Measuring economic activity: Business Cycle
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 3, Microeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
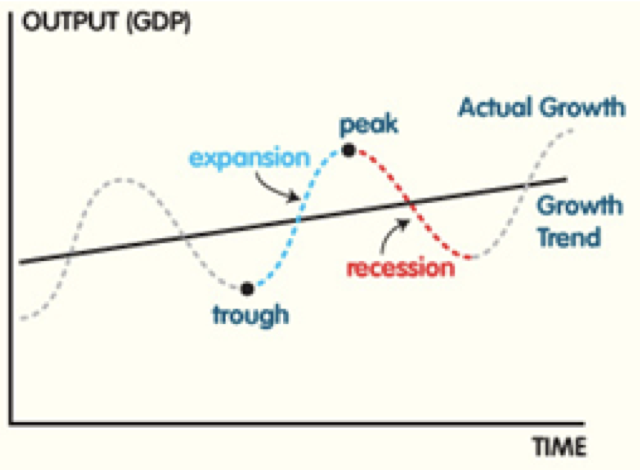
Business cycle
The short-term fluctuations of real GDP around its long-term trend (or potential output).
Long-term growth
Growth over long periods of time. In the PPC model this is shown by outward shifts of the PPC. When shown in the AD–AS model (the AD–AS model considers the AD and AS curves together), it is shown by rightward shifts in the LRAS curve.
Long-term growth trend
Refers to average growth over long periods of time shown in the business cycle diagram as the line that runs through short-term fluctuations, indicating changes in potential output
Potential output
Output produced by an economy when it is at full employment equilibrium, or long-run equilibrium according to the monetarist/new classical model.
Growth in production possibilities
When the production possibilities of a country increase because of more/better resources
and/or better technology becoming available; illustrated by a shift outwards of the PPC.
Actual growth
Occurs when real output (real GDP) increases through time and is a result of greater or better use of existing resources. In the PPC model it can be illustrated by a movement from a point inside a PPC to another point in the northeast direction.
Economic growth
Refers to increases in real GDP over time.
Short-term fluctuations of economic activity
Periods of growth of real GDP followed by periods of contraction, which are part of the business cycle.
Recession
Occurs when real GDP falls for at least two consecutive quarters.
Cyclical (demand deficient) unemployment
Unemployment that is a result of a decrease in aggregate demand and thus of economic activity; it occurs in a recession.
Business Cycle Diagram