BSCI 1511 - Gametogenesis and fertilization
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Features of Asexual reproduction
Offspring are clones
No fusion of gametes
Sexual reproduction
Non-motile egg fuses with motile sperm
Offspring are usually genetically distinct
Fertilization can be either internal or external
creates genetic variation
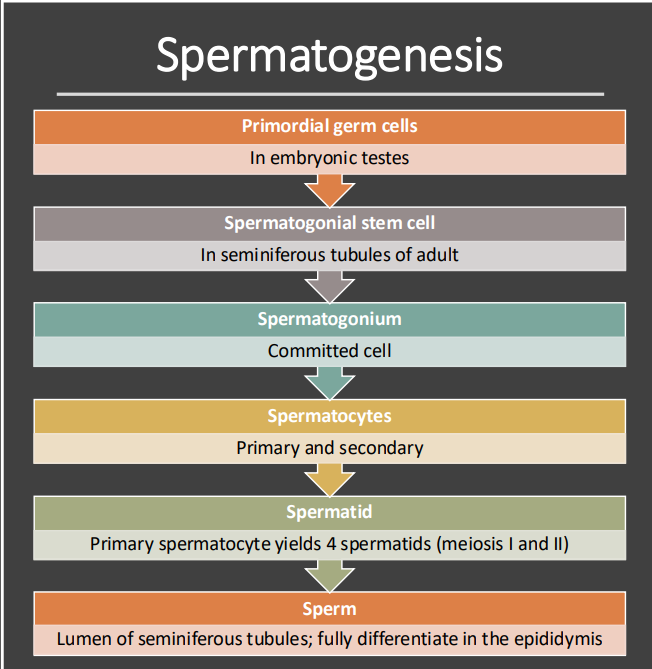
Spermatogenesis
The formation and development of sperm
Occurs in the seminiferous tubules contained within the testes
Occurs throughout adolescence and adulthood
Describe the initial stages of spermatogenesis before meiosis begins.
Journey of the Sperm steps
Testes produce sperm in highly coiled seminiferous tubules
Sperm traverse epididymis (~6 m) and complete maturation
During ejaculation, sperm are propelled via a muscular vas deferens
Vas deferens joins duct from the seminal vesicle – becomes ejaculatory duct
Ejaculatory duct joins the urinary duct – becomes the urethra
Seminal vesicles
They produce 60% of the semen: it is yellowish mucus, protein, and fructose
Prostate gland
The prostate gland produces a thin, milky fluid: anticoagulant enzymes and citrate (nutrient)
Bulbourethral glands
secretions neutralize the acidity in the urethra
They are positioned along the urethra, located just below the prostate gland
Urethra
Conduit for semen and urine
What is oogenesis?
Formation and development of oocytes
Occurs in the ovaries
immature oocytes form in the embryo and undergo developmental arrest for years or decades
The production of mature oocytes stops at around the age of 50 - menopause
Which cell types and developmental milestones are reached during oogenesis while the female is still an embryo?
Primordial Germ Cells: These cells undergo mitotic divisions to form oogonia.
Oogonia: These diploid cells also divide by mitosis and develop into primary oocytes.
Primary Oocytes: These cells begin meiosis but are arrested in prophase I before birth. They reside within follicles in the ovaries.
Follicle Formation: Each primary oocyte is surrounded by a small follicle, which consists of protective support cells.
Steps of Oogenesis - In adult
FSH stimulates a few follicles to resume growth and development
One follicle matures each month which allows primary oocyte to complete meiosis I becoming a 2ndary oocyte
The secondary oocyte, arrested at metaphase of meiosis II, is released during ovulation
Fusion of sperm and secondary oocyte triggers completion of meiosis II
Ovulation
The release of an oocyte from an ovary
After ovulation, the ruptured follicle develops into the corpus luteum
How does the presence or absence of fertilization affect the corpus luteum and the uterine lining?
If YES, the corpus luteum secretes estradiol and progesterone, maintaining the uterine lining during pregnancy
If NO, the corpus luteum degenerates, and a new follicle matures during the next cycle
Outlines the steps of human fertilization and early embryonic development
Ovulation: The ovaries release a secondary oocyte into the body cavity. This oocyte is surrounded by support cells within follicles.
Oocyte Collection: Cilia on the oviduct (fallopian tube) collect the oocyte and move it toward the uterus.
Fertilization: Sperm meets the oocyte in the oviduct. Fusion of the sperm and oocyte results in fertilization, forming a zygote.
Embryo Development: The fertilized egg undergoes cleavage (cell division) as it moves toward the uterus, becoming a blastocyst.
Implantation: The blastocyst implants in the endometrium (uterine lining) about seven days after conception.
Cervix
The neck of the uterus
Vagina
Elastic chamber where the male penis is inserted and sperm is deposited
Vestibular glands
Secrete lubricating mucus that facilitaes intecourse
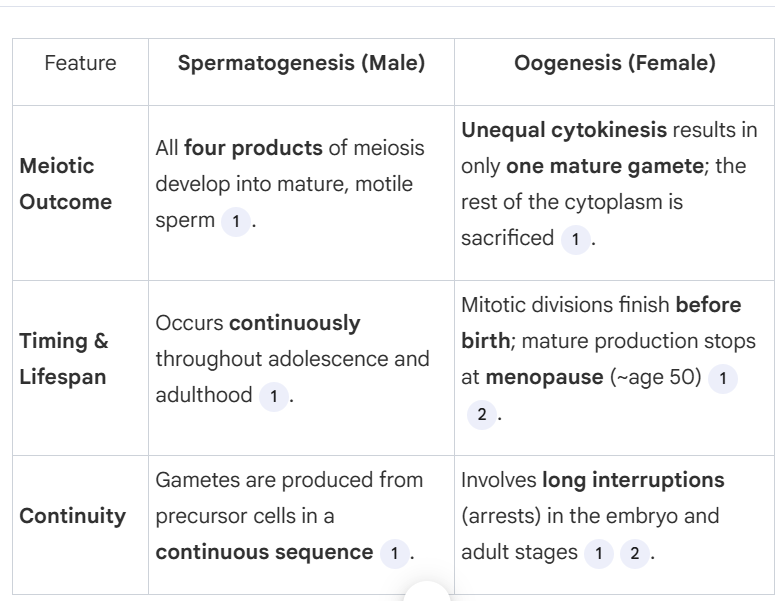
What are the three major developmental differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
4 mature gametes are produced v. only 1 mature gamete is produced
Develops throughout adulthood and adolescence v. dveloped before birth
What are the primary hormones and cell types involved in regulating the male reproductive system, and how is this system controlled through feedback?
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): Produced by the hypothalamus, it stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): Stimulates Sertoli cells in the testes to nourish developing sperm.
Luteinizing hormone (LH): Stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone.
Testosterone: Promotes spermatogenesis and regulates GnRH, FSH, and LH levels through negative feedback.
Inhibin: Produced by Sertoli cells (seminiferous tubules) it inhibits FSH secretion from the anterior pituitary.
Uterine cycle
cyclic changes in the endometrium that occur in the absence of pregnancy, including menstruation
What are the simple steps of the follicular phase in the ovarian cycle? (days 0-14)
Hypothalamus releases GnRH
Anterior pituitary releases FSH and LH
FSH stimulates growth of the follicle
Follicle produces estradiol
Estradiol level is low, inhibiting the hypothalamus and keeping FSH and LH levels low
As follicle develops, estradiol level rises steeply, stimulating a sharp increase in GnRH, FSH and LH
One day after the FSH and LH surge, the follicle ruptures and releases the secondary oocyte – ovulation
Ovarian cycle – Luteal phase (days 15-28)
LH stimulates the remaining follicular tissue to form the corpus luteum
Stimulated by LH, the corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estradiol
High concentration of progesterone and estradiol inhibit hypothalamus (GnRH) and pituitary (FSH and LH)
Very low GnRH, FSH and LH prevent another follicle from maturing
If no pregnancy, low gonadotropin concentration causes corpus luteum to disintegrate
Progesterone and estradiol concentration declines
GnRH, FSH and LH levels rise, initiating the next ovarian cycle
Describe the phases of the uterine cycle (menstrual cycle)
Menstrual Flow Phase (Days 0-5): The cycle begins with menstruation, where the uterine lining (endometrium) is shed if pregnancy does not occur. This phase corresponds to low levels of estradiol.
Proliferative Phase (Days 5-14): The endometrium thickens as estradiol levels rise, preparing for possible embryo implantation.
Ovulation (Day 14): Triggered by a surge in LH and FSH, ovulation marks the release of an oocyte.
Secretory Phase (Days 15-28): The endometrium further thickens and becomes more vascularized, supported by progesterone and estradiol from the corpus luteum.
If no fertilization occurs, the cycle repeats starting with menstruation
Steps for fertilization (pregnancy)
Sperm fuses with egg
Egg completes meiosis II
Nuclei (sperm and egg) fuse, yielding the zygote
Zygote divides to become blastocyst
Blastocyst implants in the endometrium
Pregnancy
Steps of blastocyst implantation
Blastocyst implants in the endometrium
Estradiol + progesterone from the corpus luteum signals the endometrium to nourish the embryo
Blastocyst secretes hCG
hCG maintains corpus luteum, which continues to secrete estradiol and progesterone
Endometrium is maintained AND the ovarian cycle is turned off
In the 2nd trimester, the corpus luteum disintegrates; placenta maintains pregnancy
Fertilization process (detailed steps)
Sperm penetrates any protective layer surrounding the egg and reaches the plasma membrane
Molecules on the sperm surface bind to receptors on the egg surface – ensures species compatibility
Sperm enters the egg
The surface of the egg is changed to prevent polyspermy
What is an acrosomal reaction?
The sperm release specialized enzymes to digest the eggs’ outer layers
It is necessary to allow sperm to reach and bind with the eggs’ plasma membrane, ensuring compatible sperm of the same species
Cortical reaction - slow block
Binding of sperm to the egg activates a signal transduction pathway that triggers the release of Ca2+ into the cytosol from the ER
Calcium diffuses throughout the cell
Cortical granules in the egg fuse with the plasma membrane
The contents of the cortical granules clip off spermbinding receptors and the fertilization envelope forms
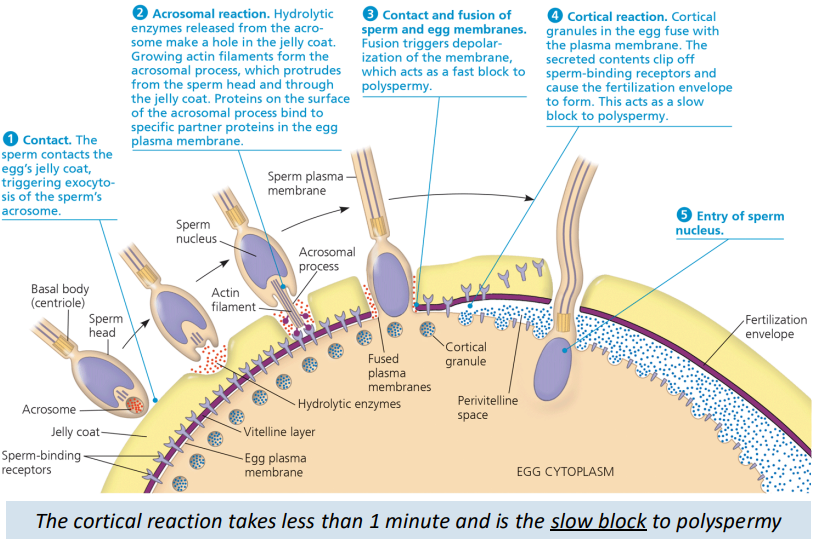
Egg activation and cleavage (steps)
The influx of Ca2+ into the cytoplasm also activates the egg
Nuclei of sperm and egg fuse
Cell division begins
Cleavage results in blastomeres that form a blastula that surrounds a blastocoel
Birth control pill
synthetic estrogens and progestins that prevent pregnancy by inhibiting the production of GnRH, LH and FSH.
Shuts down the ovarian cycle
Plan B
a type of progestin that prevents ovulation
How does The abortion pill work?
Blocks progesterone receptors in the uterus, which prevents progesterone from maintaining the pregnancy.
Prostaglandins are taken to induce uterine contractions finishing the process
Menopause
Ovarian cycle stops
Ovaries lose responsiveness to LH and FSH, thus reducing estradiol production.
Menstruation
shedding of the endometrial lining (uterine lining) that occurs in the absence of pregnancy
It is induced when ovarian hormone levels drop (specifically progesterone and estradiol) because the corpus luteum has disintegrated
Ectopic pregnancy
When the fertilized egg implants in an oviduct
Endometriosis
Uterine cells migrate to an ectopic location and respond to hormones, causing pain and discomfort.
Difference Between Primary and Secondary Oocyte
Primary Oocyte:
Formed during fetal development from oogonia.
Arrested in prophase I of meiosis until puberty.
Resides within a follicle in the ovary
Secondary Oocyte:
Formed from the primary oocyte after completion of meiosis I.
Haploid and arrested at metaphase of meiosis II.
Released during ovulation.
Completes meiosis II only if fertilized by a sperm.
What is cleavage?
rapid cell divisions that partition the cytoplasm of the fertilized egg into smaller cells called blastomeres
The process results in the formation of a blastula, a hollow ball of cells surrounding a fluid-filled cavity known as the blastocoel.
What is the role of FSH during the luteal phase?
It is suppressed during the luteal phase due to the negative feedback from the corpus luteum producing high concentrations of estradiol and progesterone
This prevents another follicle from maturing while preparing for a potential pregnancy
In humans, where does cleavage begin
In the oviduct
begins while the embryo is traveling through the oviduct (Fallopian tube) towards the uterus
What does LH do during the luteal phase?
Stimulates the ruptured follicle to transform into the corpus luteum
What does meiosis yield in oogenesis?
One gamete and three polar bodies (cytokinesis is unequal in oogenesis)
When does the sperm become capable of moving?
Epididymis, Sperm mature and become motile