💪 MUSCLE TISSUES
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
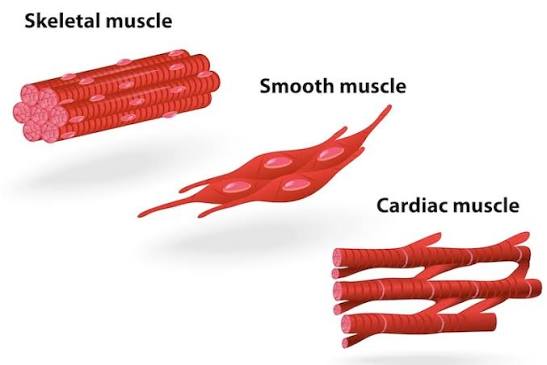
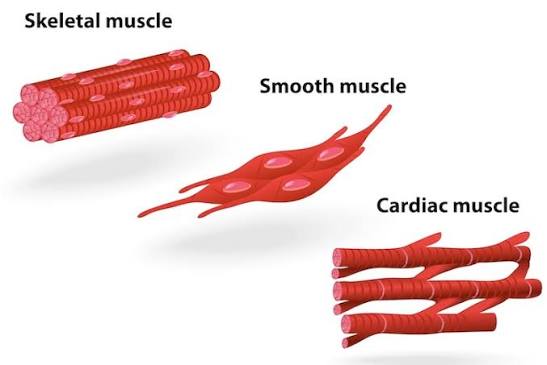
Smooth Muscle
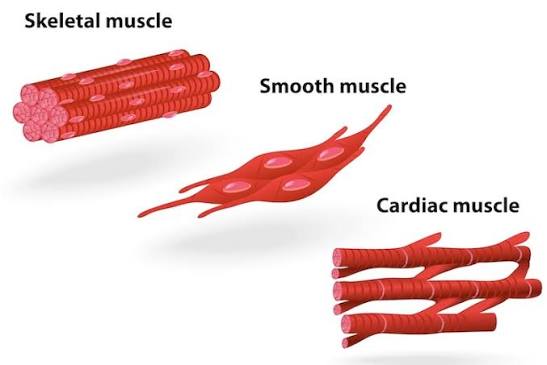
Structure: Spindle-shaped fibers with single nuclei; no striations.
Location: Walls of hollow organs (stomach, intestines, bladder).
Function: Involuntary movements of internal organs.
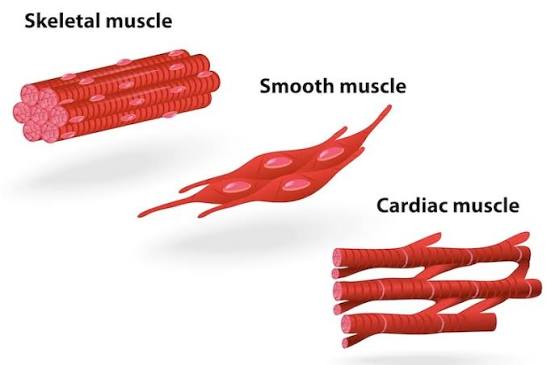
Cardiac Muscle
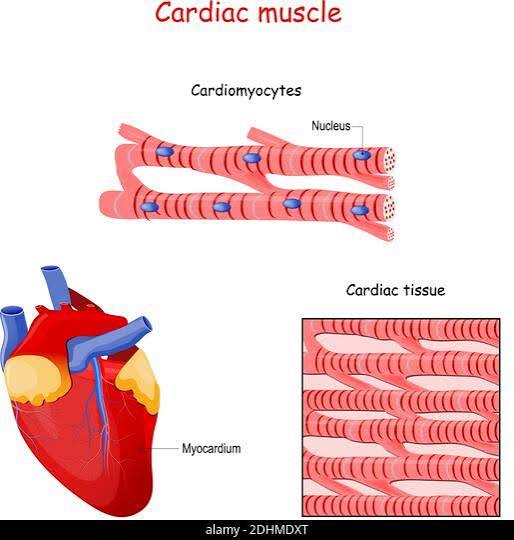
Structure: Branched, striated fibers with single nuclei; intercalated discs present.
Location: Heart wall.
Function: Involuntary contractions pump blood through the body.
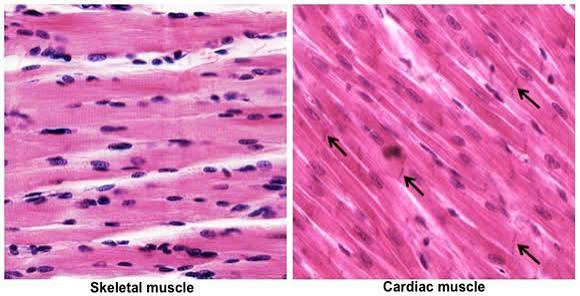
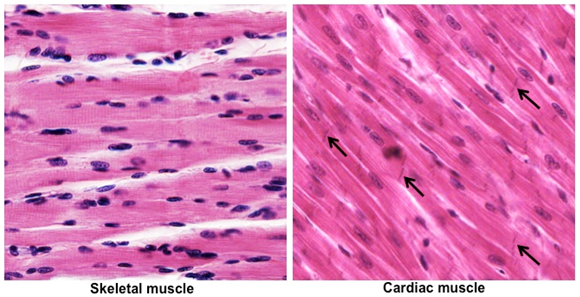
Skeletal Muscle
Structure: Long, cylindrical, striated fibers with multiple nuclei.
Location: Attached to bones.
Function: Voluntary movement, posture, and heat production.
Which type of muscle is involuntary and not striated?
🩶 Smooth muscle
Explanation:
Smooth muscle is involuntary (works without conscious control) and not striated (no visible stripes).
It’s found in the walls of hollow organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels.
What are intercalated discs, and what do they do?
❤ Intercalated discs are special junctions found between cardiac muscle cells.
They:
Connect heart muscle cells to each other
Allow electrical signals to pass quickly between cells
Help the heart contract as one unit (synchronized heartbeat)
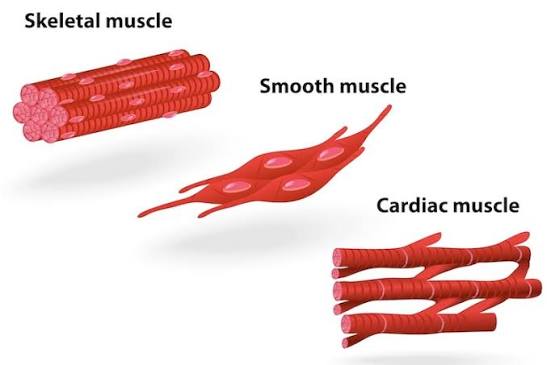
How can you identify skeletal muscle under a microscope?
Long, cylindrical fibers with striations and many nuclei along the edges.
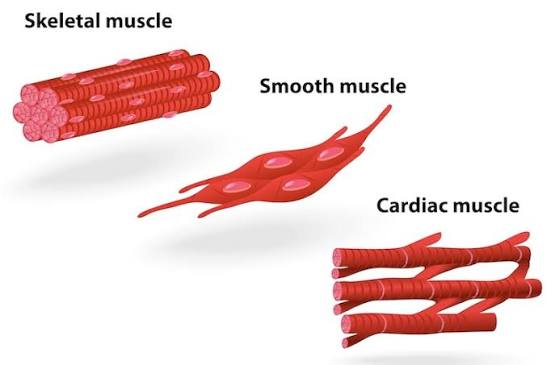
What is the main function of cardiac muscle?
Involuntary contractions to pump blood through the heart and body.
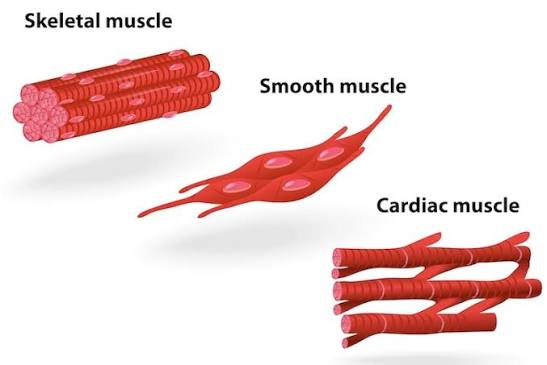
Which muscle type is voluntary and striated?
Skeletal muscle.