all of ochem 2 lol kms
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
what are carbs bro (three points)
polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones
remain sugars even if the hydroxy
groups can be removed (deoxy sugars)or replaced by amine (amino sugars)
monosaccharide
saccharides, the simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar units.
oligosaccharide
a carbohydrate composed of 2 to 10 monosaccharide units linked together by glycosidic bonds.
polysaccharide
long chains of monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds (more than 10), serving as energy storage or structural components.
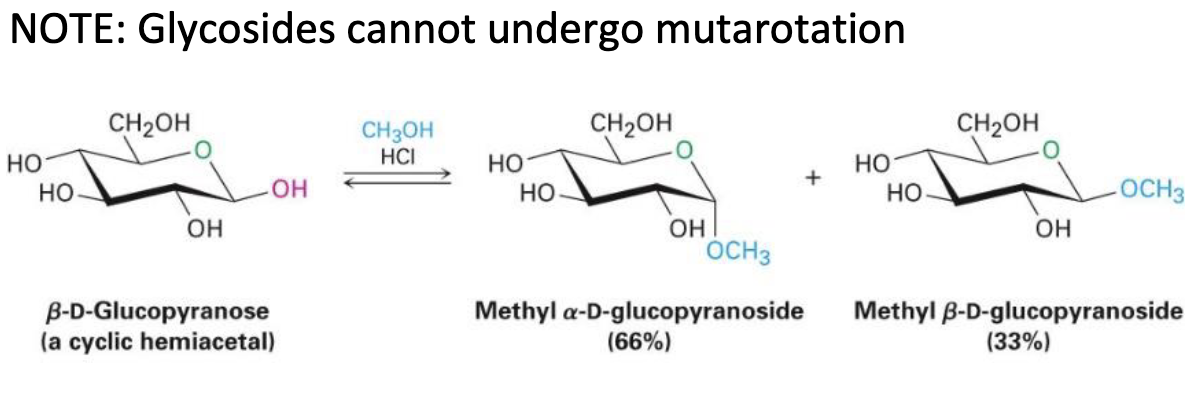
Mutarotation
is the change in optical rotation that occurs when an alpha or beta anomer of a sugar interconverts in solution, resulting in a mixture of both forms.
aldotetroses
erythrose and threose
aldopentoses
ribose, arabinose (2), xylose (3), lyxose (2,3)
aldohexose
allose, altrose (2), glucose (3), mannose (2,3), gulose (4), idose (2,4), galactose (3,4), talose (2,3,4)
anomer
A type of stereoisomer that differs in configuration at the anomeric carbon, typically found in carbohydrate chemistry.
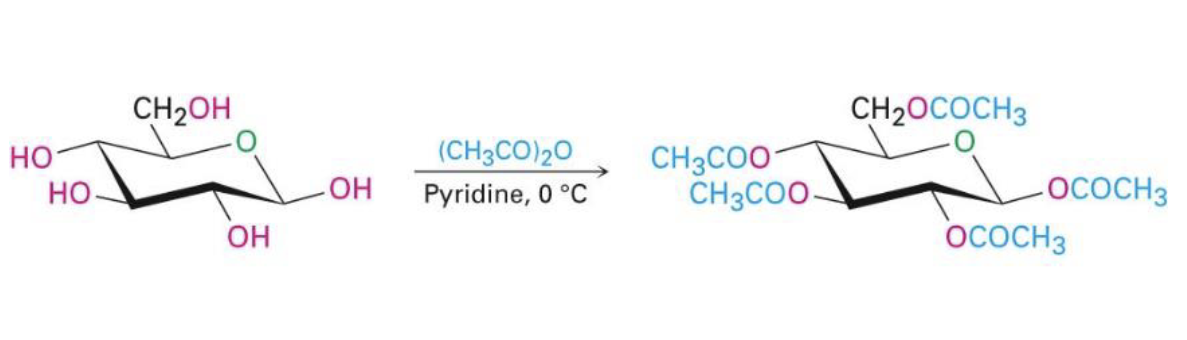
acid chloride/symmetric acid anhydride, pyridine
all oh groups react
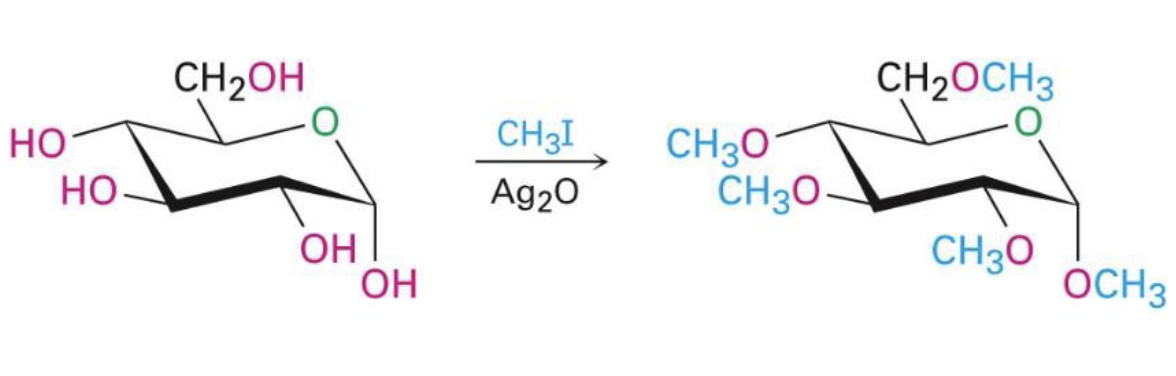
CH3I, Ag2O
all oh groups react
ROH, HCl
turns hemiacetal to acetal OR replaces anomeric OH with OR
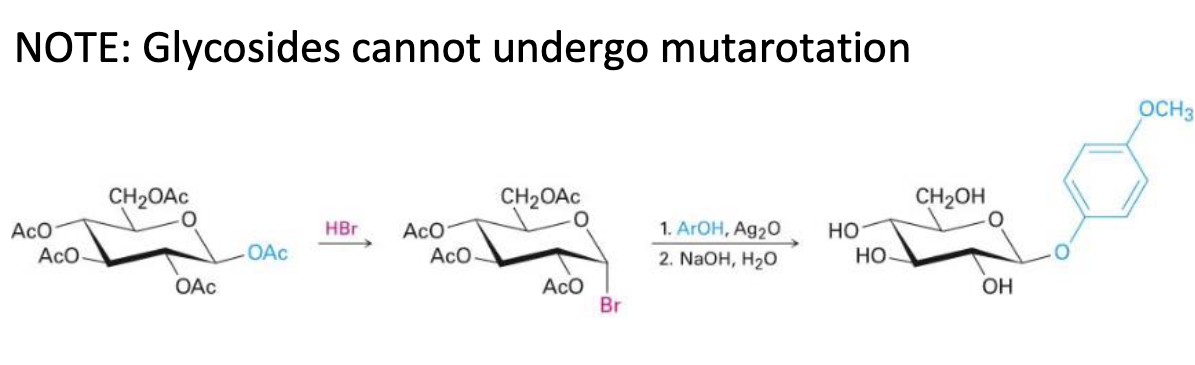
HBr
ROH, Ag2O
NaOH, H2O
koenigs-knorr reaction mechanism (c1 glycoside formation only)
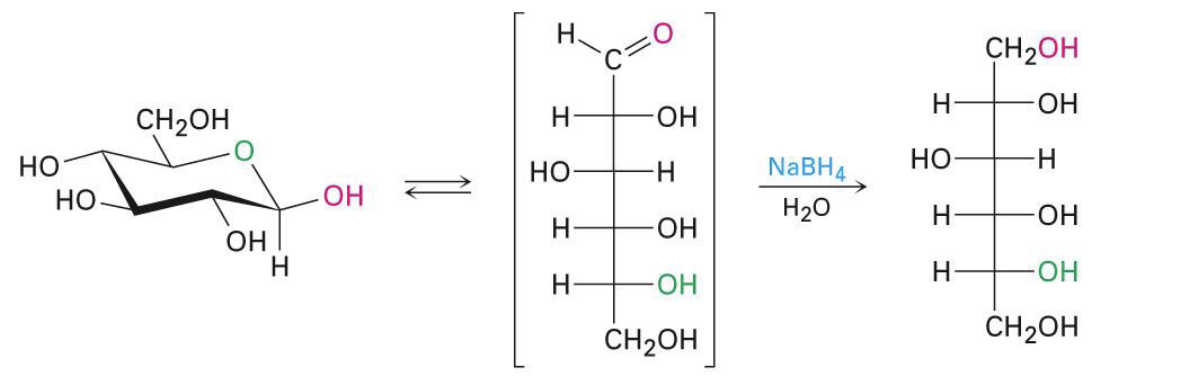
NaBH4, H2O
reduction
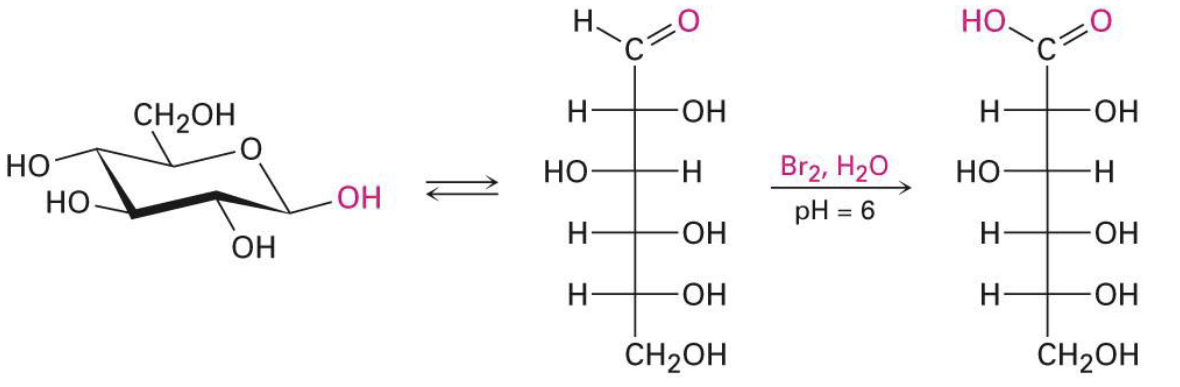
Br2, H2O
ph = 6
oxidation
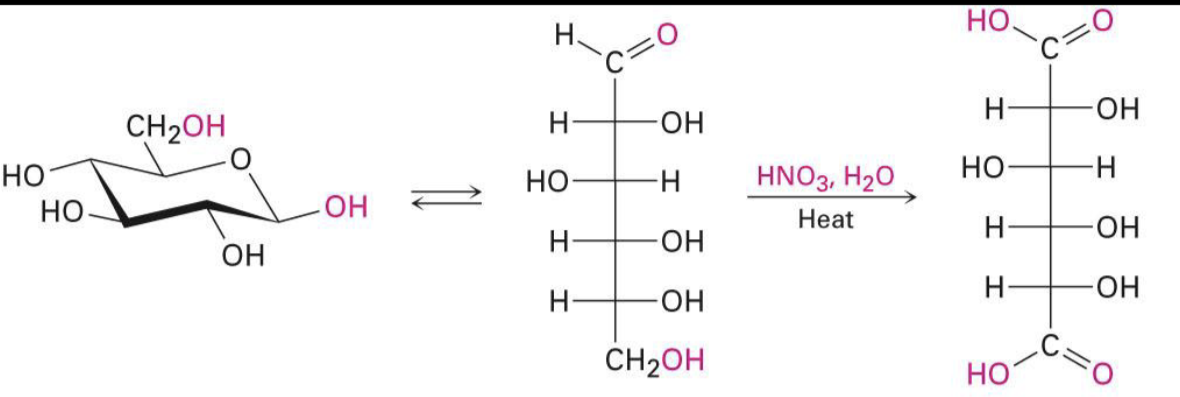
HNO3, H2O, heat
dicarboxylic acids (both top and bottom as oxidized)
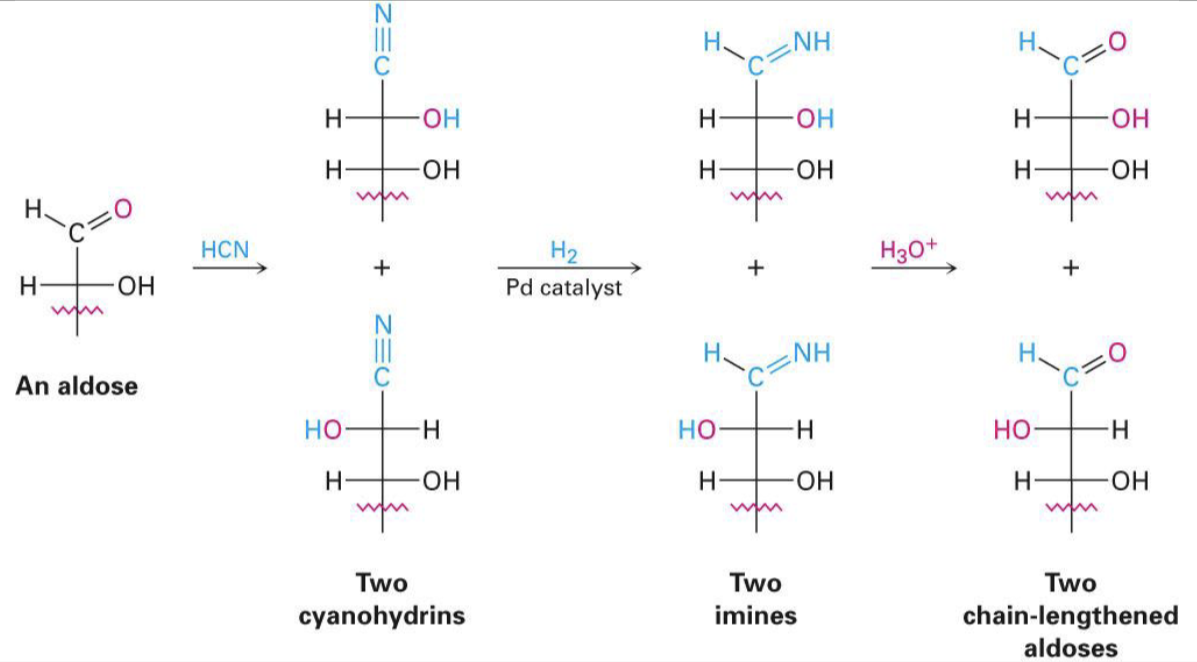
HCN, H2, H3O
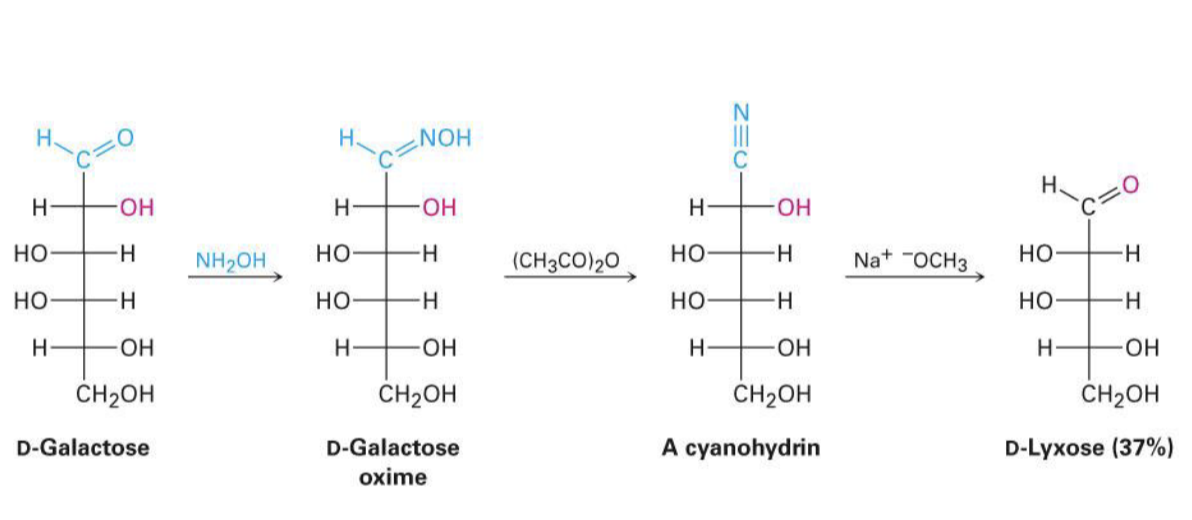
kiliani-fischer synthesis, adds a C
NH2OH, (CH3CO)2O, NaOCH3
wohl degradation, takes off a C
cellulose
monomer: glucose (pyranose form)
linkage: beta 1→4 bonds
function: structure
amylose
monomer: glucose (pyranose form)
linkage: alpha 1→4 glycoside bonds
function: energy storage
amylopectin
monomer: glucose (pyranose form)
linkage: alpha 1→4 and alpha 1→6 glycoside bonds
branching: yes
function: energy storage
glycogen
monomer: glucose (pyranose form)
linkage: alpha 1→4 and alpha 1→6 glycoside bonds
branching: yes
function: energy storage in animals
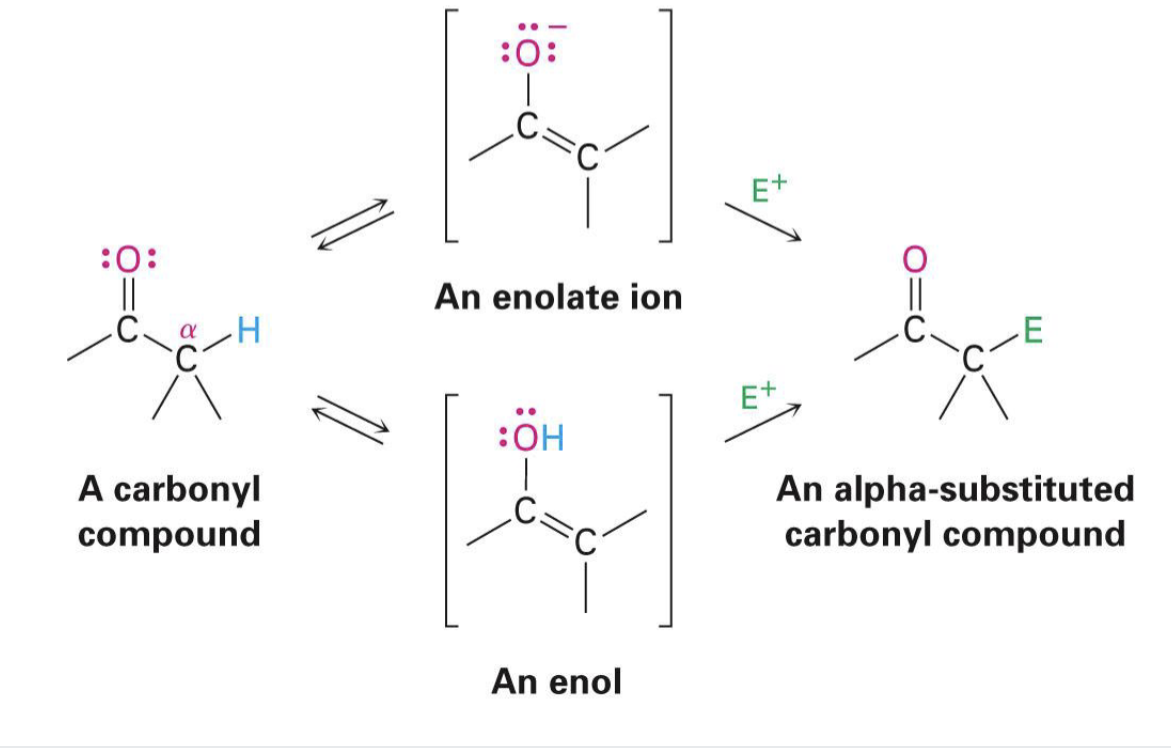
enolate
a negatively charged carbon-containing compound formed by removing a proton from the alpha-carbon
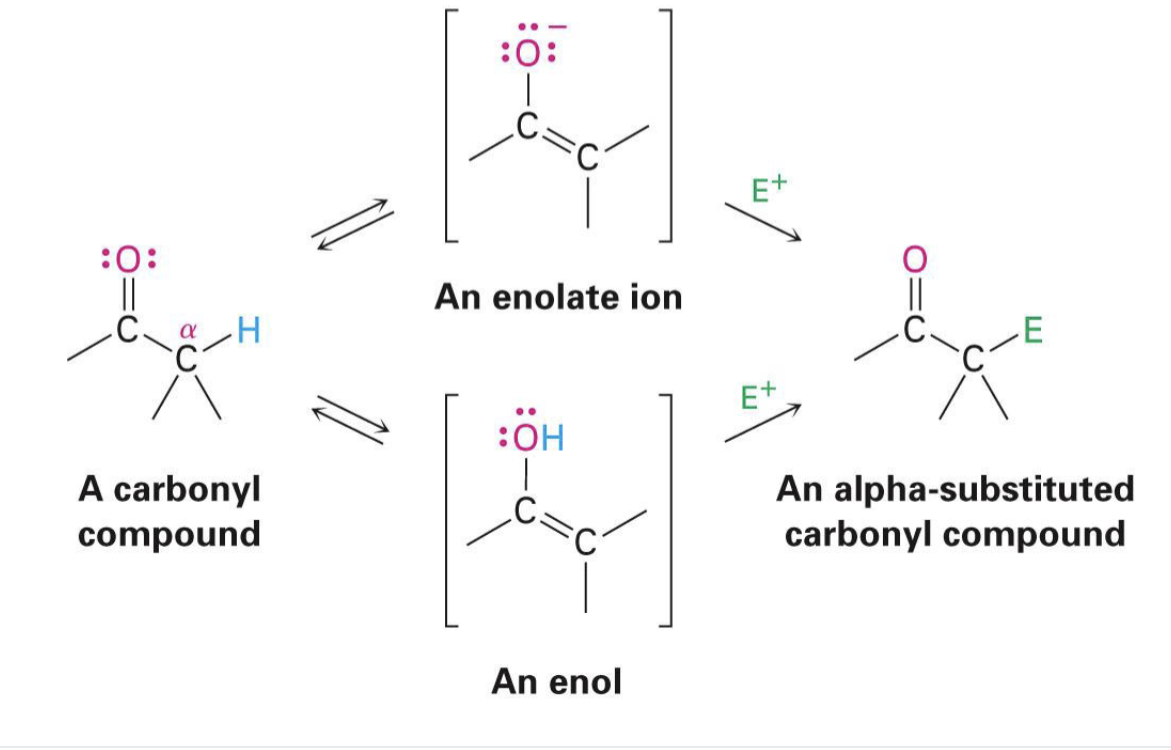
enol
an organic compound characterized by a carbon-carbon double bond (alkene) with a hydroxyl group (-OH) directly attached to one of the double bond's carbon atoms
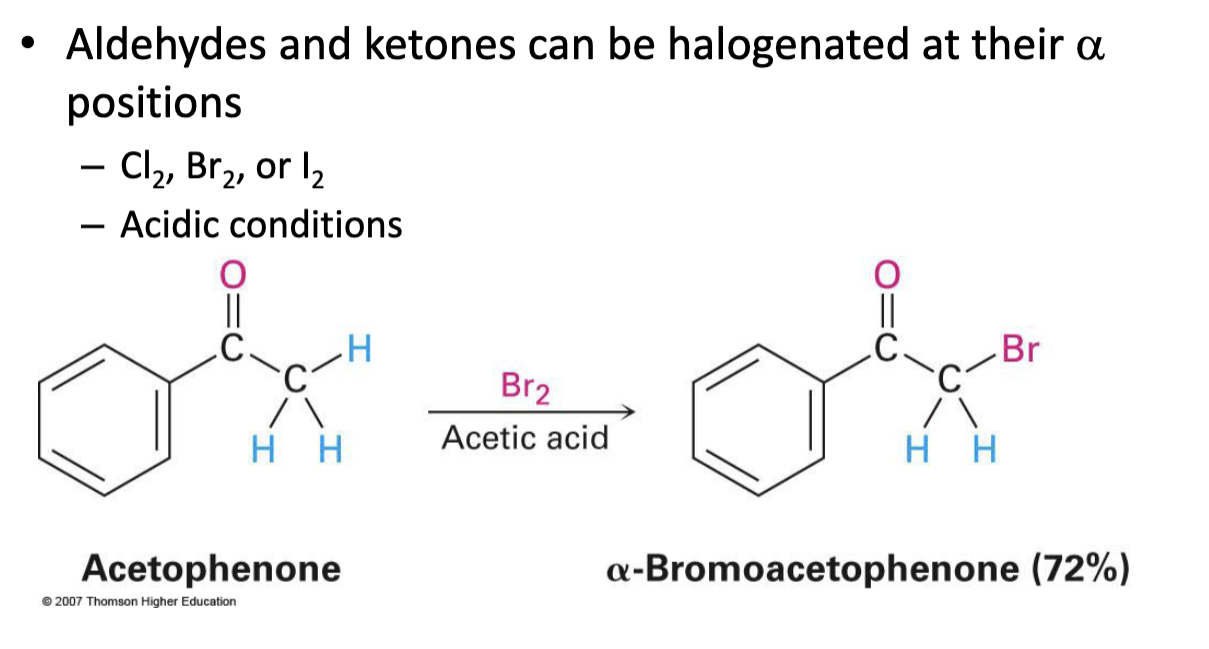
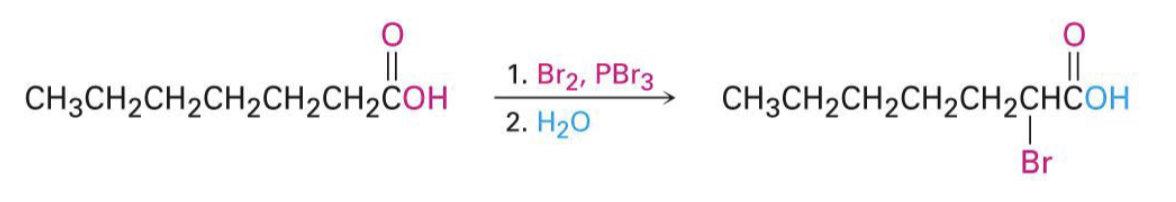
X2, acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Br2, PBr3
H2O
hell-volhard-zelinskii rxn, to brominate carboxylic acids
Relative acidity of carbonyl groups
o Carboxylic acids (MOST acidic, pKa ~5)
o diketones
o ketoesters
o diesters
o Alcohols (pKa ~16)
o Aldehydes
o Ketones
o Thioesters
o Esters (LEAST acidic)
o Nitriles
o Amides
X2, NaOH
methyl ketone that turns to COOH
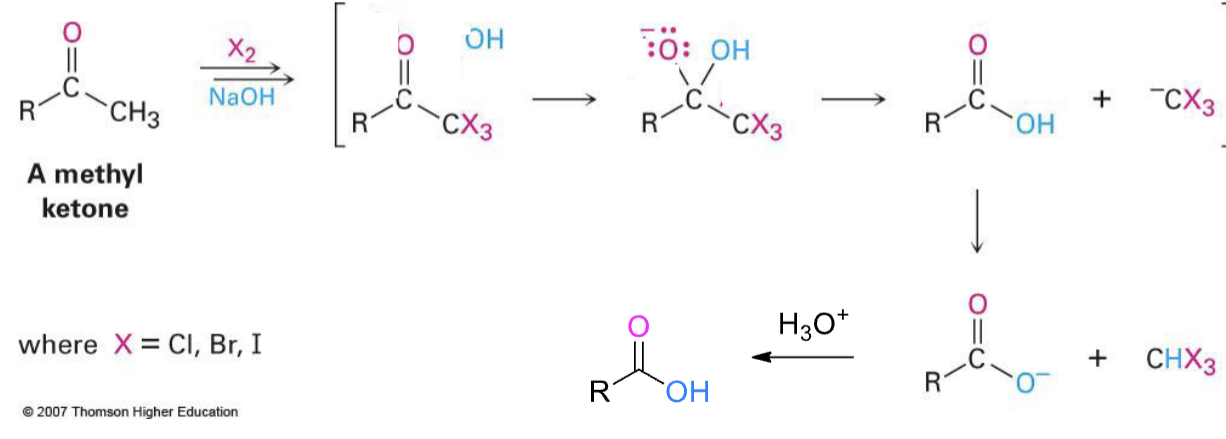
H3O, heat
boots a COOH off
NaOet, EtOH
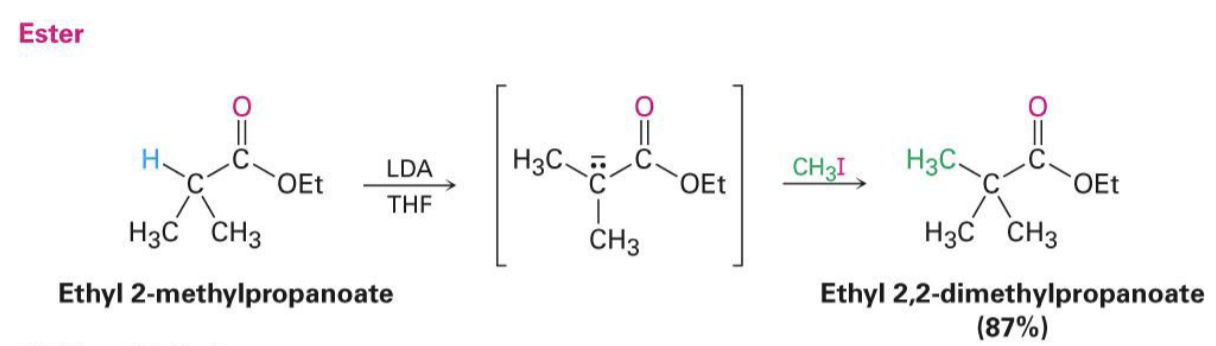
booted an H from an alpha carbon and replaces
LDA, THF → RX
boots an alpha-hydrogen for ketones, esters, and nitriles
mass spec indicates
molar mass, elements present, molecular formula, cation fragments
base peak
peak w 100% relative abundance
parent peak
aka M+ peak, the peak corresponding to the molecular ion of the compound, representing the intact molecule.
odd MW
indicates N
3:1 M & M+2
indicates Cl
1:1 M & M+2
indicates Br
branched alkane fragmentation pattern
breaks @ branch points
alcohol fragmentation pattern
alpha carbon fragmentation or dehydration (lose water, M minus 18)
amines fragmentation pattern
alpha cleavage
carbonyls fragmentation pattern
alpha cleavage and mclafferty (alpha and beta carbon bond breaks, OH forms)
finding degree of unsaturation
[(2C + 2) + N - H - X] / 2
finding number of carbons
[(M + 1)/M+] / 1.1
what is UV-vis
conjugated molecules absorb in UV region, excitation of electrons in molecular orbitals
what does IR show
presence of a functional group, bonds stretching/bending
fingerprint region on IR
400-1500
double bonds on IR
1500-2000
triple bonds on IR
2000-2500
NH, CH, and OH in IR
2500-4000
C-C-H on IR
just below 3000
C = C - H on IR
just above 3000
C =- C - H on IR
more above 3000
C - C on IR
800-1300
C = C on IR
1640-1680
C =- C on IR
2100-2260
benzene fingers
A region in the IR spectrum, typically around 1450-1600 cm^-1, associated with C=C stretching and other bending vibrations in aromatic compounds.
OH on IR
3400-3650
amine (R-N-H2) on IR
3300-3500
C=O on a saturated aldehyde on IR
1730
C=O from an aldehyde next to an aryl or double bond on IR
1705
ketones on a 6 atom ring on IR
1715
ketones on a 5 atom ring on IR
1750
ketones next to a double bond/aryl ring on IR
1690
esters on IR
1735
esters by a double bond on IR
1715
what does NMR show
number of unique C or H, func groups + connections, structure
shielding
opposing magnetic field produced by electrons surrounding nuclei to counteract external magnetic field
looking at an NMR chart
left = downfield, deshielded
right = upfield, shielded
C13 NMR vs DEPT90 vs DEPT135
shows all vs shows only CH vs CH and CH3 are positive, while CH2 is negative
enantiotopic vs diastereopic
Enantiotopic refers to groups that are related as mirror images, while diastereotopic refers to groups that are not related by such symmetry. These terms help distinguish between different types of stereoisomers.
area under an NMR peak
proportional to the # of protons → integration = relative # of protons whereas splitting shows # of adjacent protons
more conjugation
more stable, less energy, HOMO to LUMO jump is less, max wavelength increases, colors appear (400-800 nm)
lone pair on N in 6 membered ring
isn’t counted for aromaticity
lone pair on N in 5 membered ring
one pair can count for aromaticity
toluene
xylene

indene

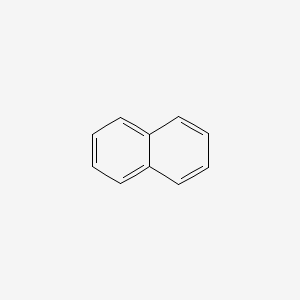
naphthalene
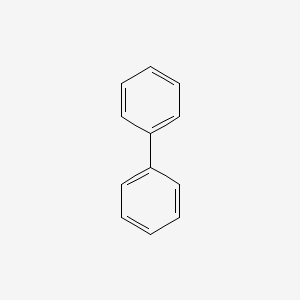
biphenyl
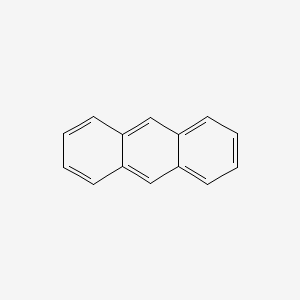
anthracene
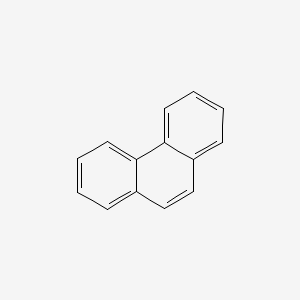
phenanthrene
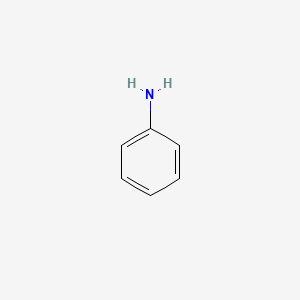
aniline
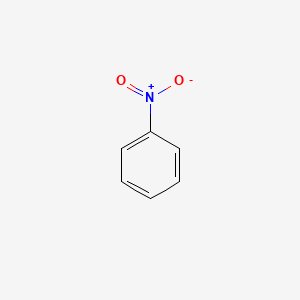
nitrobenzene
phenyl vs benzyl group
carbocation rearrangement for alkylation
benzene will stick itself to the more substituted group
flaws w/ alkylation
polyalkylation, carbocation rearrangements, can’t happen with strongly deactivating groups
friedel crafts alkylation vs acylation

Br2 / FeBr3
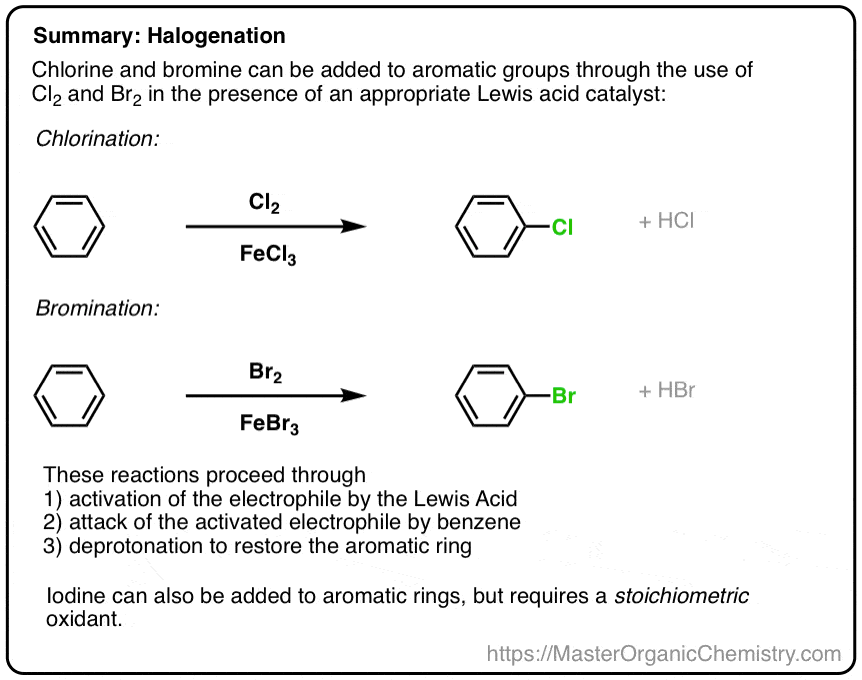
SO3 / H2SO4 and HNO3 / H2SO4
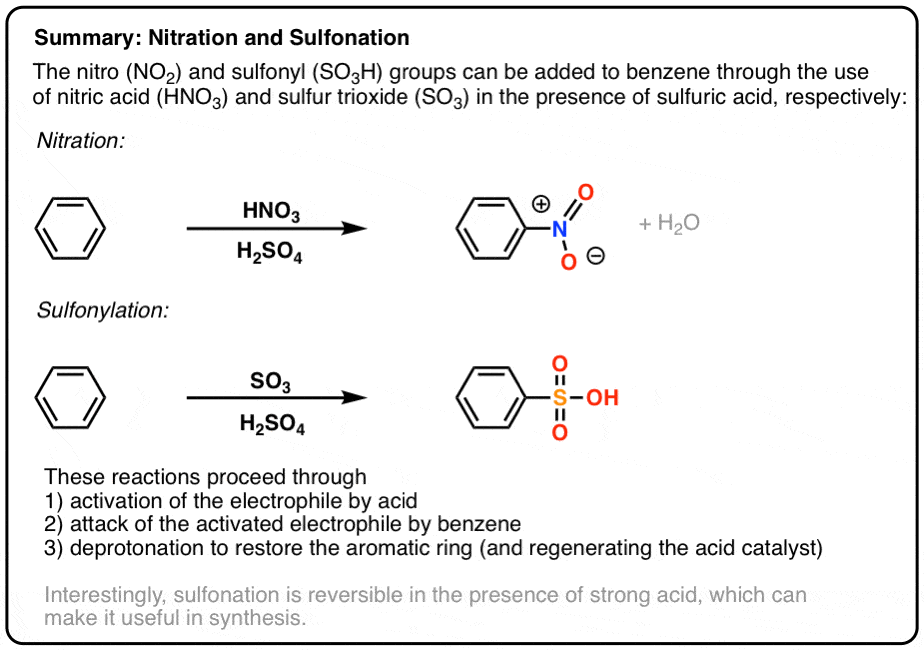
F-TEDA-BF4

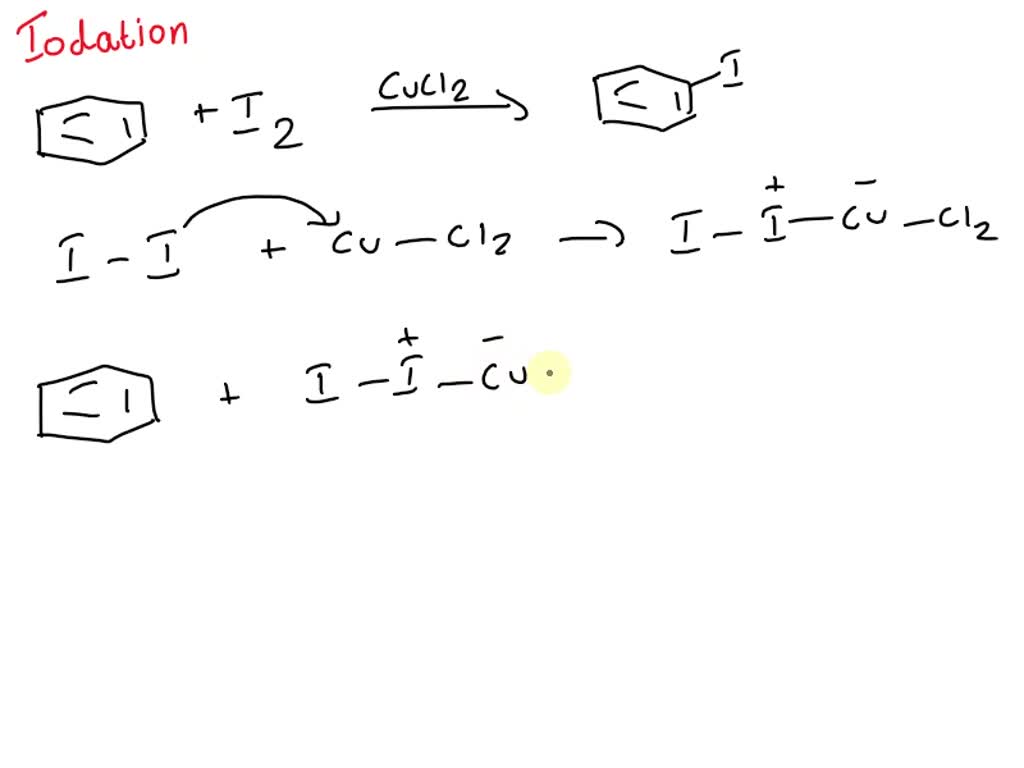
I2 / CuCl2
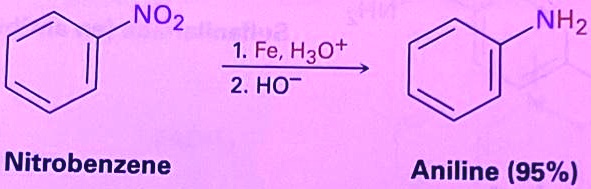
Fe, H3O+ / HO-
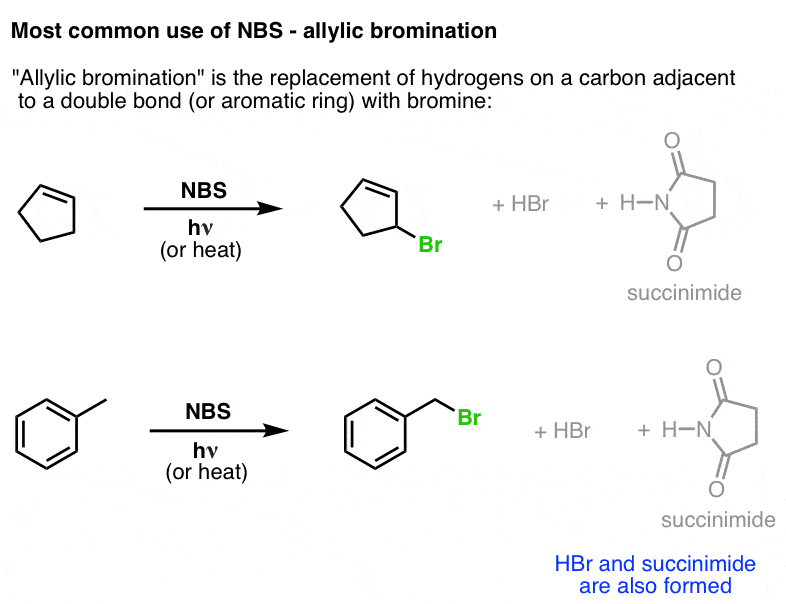
NBS
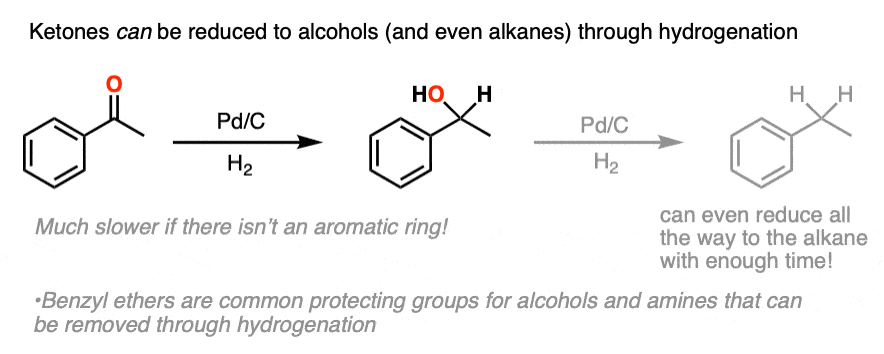
H2 / PDC
reduces alpha carbon double bond to single bond or NO2 to NH2
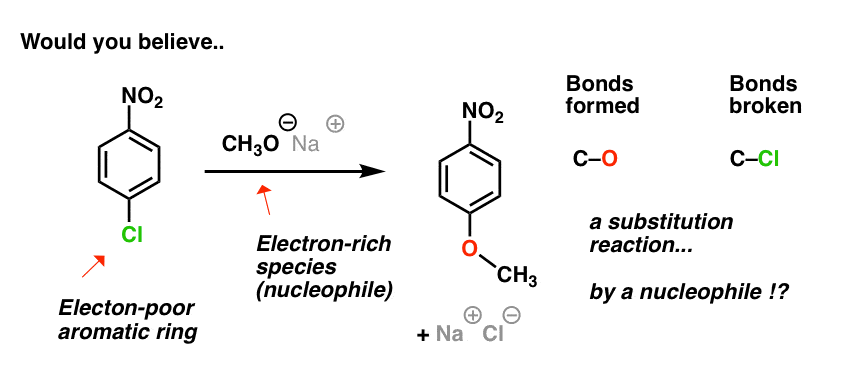
EAS vs NAS mechanism

formaldehyde

acetaldehyde

benzaldehyde

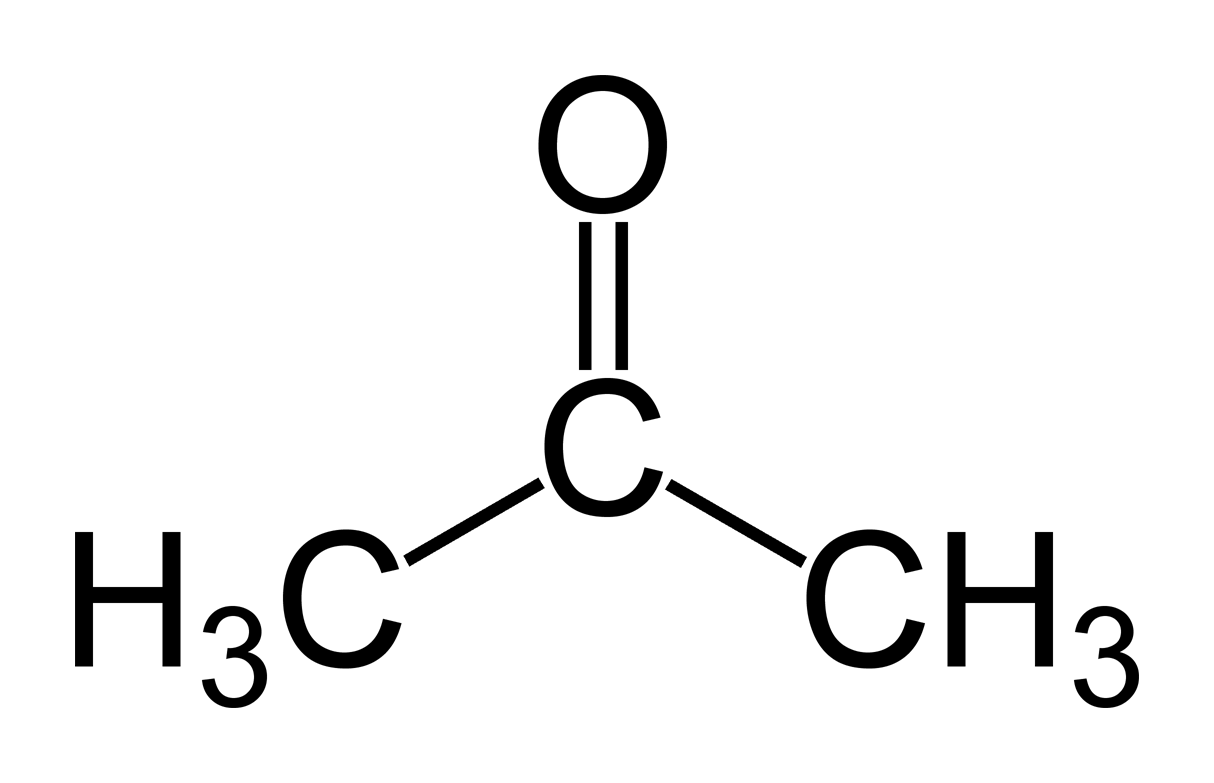
acetone
acetophenone
