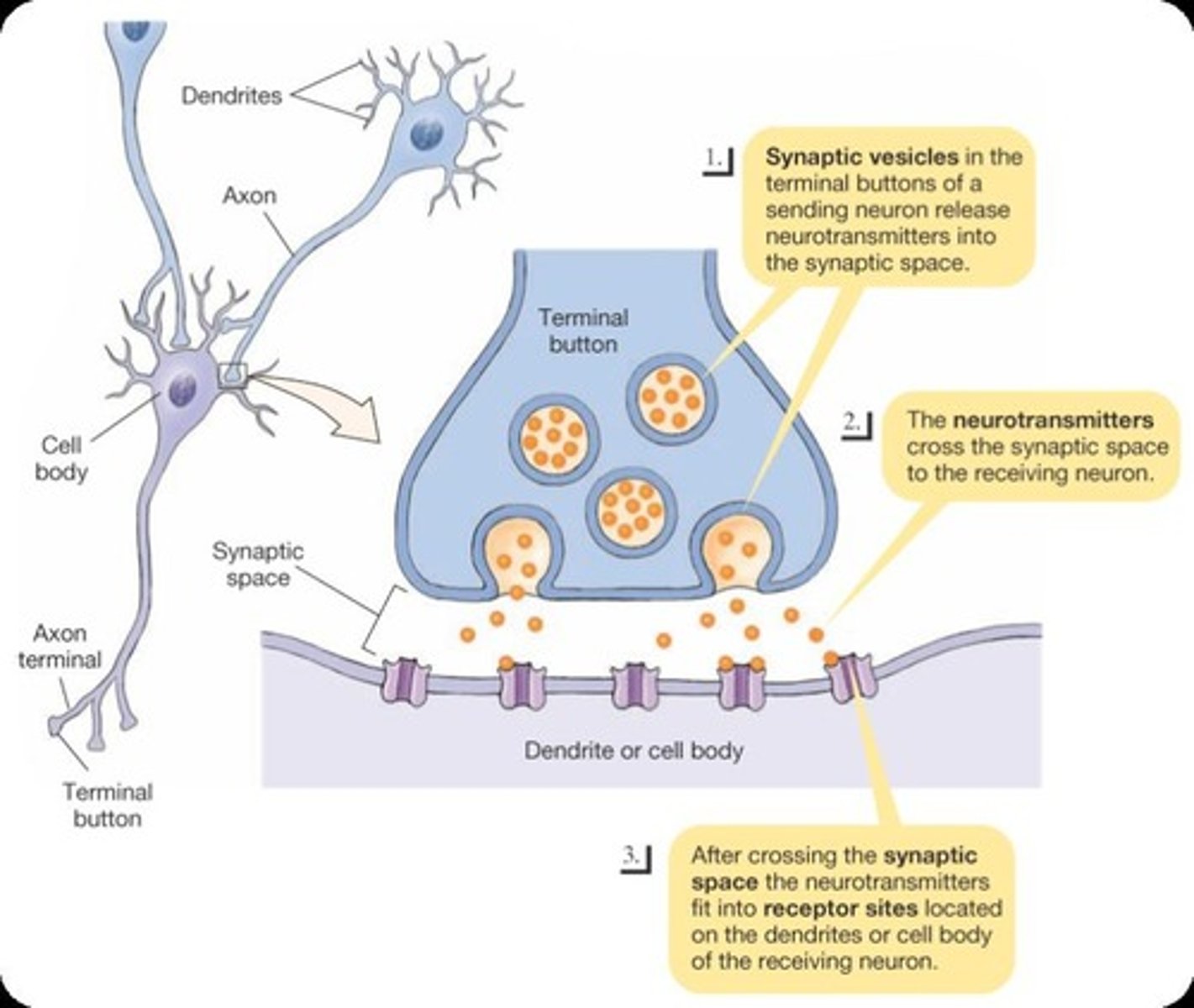
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical messengers stored in synaptic vesicles that transmit signals across synapses.
What is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)?
A postsynaptic potential that makes the neuron more likely to fire.
What is an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)?
A postsynaptic potential that makes the neuron less likely to fire.
What is reuptake in neurotransmission?
The process of neurotransmitters being removed from the synaptic cleft and taken back into the neuron.
What is the function of the thalamus?
Receives input and transmits information to the cerebral cortex.
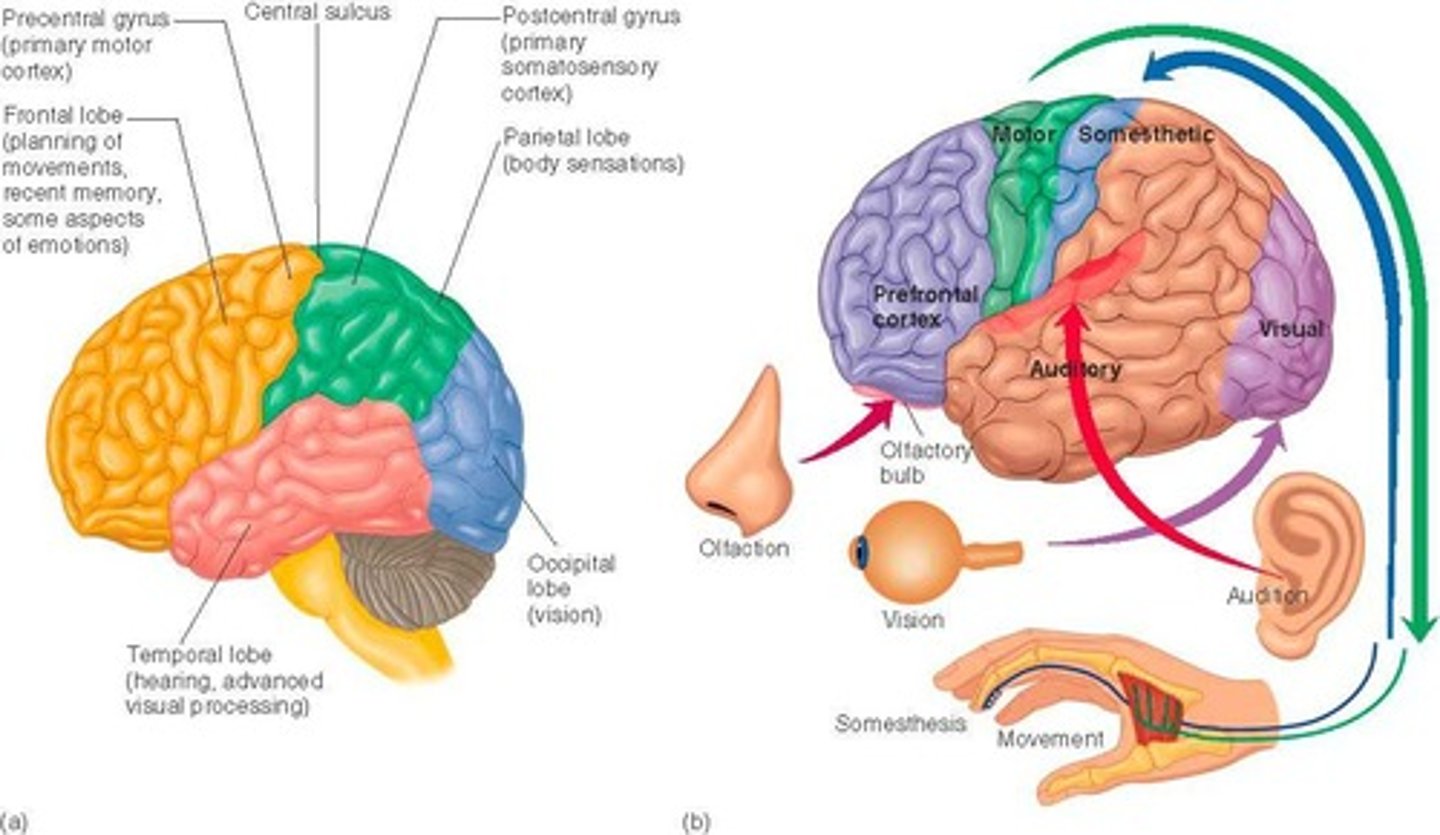
What are the four main lobes of the cerebral cortex?
Frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital.
What is the role of the limbic system?
Involved in emotional experience, control, learning, and memory.