PSCI 3500 Final Exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Monarchies rely on
Kin and family network
Royal family, succession
Ex) Qatar and Kuwait
Military dictatorships are ruled by
Committee, or junta
“Guardians of the national interest”
The biggest threat to stability is more military coups
Civilian dictatorships rely on
Regime parties or personality cults
Ex) China and North Korea
Electoral authoritarianism
leaders hold elections and tolerate some pluralism, yet democratic norms are violated
Selectorate Theory
To stay in power, leaders must keep members of their winning coalition happy
Government performance should be better in large W/S systems than small W/S systems.
Condorcet’s Paradox
A set of rational individuals may not act rationally when they act as a group
There is either no stable outcome or the outcome is determined by the rules of the game
Median Voter Theorem
the proposal matching the ideal point of the median voter will defeat all other alternatives
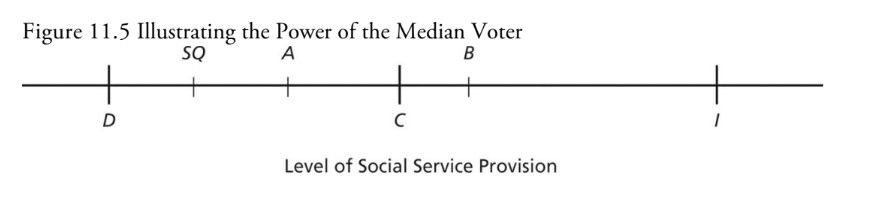
Final outcome?
B is final outcome
C determines final outcome
Sincere Vote
Vote for their “Most-Preferred Alternative”
Strategic Vote
“Think Ahead, and Reason Backwards”
Arrow’s Theorem
The pathologies of majority rule apply to “any” group decision procedure that meets some minimal standards of fairness
Presidential democracy
government does not depend on a legislative majority to exist.
Minority government is more frequent.
Parliamentary democracy
government depends only on a legislative majority to exist
Power to remove a government (no Confidence)
Semi-presidential democracy
government depends on a legislative majority and the head of state is popularly elected
fixed term of the Head of State
Prime minister, Cohabitation
Political surfing
The government does not actively manipulate the economy, but waits until the economy is at a highpoint before announcing the election
Political business cycle
The government actively manipulates the economy to engineer a short-term economic high and then calls an election
Followed by an economic decline
Result: cycles of booms and busts
Electoral Integrity
The extent to which the conduct of elections meets international standards and global norms concerning “good” elections
Three major electoral systems
Majoritarian
Proportional Representation (PR)
Mixed
A single-member district plurality (SMDP) system
The candidate with the most votes wins
unrepresentative outcomes
Ex) United States (for the House of Representatives)
Proportional Electoral Systems
a quota- or divisor-based electoral system employed in multimember districts
produce a proportional translation of votes into seats.
Electoral Thresholds
Minimum percentage of votes that a party must win to gain representation
Formal thresholds are often introduced in an attempt to reduce legislative fragmentation
Main Purposes of Political Parties
Structure the political world
Recruit and socialize the political elite
Mobilize the masses
Provide a link between the rulers and the ruled
Social Cleavages
individuals have different political identifications
Divisions/structure of party systems in society based on race/ethnicity, socioeconomic class, religion, territory/location
Types of social cleavages
Urban-rural cleavage
Confessional cleavage
Secular-clerical cleavage
Class cleavage
Post-materialist cleavage
Ethnic and linguistic cleavages
Urban-rural cleavage
One of oldest political conflicts in world
Conflict between rural and urban interests
Ex.
Early modern europe - feudal lords vs town dwellers (freemen, burghers, bourgeoise)
Economic and cultural dimension
Confessional cleavage
Different denominations in religion
Conflict over religious differences
Ex.
Europe during Protestant Reformation
Roman Catholic Church vs rising Protestantism
India
Hindus and Muslims -> creation of Pakistan
Middle Eastern countries
Sunni vs Shia muslims
Secular-clerical cleavage
Religious voters vs non religious voters
Political competition around religious issues
Conflict between growing state, that wants to dominate, and church that wants to maintain historic power
Class cleavage
Actors have have conflicting economic interests
Industrial sectors: Conflict b/w workers and capitalists
Capitalists: favor free market, small state, restricted franchise
Workers: greater state intervention in economy and franchise expansion
Agricultural sector: peasants/agricultural workers and large landowners
Involves attempts to use state to redistribute wealth from rich to poor
Post-materialistic cleavage
Different views regarding human freedom
Ex. equality, reproductive choice, and sexual freedom
Ethnic and linguistic cleavages
Differences in ethnicity and language
can be source of conflict
Ex. Canada, belgium, spain
Nonpartisan democracy
no official political parties
ex. George Washington’s Era, Small Pacific Islands
One-party dominant system
Only one particular party has a realistic chance of gaining power
Ex) Japan
Two-party system
Two major parties
Ex) US
Multiparty system
more than two parties
Ex) Germany and France
Duverger’s Theory
Electoral institutions influence how social divisions are translated into political parties.
SMDP => Two party system
PR => Multiparty system
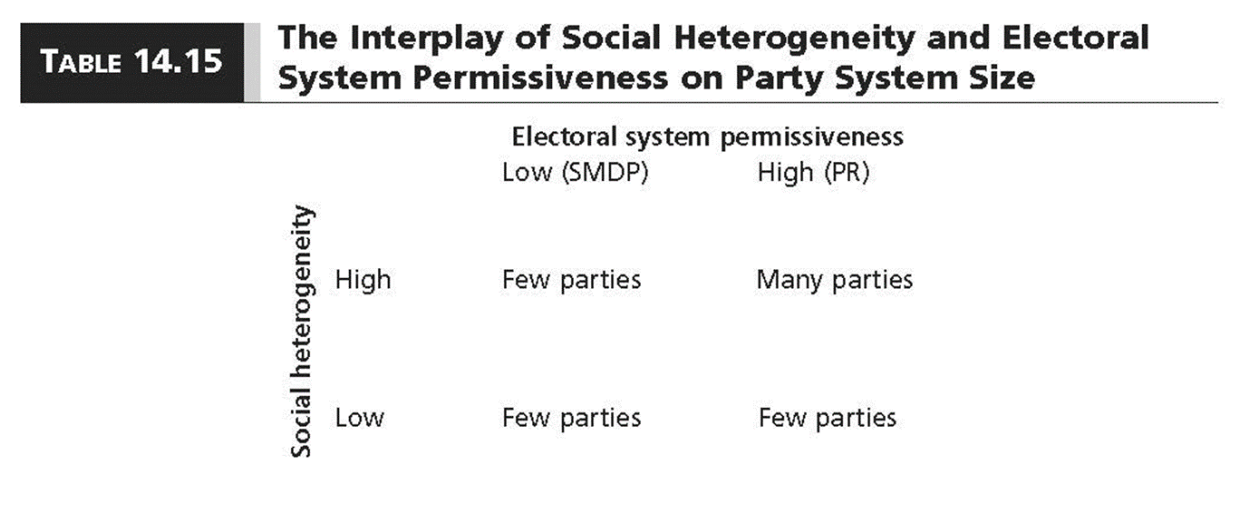
Social Heterogeneity and Electoral System Permissiveness
high social heterogeneity & permissive electoral system → many parties
more diversity leads to more demand for political parties
high social heterogeneity & nonpermissive electoral system → few parties
have many social divisions and social demands aren’t translated into political parties
low social heterogeneity & nonpermissive/permissive electoral system→ few parties
less diversity → less demand for political parties
Federalism
Sovereignty is constitutionally split between at least two territorial levels
Federal (10 % of the World) vs. Unitary States
Devolution
A unitary state grants powers to subnational governments but retains the right to unilaterally recall or reshape those powers
Why Federalism?
bargaining process to achieve security and economic goals
Diffuse secessionist pressures
U.S.
Big vs small states
Large state: want strong central gov
Small state: don’t want strong central gov
Why? Bigger states have more power
Bicameralism
Two distinct assemblies (41% of the world)
ex. U.S. Legislative (Congress composed of Senate and House of Representatives)
Unicameralism
Single assembly
ex. Denmark
Veto Player Theory
A veto player is an actor whose agreement is necessary for a change in the political status quo
An increase in the number of veto players produces
Greater policy stability
Smaller policy shifts
Less variation in the size of policy shifts
Weaker agenda-setter powers