Diseases of the Uvea
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Uveitis (General)
inflammation of the uvea tract
responsible for 10-15% of total blindness cases
Onset: varies with peak incidence between 20-59 years of age
incidence increases with age
In adult patients, female are affected more than males
In pediatric patients, males are affected more than females
Multiple Causes:
Idiopathic
Non-infectious or immunologic: with and without known systemic association
Infectious: caused by bacteria, virus, fungus, parasite or other infectious agents
Traumatic: includes surgery
Masquerade: neoplastic or non-neoplastic conditions
Uveitis Classifcations
Primary site of inflammation:
Anterior uveitis: inflammation of the anterior chamber (most common)
Intermediate uveitis: inflammation of the vitreous (least common)
Posterior uveitis: inflammation of the retina and/or choroid
Panuveitis: inflammation of all uveal structures
Onset:
Sudden: characterized by pain, redness and photophobia
Insidious: characterized as white and painless
Duration:
Limited: less than or equal to 3 months
Persistent: >3 months
Clinical Course:
Acute: sudden onset and limited duration
Chronic: persistent uveitis with relapse in less than 3 months after discontinuing tx
Recurrent: characterized by repeated episodes separated by periods of inactivity without tx greater than or equal to 3mon long
Remission: no visible cells (inactivity) for 3 months or longer
Histopathology:
Non-granulomatous (more common)
Granulomatous
Laterality:
Unilateral is more common than bilateral
Bilateral is more common with systemic non-infectious conditions
Anterior Uveitis General Symptoms
Pain: w/ acute inflammation of iris & ciliary body
muscles spasm = dull, achy, throbbing, radiating
worse when looking at light or up close
Photophobia: caused by ciliary muscle spasm
Anterior Uveitis General Signs
Conjunctival injection/circumlimbal injection: enlargement of episcleral vessels around limbus
diffuse redness can accompany it
dark red
Keratic precipitates: inflammatory deposits on the endothelium
usually in inferior endothelium as triangle = Arlt triangle
d/t convection current
Fine dusting keratic precipitates: made up of neutrophils and lymphoplasmacytic cells
small and white
Seen with non-granulomatous uveitis
Granulomatous keratic precipitates: made up of lymphocytes, macrophages and epithelioid cells
larger, 1mm
greasy appearance
mutton fat
Seen with granulomatous uveitis
Aqueous cells: mostly made up of lymphocytes
large collection in ant. chamber = hypopyon
Anterior chamber flare: result of the breakdown of the blood aqueous barrier; protein leaks into ant. chamber
Iris nodules: accumulation of epithelioid cells and lymphocytes
Koeppe: located on the pupillary margin (non- and granulomatous)
Busacca: located in the iris stroma (granulomatous)
Berlin: located in the anterior chamber (granulomatous)
Anterior synechia: adhesions in the iridocorneal angle
can lead to angle closure
Posterior synechia: adhesions between the iris and the anterior capsule of the lens
Seclusio pupilla: a posterior synechia 360°; leads to ris bombé and angle closure
Intraocular pressure (elevation or reduction)
Elevation = blockage of TM by inflammatory cells, peripheral anterior synechia, posterior synechia w/ iris bombé, inc aqeuous viscosity
common in chronic uveitis
Reduction: due to reduced aqueous production due to ciliary body inflammation & inc aqueous outflow
common in acute
Pupil miosis: due to iris sphincter spasm
Increases the risk for a posterior synechia
Hypopyon
inflammatory cells and fibrin that have settled in the inferior portion of anterior chamber; Commonly seen with HLA-B27 uveitis and Behçet’s uveitis
Anterior Uveitis General Complications
band keratopathy
glaucoma
cataracts
Cystoid macular edema (from chronic inflammation)
Anterior Uveitis General Treatment
Topical corticosteroid
Topical cycloplegic: helps with pain management and prevents the formation of a posterior synechia
Causes of anterior uveitis
Idiopathic (most common)
Non-infectious or immunologic (2nd most common)
Seronegative HLA-B27 associated arthropathies are the most common cause
Ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease
Infectious
Herpetic keratouveitis infections are the most common
Masquerade
Trauma
Characteristics of Seronegative Spondylarthropathies
Individuals will be rheumatoid factor (RF) and antinuclear antibody (ANA) negative
Individuals will have a strong HLA-B27 positive association
Anterior uveitis is a common ocular manifestation
Ankylosing spondylitis
males > females
caucasian
Onset: teens to early adulthood
25% develop anterior uveitis
ANY laterality, unilateral most common
recurrent
non-granulomatous
Signs:
Circumlimbal hyperemia
Cells and flare in the anterior chamber with hypopyon development
Fine white/grey keratic precipitates
Work Up:
Imaging of the lower back (MRI or X-ray)
HLA-B27
Complications:
Secondary glaucoma
Cataract
Maculopathy in prolonged or severe cases
Treatment:
Topical cycloplegic
Topical corticosteroids
Other ocular manifestations: conjunctivitis and ssc
Reactive arthritis
Onset: 18-40 years of age
males > females
Classic triad: Arthritis, urethritis, conjunctivitis
3-12% of individuals will have anterior uveitis
acute
unilateral
non-granulomatous
Symptoms: pain, photophobia
Presentation:
Circumlimbal hyperemia
Fine to medium white keratic precipitates
MORE cells and flare in the anterior chamber
Hypopyon may develop in severe cases
Complications:
Secondary glaucoma
Maculopathy
Treatment:
Topical cycloplegic
Topical corticosteroids
Other ocular manifestations: Conjunctivitis, episcleritis, scleritis
Psoriatic arthritis
Onset: 30 to 40 year olds
females > males
Most common ocular manifestation is anterior uveitis
acute
non-granulomatous
Signs: pain, photophobia
Presentation:
Circumlimbal hyperemia
Fine white keratic precipitates
Cells and flare in the anterior chamber
Hypopyon occasionally occurs
Complications:
secondary glaucoma
maculopathy
Treatment:
topical cycloplegic
topical corticosteroids
Other ocular manifestations: Conjunctivitis, episcleritis, scleritis
Enteropathic Arthritis (IBD w/ arthritis)
Crohn’s or Ulcerative Colitis w/ peripheral arthritis or spondyloarthropathy
Anterior uveitis will occur in 2-11% of individuals with IBD
insidious (no symptoms)
recurrent or chronic
bilateral
non-granulomatous
Symptoms: none
Presentation:
Absent circumlimbal hyperemia
Fine white keratic precipitates
Cells and flare in the anterior chamber
Complications:
Secondary glaucoma
Cataract
Treatment
Topical cycloplegic to prevent post. synechia
Topical corticosteroids
Other ocular manifestations: Episcleritis, scleritis, keratitis
Behçet’s Disease
Characterized by:
Oral and genital ulcers
Skin lesions
Ocular inflammation: anterior and posterior uveitis may be present
Anterior uveitis will be present in 19-31%
sudden onset
acute
non-granulomatous
Symptoms: pain, photophobia, redness
Presentation:
Circumlimbal injection
Cells and flare in the anterior chamber
Hypopyon may be present; can shift with head movement
Complications:
Secondary glaucoma
from post synechia, peripheral anterior synechia, or neovascularization
neovascularization is more common with posterior segment involvement; ischemic retina
Iris atrophy
cataract
Treatment:
Topical cycloplegic drop
Topical or systemic corticosteroids
Fuchs’ Heterochromic Iridocyclitis
Typically unilateral but can be bilateral
Affects males and females equally
Onset: all ages
Characterized by:
Iris heterochromia
Caused by iris atrophy of the anterior layers of the iris
Blue irides may appear darker and brown irides may appear lighter
Anterior uveitis
insidious
chronic
non-granulomatous
Symptoms: none
Presentation:
Small, diffuse, stellate keratic precipitates
Cells and flare
minimal flare
Iris nodules: Koeppe or Busacca nodules
tend to be small and transparent
Russell bodies: minute, crystalline, highly refractile deposits on the iris surface
Complications:
Secondary glaucoma (59%)
cataract
Treatment:
Short course of topical steroids when indicated
Treatment of the ocular complications
Sarcoidosis
multisystem granulomatous disease that primarily affects the lungs, skin, eyes and lymph nodes
Affects both males and females
Females are more likely to have ocular manifestations
Affects all ethnicities but is most severe in African American individuals
Onset occurs in two peaks: 20-30 year olds and 50-60 year olds
Anterior uveitis is the most common ocular presentation
tends to be bilateral
onset is sudden or insidious
clinical course is acute or chronic
granulomatous
Symptoms: asymptomatic (if insidious), pain, photophobia, redness
Presentation:
Mutton fat keratic precipitates
Cells and flare
hypopyon uncommon
Iris nodules: Koeppe or Busacca
Tent shaped peripheral anterior synechia
Work-up: Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), chest X-ray
Complications:
Secondary glaucoma
Cataract
band keratopathy
Treatment:
Topical cycloplegic drops
Topical corticosteroids
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease (VKH Disease)
Autoimmune disorder that affects the eyes, auditory system, nervous system and skin
Melanin containing cells are commonly “attacked” in VKH
More common in darkly pigmented individuals
Affects females more than males
Onset: second to fifth decade
4 Stages:
Prodromal stage: mimics a viral infection
Neurological and auditory manifestations are common
Acute uveitis stage: this stage may last for several weeks
bilateral
granulomatous
Posterior uveitis is commonly seen prior to anterior uveitis
mutton fat keratic precipitates and iris nodules
Convalescent: this stage will be seen one to three months after onset, may last for several months
Depigmentation of the skin and uvea will be seen
Chronic recurrent: this stage may interrupt convalescent
Anterior uveitis will be present in this stage (granulomatous + iris nodules)
Posterior segment involvement is rarely seen in here
Complications: more common with long durations of the disease, multiple recurrences, and older age
cataract
Glaucoma
Retinal neovascularization
Treatment:
Systemic: systemic corticosteroids
Ocular treatments: topical corticosteroids and topical cycloplegic drops
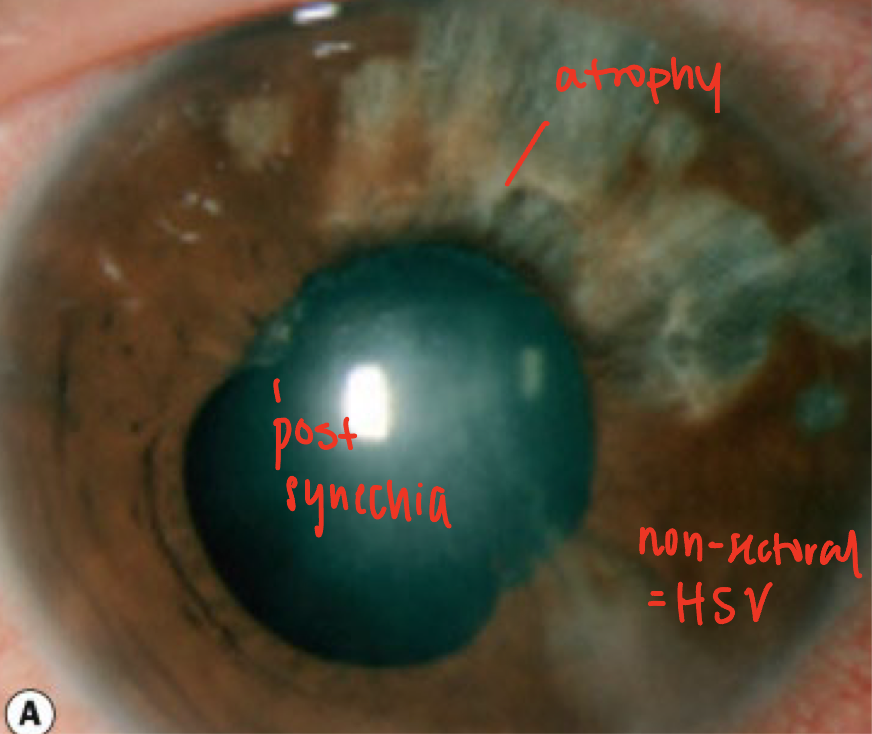
Uveitis from Herpes Simplex and Herpes Zoster
causes 8% of uveitis cases
The clinic course can be acute, chronic or recurrent
Granulomatous
Can cause anterior or posterior uveitis
Presentation:
Decrease corneal sensation
Keratic precipitates will have a stellate appearance rather than an inferior deposition
Sectoral or non-sectoral iris atrophy
non-sectoral = HSV
sectoral = HZO
Acute uveitis will present with elevated intraocular pressure
d/t trabeculitis
Complications
Secondary glaucoma
Hypotony
Iris atrophy
Cataract
Treatment:
Oral antiviral medications
Topical corticosteroids