Anatomy 1
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
anatomy skin, bones
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Posterior (Dorsal) Towards the back
Anterior (Ventral) Towards the front
Towards the head
Superior / Cranial
Towards the feet
Inferior / Caudal
Towards the midline
Medial
away from the midline
Lateral
Towards the root of attachment
proximal
away from the root of attachment
distal
Towards the surface of the body
superficial
away from the surface of the body
deep
sagittal / median plane
front / coronal plane
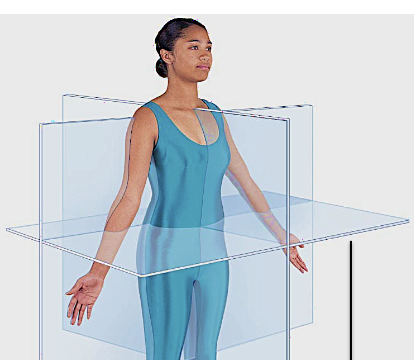
transverse / horizontal plane
what is the watery medium cells float in called?
Extracellular fluid
Examples of non membrane bound organelles
Cytoskeleton, Microvilli, centrioles, cillia, flagella, ribsosomes
Examples of membrane bound organelles
mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, lysosomes, preoxisomes
extracellular is high in
sodium ions and chloride ions
cytosol (intracellualr fluid) is high in
potassium, protiens, amino acid
function of microvilli
increase surface area of the cell, which allows more absorption
cytosol is low in
sodium and carbohydrates
Which organelle is responsible for synthesizing proteins?
Ribosomes
Which organelle houses DNA?
Nucleus
What are the supporting cells of the nervous system called?
(nuero)Glia
Which type of tissue has cells that have an obvious "top" and "bottom"? (polarity)
Epithelial
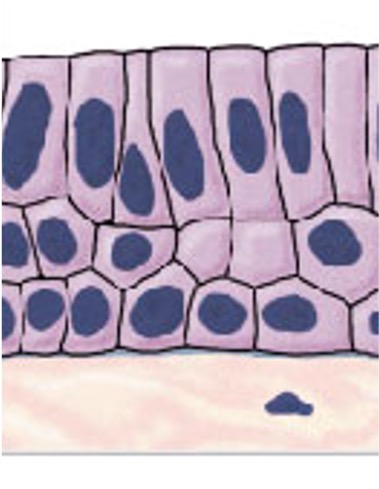
What is this an example of?
Stratified epithelium
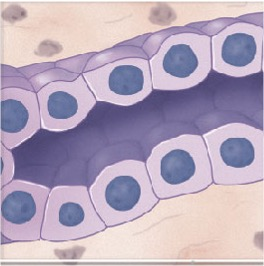
What is this an example of
simple cuboidal
What are the 2 types of cells?
Sex and somatic
Peripheral protiens
attached to either the inner or outer surface, but can detach
What do mitochondria produce the most of in the cell?
ATP
Describe the mitochondrias membrane
double layered, inner membrane folds into cristae (crests) to increase surface area and make more ATP
The nucleus is the ____, surrounded by ____, which is pierced by____, and filled with ______.
control center, nuclear envelope, nuclear pores, nucleoplasm
What are the functions of the ER? (what occurs, what is stored and what is transported)
synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins, storage of certain synthesized molecules, transports other molecules
Rough er
has ribosomes for protein synthesis and export out of the cell
smooth er
synthesis of lipids and carbohydrates
What does the smooth er not have?
ribosomes or proteins
Golgi
synthesis and packaging of secretions, esp protiens
Lysosomes
removes bacteria from cytoplasm through exocytosis, contains digestive enzymes, releases nutrient components into cytosol
Cytoskeleton
Network of of filaments that gives strength and flexibility to cell
4 Cytoskeletal elements
Microfilaments (actin), intermediate filaments, thick filaments (myosin), microtubules
Cilia
Larger microvilli, 9 pairs of microtubules surrounding a central pair (9+2 array), Cilia anchored to compact basal body at base
How do cilia move fluids across the cell surface
they beat rhythmically
Flagella
moves through fluid, only one in humans is sperm
What do ribosomes manufacture?
Proteins
Epithelial Tissue, examples
Covers exposed surfaces, lines internal passageways, produces glandular secretions, skin, mucus, saliva, sebum
Connective Tissue, examples
Fills internal spaces, provides structural support, stores energy, bones, cartilage
Muscle Tissue
Contracts to produce movement
Nervous Tissue
Conducts electrical impulses, carries information
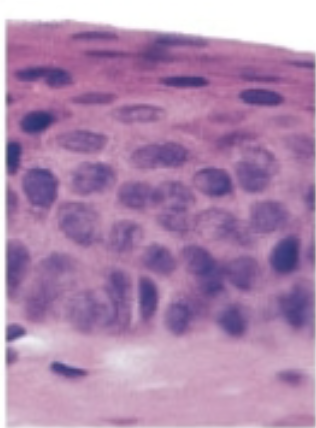
Epithelial Tissue
Connective tissue
Muscle Tissue
Nervous tissue
Cells exhibit____, where the top is _____ and the bottom is _____
polarity, apical surface, basal surface
cells connect to one another at ____
lateral surface
One layer=_____, Several layers=______
simple, stratified
Flat, square/cube, taller than they are wide
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
Location of transitional, Function of transitional
urinary tract, can expand and recoil
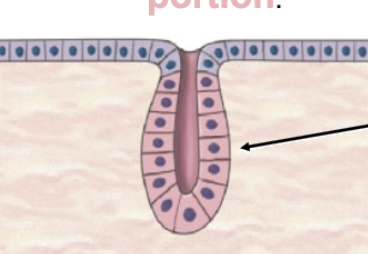
Tubular
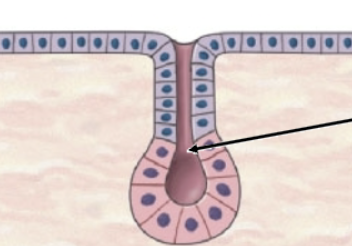
Aveolar
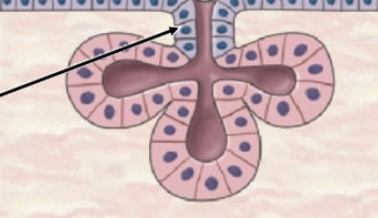
simple
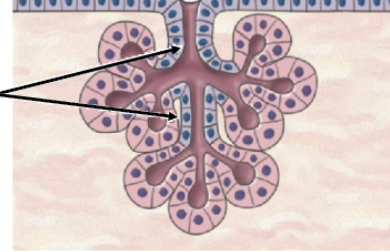
compound
Which of the sweat glands are distributed only in certain areas and become active during puberty?
Apocrine sweat glands
Eccrine/ merocrine mechanism of secretion
secretion by exocytosis (vesicles), only thing released is secretion
Apocrine secretion
Apical portion of cytoplasm is shed, including secretory vesicles
holocrine secretion
Entire cell becomes packed with secretory product and then bursts, Cells replaced by division of basal cells
4 components of connective tissue
cells, protein fibers, ground substance, matrix
5 functions of connective tissue
Transports fluid, protects organs, Supports, surrounds and connects tissues, Stores energy, Defends body from invasion
Fluid connective tissue
collections of cells on a watery matrix
collagen fibers
most common and strongest
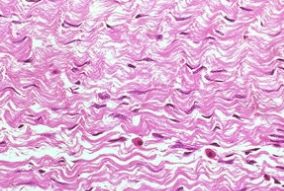
collagen
elastic fibers
contain elastin protein, can branch, stretch and recoil
The concentric rings of bony matrix arranged around Central canals are called
Lamellae
Which type of cartilage has closely-packed collagen fibers in a translucent matrix?
Hyaline cartilage
Which type of cells lay down matrix in order to form bone?
osteoblasts
What do reticular fibers form?
A meshwork
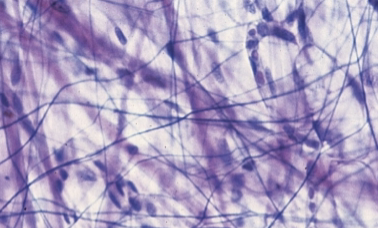
elastic fibers
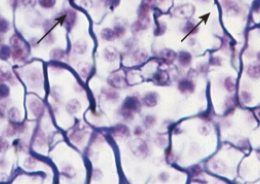
reticular fibers
skeletal muscle
striated (has stripes), voluntary, long, cylindrical, multinucleate
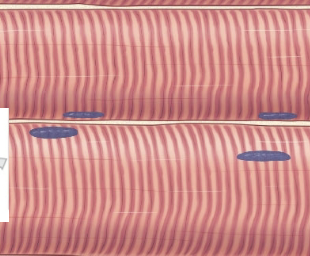
what muscle is this?
skeletal
what muscle is this?
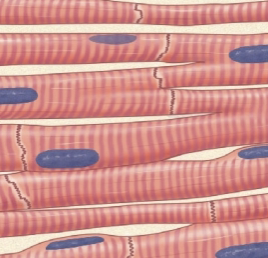
cardiac
Cardiac Muscle
Striated (has stripes), involuntary, short, branched, connected by intercalated discs
Smooth muscle
not striated (no stripes), involuntary, short, spindle-shaped, one nucleus in middle of cell
what type of muscle is this?
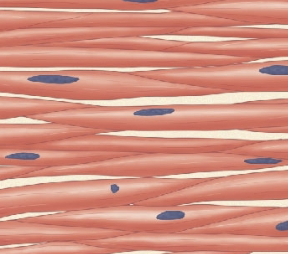
smooth
nervous tissue
conducts electrical impulses from one area of body to another
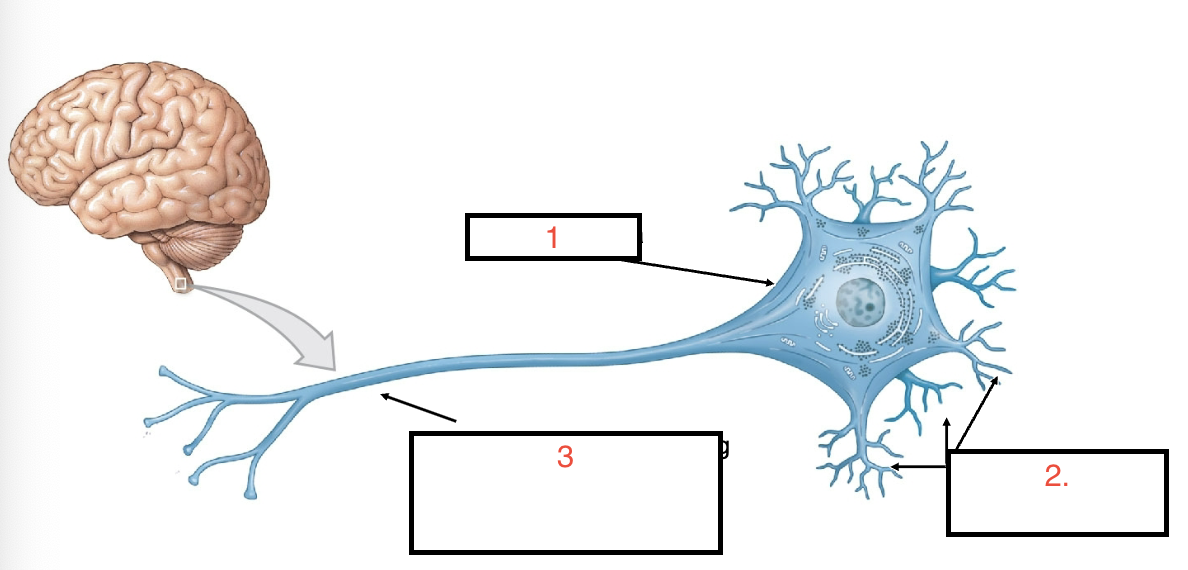
Name 1,2,3
Cell body/ soma, dendrites, axons
What do dendrites do?
receive incoming signals
what do axons do and what is a collection of axons called?
sends outgoing signals, a nerve
What are neuroglia?
support cells
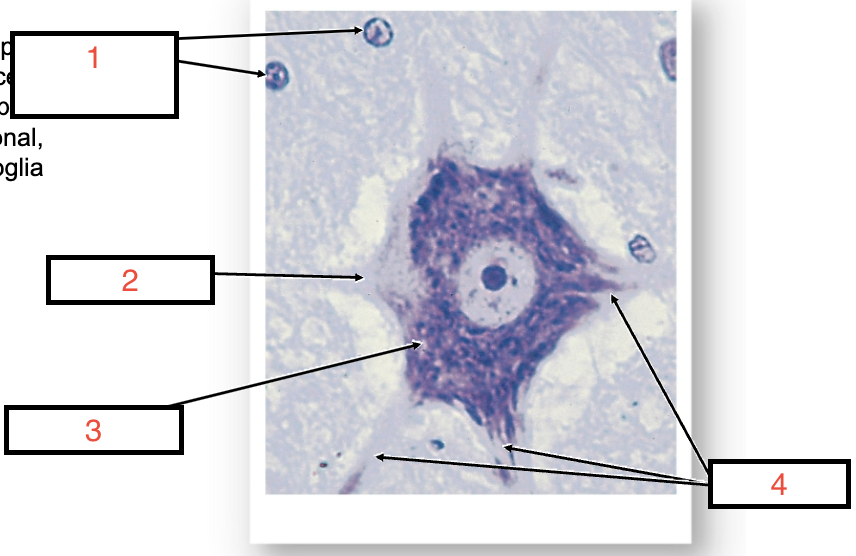
name 1,2,3,4
Neuroglia, axon, soma, dendrites
Why do we have cilia in our respiratory epithelium?
their beat gets rid of particles and moves mucus
Layers of epidermis from top to bottom
(stratum) Corneum, Lucidum, Granulosum, Spinosum, Basale
what cells are in the stratum basale?
keratinocytes, merkel cells and melanocytes
what joins the spines in stratum spinosum?
desmosomes
What layer of the epidermis forms a lipid-rich substance?
stratum granulosum
what is the glassy layer of the epidermis?
stratum lucidum
What binds keratinocytes together in stratum spinosum?
maculae
What is the most abundant cell type in the epidermis?
Keratinocytes
Melanocytes are only found where?
stratum basale
Langerhans’ Cells
Antigen-presenting cells of the epidermis
Where are Merkel Cells found?
stratum basale
Skin color is determined by
rate, amount and ratio