MODULE 2 AGGREGATES CMT
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts, definitions, and classifications related to aggregates and their roles in concrete applications.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Aggregates
Materials used as a base for foundations and in concrete mixes.
Gradation
The distribution of different particle sizes in an aggregate.
Specific Gravity
The ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance, typically water.
Aggregates from Igneous Rocks
have massive structure, entirely crystalline or wholly glassy or in combination in between, depending upon the rate at which they were cooled during formation
Aggregates from Sedimentary Rocks
may vary from soft to hard, porous to dense and light to heavy
The thickness of the stratification of _______rocks may vary from a fraction of a centimeter or more
Aggregates from Metamorphic Rocks
Both igneous rocks and sedimentary rocks may be subjected to high temperature and pressure which causes metamorphism which changes the structure and texture of rocks.
show foliated structure. The thickness of this foliation may vary from a few centimeters to many meters.
Fine Aggregates
Aggregates that pass through a 4.75mm sieve, generally used in concrete.
Coarse Aggregates
Aggregates that do not pass through a 4.75mm sieve, used in structural concrete.
Fineness Modulus
A measure of the average size of particles in an aggregate, calculated based on sieve analysis.
Water-Cement Ratio
The ratio of the mass of water to the mass of cement used in a concrete mix, affecting its strength.
Soundness
The ability of an aggregate to resist weathering and degradation.
Shape of Aggregate
The geometric form of aggregate particles, influencing workability and strength of concrete.
60% to 75%
IN PORTLANT CEMENT, HOW MUCH PERCENTAGE OF VOLUME OF AGGREGATES ARE THERE
79% to 85%
IN PORTLANT CEMENT, HOW MUCH PERCENTAGE OF THE WEIGHT OF AGGREGATES ARE THERE
80mm
the maximum size of aggregates that could be conveniently used for concrete making.
Using the largest possible size will result in:
i. Reduction of cement content;
ii. Reduction of water requirement;
iii. Reduction of drying shrinkage
the maximum size of aggregate that can be used in any given condition may be limited by the following conditions:
i. Thickness of section
ii. Spacing of reinforcement
iii. Clear cover
iv. Mixing, handling, and placing techniques
FACTORS AFFECTION CHOICE OF AGGREGATES
Shape
A. Rounded gravel
Fully water worn or completely shaped by attrition. Examples: River or seashore gravels; desert, seashore and windblown sand
FACTORS AFFECTION CHOICE OF AGGREGATES
Shape
B. Irregular or partly rounded gravel.
Naturally irregular or partly shaped by attrition, having rounded edges Examples: Pit sand and gravel; land or dug flints, cuboid rock
FACTORS AFFECTION CHOICE OF AGGREGATES
Shape
C. Angular gravel
Possessing well-defined edges formed at the intersection of roughly planar faces Examples: Crushed rocks of all types, talus, screes
FACTORS AFFECTION CHOICE OF AGGREGATES
Shape
D. Flaky gravel.
Material, usually angular, of which the thickness is small relative to the width and/or length Example: Laminated rocks
FACTORS AFFECTION CHOICE OF AGGREGATES
Texture
As surface smoothness increases, contact area decreases, hence a highly polished particle will have less bonding area with the matrix than a rough particle of the same volume
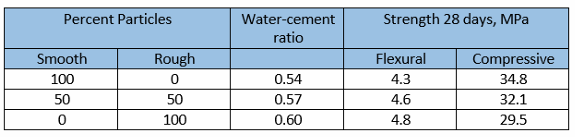
texture representation
FACTORS AFFECTION CHOICE OF AGGREGATES
Strength
Since concrete is an assemblage of individual pieces of aggregate bound together by cementing material, its properties are based primarily on the quality of cement paste.
is dependent also on the bond between the cement paste and the aggregate.
SAND
naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles
SOURCE OF SAND
I. Natural sand
a. Pit sand.
found as deposits in soil. It is obtained by making pits into soil
SOURCE OF SAND
I. Natural sand
b. River sand
obtained from banks or river beds
SOURCE OF SAND
I. Natural sand
c. Sea sand.
obtained from seashores
SOURCE OF SAND
II. Artificial sand or robo sand
The artificial sand produced by crushing stones can be a better substitute to river sand. The process of manufacturing robo sand is totally different from ordinary stone crushers from which we get 40mm, 20mm, 10mm size coarse aggregate
LIMITS OF FINENESS MODULUS OF COARSE AGGREGATES
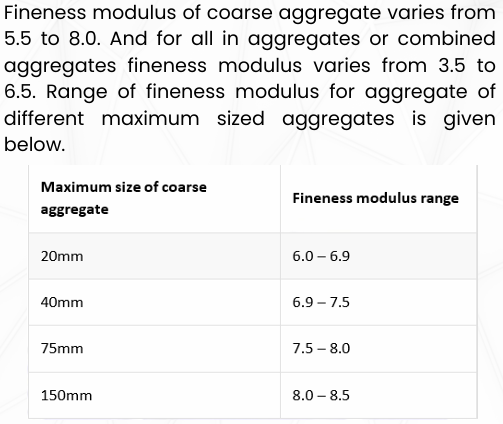
LIMITS OF FINENESS MODULUS OF FINE AGGREGATES
