5 Peds Final (Lec 12): Management of Traumatic Injuries in the Primary and Permanent Dentitions
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
when they 1st start walking
When is the 1st peak of when children experience dental trauma?
when they 1st start sports
When is the 2nd peak of when children experience dental trauma?
custom fabricated
what is a type 1 mouth guard?
mouth-formed guard
what is a type 2 mouth guard?
stock mouthguard
what is a type 3 mouth guard?
3 mm
for a mouth guard to be affective, what is the optimal thickness of the incisal and occlusal surfaces?
-Medical history
-Neurologic Evaluation
-Clinical Examination of Head and Neck
-Intraoral Examination
-Radiographic Examination
-Photographic Documentation
When a traumatic injury occurs, what are your steps to diagnose the patient?
uncomplicated tooth fracture
pt presents with the following. What is the diagnosis?
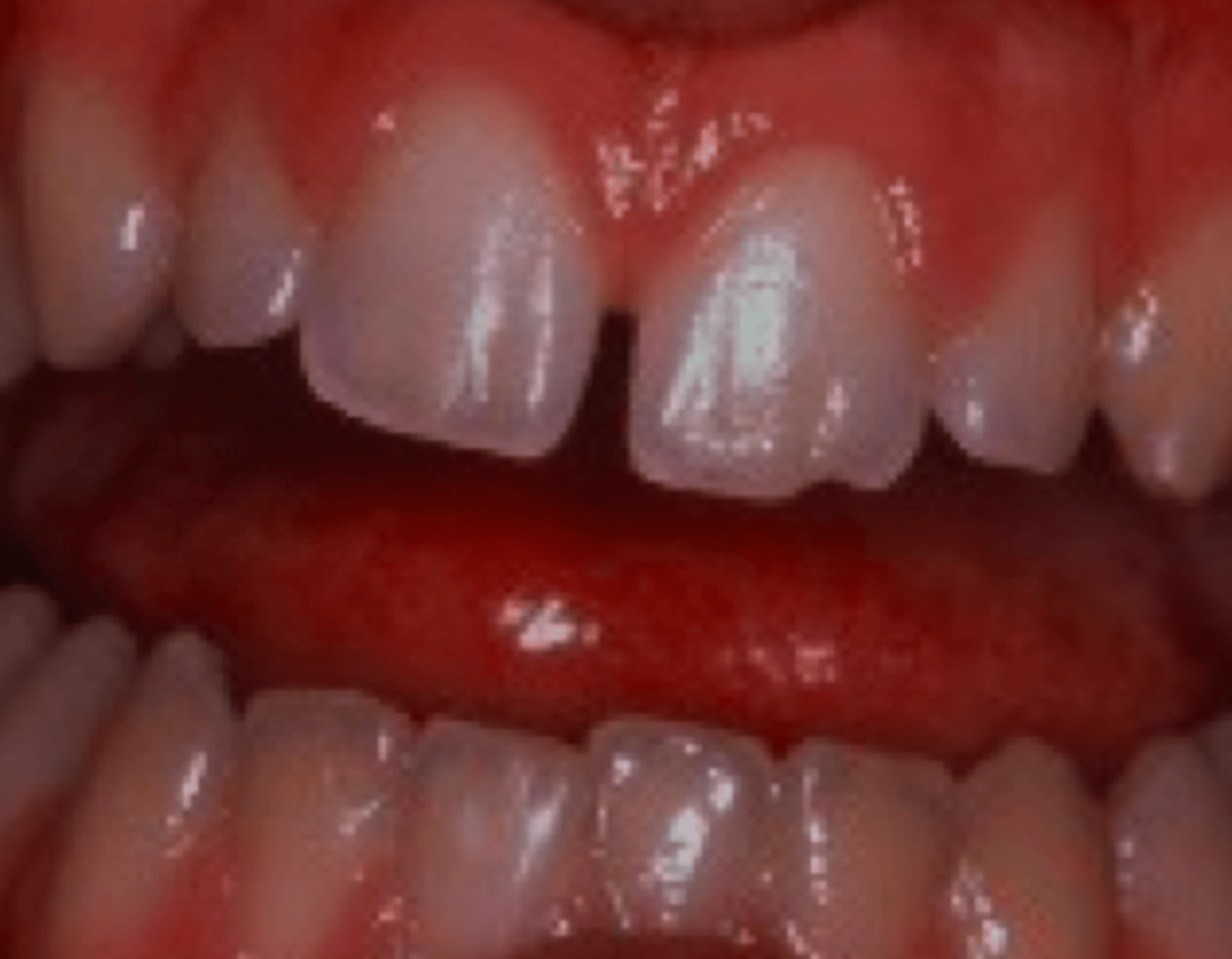
dental pulp
The difference between a complicated and a non-complicated tooth fracture is the involvement of ______
•Radiographs
•Smooth off rough edges
OR
•Restore with Composite Restoration
Follow Up:
6-8 wks , 1yr (clinical, xrays)
What is the treatment for an enamel fracture (permanent dentition)?
•Radiographic Evaluation
•Bonding of the Tooth fragment
•Restore with Resin Restoration (if exposed dentin within 0.5mm of pulp place CaOH2 and GI)
Follow Up:
3-4 weeks
What is the treatment for an enamel + dentin fracture (permanent dentition)?
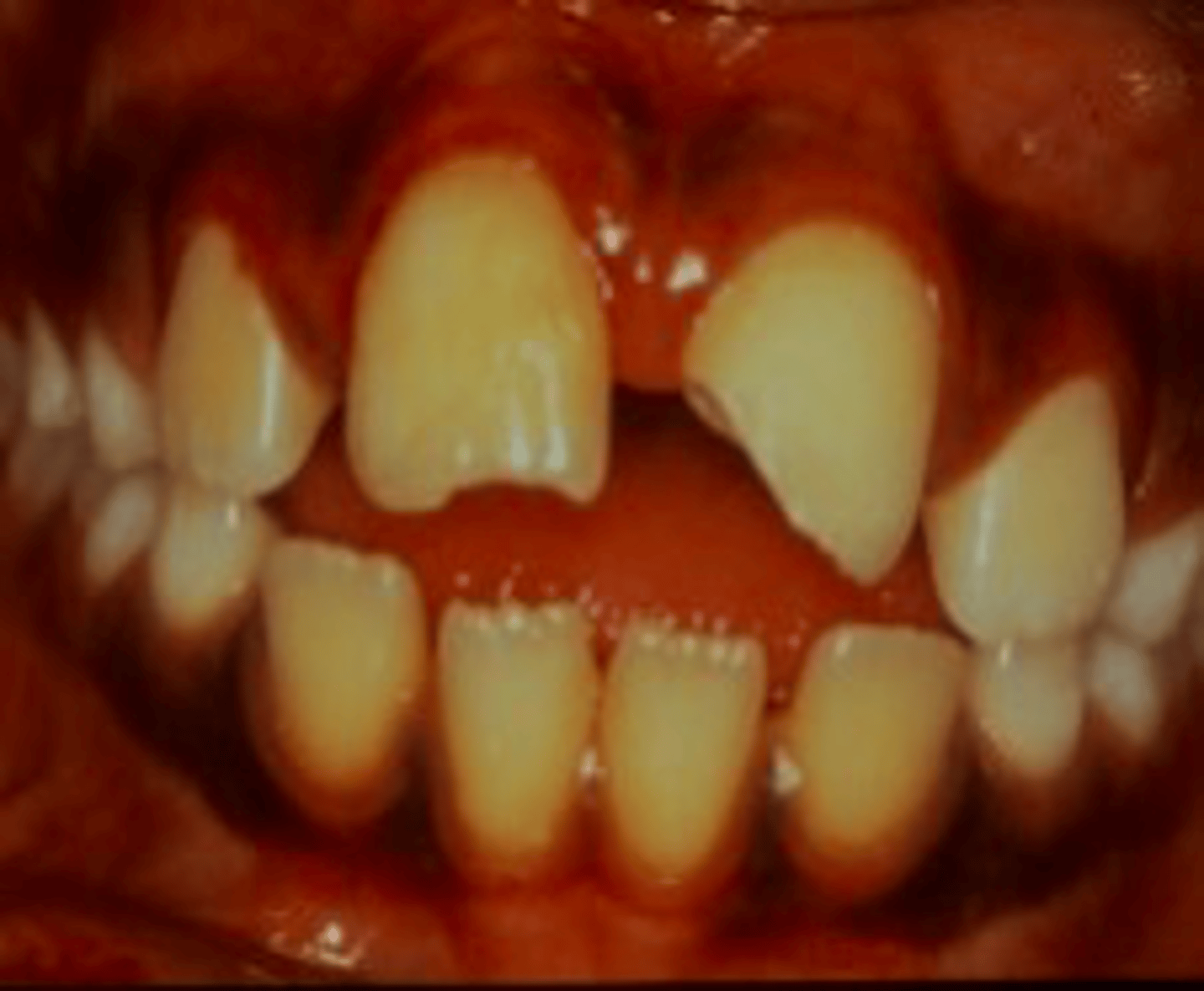
apical development
When a tooth experiences a complicated crown fracture, what is it important to evaluate?
pulp capping
For a crown fracture with pulp exposure that is small, there is little bleeding, it has been less than 2hrs since the trauma occurred and the root has a mature/complete apex, what is the ideal treatment for the pulp before restoring?
pulpotomy
For a crown fracture with pulp exposure that is large, there is bleeding, it has been less than 2hrs since the trauma occurred and and the root has an immature apex, what is the ideal treatment for the pulp before restoring? (permanent dentition)
pulpectomy/RTC
For a crown fracture with pulp exposure that is large, there is bleeding, it has been more than 2hrs since the trauma occurred and and the root has an mature apex, what is the ideal treatment for the pulp before restoring? (permanent dentition)
apexogenesis
a procedure where vital tissue within the tooth with an open apex is maintained using Ca(OH)2 to facilitate continued development of the immature root:
apexification
a procedure whereby the root canal of a non vital tooth with an open apex tooth is filled with calcium hydroxide to stimulate the formation of a hard tissue barrier at the apical portion of the root:
root fracture
Patient presents with a mobile tooth that is bleeding from the gingival sulcus. The tooth is tender on percussion. The crown is intact, but mobile. The tooth responds negative to sensibility testing (but that is unreliable). Radiograph shows a line through the root What is the diagnosis?(permanent dentition)
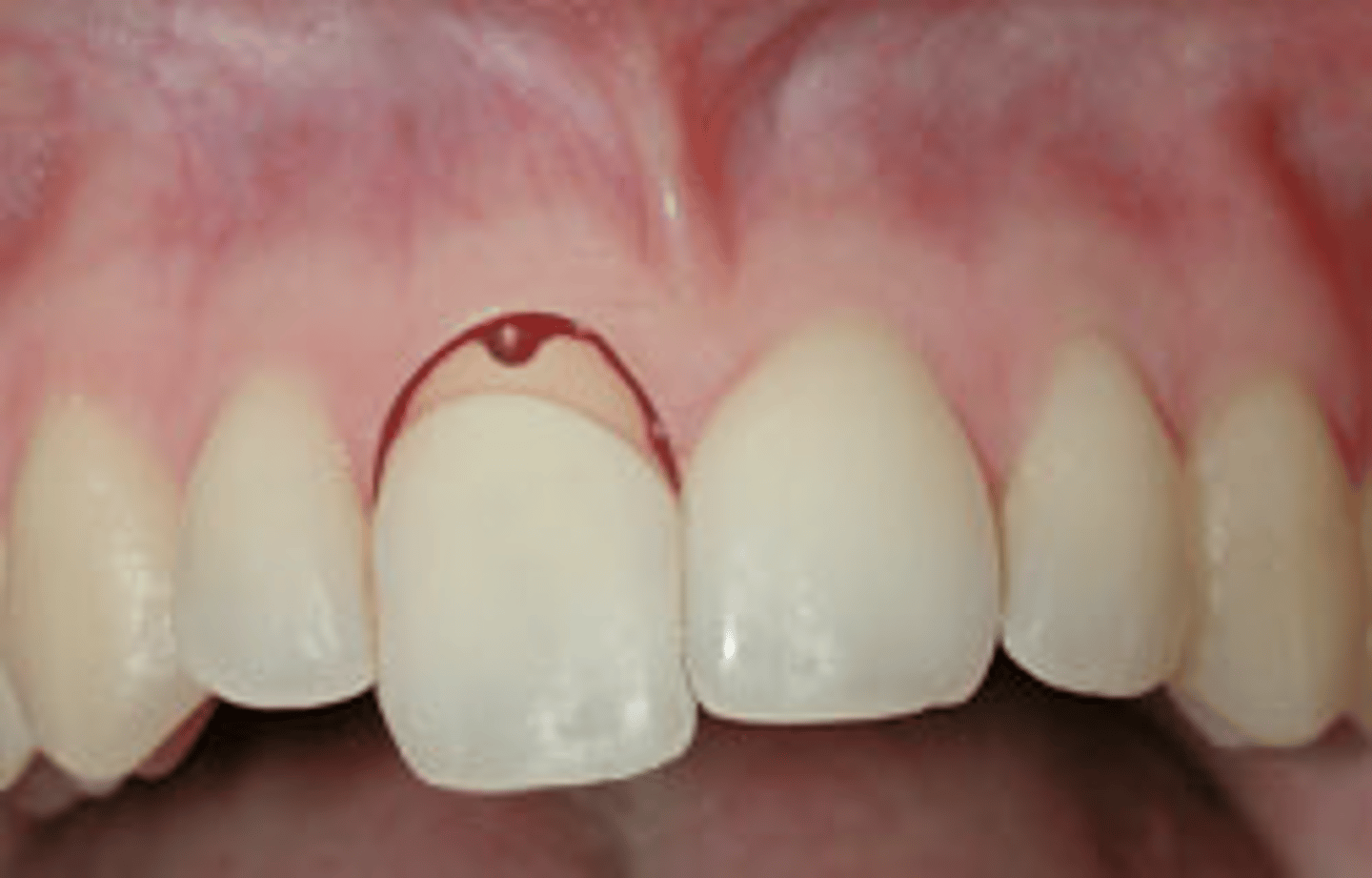
cervical
horizontal root fractures commonly occur in the ______ 1/3 of the root
PA radiograph
What type of radiograph is best to visualize a horizontal root fracture in the coronal 1/3 of the root?
apical
oblique root fractures commonly occur in the ______ 1/3 of the root
occlusal radiograph
What type of radiograph is best to visualize an oblique root fracture in the apical 1/3 of the root?
•Reposition if displaced ASAP
•Verify position with radiographs
•Stabilization of tooth 4 weeks
•Fracture near Cervical area:
Longer period beneficial (up to 4 months )
•Monitor Healing for up to 1 year*
•If necrosis, RCT indicated
Follow Up:
6,8 wks /4 mo / 6mo/1yr/ 5yrs
What is the treatment for a root fracture (permanent dentition)?
4 weeks
if a root fracture occurs more apically, in may be best to stabilize the tooth for how long?
4 months
if a root fracture occurs more coronally, in may be best to stabilize the tooth for how long?
concussion
Patient presents with tender tooth from bumping it on a table when they fell. There is no displacement and no mobility. The tooth responds positively to sensibility testing. There are no radiographic abnormalities. What is the diagnosis?(permanent dentition)
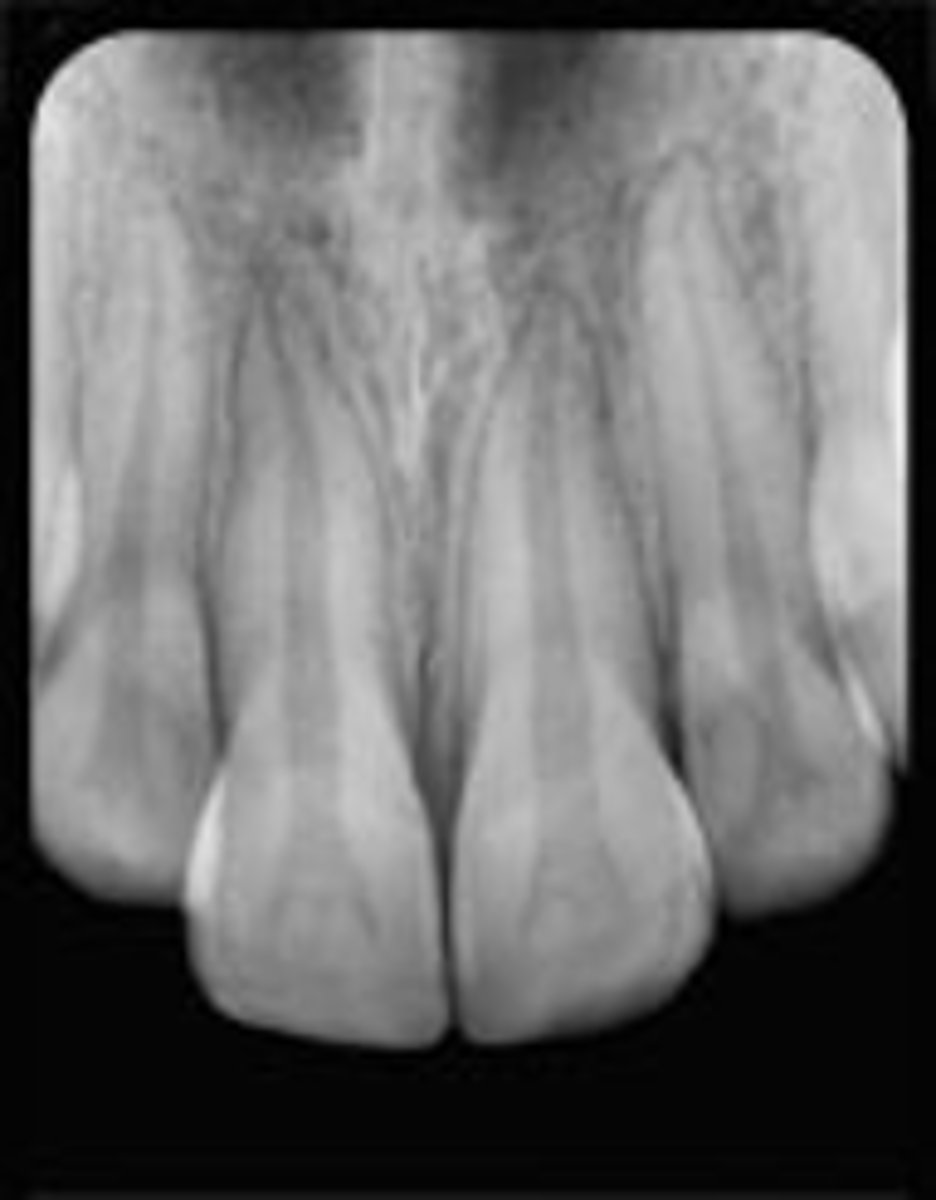
- no treatment, Monitor pulpal condition for 1yr
Follow Up:
4 Weeks clin+ xray /6-8wks / 1yr
What is the treatment for a tooth that has experienced concussion? (permanent dentition)
subluxation
Patient presents with tender tooth from bumping it on a table when they fell. It is tender to palpation. There is slight bleeding from the gingival crevice. There is no displacement, but the tooth has slight mobility. The tooth responds negative to sensibility testing (but that is unreliable). There are no radiographic abnormalities. What is the diagnosis?
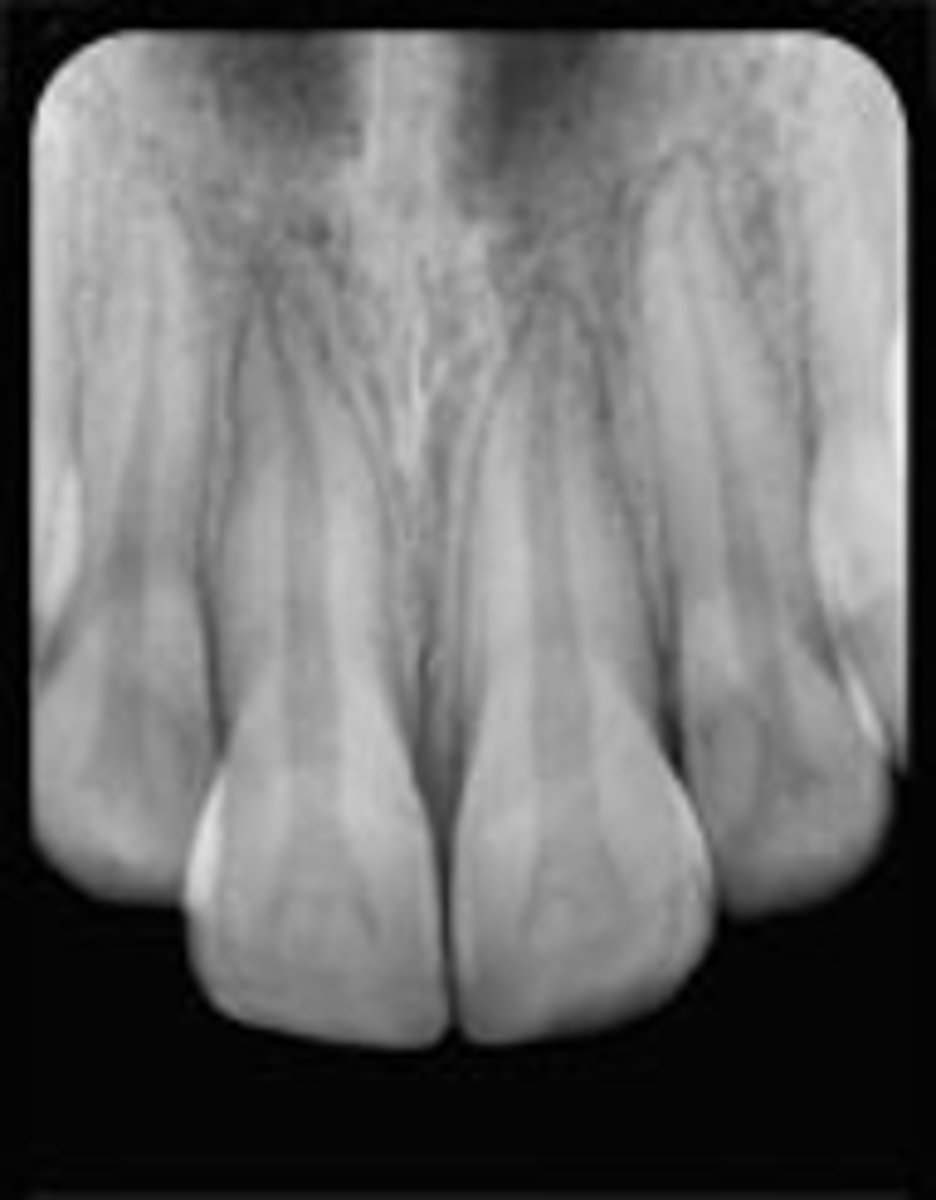
No Treatment needed
*Stabilize tooth for patient comfort
(2 weeks)
Follow up:
2 wks / 4 wks /6-8 wks / 6 mo/1yr
What is the treatment for a tooth that has experienced subluxation? (permanent dentition)
extrusive luxation
Patient presents with tender tooth from bumping it on a table when they fell. It is tender to palpation. There is slight bleeding from the gingival crevice. The tooth is displaced to appear elongated and is excessively mobile. The tooth responds negative to sensibility testing (but that is unreliable). Radiographic shows a PDL space increased apically . What is the diagnosis?
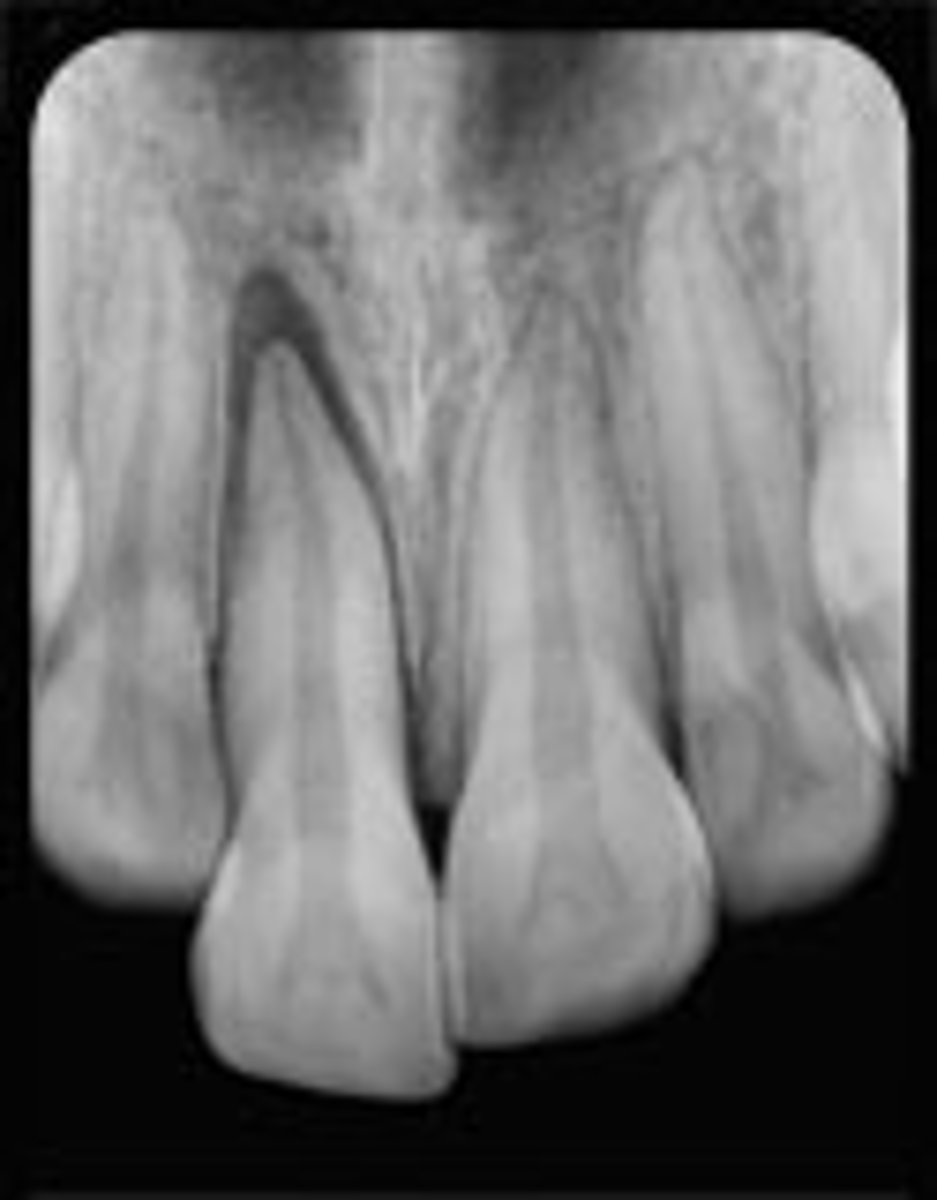
•Reposition by re-inserting gently into its socket
•Splint for 2 weeks (unless breakdown from marginal bone then splint 3-4 weeks additionally)
•RCT if: Mature teeth where pulp necrosis is anticipated
•Evaluate for sign and symptoms that indicate necrosis
Follow up:
•2 wks / 4 wks /6-8 wks / 6 mo/1yr
•Yearly 5 yrs
What is the treatment for a tooth that has experienced extrusive luxation? (permanent dentition)
lateral luxation
Patient presents with tender tooth from bumping it on a table when they fell. The tooth is displaced palatally, no mobility and there is a high metallic sound at percussion. The tooth responds negative to sensibility testing (but that is unreliable). Radiographic shows a widened PDL space and possible alveolar fracture. What is the diagnosis?
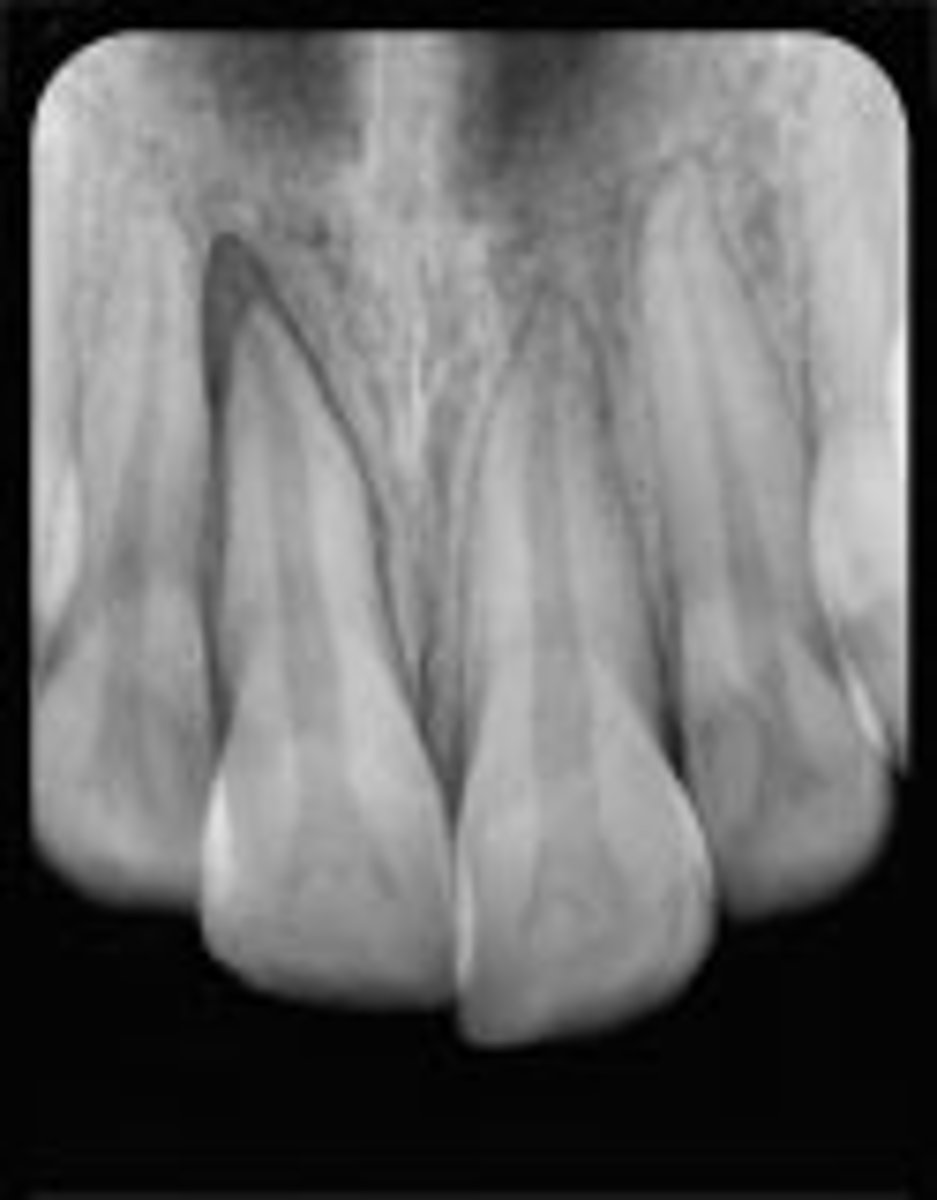
intrusive luxation
Patient presents with tender tooth from bumping it on a table when they fell. The tooth is displaced to appear shortened and is not mobile. The tooth responds negative to sensibility testing (but that is unreliable). Radiographic shows absent PDL space and the CEJ located more apically . What is the diagnosis?
allow to erupt, if no movement after 2-4 weeks reposition surgically/ortho
What is the treatment for a tooth with complete root formation that has intrusive luxation on less than 3mm? (permanent dentition)
-re-position surgically*
-Pulp likely to become necrotic in teeth with complete root formation (RCT w/ CaOH2 2-3 weeks after surgery)
-After reposition, Splint for 4-8 weeks
What is the treatment for a tooth with complete root formation that has intrusive luxation on less more than 7mm? (permanent dentition)
avulsion
Patient presents with missing tooth and wearing dirty baseball uniform. They have the tooth with them sitting in a bag of milk. What is the diagnosis?
Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS)
What is the BEST medium for storing an avulsed tooth?
water
What is the WORST medium for storing an avulsed tooth?
•Reposition as soon as possible or Transfer tooth into reconstituting media
•Take radiograph
•Anesthetize patient
•Replace tooth into socket
•Place non-rigid splint
•Antibiotics 7-10 days
•Chlorhexidine rinses twice a day for 1 week
•Tetanus booster if indicated
•Soft diet for up to 2 wks
Follow-up:
4 weeks
What is the treatment for a tooth that has experienced avulsion? (permanent dentition)
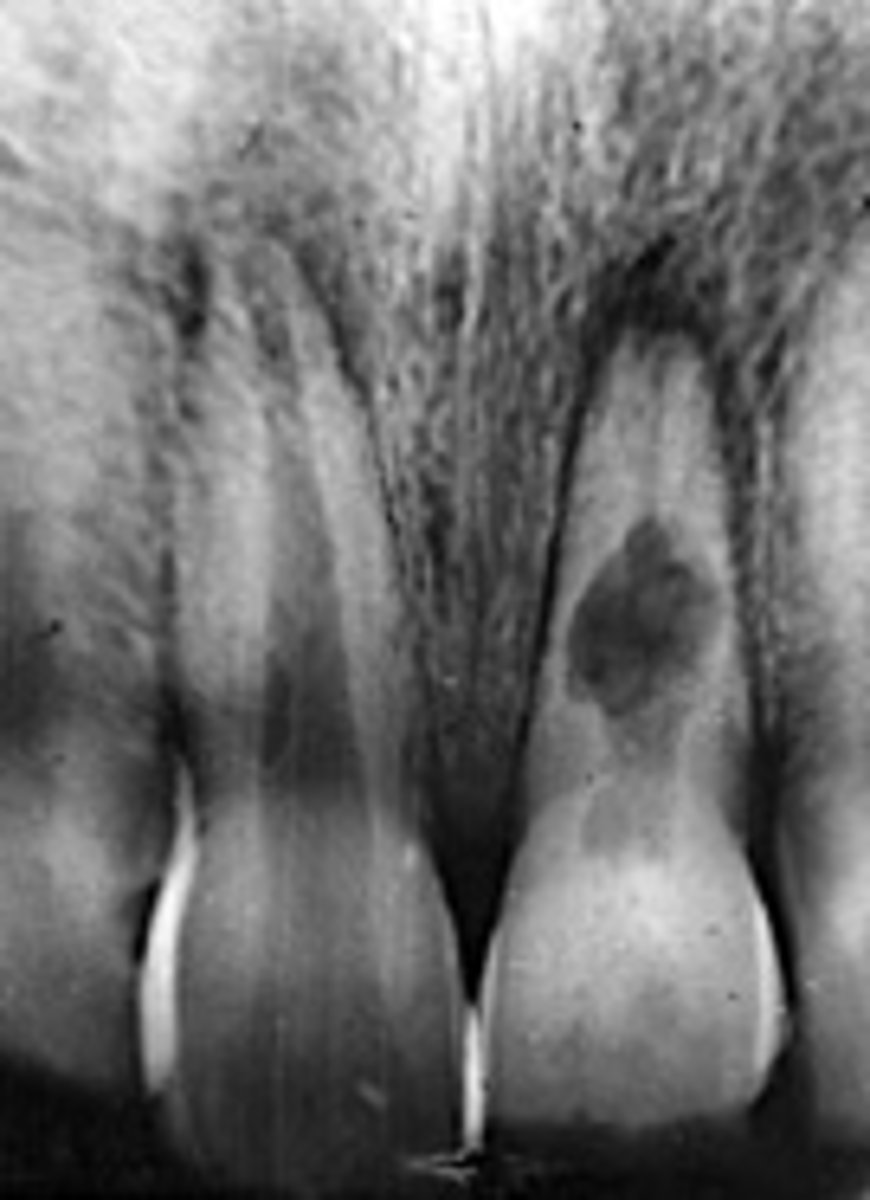
internal resorption
ID the type of resorption:
•pulp is inflamed causing expansion of pulp space
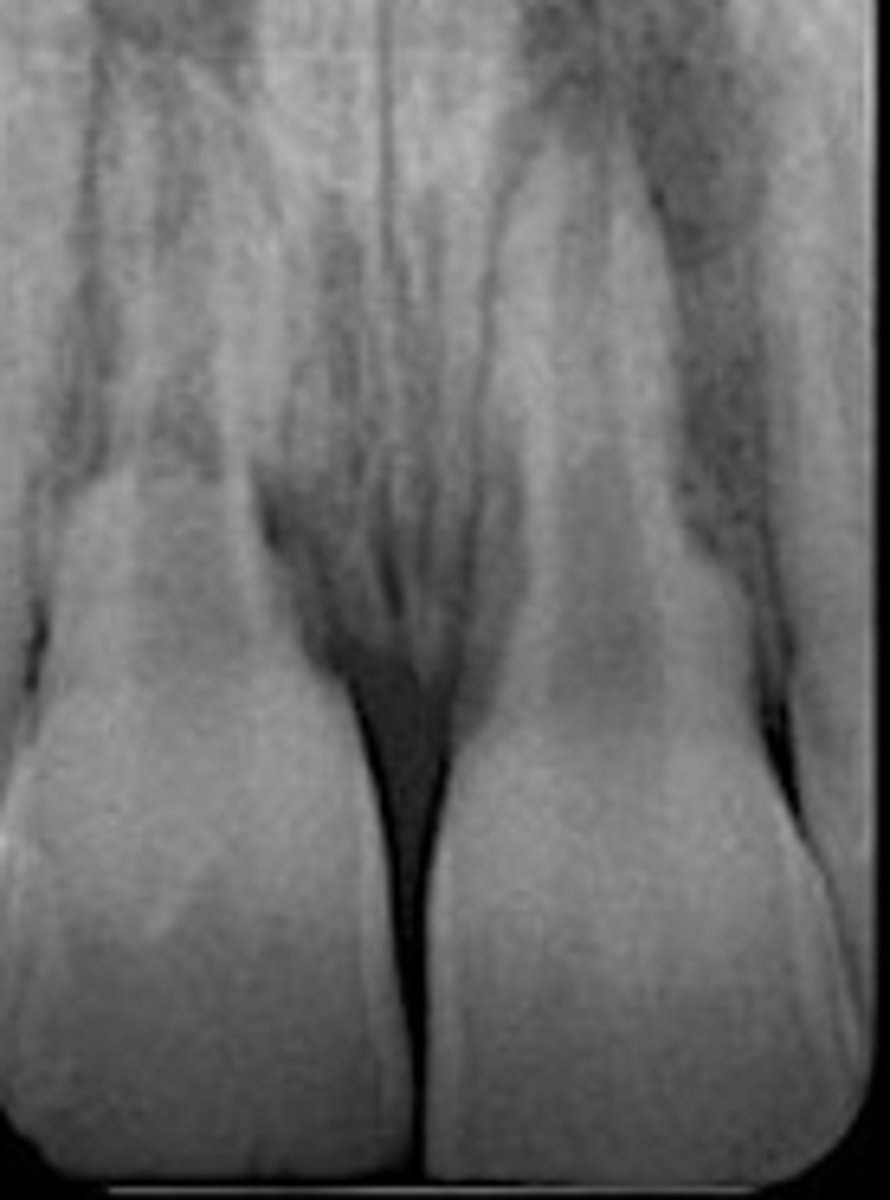
external root resorption
ID the type of resorption:
•widen PDL space and irregular
root surface.
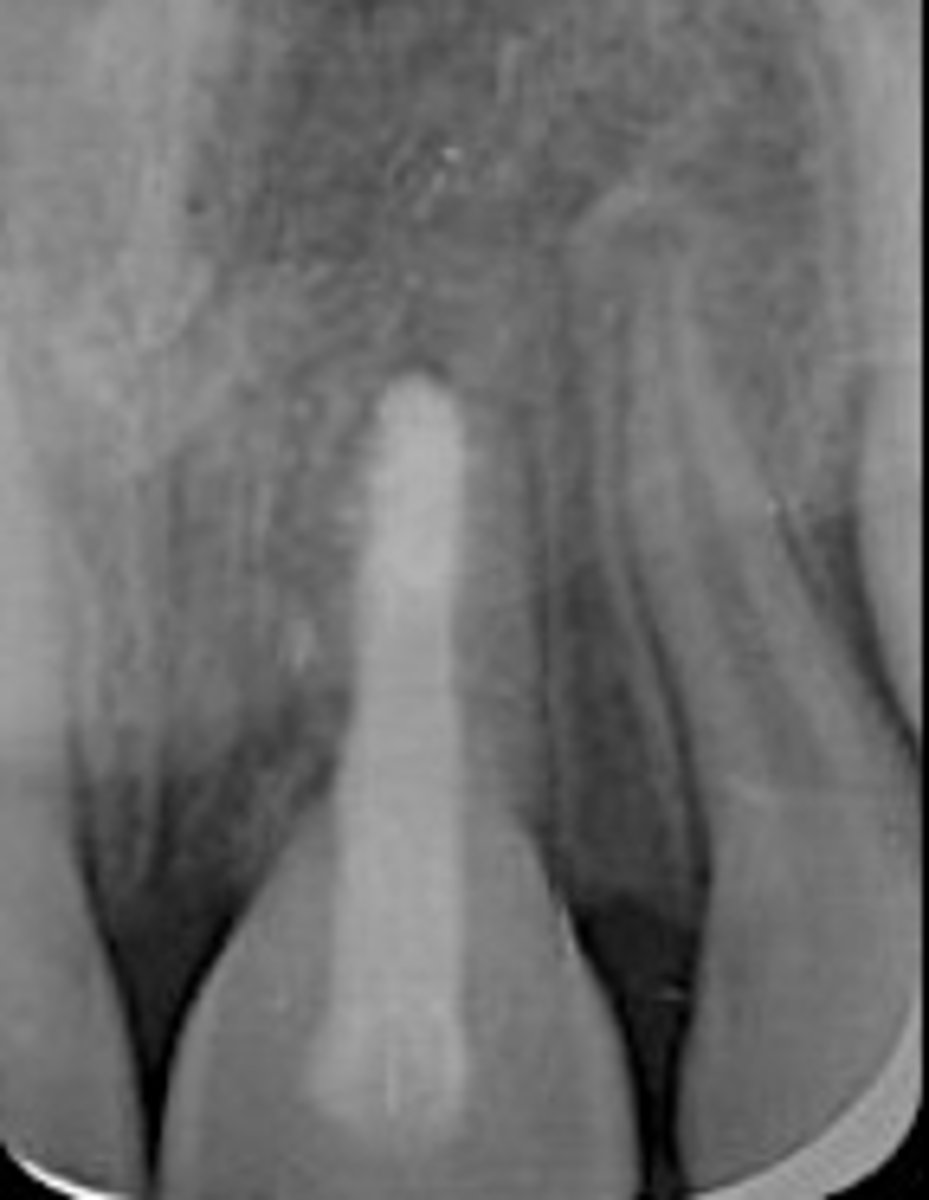
replacement resorption (ankylosis)
ID the type of resorption:
•irreversible injury to PDL, alveolar bone directly contacts and becomes fused with the root surface.
revascularization
For avulsed teeth, antibiotic treatment reduce contamination of the root surface / pulp space, thereby creating a biological environment that aids _______
-change transport to HBSS
-clean root surface and apical foramen with saline
-Soak in doxycycline or Arestin solution for 5 min, replant
-splint up to 2 weeks (7-10days), monitor
-if no revascularization (necrosis) start with RCT.
What is the treatment of an immature avulsed tooth with dry time <60 min?
-change transport to HBSS
-clean root surface and apical foramen with saline, irrigate socket, replant
-Splint up to 2 weeks (7-10days)
-initiate RCT within 7-10 days (CaOH2 for up to a month), complete RCT, monitor.
What is the treatment of a mature avulsed tooth with dry time <60 min?
to prevent external root resorption
Why is a pulpectomy initiated early in a mature avulsed tooth with a dry time of less than?
false
t/f: When a tooth has been out of the oral cavity and with dry time greater than 60min, the PDL still has a chance of survival
replacement resorption (ankylosis)
When a tooth has been out of the oral cavity and with dry time greater than 60min, the PDL has no chance of survival. If such a tooth is replanted, it is likely to undergo ________
-Remove attached non viable soft tissue from root with gauze
-RCT can be started outside the mouth
-replant, splint 4 weeks.
Poor long term prognosis
What is the treatment of an immature avulsed tooth with dry time >60 min?
-Remove attached non viable soft tissue with gauze
-RCT can be carried outside the mouth or 7-10 days after replantation
-replant, splint for 4 weeks.
What is the treatment of an mature avulsed tooth with dry time >60 min?
•Immunocompromised patients
•Severe congenital cardiac anomalies
•Severe uncontrolled seizure disorder
•Severe mental disability
•Severe uncontrolled diabetes
•Lack of alveolar integrity
What are 6 contraindications for the re-implantation of avulsed teeth?
•Smooth rough edges
OR
•Restore with Bonding Agent and Composite Resin
What is the treatment for an enamel fracture (primary dentition)?
•Restore with Resin Restoration or GI to prevent microleakage
Follow up:
3-4 weeks
What is the treatment for an enamel + dentin fracture (primary dentition)?
•Preserve Pulp vitality w/ Partial Pulpotomy CaOh2
•Extraction if:
-Patient's ability to cope with procedure
What is the treatment for an enamel crown fracture with pulp exposure (primary dentition)?
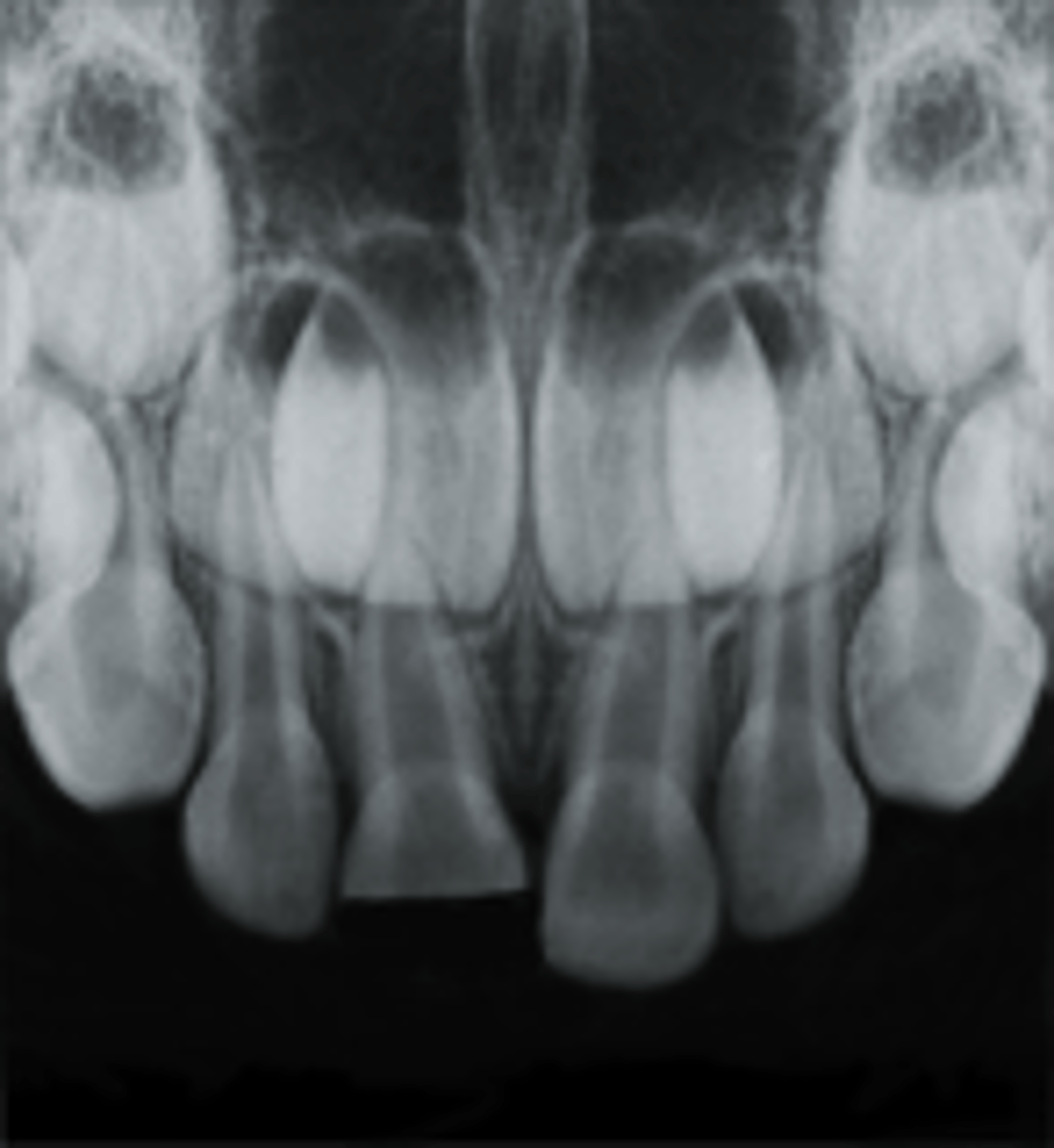
•Fragment Removal: only If fracture involves small part of root and stable fragment large enough to allow coronal restoration.
What is the treatment for a fracture involving enamel, dentin , root structure, pulp NOT exposed (primary dentition)?
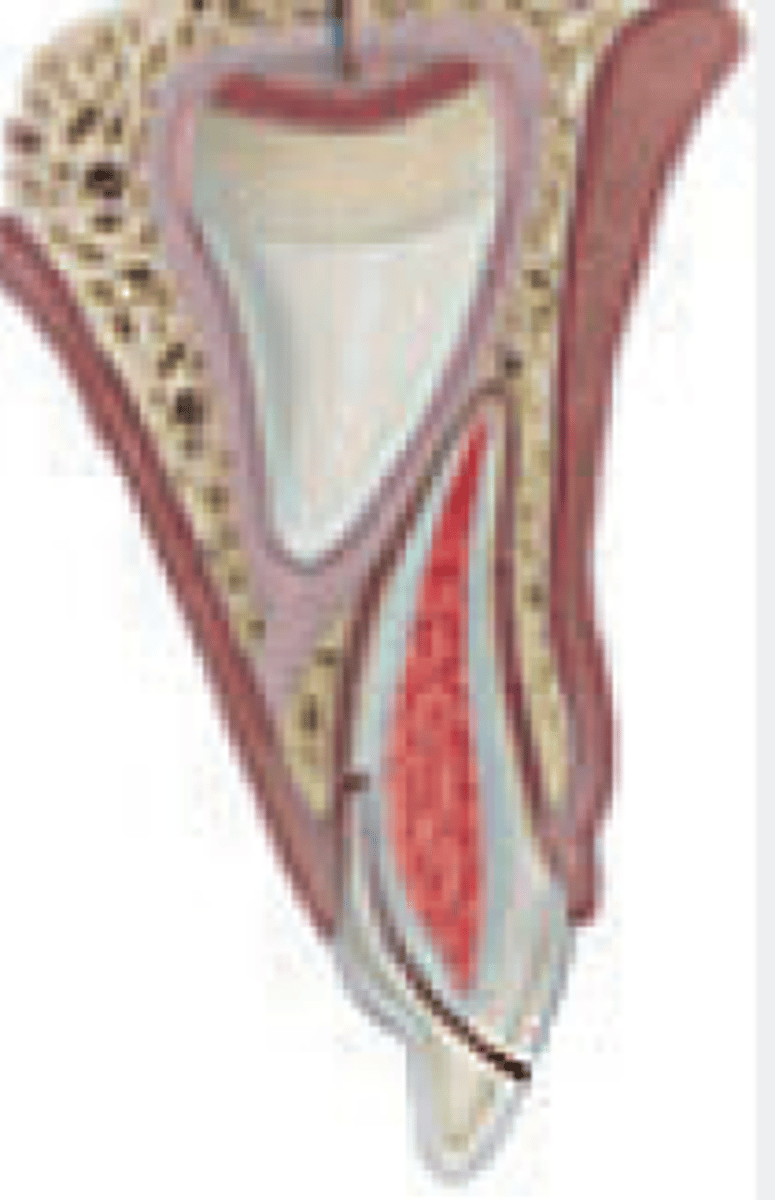
extraction
What is the treatment for a fracture involving enamel, dentine , root structure AND pulp (primary dentition)?
-no treatment
- follow up 1 wk, 6-8wks, 1yr, yearly until exfoliation
What is the treatment for a root fracture with no displacement (primary dentition)?
-Reposition
-Splint
OR
-Extraction of fragment, apical fragment left to be resorbed
What is the treatment for a root fracture with coronal displacement (primary dentition)?
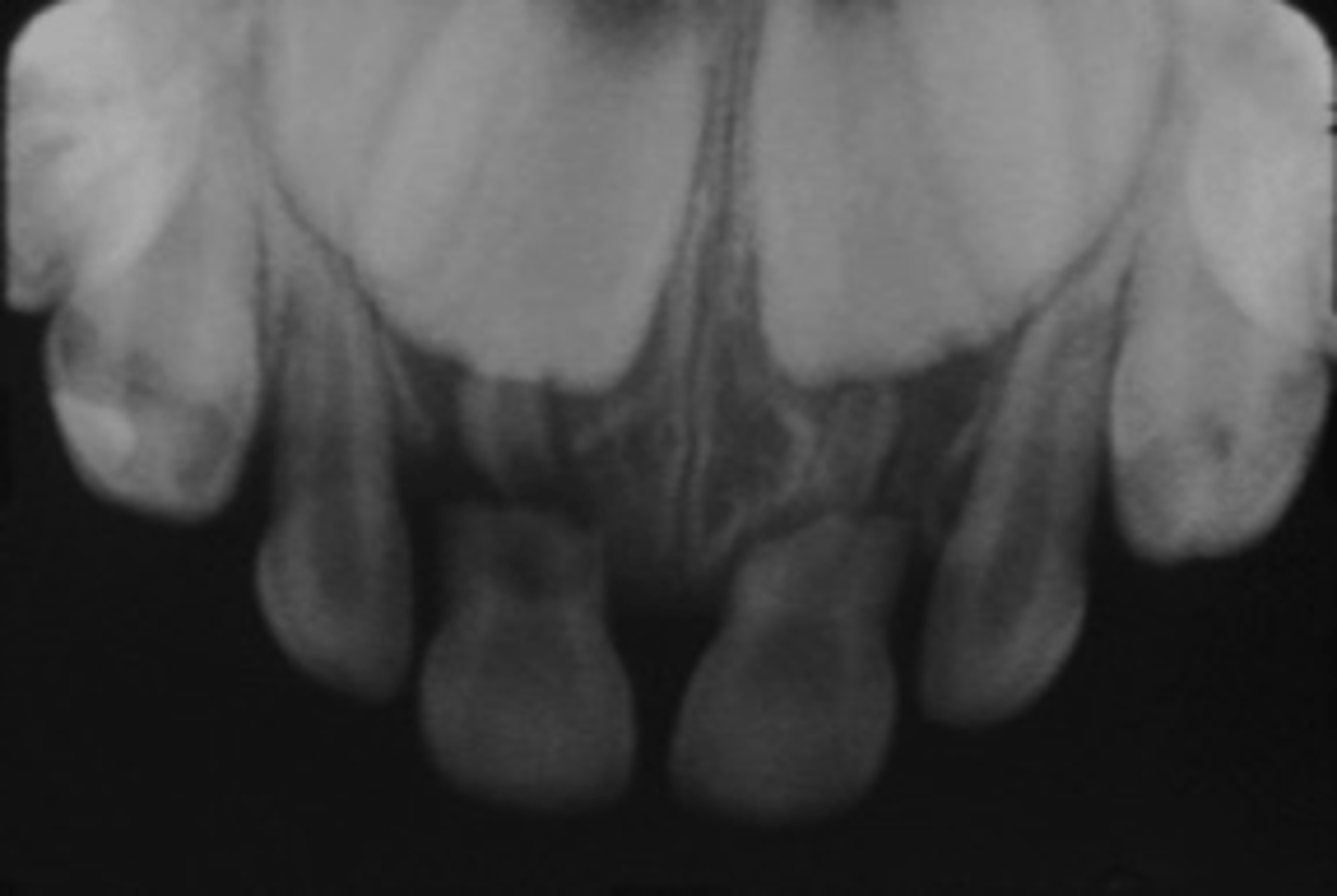
-Reposition displaced segments, splint
-Stabilization segment 4 weeks
-GA often indicated
-Monitor teeth on fracture line
Follow Up;
1 wk,3-4 wks, 6-8 wks, 1 yr and yearly until exfoliation
What is the treatment for an alveolar fracture (primary dentition)?
-Take radiograph (occlusal)
-Palliative treatment
-Inform parents about possible pulpal complication
-Appearance of a vestibular sinus tract, color change of the crown associated with sinus tract indicate pulpal treatment or extraction.
What is the treatment for a concussion or subluxation (primary dentition)?
-Leave for spontaneous alignment
What is the treatment for an extrusive luxation less than 3mm? (primary dentition)?
extraction
What is the treatment for a severely extrusive luxation ? (primary dentition)?
-Leave for spontaneous alignment
What is the treatment for a lateral luxation with no occlusal interference? (primary dentition)?
extraction
What is the treatment for a lateral luxation with severe displacement? (primary dentition)?
-Leave for spontaneous alignment
What is the treatment for an intrusive luxation with the root apex displaced towards or through buccal plate? (primary dentition)?
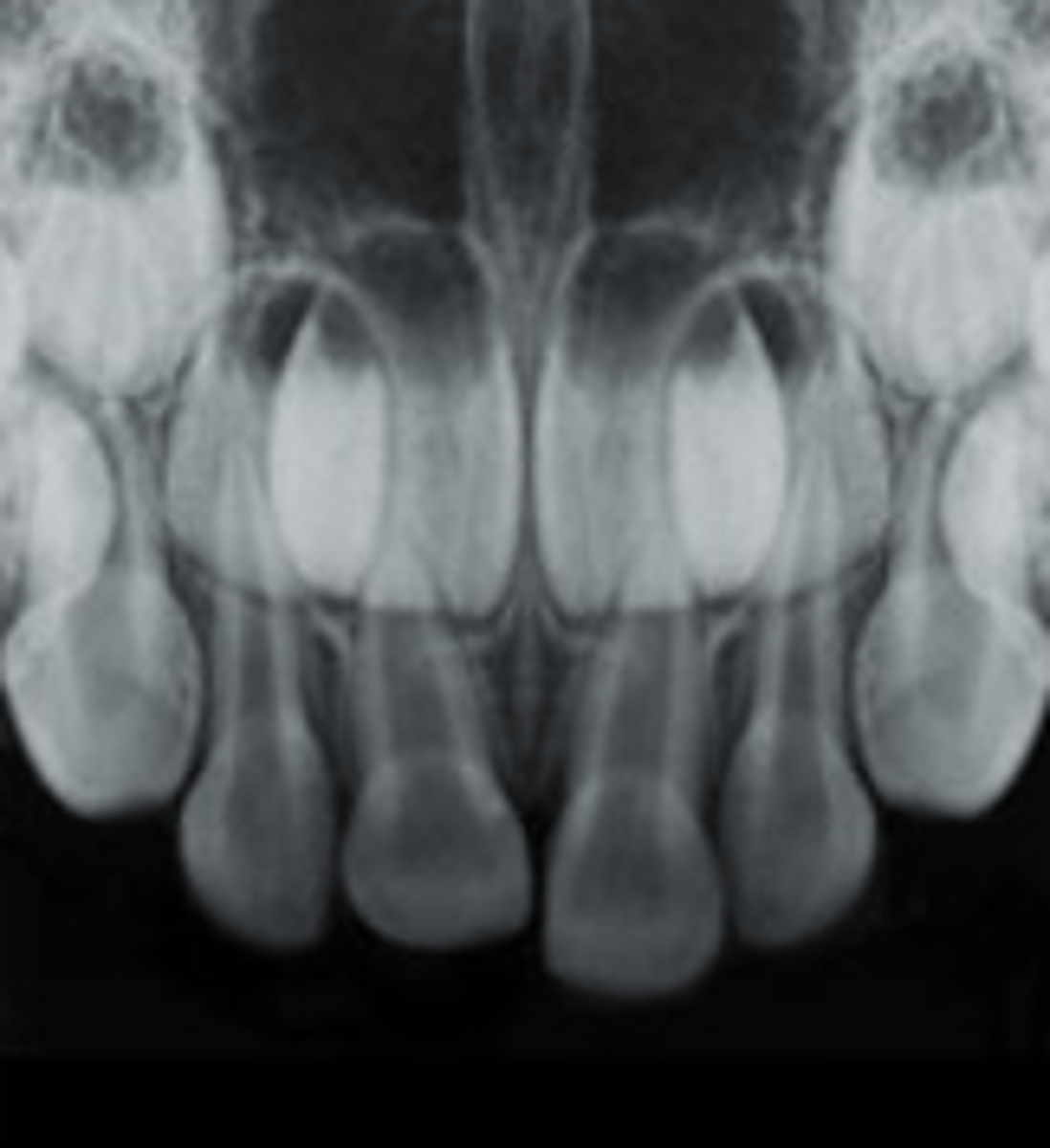
extraction
What is the treatment for an intrusive luxation with the root apex displaced into the developing towards permanent tooth germ? (primary dentition)?
no treatment. Do not reimplant
What is the treatment for a avulsed primary tooth?
- Enamel hypoplasia,
- Hypocalcification
- Crown/root dilaceration
- Disruptions in eruption pattern or sequence
What are some Complications on Permanent Tooth after Primary Tooth's Displacement?