Block 2 Week 3 ECG
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
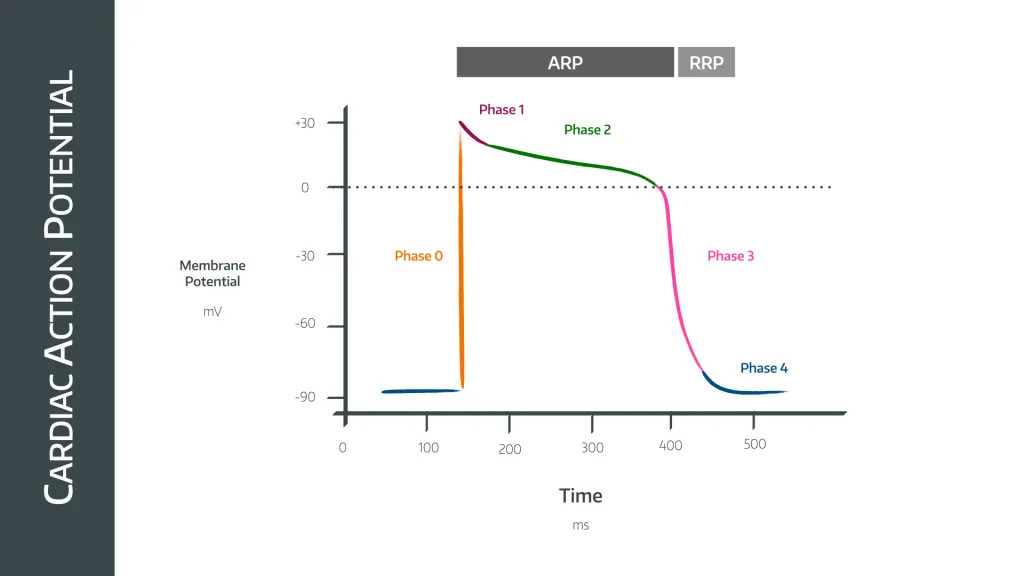
what occurs during phase 0 - cardiac action potential
rapid upstroke - Na+ channel opening
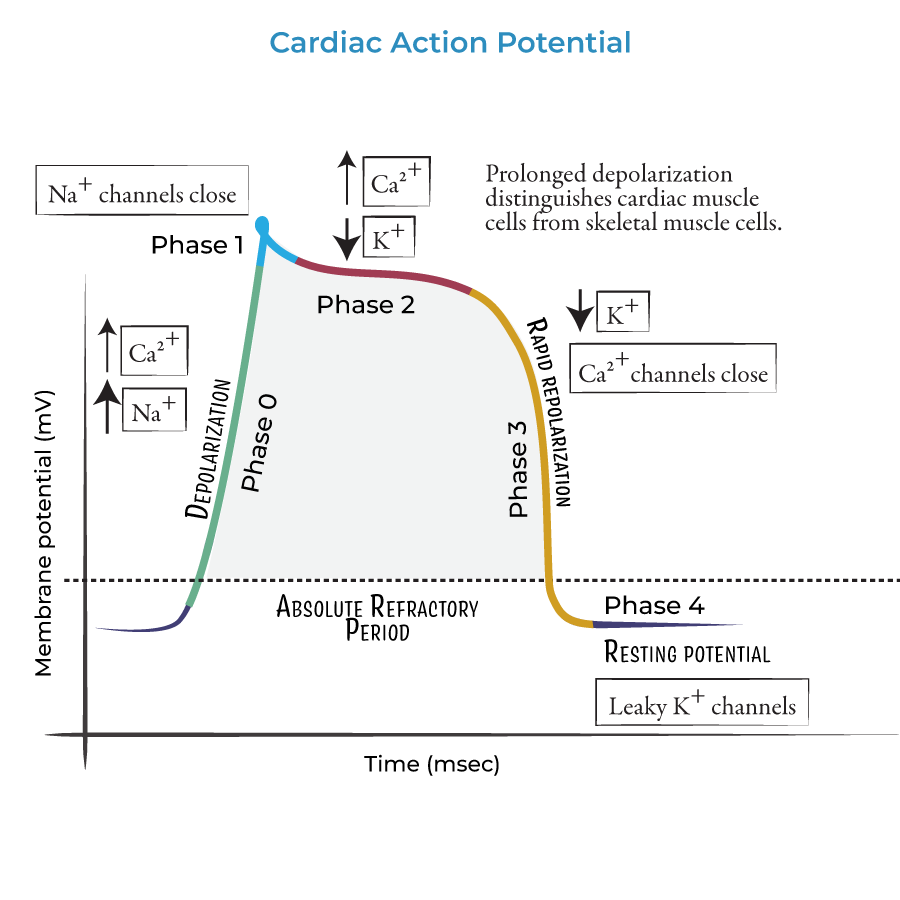
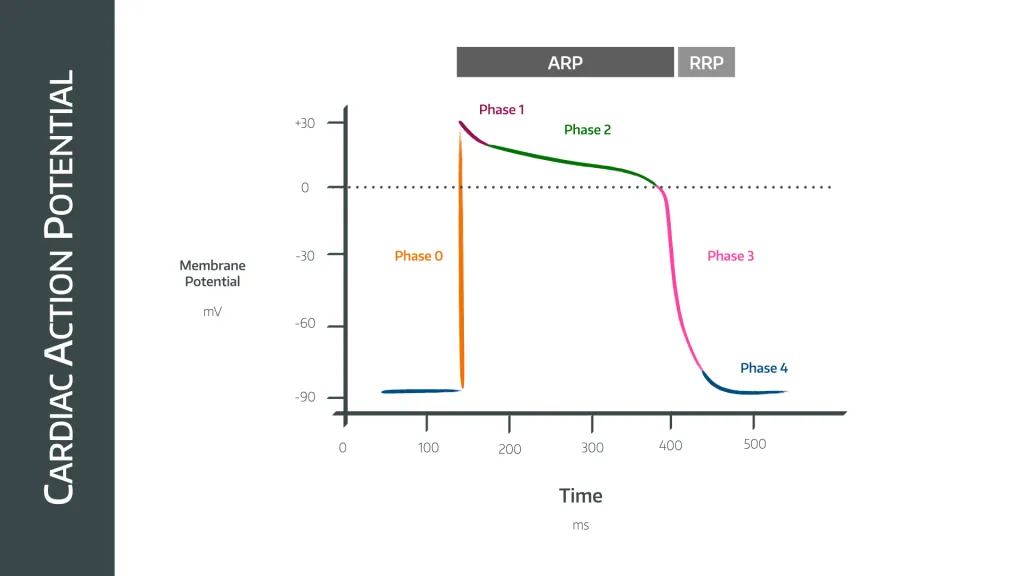
what occurs during phase 1 - cardiac action potential
early rapid depolarisation - inactivation of Na+ channel, opening of K+ channels
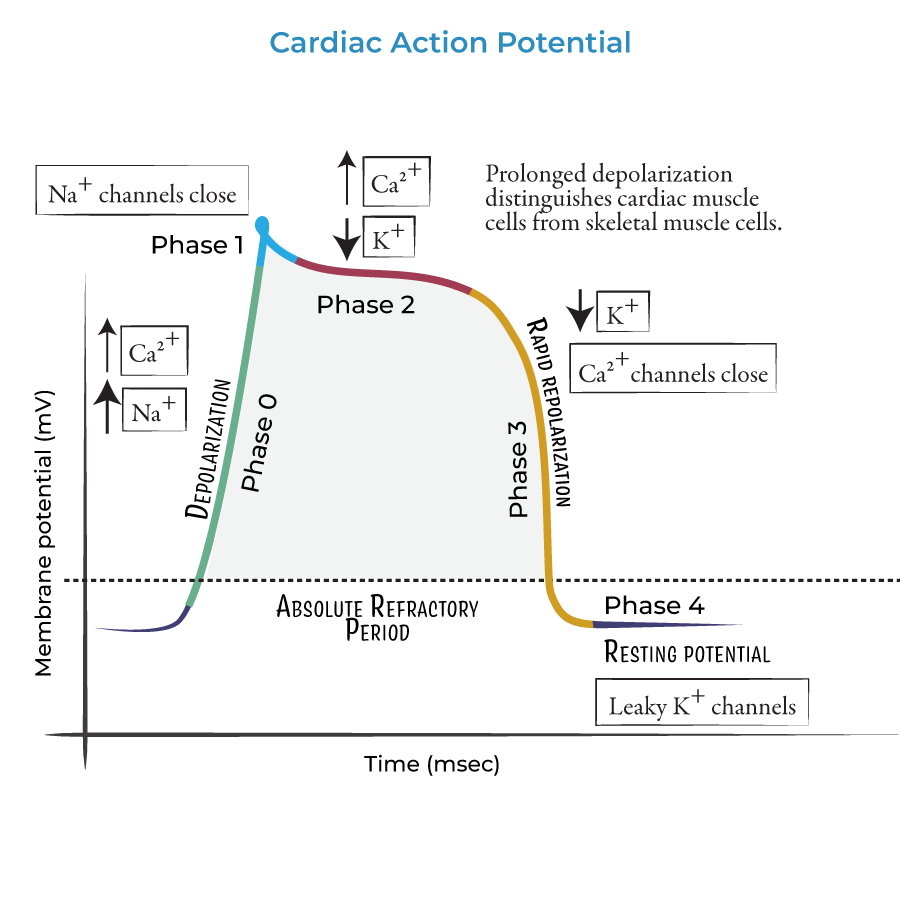
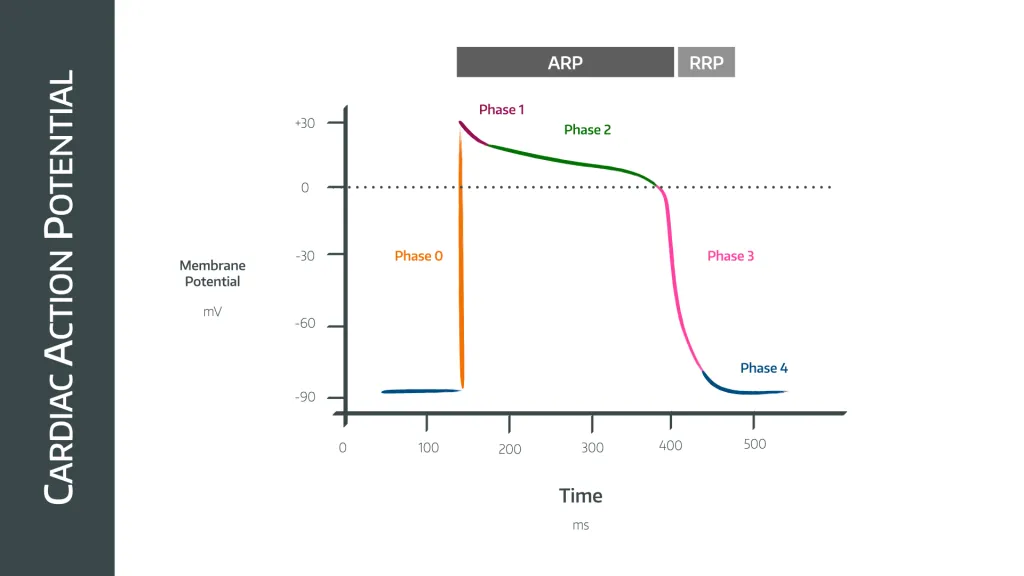
what occurs during phase 2 - cardiac action potential
plateau phase - balance between K+ and Ca2+
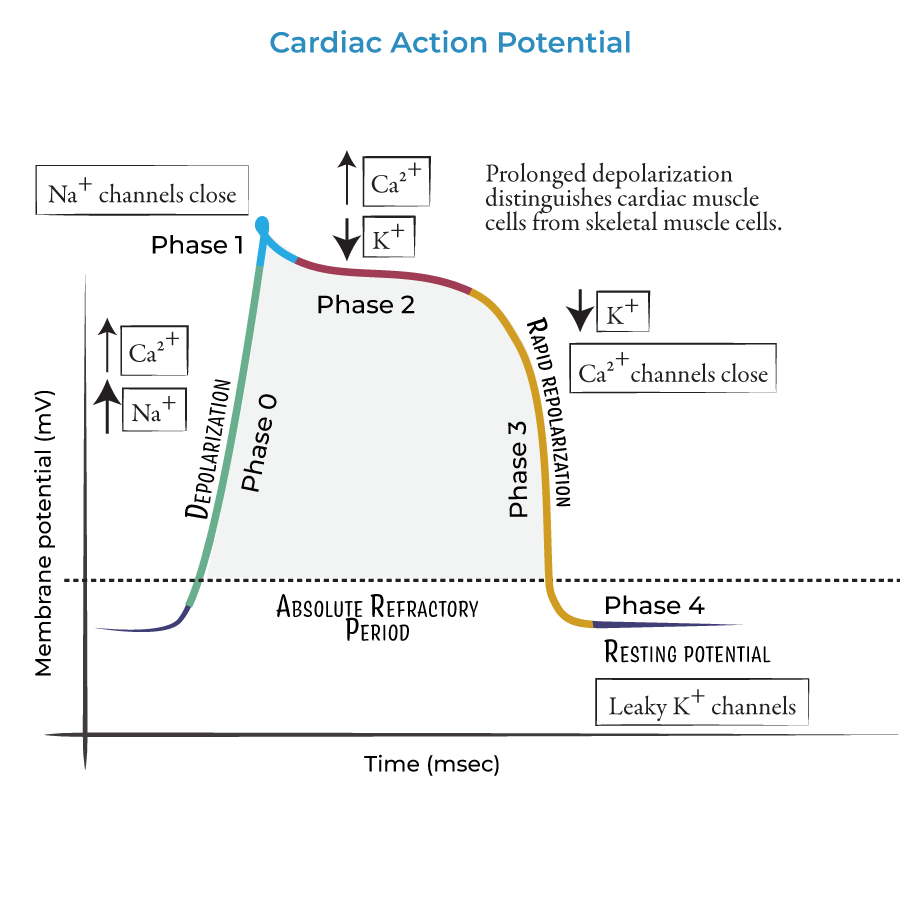
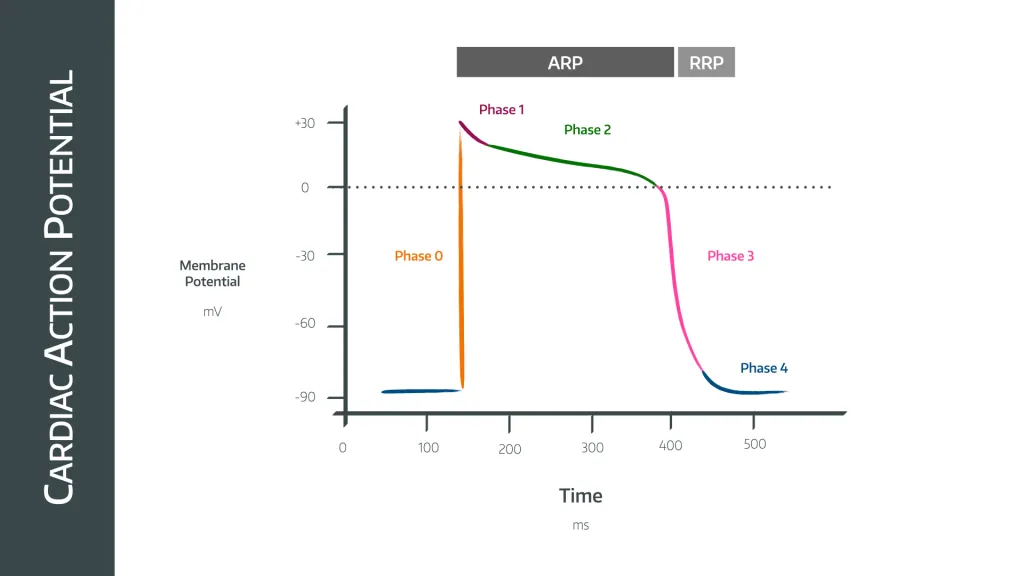
what occurs during phase 3 - cardiac action potential
final repolarisation - activation of Ca2+ channels
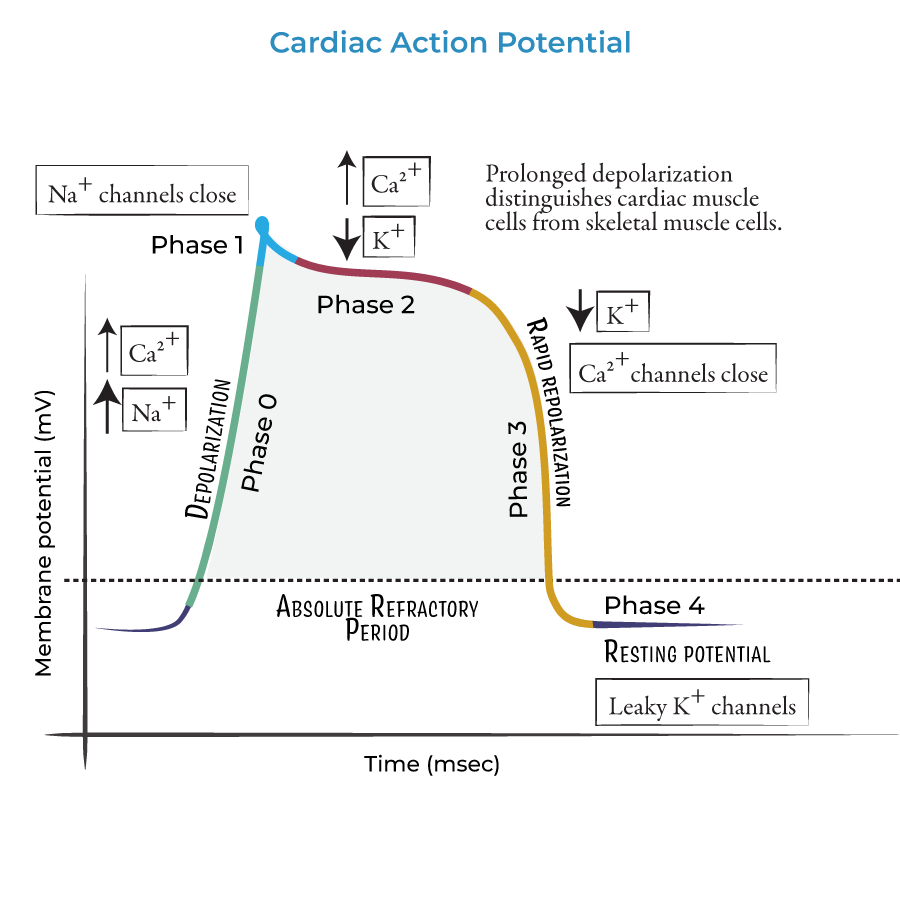

what occurs during phase 4 - cardiac action potential
resting membrane potential - rectifier k+ channels open with some Na+ influx.
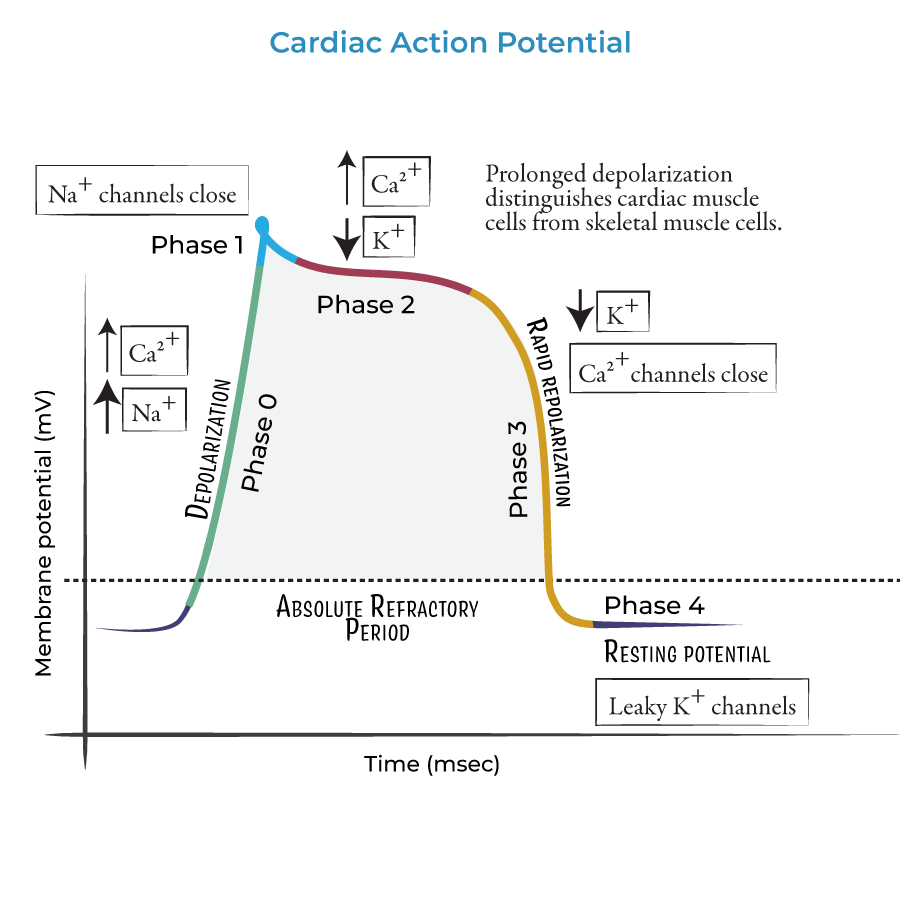
what is “automaticity”?
pacemaker cells generate the action potential spontaneously due to unstable membrane potential due to constant influx of ions.
how do the sympathetic fibres affect heart contraction?
increase the force and rate of contraction; increase in chronotropic and inotropic
how do the parasympathetic fibres affect heart contraction?
decrease force and rate of contraction; decrease in chronotropic and inotropic
what is chronotropic?
timing
what is inotropic?
force
what is the affect of adrenaline?
positive chronotropic effect,
positive inotropic effect
where is adrenaline produced?
synthesised in the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla of the adrenal gland.
where does adrenaline act?
on beta 1 adrenoreceptors
what inhibits adrenaline?
competitively inhibited by B-Blockers (bisoprolol, atenolol).
what does an ECG represent?
the net sum of depolarisation and repolarisation of all myocardial structures.
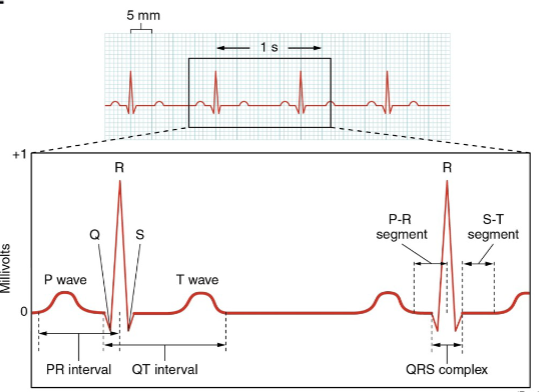
what do the squares of an ECG represent?
1 big square = 0.2s
1 small square = 0.04s.
what is the P wave of the ECG?
atrial depolarisation - stimulus spreads across the atrial surface and reaches the AVN.
rush of sodium ions into cells.
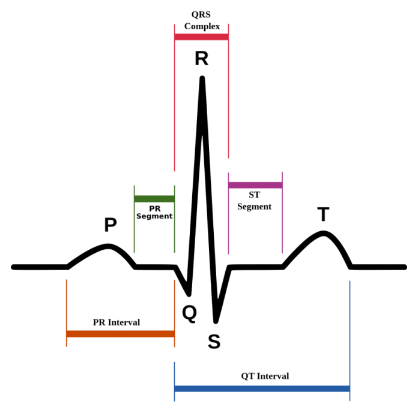
what is the P-R interval wave of the ECG?
conduction through AV node and AV bundle - delay of 100ms at AV node, atrial contraction begins
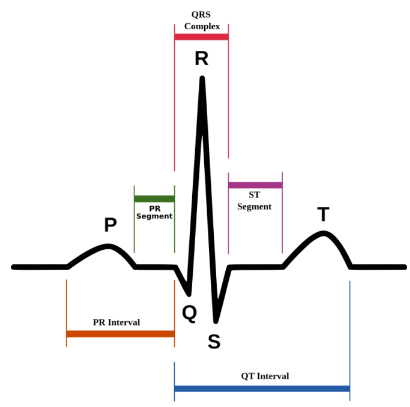
what is the Q wave of the ECG?
beginning of ventricular depolarisation - impulse travels along interventricular septum within the AV bundle and the bundle branches to the Purkinje fibres, and by the moderator band to the papillary muscles of the right ventricle.
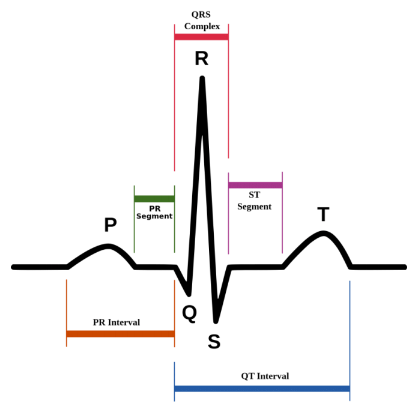
what is the QRS complex of the ECG?
completion of ventricular depolarisation - impulse is distributed by purkinje fibres and relaxed throughout the ventricular myocardium.
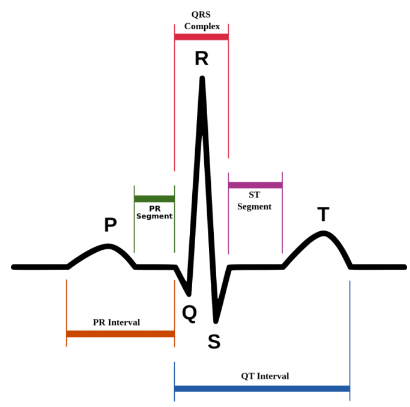
what is the T wave?
ventricular repolarisation - occurs just as the ventricles are starting to relax.
The T wave is smaller and wider than the QRS complex because repolarisation occurs more slowly than depolarisation
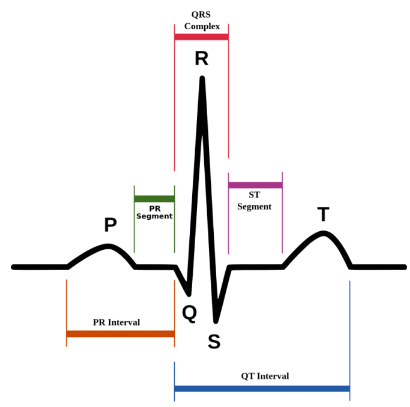
what does a larger P wave indicate?
enlargement of an atrium
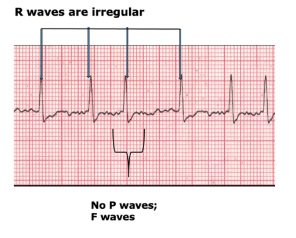
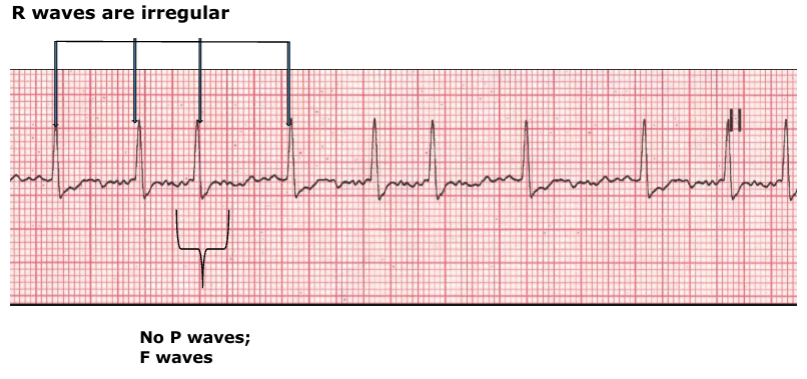
what does an absence of a P wave indicate?
atrial fibrillation
what does a larger Q wave indicate?
myocardial infarcation
what does a larger R wave indicate?
enlarged ventricles
what does a flatter T wave indicate?
insufficient oxygen supplied to the heart muscle - coronary heart disease
what does a higher T wave indicate?
hyperkalaemia (high K+)
what are “Tail-Tented T waves”?
high T waves
what is tachycardia?
fast heart rate - above 80bpm
what is bradycardia?
slow heart rate - above 60bpm
what does a wide QRS indicate?
poor ventricular conduction
what are the risks of atrial fibrillation?
increased risk of stroke and heart failure
what is atrial fibrillation?
there is a chaotic range of signals moving around the AV node,
this stimulates fibrillation instead of contraction in unison
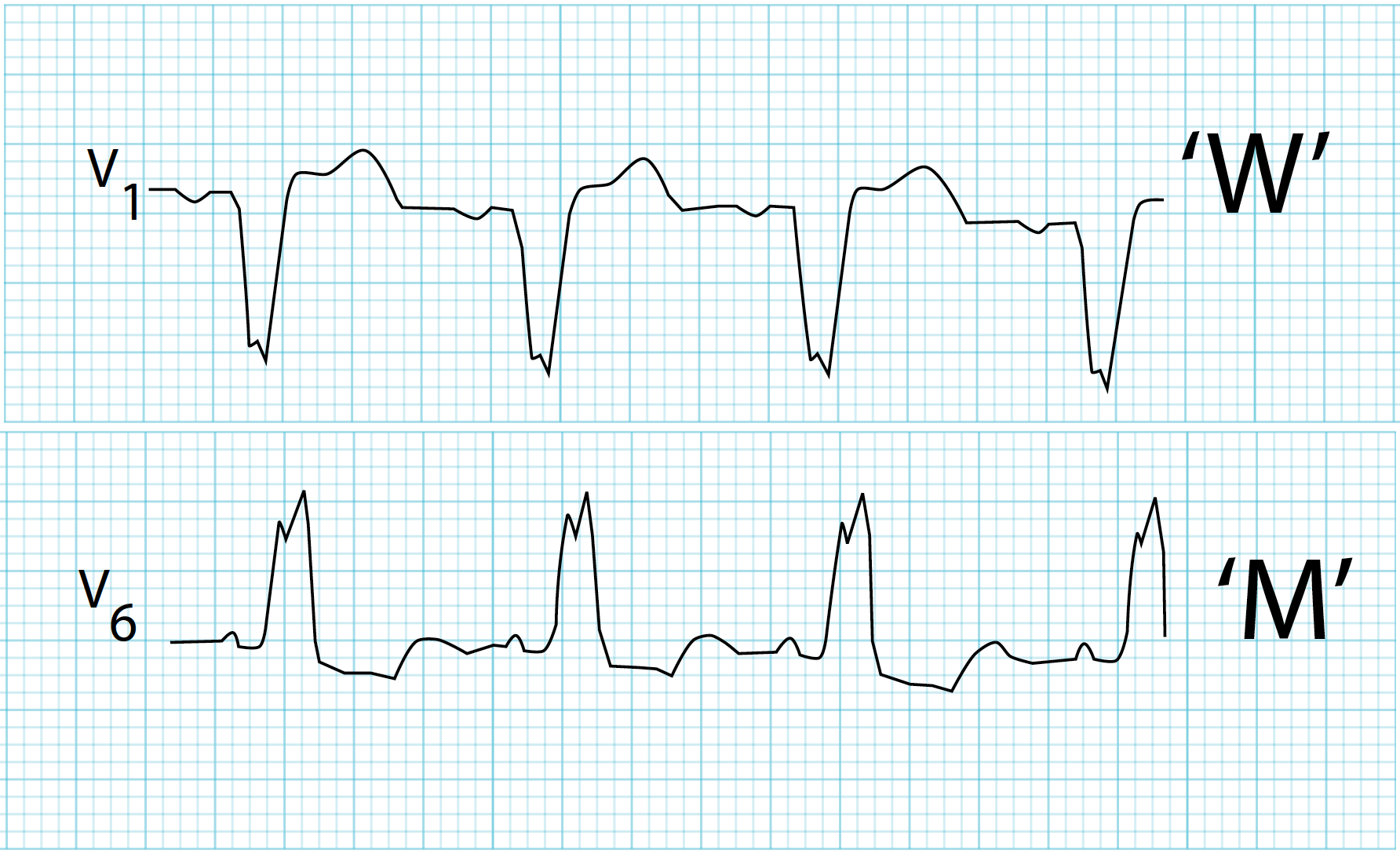
what does a left bundle branch block look like?
QRS complex starts like a W and moves towards being more like an M.
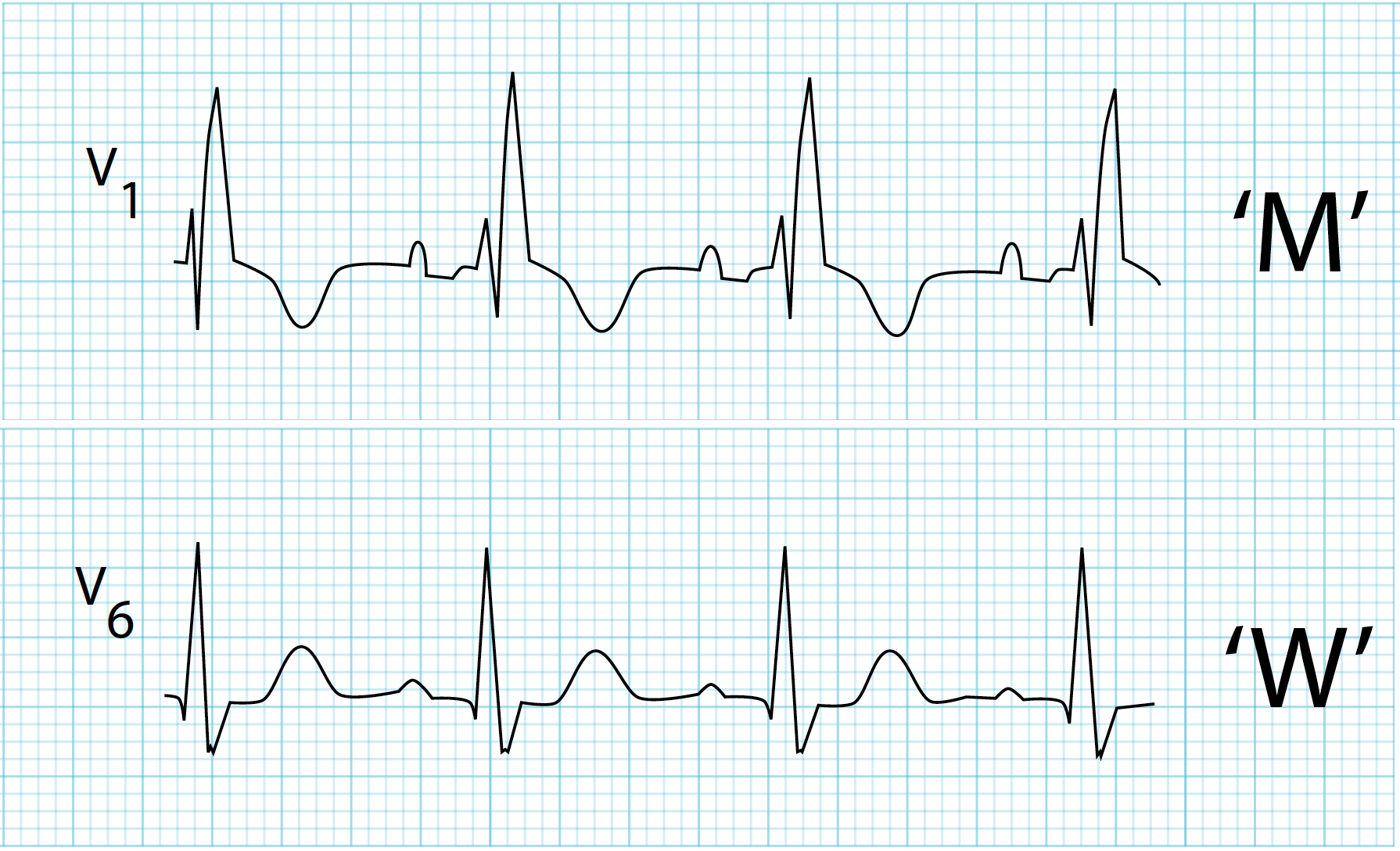
what does a right bundle branch block look like?
QRS complex starts like an M and moves towards being more like a W.
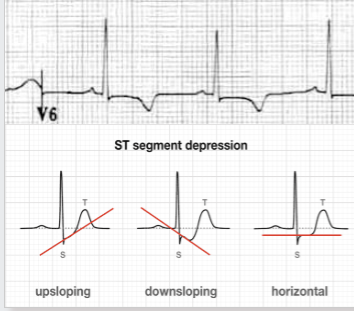
how may ischemic changes present on an ECG?
inverted T waves and ST segment can upslope, downslope or be horizontal.
why does atrial fibrillation increase the risk of stroke and heart disease?
blood will not flow in the absence of contraction and this causes haemostasis, increased clotting
what drugs are used to control anticoagulation associated with atrial fibrillation?
Warfarin
Novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) e.g. Apixaban or Dabigatran.
what drugs are used to control ventricular rate associated with atrial fibrillation?
B-blockers,
Non-dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel antagonists (verapamil and diltiazem).
what is digoxin?
cardiac gylocside
how does digoxin affect the heart?
increases parasympathetic action of vagal nerve = SAN firing decreases HR.
reduces conduction of AVN,
reduces ventricular rate in flutter and fibrillation
how does digoxin manage atrial fibrillation?
Inhibits Na+-K+/ATPase membrane pump.
This increases intracellular Na+.
The sodium is pumped out in exchange for Ca2+.
Ca2+ binds troponin and activates contractile proteins.
Contractility increases to give positive inotropic effect.
what are the causes of atrial fibrillation?
ischaemic heart disease,
hypertension,
alcohol,
cardiomyopathy (diseased heart muscle)
why is digoxin less used?
digitalis - deadly poison,
safer drugs are now available
what are ventricular ectopics?
These are shown when there is a wide QRS complex that is not proceeded by a P wave.
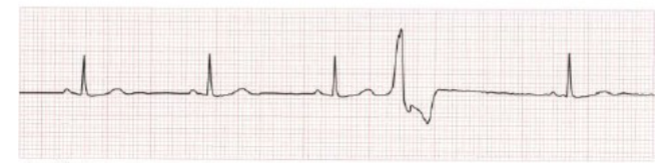
what are risk factors for ventricular ectopics?
alcohol, caffeine, smoking, medications, stimulants, high levels of adrenaline.
what are the 3 regions of the heart an ECG monitors?
lateral region.
inferior region.
septal anterior region.
what blood vessel supplies the lateral region of the heart?
left circumflex
what blood vessel supplies the inferior region of the heart?
right coronary artery (right marginal and part of right posterior descending).
what blood vessel supplies the septal anterior region of the heart?
left anterior descending
what are the 12 regions of an ECG?

I, II, III.
aVR, aVL, aVF.
V1-V6
what regions of an ECG measure the lateral region of the heart?
Leads:
I, II, aVL, V5, V6
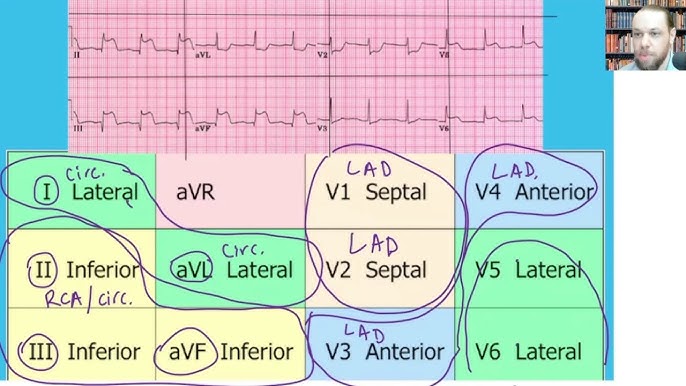
what regions of an ECG measure the inferior region of the heart?
Leads:
II, III, aVF
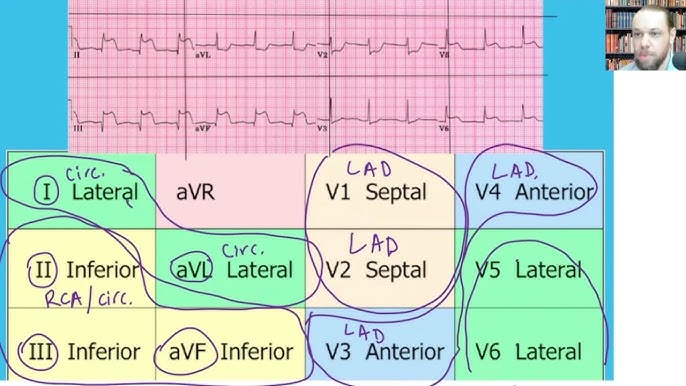
what regions of an ECG measure the septal anterior region of the heart?
Leads:
V1, V2, V3, V4
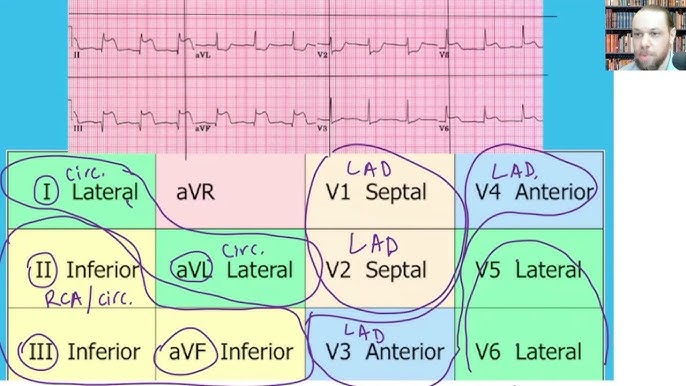
when would you order an extended ECG?
to get a view of the posterior region of the heart,
so when you suspected issues with posterior descending artery.
what cardiac artery supplies the SAN?
right coronary artery
what cardiac artery supplies the AVN?
right posterior descending
what cardiac artery supplies the Bundle of His?
Left anterior descending.