Cartões: Stoichiometry and Chemical Formulas | Quizlet
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Molar Mass
Mass of one mole of a compound.
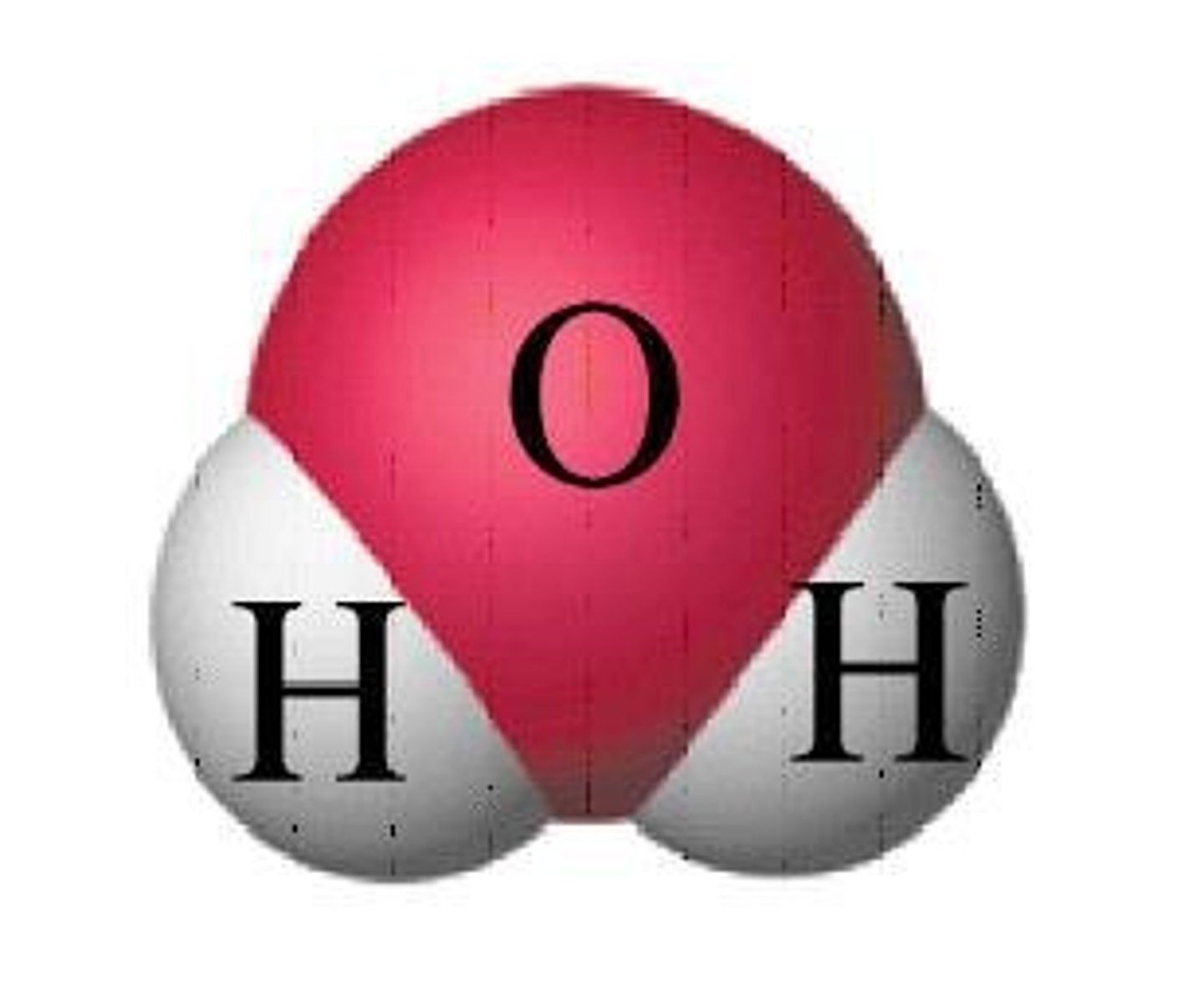
Molecular Mass
Mass of one molecule in amu.
Formula Mass
Mass of one formula unit in amu.
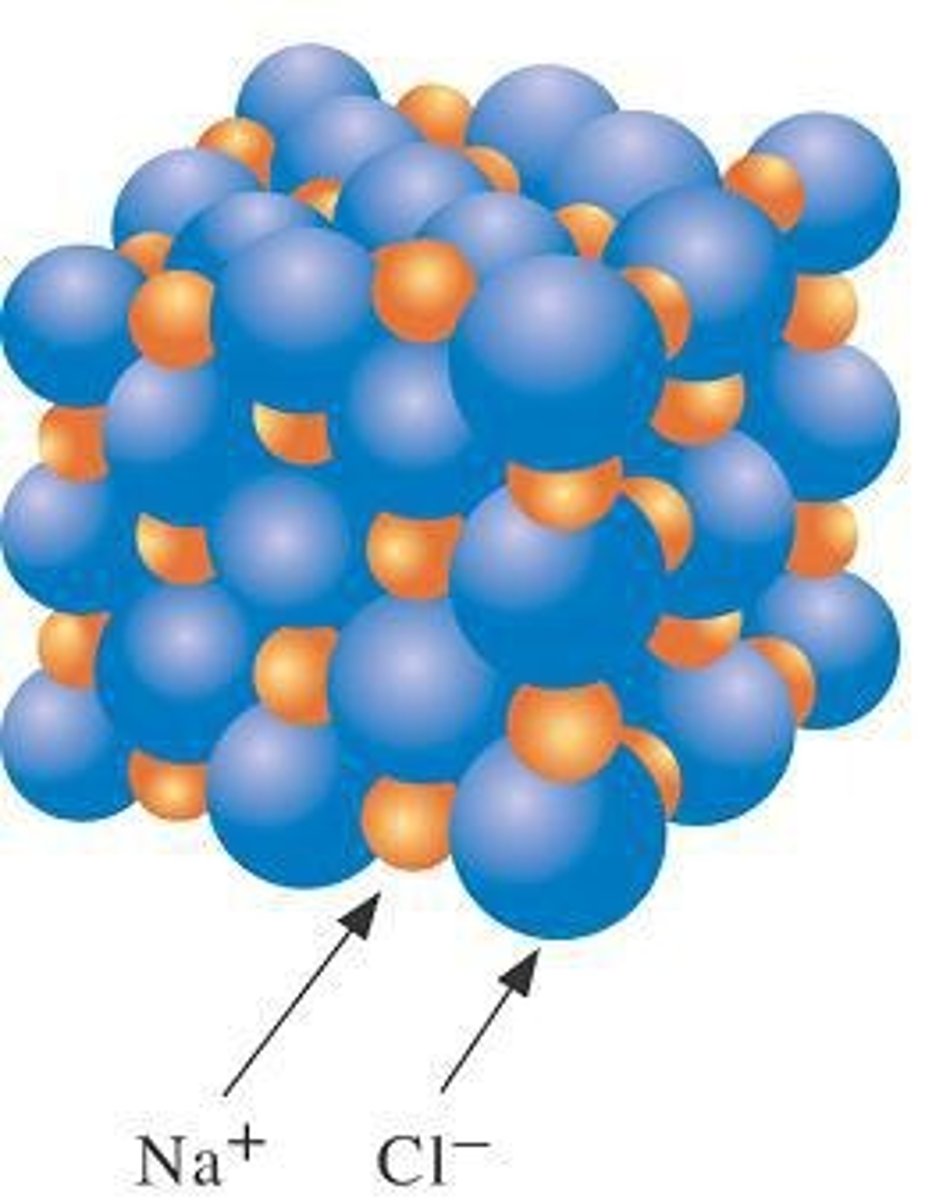
Empirical Formula
Simplest whole-number ratio of atoms.
Molecular Formula
Actual number of atoms in a compound.
Mass Percent Composition
Percentage of each element's mass in compound.
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in reactions.
Limiting Reactant
Reactant that limits product formation.
Percent Yield
Actual yield divided by theoretical yield.
Diatomic Elements
Elements that exist as two-atom molecules.
Mole
6.022 x 10^23 particles.
Chemical Formula
Representation of a compound's composition.
Stoichiometry
Calculation of reactants and products in reactions.
Conversion Factor
Ratio used to convert between units.
Molar Mass of H2O
18.02 g/mol for water.
Molar Mass of NaCl
58.44 g/mol for sodium chloride.
Molar Mass of Ca(OH)2
74.09 g/mol for calcium hydroxide.
Molar Mass of C2H5OH
46.07 g/mol for ethanol.
Mole Ratio
Ratio of moles of reactants/products.
Chemical Equation
Symbolic representation of a chemical reaction.
Mass to Mole Conversion
Mass divided by molar mass.
Mole to Mass Conversion
Moles multiplied by molar mass.
Mole to Particle Conversion
Moles multiplied by Avogadro's number.
Particle to Mole Conversion
Particles divided by Avogadro's number.
Hydroxide Ion (OH-)
An ion consisting of one oxygen and one hydrogen.
Avogadro's Number
6.022 x 10^23, number of particles in a mole.
Molar Mass Calculation
Sum of atomic masses in a compound.
Percent Composition Calculation
Mass of part divided by total mass.
Empirical Formula Mass
Mass calculated from empirical formula.
Multiplying Factor (n)
Factor to convert empirical to molecular formula.
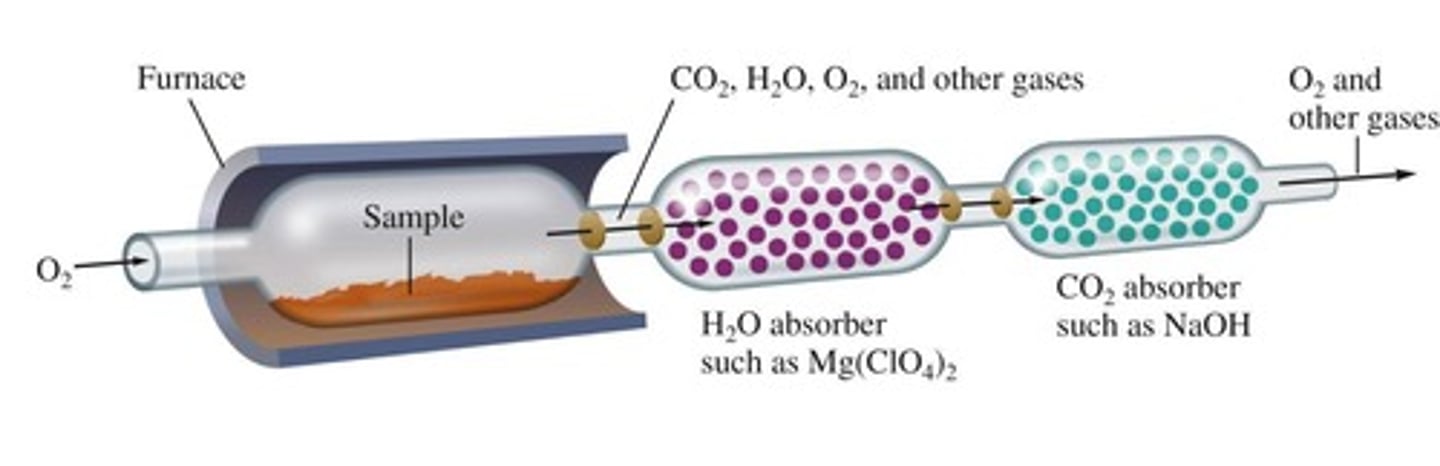
Combustion Analysis
Technique to determine empirical formulas using combustion.
Pseudoformula
Initial formula representation using moles.
Mass % Composition
Percentage of each element in a compound.
Reactants
Substances consumed in a chemical reaction.
Products
Substances formed in a chemical reaction.
Coefficients
Numbers indicating amounts of reactants/products.
Physical States Symbols
Indicate states: (s), (l), (g), (aq).
Balancing Equations
Adjusting coefficients to equalize atom numbers.
Whole Numbers
Coefficients must be smallest integers.
Combustion Products
CO2 and H2O produced from combustion.
Mass of Carbon
Derived from mass of CO2 produced.
Mass of Hydrogen
Derived from mass of H2O produced.
Mass of Oxygen
Calculated from total mass minus C and H.
Stoichiometric Calculations
Calculations based on balanced chemical equations.
Dimensional Analysis
Method to convert units using conversion factors.
Subscripts
Indicate number of atoms in a formula.

Chemical Change
Transformation resulting in new substances.
Color Change
Visual indicator of a chemical reaction.
Gas Evolution
Production of gas during a reaction.
Solid Precipitate
Solid formed from a solution during a reaction.
Excess Reactant
Reactant that remains after the reaction completes.
Stoichiometric Amount
Exact amount of reactants as per balanced equation.
Balanced Equation
Equation showing equal moles of reactants and products.
Mole-Mole Conversion
Ratio of moles of two substances in a reaction.
Mass to Mass Conversion
Calculating mass of one substance from another's mass.
Theoretical Yield
Maximum product formed from limiting reactant.
Molar Mass (MM)
Mass of one mole of a substance in grams.
Equivalence Statements
Statements relating moles and grams of substances.
Stoichiometric Mixture
Mixture with reactants in exact stoichiometric ratios.
Actual Yield
Amount of product actually obtained from a reaction.
Chemical Reaction
Process where reactants transform into products.
Conversion Steps
Process of changing from one unit to another.
Product Formation
Amount of product produced from reactants.
Limiting Reactant Determination
Identifying which reactant produces less product.
Grams of N2 Calculation
Determining mass of nitrogen produced from reaction.
Percent Yield Calculation
Formula: (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100.
Ammonia Production
Formation of NH3 from H2 and N2 in reactions.
Reaction Example
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) shows stoichiometry.
Conversion of Grams to Moles
Using molar mass to convert grams to moles.
CuO Reaction
Reaction involving copper(II) oxide and ammonia.
Stoichiometric Ratios
Proportions of reactants and products in reactions.