Management of Patients with Burns
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to burn management, types of burns, treatment strategies, physiological responses, and psychological impacts of burn injuries.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What are the key characteristics of burn injuries?
Burn injuries are painful, costly, disfiguring, require intensive rehabilitation, and often lead to long-term disability.
What type of burn involves only the outermost layer of skin?
First-degree burns.
What are the main predictors for mortality in burn injuries?
Increased percent of TBSA burned, presence of inhalation injury, and increased age.
What method estimates burn extent using approximate percentages for each body part?
The rule of nines.
What is the classification for burns that involve total destruction of the epidermis and dermis?
Third-degree (full-thickness) burns.
What is a common complication associated with burns on the face and neck?
Respiratory obstruction due to mechanical obstruction from edema.
What phase of burn recovery begins immediately after injury and lasts until fluid resuscitation is complete?
Emergent/resuscitative phase.
What are the three phases of burn recovery?
Emergent/resuscitative, acute/intermediate, and rehabilitation.
What are key signs that may indicate an inhalation injury?
Hoarseness, singed facial hair, and carbonaceous sputum.
What is the significance of the zone of coagulation in burn injuries?
It's the central area of tissue necrosis that occurs during the injury.
What is the typical resuscitation fluid for burn patients?
Lactated Ringer's (LR) solution.
What is the recommended urinary output for proper fluid resuscitation in adults with burns?
0.5 to 1 mL/kg/h.
What type of scars may form after deep burns?
Hypertrophic scars and keloid scars.
What is the goal of nutritional support for burn patients?
To promote a state of nitrogen balance and match nutrient utilization.
What is a common breast injury associated with burns to the chest?
Possible respiratory obstruction due to circumferential burns.
What is a major risk factor for developing complications in burn patients?
Preexisting cardiovascular, respiratory, or renal disease.
What are the main factors that determine the severity of a burn?
Patient age, burn depth, %TBSA burned, presence of inhalation injury, and comorbid conditions.
What is the primary goal of burn prevention?
Nearly all burns are preventable.
What are the treatment options for managing burn pain?
Use of opioids, NSAIDs, anxiolytics, and anesthetic agents.
What are common signs of systemic infection in burn patients?
Increased temperature, tachycardia, tachypnea, and leukocytosis.
How does early excision of burn wounds impact recovery?
It reduces risks of complications and supports faster healing.
What is the recommended positioning strategy for patients with extensive burn injuries?
Elevate burned extremities above heart level.
What is a potential psychological response of burn patients during recovery?
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Severity of a Burn Factors
• Age
• Depth
• Extent
• Location
• Patient risk factors
Classification of Burns
• First-degree
• Second-degree
• Third-degree
• Fourth-degree
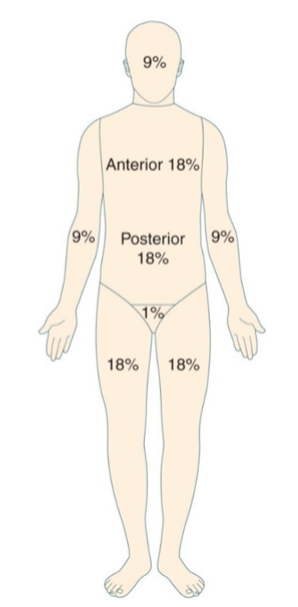
Extent of Burns
• Rule of Nines
• Lund and Browder method
• Palmer method
A client is admitted to the ED with burns to the face, anterior trunk and both
arms. Using the Rule of Nines – what is the TBSA burned?
Face is 4.5
Anterior Trunk 18
Both arms 9 + 9 = 18
18 + 18 + 4.5 = 40.5%
Pathophysiology of Burns
• Cause
• Zones
• Depth
Effects of Major Burn Injury
• Cardiovascular
• Fluid and electrolyte
• Pulmonary injury
• Renal
• Immunologic/Thermoregulation
• GI
Phases of Burn Injury
• Emergent or resuscitative phase
• Acute or intermediate phase
• Rehabilitation phase
Emergent/Resuscitative Phase
On-the-Scene Care
• Prevent injury to rescuer
• Stop injury: extinguish flames, cool the burn, irrigate
chemical burns
• ABCs: establish airway, breathing, and circulation
• Start oxygen and large-bore IVs
• Remove restrictive objects and cover the wound
• Do assessment surveying all body systems and obtain a
history of the incident and pertinent patient history
• Note: Treat patient with falls and electrical injuries as for
potential cervical spine injury
Breathing must be assessed and patent airway established immediately during the initial minutes of emergency burn care
True
Fluid and Electrotype Shifts—Emergent/Resuscitative Phase
• Generalized dehydration
• Reduced blood volume and
hemoconcentration
• Decreased urine output
• Trauma causes release of potassium into
extracellular fluid: hyperkalemia
• Sodium traps in edema fluid and shifts into
cells as potassium is released: hyponatremia
• Metabolic acidosis
Emergent/Resuscitative Phase
• Patient is transported to emergency department
• Fluid resuscitation is begun (ABA formula)
• Foley catheter is inserted
• Patient with burns exceeding 20% to 25% should have an
NG tube inserted and placed to suction
• Patient is stabilized and condition is continually monitored
• Patients with electrical burns should have ECG
• Address pain; only IV medication should be administered
• Psychosocial consideration and emotional support should
be given to patient and family
The ABA fluid resuscitation formula:
• For thermal or chemical burn
• 2 mL LR × patient’s weight in kilograms × %TBSA second-, third-, and fourth-degree
burns
• For adults with electrical burns:
• 4 mL LR × patient’s weight in kilograms × %TBSA second-, third-, and fourth-degree
burns
• ½ give over 1st 8 hours from initial burn
• ½ given over next 16 hrs
A patient presents to the ED 2 hours after the initial burn with a 50% TBSA
thermal burn. He has receive 1 L in the field. He is 80kg. What will you set
the fluid rate at on your pump initially?
2 X 80 x 50 = 8,000ml/24 Half is 4,000
3,000/6 = 500 ml/hr
Formulas are only a guide for burn care fluid resuscitation. How often
must the patient’ s response to fluid therapy (heart rate, blood
pressure, and urine output) be evaluated?
A. Every hour
B. Every 2 hours
C. Every 3 hours
D. Every 4 hours
Every hour
Acute/Intermediate Phase of Burn Injury
• Promoting adequate ventilation
• Restoring fluid/electrolyte balance
• Preventing infection
• Modulating hypermetabolism
• Promoting skin integrity
• Relieving pain and discomfort
• Promoting mobility
• Strengthening coping strategies
• Supporting patient and family processes
• Monitoring and managing complications
Potential Complications during the Acute/Intermediate Phase
of Burn Injury
• Acute respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome
• Heart failure and pulmonary edema
• Sepsis
• Delirium
• Visceral damage (electrical burns)
Burn Wound Care
• Wound cleaning
• Use of topical agents
• Wound debridement
• Wound dressing, dressing changes, and skin grafting
Débridement
• Natural
• Surgical
• Mechanical
• Chemical
Grafting
• Autografts
• Homografts
• Xenografts
• Biosynthetic and Synthetic Dressings
Rehabilitation Phase
• Highest level of function possible
• Limit scarring
• Prevent complications
Rehabilitation Phase
• Rehabilitation is begun as early as possible in the emergent
phase and extends for a long period after the injury
• Focus is on wound healing, psychosocial support, self-
image, lifestyle, and restoring maximal functional abilities so
that the patient can have the best quality life, both
personally and socially
• The patient may need reconstructive surgery to improve
function and appearance
• Vocational counseling and support groups may assist the
patient
What factors affect the severity of burn injury?
The severity of burn injury is affected by factors such as the thickness and extent of the burn, the location on the body, the age and health of the individual, and the cause of the burn.
What are the local effects of a major burn injury?
Local effects of a major burn injury include tissue damage, pain, swelling, and open wounds that may lead to infection.
What are the systemic effects of a major burn injury?
Systemic effects include fluid loss, hypovolemic shock, electrolyte imbalances, increased metabolic demands, and potential respiratory issues.
What are the priorities of care in the emergent phase of burn recovery?
In the emergent phase, priorities of care include securing the airway, breathing and circulation (ABCs), controlling pain, preventing infection, and initiating fluid resuscitation.
What are potential complications in the acute phase of burn recovery?
In the acute phase, potential complications include infection, sepsis, fluid overload, and organ failure.
What are the priorities of care in the rehabilitation phase of burn recovery?
In the rehabilitation phase, priorities include maximizing physical function, preventing contractures and psychological effects, and promoting social reintegration.
How can fluid replacement requirements be planned during the emergent phase of a burn injury?
Fluid replacement can be planned using the ABA formula and the Rule of Nines to determine the percentage of body surface area burned and the fluid needs.
What is the nurse’s role in burn wound management during the acute/intermediate phase?
The nurse's role includes assessing the wound, administering medications, performing dressing changes, monitoring for infection, and educating the patient about wound care.
What is involved in the rehabilitation phase of burn management?
The rehabilitation phase involves physical therapy, occupational therapy, psychosocial support, and ongoing wound care to promote recovery and independence.