Week 2: Seeds of Global Civilization adn Settle Agriculture
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
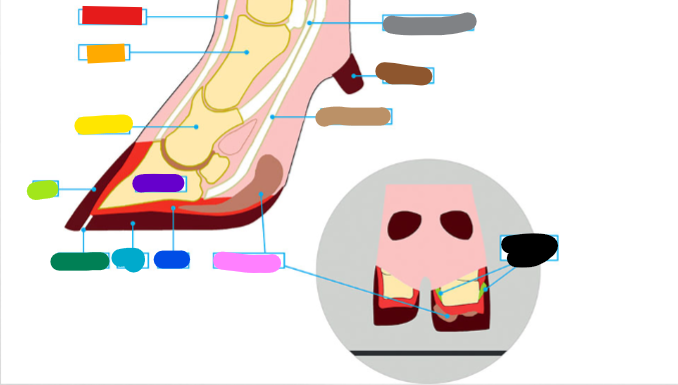
What is the red?
Extensor tendon
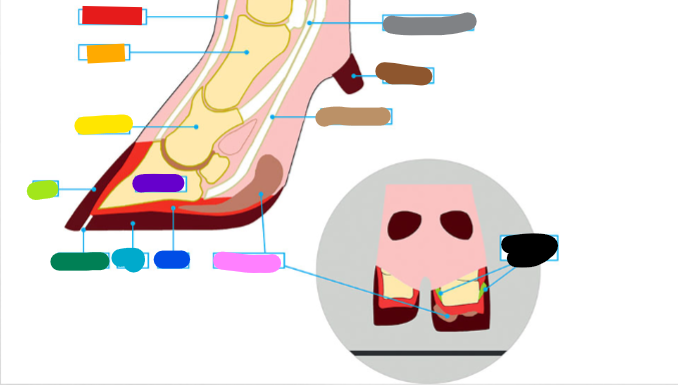
What is the orange?
1st phalanx
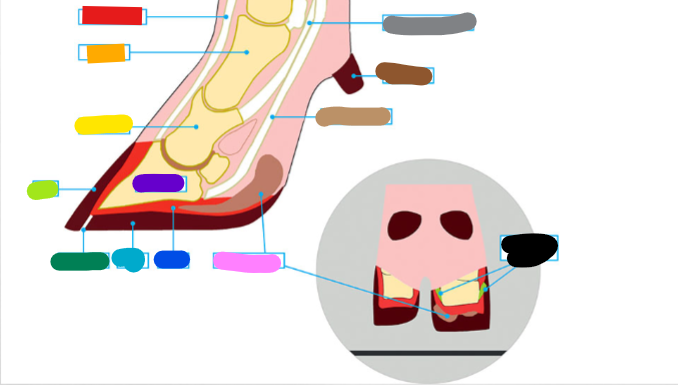
What is the yellow?
2nd phalanx
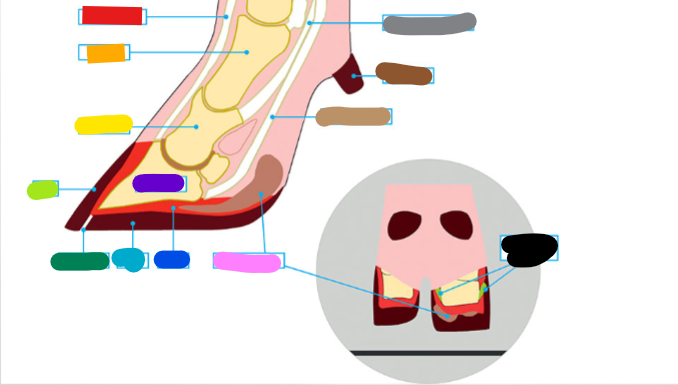
What is the light green?
Wall
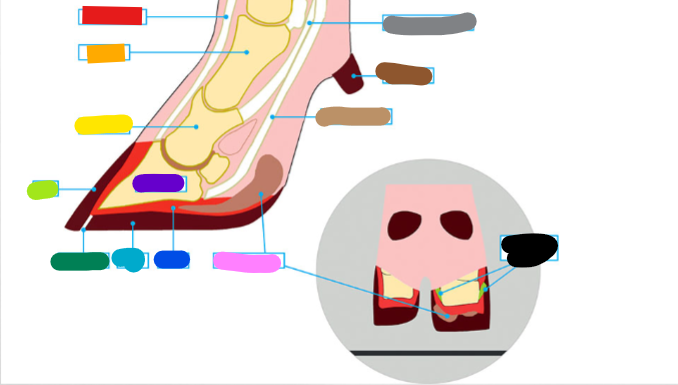
What is the dark green?
White Line
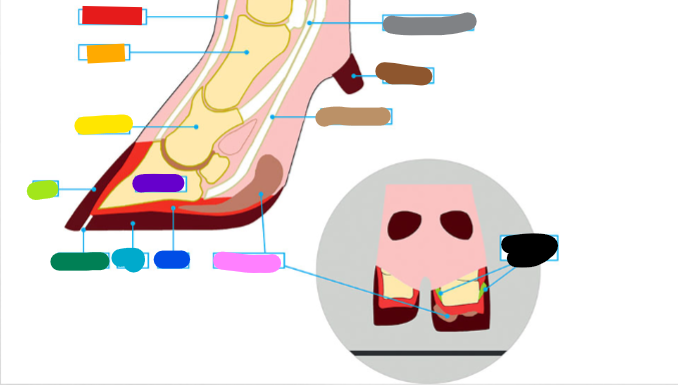
What is the light blue?
Sole
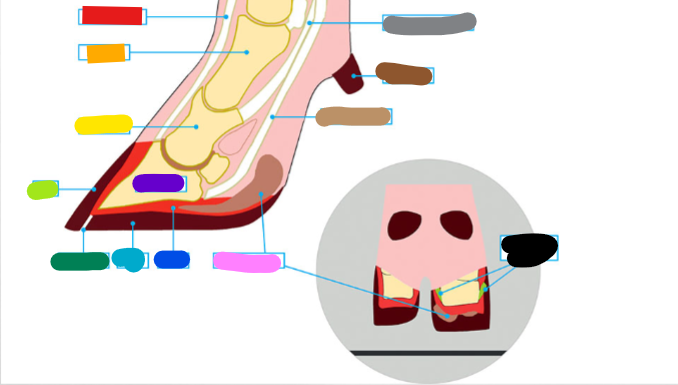
What is the dark blue?
Corium
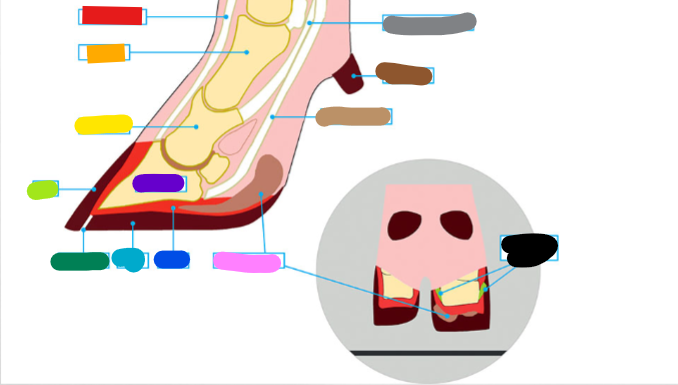
What is the purple?
3rd phalanx
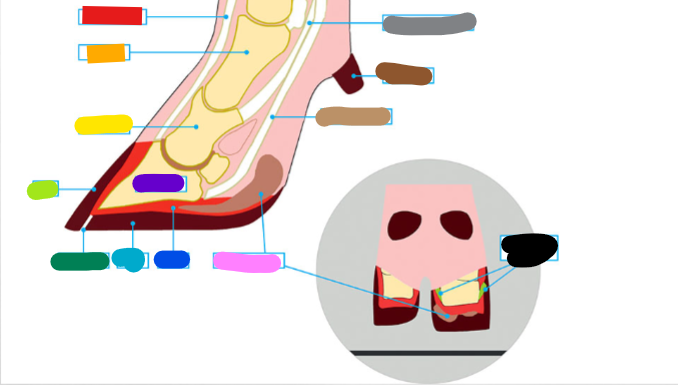
What is the Light Brown?
Deep flexor tendon
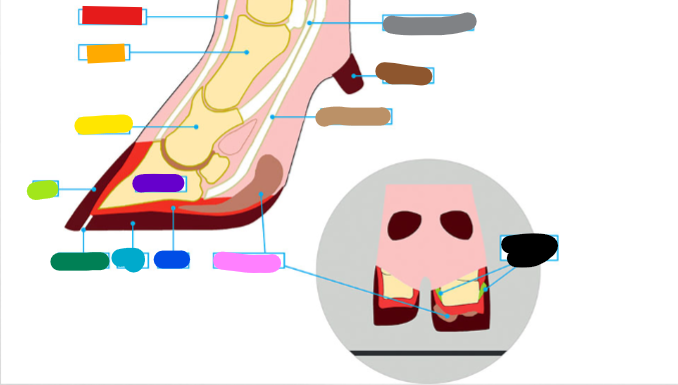
What is the Brown?
Dew claw
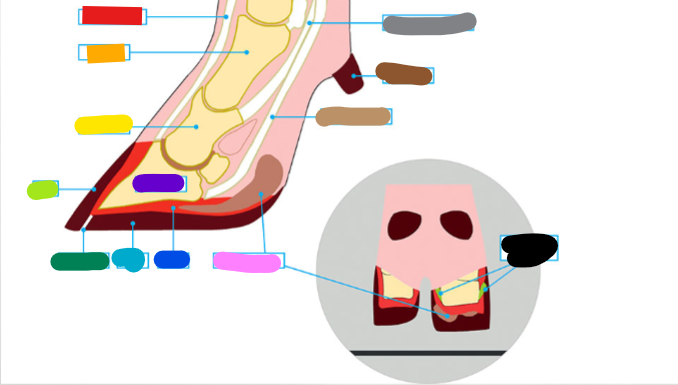
What is the Black?
Suspensory Ligaments
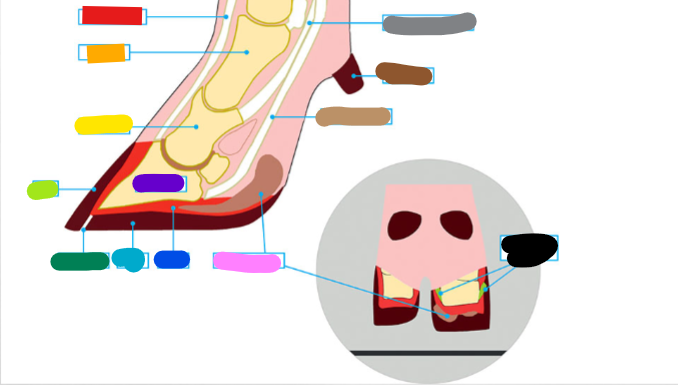
What is the grey?
Superficial flexor tendon
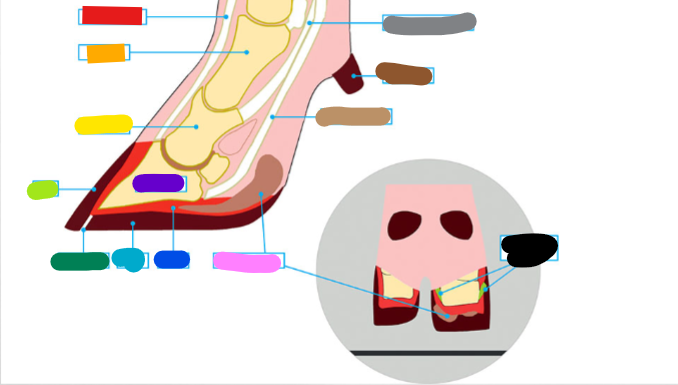
What is the pink?
Digital cushion
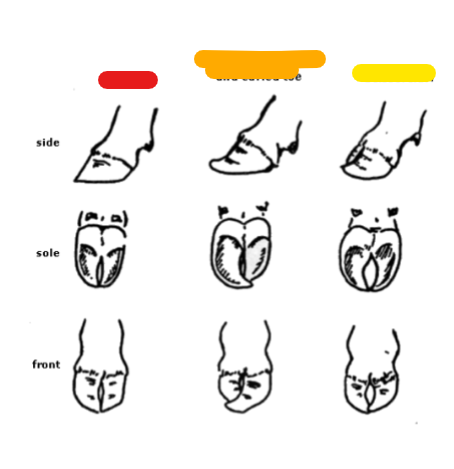
What is the red?
Normal
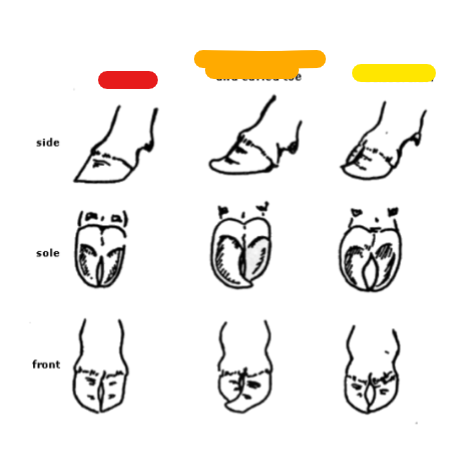
What is the orange?
Large outside claw and curled toe
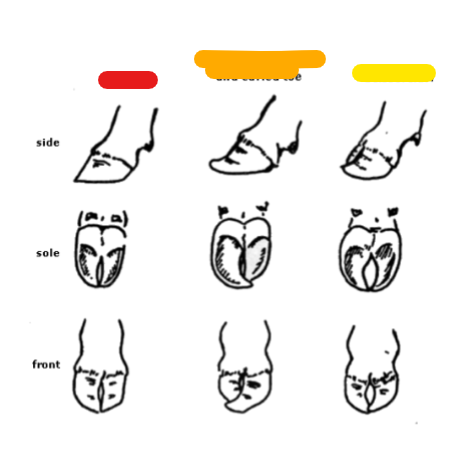
What is the yellow?
Scissorclaw
What makes up the hoof?
Keratin
What body “organs” are in the hoof?
Blood vessels and nerves
What kind of hooves do cattle have?
Cloven hooves/cleft hoof (divided into two parts/two toes)
Rectal Temp of cattle (F)
100.4-102.5
Rectal Temp of cattle (C)
38-39
Heart Rate of Cattle
48-84 bpm
Respiratory rate of cattle
27-40bpm
Are Dictyocaulys viviparus an internal or external parasite?
Internal e
What are lung worms technical name?
Dictyocaulus Viviparus
Where are Dictyocaulus Viviparus found?
Bronchi
Symptoms of Dictyocaulus Viviparus
Coughing, eggs seen in mucosal discharge
What test do you perform for Dictyocaulus Viviparus?
Fecal Float Test
Are Rumen and Liver Flukes internal or external parasites?
Internal
What family do rumen flukes belong to?
Amphistomes (“Both Side”)
What is the name of liver flukes?
Fasciola Hepatica
What parasite causes obstruction of the bile ducts which leads to liver failure?
Liver Flukes
What is the first host of flukes?
Aquatic snails
Are coccidial-like parasites internal or external?
Internal
Causes an inflammation of the mucosal cells lining intestinal walls
Cryptospiridium
Which parasite is coccidial-like?
Cryptosporidium
Most common clinical sign is diarrhea
Cryptospiridium
This is a zoonotic disease?
Cryptospiridium
What test is used to test for coccidial-like parasites?
Fecal floats
This parasite has oocysts
Coccidial-like
A test to diagnose internal parasites using fecal matter from infected species
Fecal Floatation
Are horn flies internal or external parasites?
External
Scientific name of horn flies
Haematobia Irritans
Where are horn flies found on the cattle?
Horns, shoulders, back, sides
Cause irritation and annoyance
Horn flies
Found exclusively on cattle in North America
Horn Flies
Are no-see ums internal or external?
external
Tiny gnats
No-see ums
Developmental stages are primary aquatic, adults can be found around aquatic or semiaquatic breeding grounds
No-see ums
Are ticks internal or external?
External
What kind of tick is found on cattle (non-scientific name)?
Texas Cattle Fever Tick
What kind of tick is found on cattle (scientific name)?
Boophilus annulatus
Must report immediately if found in U.S
Texas Cattle Fever Tick
Causes irritation that leads to raw infection sites and anemia
Texas Cattle Fever Tick
Clinical Signs: Increased respiratory effort, droopy ears. poor appetite, coughing, abnormal nasal discharge
Bovine Respiratory Disease
Preventative measures: Vaccinate for Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis
Bovine Respiratory Disease
Treatment: Antibiotics (exceed, enrofloxacin, nuflor)
Bovine Respiratory Disease
Clinical Signs: Protruding of the left side abdomen, labored breathing, salivation or foaming, staggered gait
Bloat
Preventative measures: Bloat guard blocks, monitor cattle grazing pasture
Bloat
Treatment: If condition allows it, pass a stomach tube and feed into rumen or use bloat trocar (emergency cases)
Bloat
Clinical signs: Diarrhea, decreased nursing, depression
Calf Scours
Preventative care: Vaccinate against with Ultrabac 8
Calf Scours
Treatment: Administer oral antibiotics (sulfonamide or ceftiofur)
Calf Scours
Clinical signs: Excessive tearing, ocular discharge, inflammation of eye, cloudiness
Pink eye/ Foreign body
Preventative care: Manage fly control, check herd daily if tall grass pasture
Pink eye/foreign body
Treatment: Remove foreign body, administer nuflor
Pink eye/foreign body
Clinical sings: Limping, swelling of leg, not putting pressure on foot
Foot Rot
Preventative measures: Clean, dry environments
Foor Rot
Treatment: Clean the foot and administer antibiotics
Foot Rot
Clinical Signs: Animal separates herself from herd, fetal membrane or fetus protruding from vulva, prolonged straining by cow/vocalization
Dystocia
Preventive care: Selective breeding, monitoring calving dates
Dystocia
Treatment: Assist with calving if applicable, culling
Dystocia
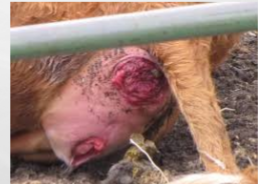
What prolapse is this?
Rectal prolaspe
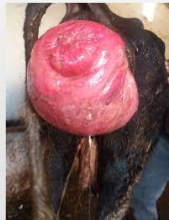
What prolapse is this?
Cervical/vaginal prolapse
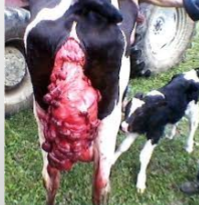
What prolapse is this?
Uterine prolapse
Clinical signs: swollen/hardened udder, painful nursing, anorexia
Mastitis
Preventive care: Conduct a subclinical mastitis test
Mastitis
Treatment: Treat with antibiotics or amputate the udder
Mastitis
A qualitive test used to detect the presence of bacterial infection and stomatic cell count in a cows milk
California Mastitis Test (CMT)
A measure of the inflammation within a quarter and can e scored based on degree of gel formation
California Mastitis Test (CMT)
What color indicates positive on a California Mastitis Test?
Deep purple
What bacteria is the most common for Mastitis?
Staphylococcus aureus
Phenobarbital based solution administered intravenously to euthanize cattle
Barbiturates
Place firmly against skull and fire into brain (euthanasia)
Captive Bolt Gun
A puncture wound that serves major blood vessels causing blood to drain (most common place is base of neck- also called sticking) for euthanasia
Exsanguination