Calcium ion channels
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What type of voltage gated Ca2+ channel (CaV) do CCBs act on?
L-type (CaV1)
What are L-type calcium channels made up of?
4 different α-1 subunits which are encoded by 4 separate genes
What are the names of the α-1 subunits which make up L-type calcium channels?
CaV 1.1
CaV 1.2
CaV 1.3
CaV 1.4
Where are L-type calcium channels found?
Heart and Vascular smooth muscle
How do calcium channel blockers work?
They block receptors on L-type calcium channels in the heart and vascular smooth muscle which cause the channel to blocked preventing the influx of calcium so that heart rate and vascular tone can be controlled.
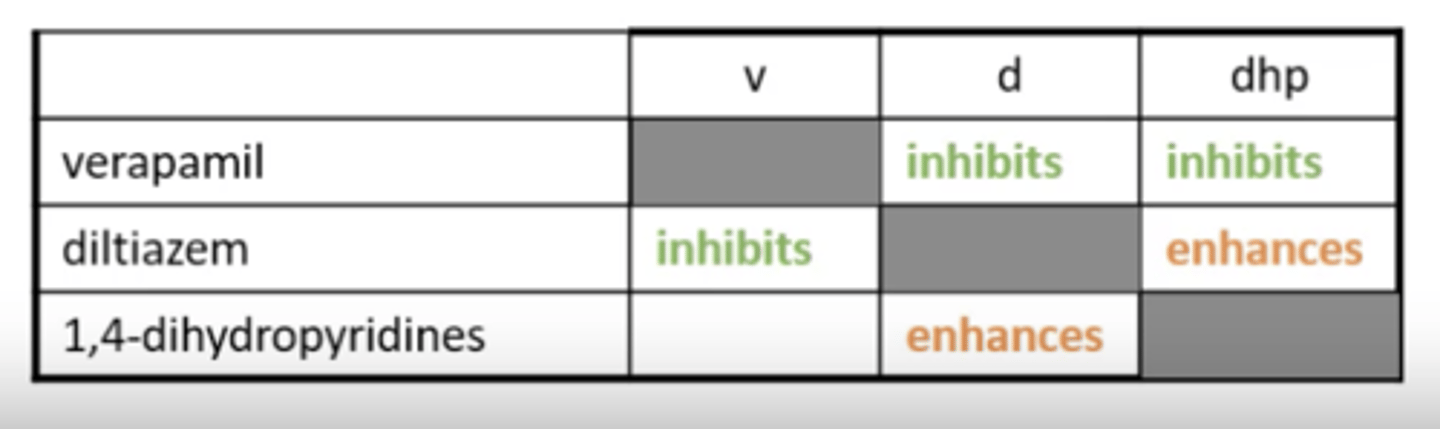
What are the 4 classes of CCB drugs that can act on L-type calcium channels?
- Phenylalkylamines e.g., verapamil
- Dihydropyridines (DHPs)e.g., nifedipine
- Benzothiazepines e.g., diltiazem
- Diaminopropanol ethers e.g., bepridil
How do L-type calcium channel blockers work?
- All bind to α-1 subunit, different CCBs work on different transmembrane domains.
- They interfere between inactivated and resting states as they have a higher affinity to the inactivated state.
How do ion channels work?
- Normally closed
- Open in response to depolarisation allowing ions to pass.
- Channel then becomes inactivated (unable to be stimulated) before returning to closed/resting state
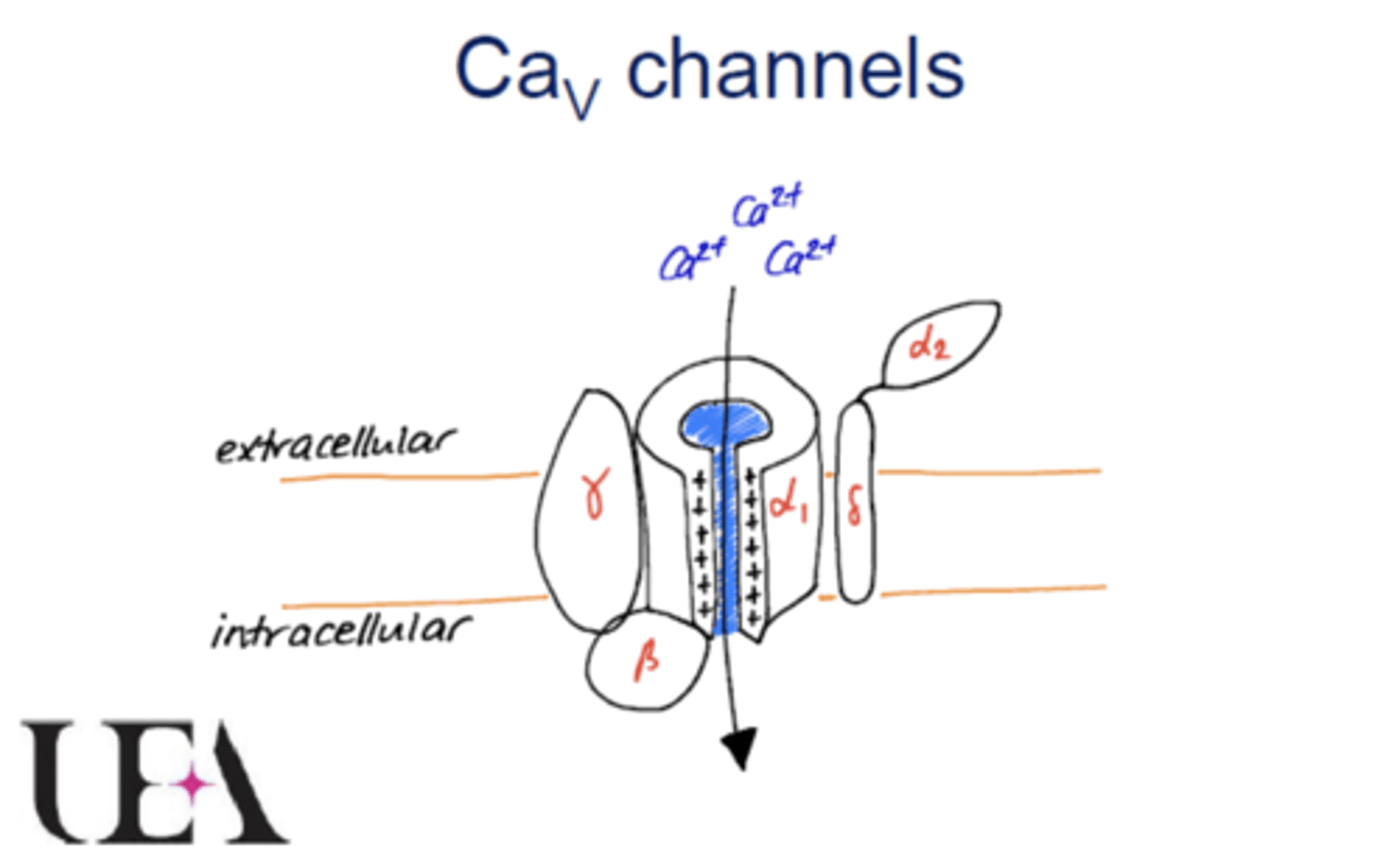
Describe the structure of an L-type calcium channels.
- Contains the main α1 subunit as well as auxiliary subunits e.g., β subunit, γ subunit and an α2 subunit connected to δ subunit.
- α1 subunit forms a pore in which Ca2+ ions move through.
- Auxiliary subunits are beside the main α1 subunits.
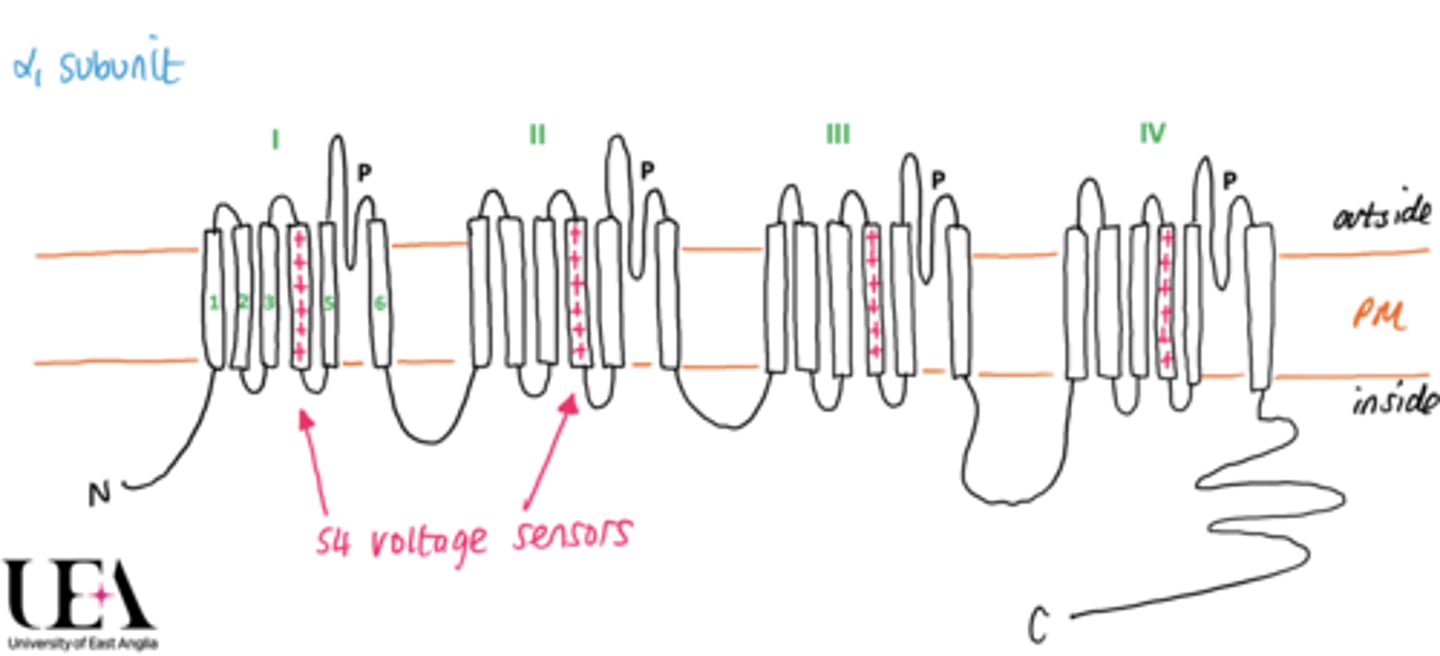
Describe the structure of the main α1 subunit.
- 4 repeating subunits with each containing 6 transmembrane domains.
- 4th transmembrane domain acts as a voltage sensor.
- Each transmembrane domain is connected across all repeating subunits.
- Contains a P loop which acts as a selectivity filter to control which ions move through channel.
- Contain an N-terminus and a C-terminus which are both intracellullar.
How are different classes of CCB similar and dissimilar to each other?
They all work on L-type calcium channels however they work on different sites on the transmembrane domains so they don't have a similar structure.
How do CCBs work?
They bind to receptors on the L-type calcium channel which cause a conformational change of shape in the channel which blocks the flow of Ca2+
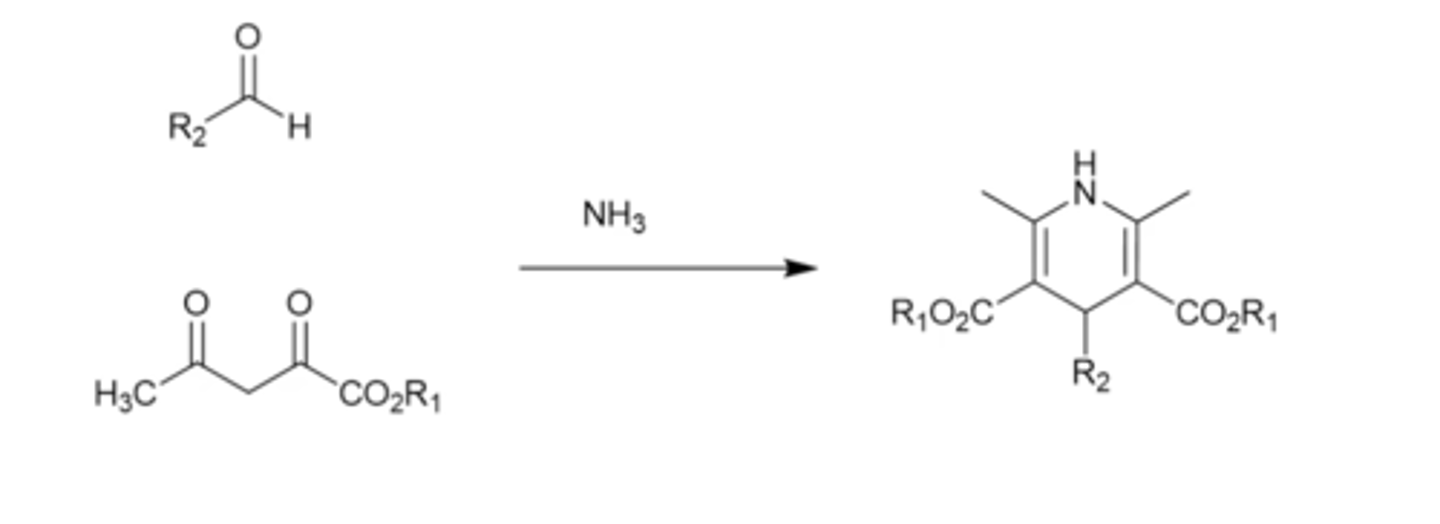
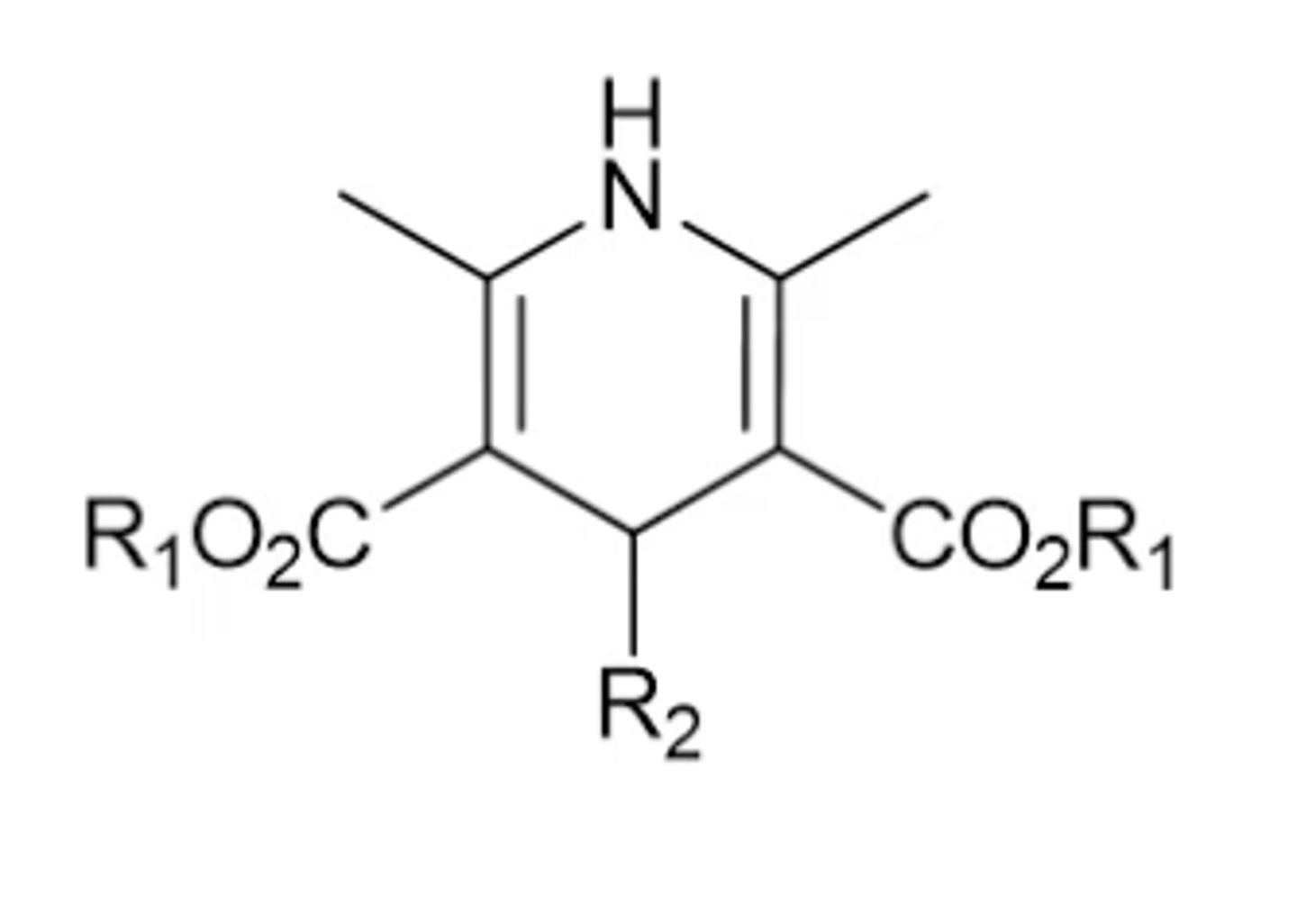
How are 1,4-DHPs formed?
Synthesis between an aldehyde and a beta-keto-ester in the presence of ammonia
What can be altered in 1,4-DHPs to affect activity?
- Ester groups (R1)
- Alkyl substituents.
- The substituent on the para carbon (R2)
- Modification of the amine
How can you affect the substituent on the para carbon of 1,4-DHPs to affect activity?
- Adding an aromatic group is ideal with benzene being the best.
- Adding substituents to the ortho or meta groups on the new aromatic ring can increase activity. Adding to para carbon or adding no substituents decreases activity.

How does adding a substituent to the para carbon of 1,4-DHP increase activity?
Substituents act as a steric clash which forces rings into a perpendicular conformation. This. reduces the number of conformers that are available to the molecule increasing specificity to the L-type channel.
How does modification of amine on 1,4-DHP affect activity?
It causes an alteration of oxidation state on the ring which abolishes activity.
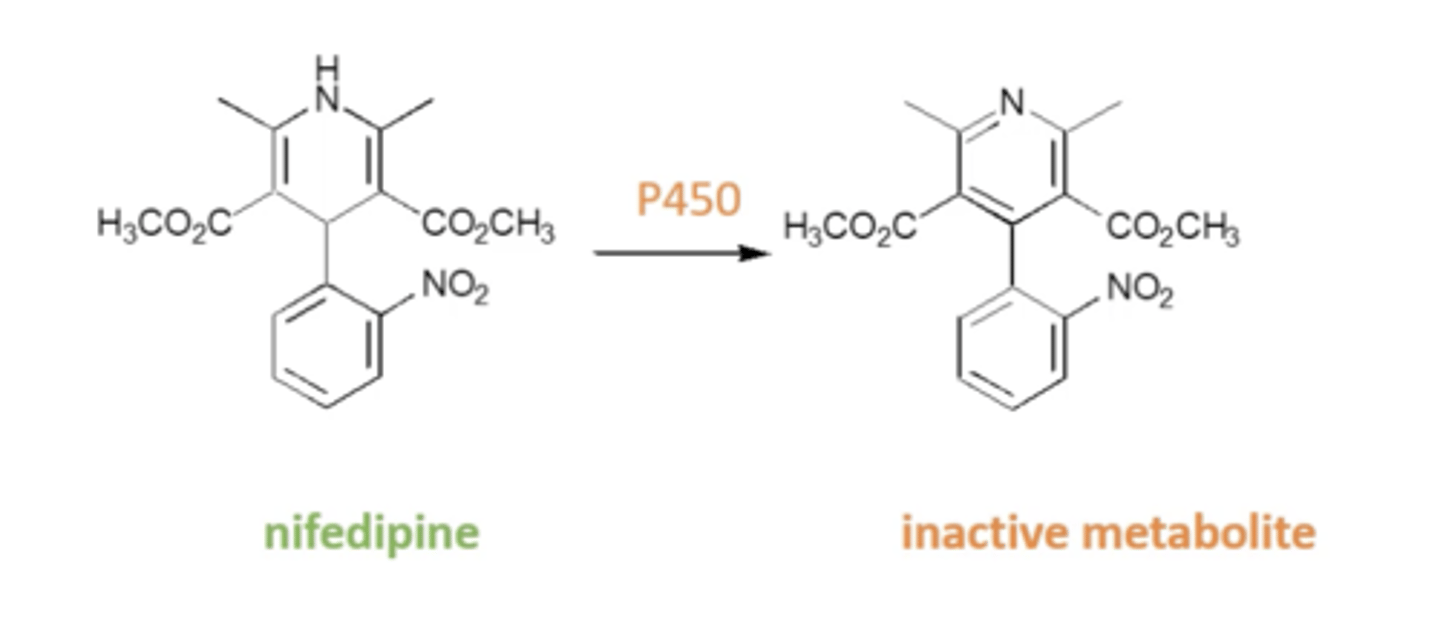
How does modifying the ester on 1,4-DHP affect activity?
- Can decrease activity if a any of the esters is removed or changed to another group.
- Can alter activity to produce calcium channel activators which induce vasoconstriction.
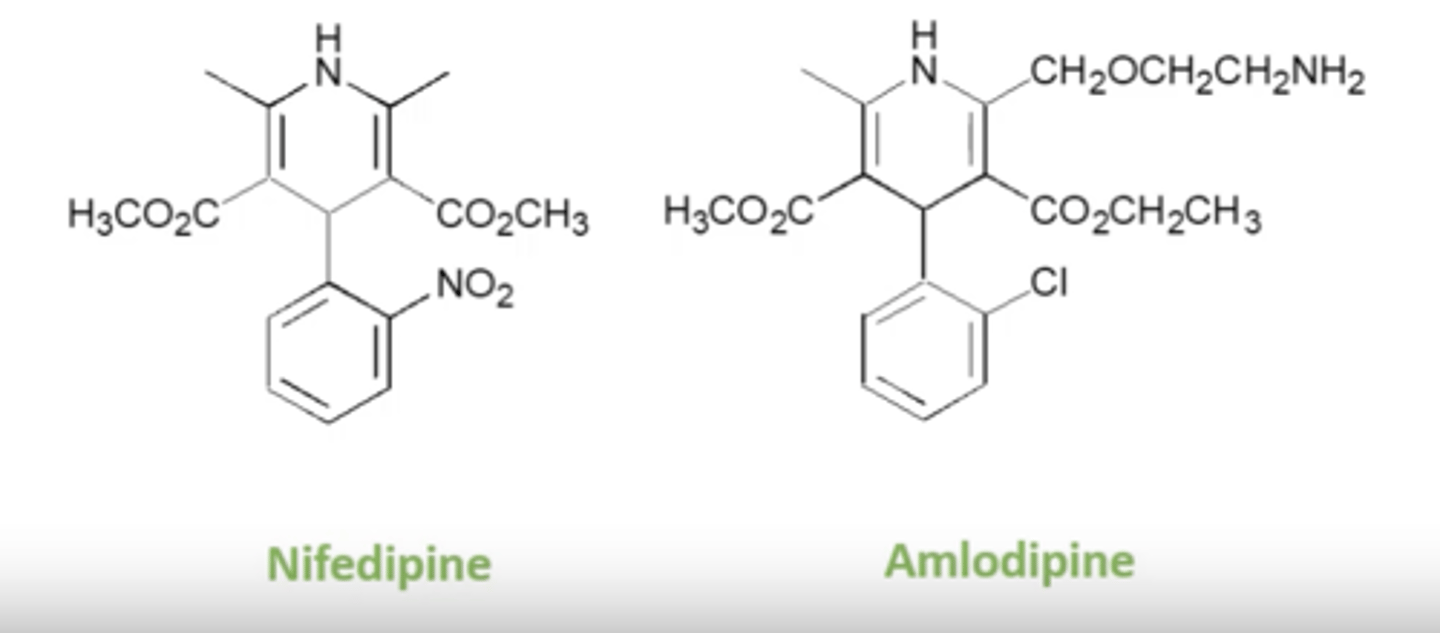
How does modifying of alkyl chains affect activity of 1,4-DHP?
- Longer chains can increase activity.
- This indicates binding site can accommodate larger groups therefore additional H-bonding activity may enhance activity.
- Amlodipine has greater activity than nifedipine supporting this.
What is the allostery of CCBs?
They contain an allosteric site, which when bound, can enhance or reduce activity/binding at another receptor.
What is the negative allosteric effect?
When binding to an allosteric site causes reduced binding at another receptor.
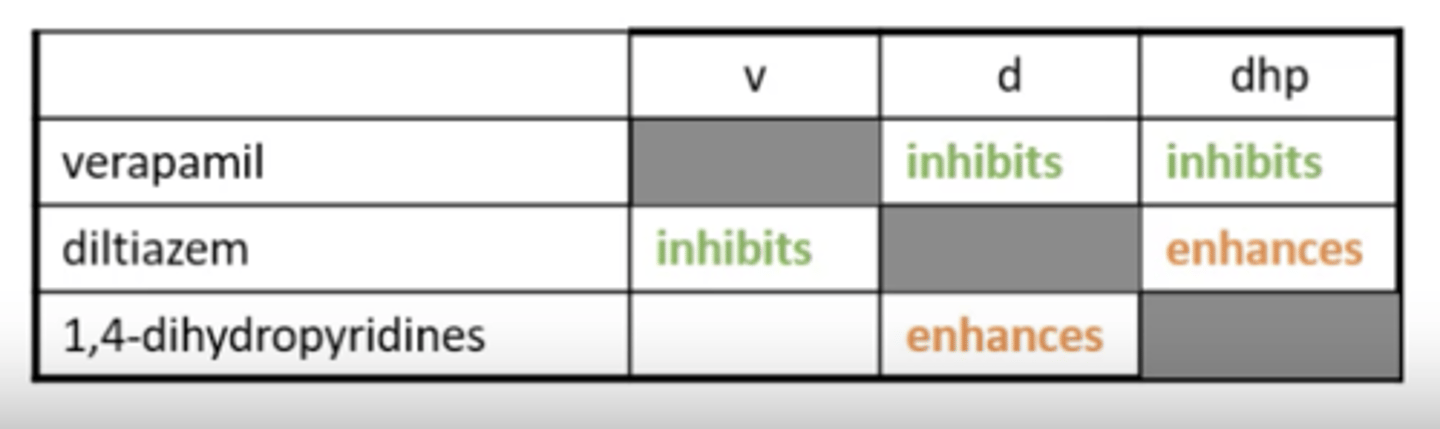
What is the positive allosteric effect?
When binding to an allosteric site causes increased binding at another receptor.