Promoting Culturally Effective Care for Hispanic Families (NOT in midterm)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is culture?
Culture is the integrated pattern of human behavior that includes thoughts, communications, actions, customs, beliefs, values, and institutions of a racial, ethnic, religious, or social group
A child’s occupations are ingrained in the cultural values of their family
The traditional ideologies of occupation have originated from western culture and may not represent pediatric patients whose bases of meaningful activities evolve from different beliefs, values, and worldviews
Culture may influence many factors impacting a child’s occupations, such as parenting styles, views on independence, expectations of child behavior, and family roles
The Cognitive Behavioral Approach to Pediatric Culturally Effective Care (CB-PCE) is based on Cognitive behavioral therapy
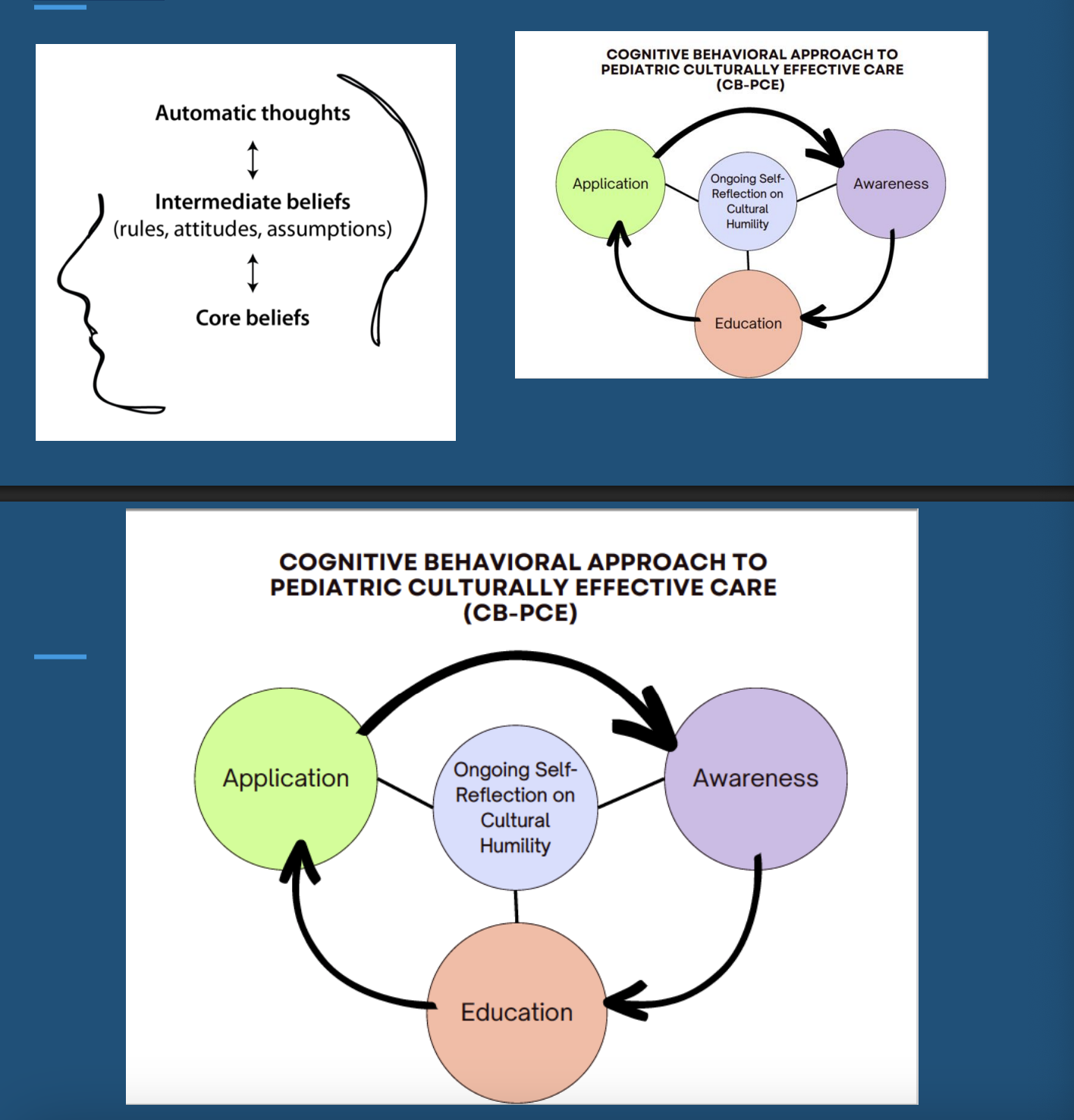
Exploring Bias
What is Implicit Bias?
Implicit bias is a type of automatic thought that an occupational therapist might not be consciously aware of forming, including attitudes or assumptions about a group of people
Why?
Implicit bias occurs unintentionally due to cognitive associations and leads to negative views of a person based on irrelevant factors such as race or ethnicity, which may impact practice
Ethnocentrism and OT practice
Strategies found to reduce implicit bias
Stereotype replacement
Become aware of the automatic thoughts that are stereotypical
Recognize response and identify why it may have occurred
Think about alternative future responses and start consciously using unbiased alternatives
Perspective taking
Research found that perspective-taking can combat automatic expressions of racial biases without simultaneously decreasing sensitivity to ongoing racial disparities
Increased contact with individuals from different racial/ethnic groups
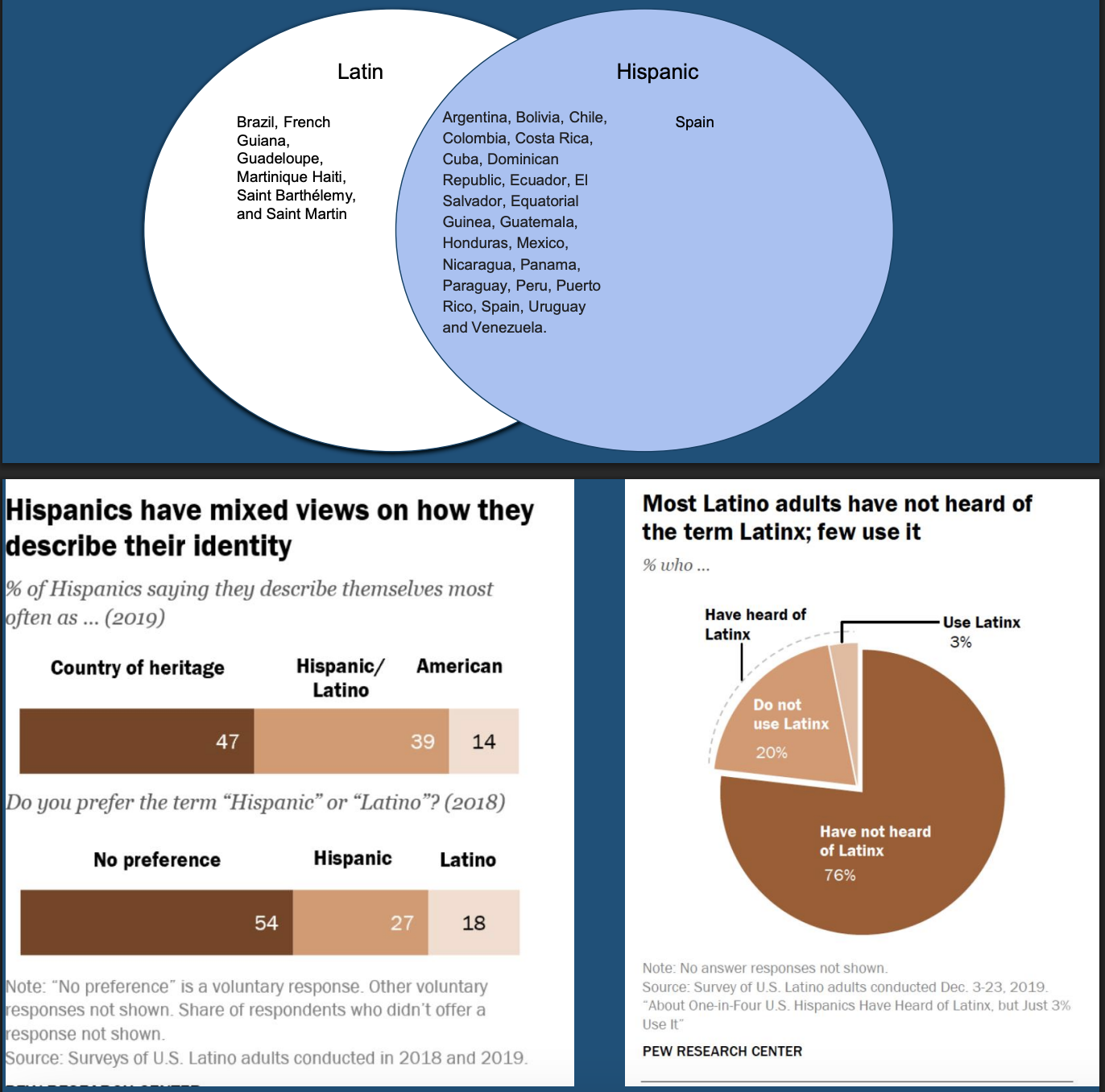
Who is considered Hispanic, Latino/a, or Latinx?
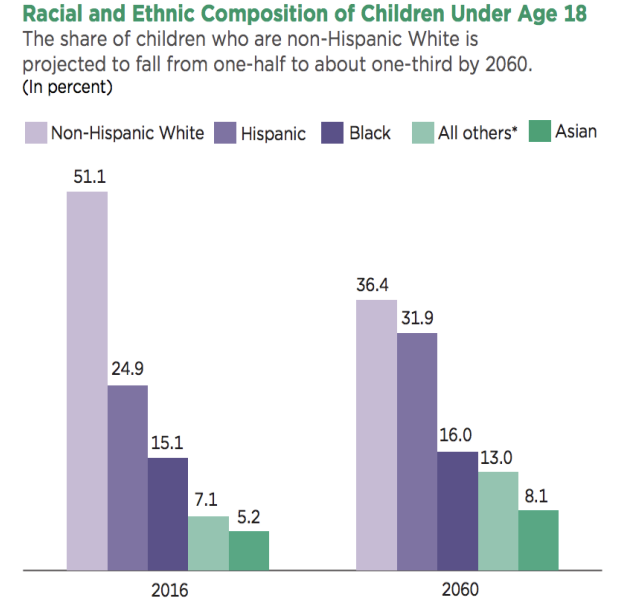
Hispanic Youth Population Growth in the U.S.
One in every 4 children in the U.S. were of Hispanic origin in 2020
One-third of children in the U.S. are projected to be Hispanic by 2060
The Hispanic population makes up the second largest racial/ethnic group in the country and in NYC
AOTA Code of Ethics: Core Value of Justice
“Occupational therapy personnel, by virtue of the specific nature of the practice of occupational therapy, have a vested interest in social justice: addressing unjust inequities that limit opportunities for participation in society”
Occupational injustices are “socially structured, socially formed conditions that give rise to stressful occupational experiences”
Health Disparities
“Health disparities are preventable differences in health and healthcare outcomes due to social, economic, and environmental disadvantages experienced by different populations”
Social determinants of Health
Social and Environmental factors
Socioeconomic Status
Education
Housing
Employment
Racism and Discrimination
Political Factors
Access to Care
Underrepresentation
Laws, services, systems
Cultural & Psychological factors
Beliefs
Values
Spirituality
Access to Care
32% of the Hispanic population is uninsured in the U.S. which is the highest out of any racial or ethnic group
50% of first generation Hispanics are uninsured
Absence of insurance leads to fewer primary care visits and more frequent admissions to emergency rooms
Impact of Immigration Status on Occupational Engagement in the U.S.
Hispanic immigrants make up largest undocumented population in the U.S.
Threat of deportation leads many undocumented Hispanics to
Withdraw from meaningful occupations
Alter engagement in required occupations
Be at risk for exploitation by employers
Fear driving and occupation participation outside of home
Occupations that rely heavily on Mexican immigrant labor pay low wages and seldom offer health insurance, which poses health risks for workers and their families
Primary Barriers to culturally effective care in rehab
Language: Identified as primary cause of health disparities for Hispanic patients
Leads to:
miscommunication of medical information
an increase in unnecessary intubation of trauma patients
Limited Resources
Cultural Barriers
decreased patient satisfaction and quality of care
Primary Facilitators to culturally effective care in rehab
Cultural Awareness amongst practitioners
Cultural Awareness in Services
Use of culturally appropriate assessments and interventions
translated material/resources (always print papers and brochures in Spanish as well!)
Use of visuals for patients without literacy skills
Longer appointments for patients who do not speak English (to account for the time it takes to translate)
Explanations of Health Care Systems
What is the purpose of OT?
What is the role of family members in treatment?
Family-Centered Care
Family-centered care focuses on 3 core concepts
Respect for families and children
Understanding the family’s impact on the child’s well-being
Family-professional collaboration
Values ~ Familismo & Respecto
Dedication, commitment, and loyalty to the family
Collectivist: Group over individual
Respect and obedience for authority figures such as elders and parents
Higher expectations regarding family responsibility & roles compared to non-Latino whites
Higher level of perceived family support
Greater levels of familismo associated with fewer depressive symptoms, behavior problems, and academic difficulties in Latino adolescents
Structure of the Family
Extended Families:
Common to see different generations living in the same household
Family members may be consulted before making medical decisions
Hispanic families often care for elders in the home opposed to nursing homes
Children are often expected to “do better” than the previous generation
How would caregiving for a child and grandparents at the same time impact a parent?
Gender Roles “Machismo y Marianismo”
Men traditionally take on the role of the provider, decision-maker, protector, and leader in the family
Women are expected to care for the home, children, and to be very selfless
Beliefs Regarding Health
Views on Disability
Many Hispanic families view their child’s disability as coming from God
Some Hispanics view disability as a punishment from God due to the sins they had committed
Others view disability as a gift from God
It is common to view disability as belonging to the family and not just the child
Shame may be associated with a genetic defect
Physical Disability is more acceptable than mental illness
Mental health stigmas “nervios”
Medicine
Common to combine natural home remedies with Western medicine
Home & Folk remedies
Curandismo: Folk healer
Natural herbs and tea are commonly used
Sobador/a: person gives a massage to treat a condition (ex., indigestion)
Santero: Santeria traditional healer
Religion
The majority of Hispanics are Christian with Roman Catholic being the most popular denomination
Faith is often center of family
Support System
Counseling Services
Community Life & Celebrations (ex., quinceaneras)
Strategies to enhance treatment engagement & rapport
Overcoming Language Barriers
Developing Shared Understanding of child’s disability
Collaborating with caregivers
Ensuring caregivers understand the treatment process
Communication with Hispanic families:
Verbal communication should be respectful avoid calling parents by first name unless they identify a preference
Physical connection very common; typical greetings include a hug and kiss on the cheek
Important to know Spanish varies from country to country with different dialects, phrases, and norms
Strategies for OT Evaluations
Collaborate with child and caregivers to understand child volition by exploring child and family cultural interests, beliefs, and values that impact child occupations
Identify habits and roles the family and child prioritize and exploring how culture influences expectations associated with the roles
Assess how environmental factors such as physical, social, cultural, economic, and political factors can either facilitate or hinder a child’s occupational performance
Environmental stressors:
Discrimination, exclusion, etc.
Implement language translation services when necessary to effectively communicate with the child and caregivers.
Tips for Using Interpreters
Introduce yourself to interpreter
Speak directly to patient during session
Pause often so all information can be translated in its entirety
Ask one question at a time
Ask about potential cultural misunderstandings
Insist that everything patient says gets interpreted
Ask patient to repeat back information that you want to make sure they understand
Surnames
Common to have multiple Surnames
Important to include proper Surnames in billing and documentation
Inconsistent documentation of multiple surnames contributes to patient errors and delays in receiving services due to misidentification
Documentation
Assessments
Identify assessments available in patient’s preferred language
Use translator when able to
Family translators might re-word during translation using a translator helps with validity of results
Patient Education
Use pictures when possible
Demonstrate activities and have patient imitate
Notes
Document use of translator
Becoming Agents of Change
Advocate for patients from culturally diverse backgrounds
Create inclusive environments in work sites
Seeking resources to continue to learn and develop culturally effective practice
Work towards promoting diversity within OT
Recruitment
High school/college presentations in diverse communities
Media representation
Retention:
Inclusive environment in education
Cultural resources for students