Using resources
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Ammonia is an industrial product mainly used to make ___
Fertilisers
Ammonia is manufactured using the __ __
Haber process
The haber process involves a ___ reaction between n____ and h____
Reversible, nitrogen, hydrogen
The reaction used in the Haber process can reach a ___ ___
Dynamic equilibrium
What is defined as ‘when a reversible reaction in a closed system reaches a balance where the rate of the forward reaction = the rate of the reverse reaction’?
Dynamic equilibrium
In the Haber process, what is the pressure of the mixture of gases increased to?
200 atmospheres
During the Haber process, what temperature is the pressurised mixture of gases heated to?
450 degrees
During the Haber process, the mixture of gases is passed through a tank containing an ___ ___
Iron catalyst
At the end of the Haber process, the reaction mixture is cooled so that ___ liquifies and can be removed
Ammonia
At the end of the Haber process, unreacted nitrogen and hydrogen are ___
Recycled
Fertilisers provide ___ ___ needed for healthy growth in plants
Mineral ions
Fertiliser is added to plants to increase the ___ of certain mineral ions
Concentration
What elements are found in NPK fertilisers?
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium
Fertiliser compounds must be ___ in water so they can be absorbed by the root hair cells
Soluble
Is potable water the same as pure water?
No
What is the name for water that has sufficiently low levels of dissolved salts and microbes so that it is safe for humans?
Potable water
What is the name of the process that makes potable water from sea water?
Desalination
Name 2 ways that desalination can be achieved
Distillation, reverse osmosis
Distillation requires a lot of ___ and the waste water is so salty that it can be difficult to dispose of ___
Energy, safely
Which type of desalination occurs when water is put under high pressure and passed through a membrane that prevents most ions and molecules that aren’t water from passing through?
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis requires ___ membranes and its efficiency is often quite ___
Expensive, low
What does LCA stand for?
Life cycle assessment
Stage 1 of an LCA is extracting and processing the ___ ___ needed
Raw materials
Stage 2 of an LCA is ____ the product and its packaging
Manufacturing
Stage 3 of an LCA is using the product during its ___
Lifetime
Stage 4 of an LCA is disposing of the product at the end of its ___ ___
Useful life
At (some/all) stages, an LCA can include information about energy use, transport of materials and the release of waste substances
All

Which biological method of metal extraction is shown below?
Phytomining
Phytomining is a (slow/fast) process
Slow
Phytomining reduces the amount of __ __ that must be disposed of after traditional mining
Rock waste
Phytomining ___ the limited supplies of high grade ores
Conserves
Which biological method of metal extraction uses bacteria to break down low grade ores into an acidic solution containing copper ions?
Bioleaching
What is the name of the acidic solution produced by bacteria during bioleaching?
A leachate
Bioleaching produces (safe/toxic) substances including s__ a___
Toxic, sulfuric acid
Phosphate rock reacts with ___ ___ to produce calcium nitrate and phosphoric acid
Nitric acid
Phosphate rock reacts with ___ ___ to produce single superphosphate
Sulfuric acid
Phosphate rock reacts with ___ ___ to produce triple superphosphate
Phosphoric acid
Ammonium sulfate is a salt used as a ___
Fertiliser
Ammonia + ___ ___ —> ammonium sulfate
Sulfuric acid
Sulfur, oxygen and water are the raw materials that make up ___ ___
Sulfuric acid
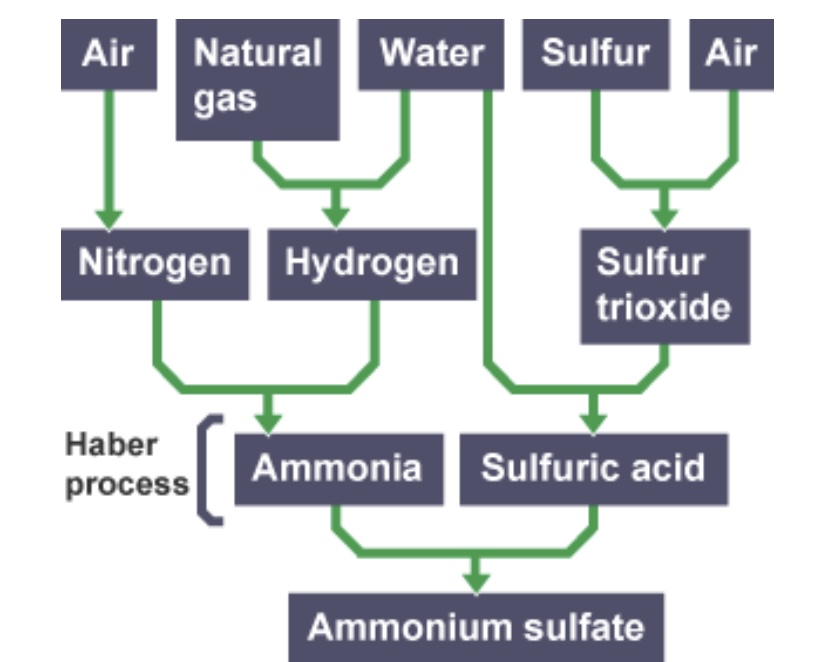
What temperature does the reaction between ammonia gas and sulfuric acid take place at?
60 degrees
Sometimes during the Haber process, the energy from the exothermic reaction can be used to generate ____
Electricity