Lecture 49: Liquid dosage forms suspensions and emulsions 2
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what are the advantages of pharmaceutical oral suspensions?
delivery system for low sol drugs
avoid large volume of solvent
avoid precipitation when storing when cosolvent is used
taste masking
difficulty swallowing solid forms
controlled drug delivery
what are disadvantages of pharmaceutical oral suspensions?
correct dose of drug?
unstable, formulation to ensure stability over period of shelf life
aesthetic suspension: difficult
bulky so difficult for patient to carry
pharmacokinetics after administration of oral suspension:
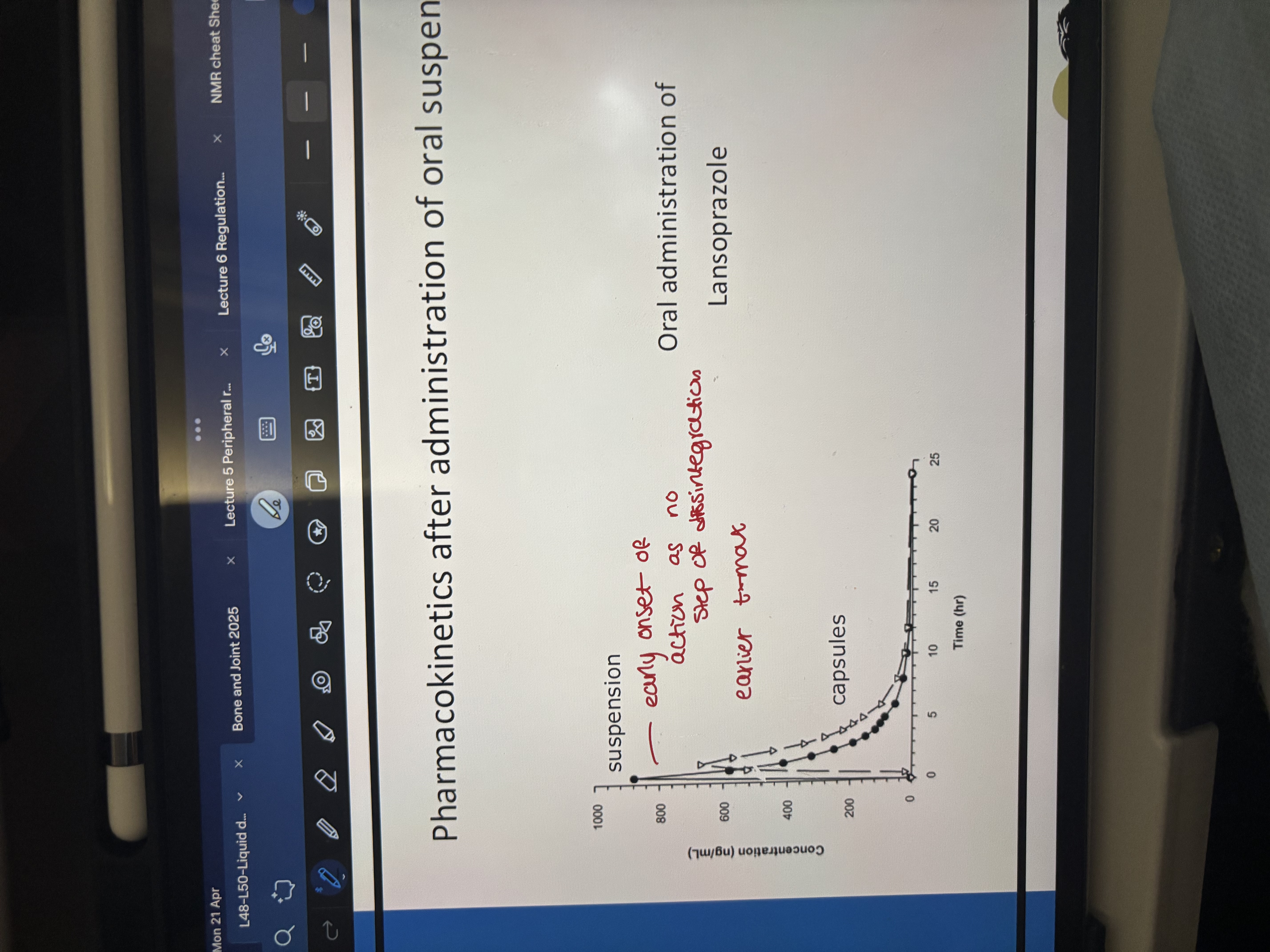
what are some of the challenges with oral suspensions
stability: can lead to sedimentation leading to particle particle interactions and caking
need to know the particle size of the dispersed phase, excipients
an alternative is producing solutions with solubilising agents
what are the key parameters which should be controlled?
electrical properties of dispersed particles
effect of distance of separation between particles on interaction(no interaction, agglomeration, floccules)
viscosity
what are the 2 physical properties that need to be considered for the formulation?
Particle size: the larger the radius the more sedimentation. increasing stability by modifying rate of particle sed
therefore particle size should be minimised. can be done by chemical methods(controlled precipitation) or physical methods(milling)
Wetting properties of drug:
insoluble drug particles: hydrophobic and not easily wetted
surface active agents: decrease interfacial tension
particles poorly wetted: aggregation
what are the features of crystal growth?
smaller particles dissolve better than large particles when dispersed in an aqueous vehicle
an increase in storage temp caused smaller particles to dissolve in the vehicle
crystallisation of dissolved drug may occur on surface of larger particles
particles will have crystal growth around other particles when cold
hydrophilic polymers decrease crystal growth by adsorbing on to suspended drug particles for protection
crystal growth can be controlled by temperature cycling, monitor particle diameter and physical stability
what are the components of oral suspensions?
Vehicle: purified water USP, buffers(citrate commonly used)
excipients: they can physically stabilise suspensions, control rate of particle/ floccule sedimentation
what are the types of excipients and what do they do?
electrolytes: they control flocculation by reducing zeta potential
surface active agents:wetting, facilitating flocculation at conc less than 0.5% w/w
non ionic preferred: polyethylene fatty acid sorbitan esters, lecithin
ionic surfactants: greater toxicity
what are the types of excipients and what do they do? pt 2
Hydrophilic polymers: physical stability and affect flow properties
they adsorb on to surface of suspended drug particles
due to large MW, one section of polymer chain adsorb on to particles, the rest of the chain into an aqueous vehicle
2 polymer coated particles approach each other which prevents particles coming into close contact
has the ability to stabilise suspensions: C, type of polymer
increases viscosity which decreases sedimentation and increases physical stability giving it better flow properties making it easier to give to someone
what are the features of hydrophilic polymers in oral suspensions?
they are cellulose derivatives, branched polymers, methycellulose, hydroxyethylcellulose or hydroxypropylmethylcellulose
polyvinylpyrrolidone
sodium aginate(ionic)
acacia,tragacanth and xanthan gum: natural polysaccharide based polymers, low C
hydrated silicates: for theological structuring, 5% swell in water leading to a vehicle with plastic flow
what are the other components of pharmaceutical oral suspensions ?
Preservatives:
usually the external phase is water therefore there’s possible microbial growth
highly pathogenic microorganisms (e coli) absent
parables, organic acids such as benzoin acid
interaction with hydrophilic polymers always required free C of preservatives available
Antioxidants: control degradation in preference of drug
sweetening agents/flavours: as for oral solutions

what are the features of direct incorporation?
the mixing rate is an important determinant
if suspension is flocculated, high speed mixing is used
if flocculation properties are poor, high speed mixing results in an increase in viscosity(it’s hard to mix homogeneously)
the particle size of suspended drug may decrease using a ball mill. alternatively the particle size of the drug optimised by particle size reduction techniques
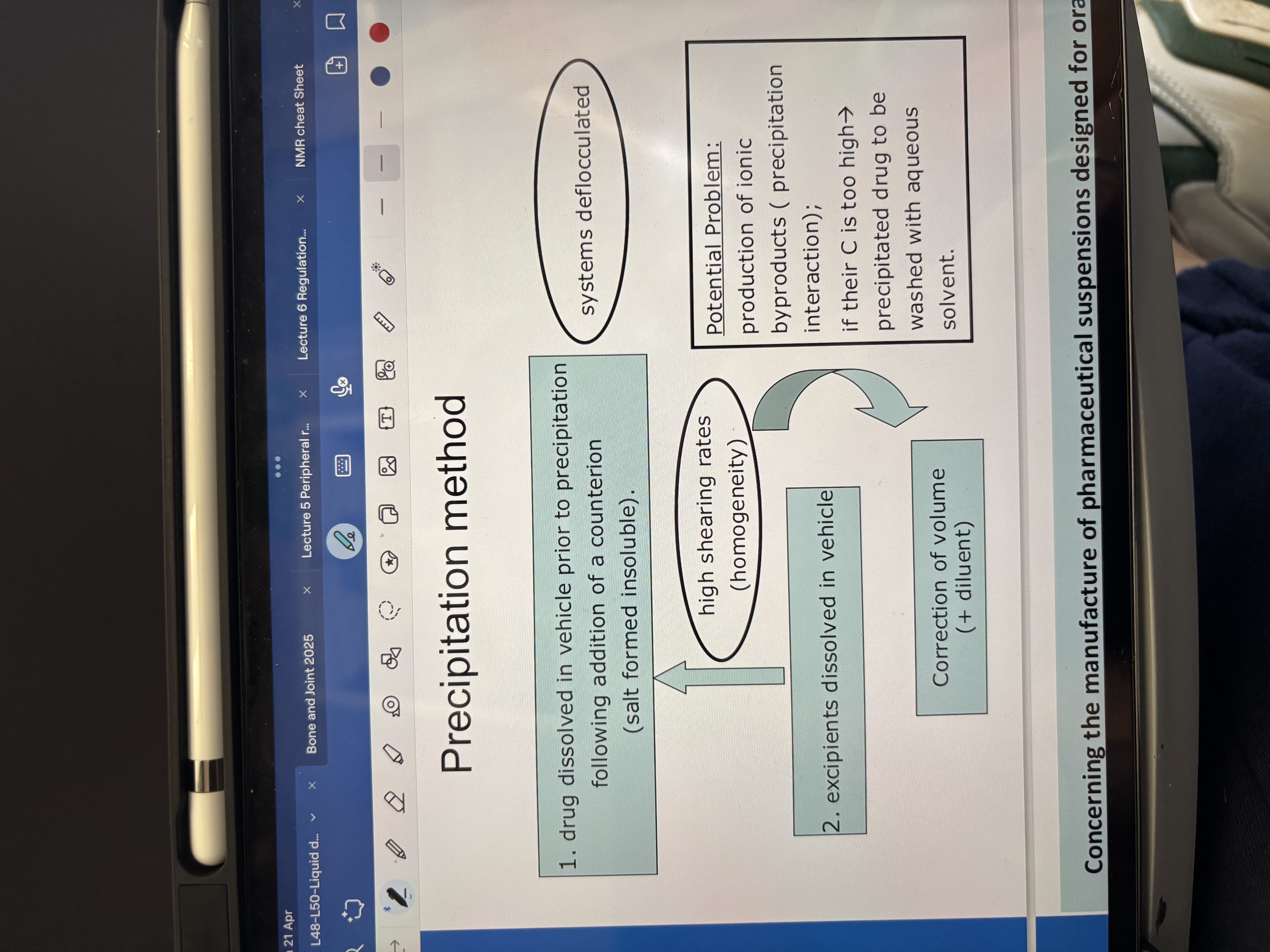
what is the precipitation method?
a drug is dissolved in vehicle prior to precipitation following addition of a counter ion(salt formed insoluble)
excipients dissolved in vehicle
watch video
C

A , B, C