BIOL2402 Lab Final
1/446
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
447 Terms
what does the dome represent in the bell model
thoracic cavity
what do the balloons represent in the bell model
lungs
what does the rubber membrane represent in the bell model
diaphragm
what does the tube entering the hole at the top of the ventilation model represent
trachea
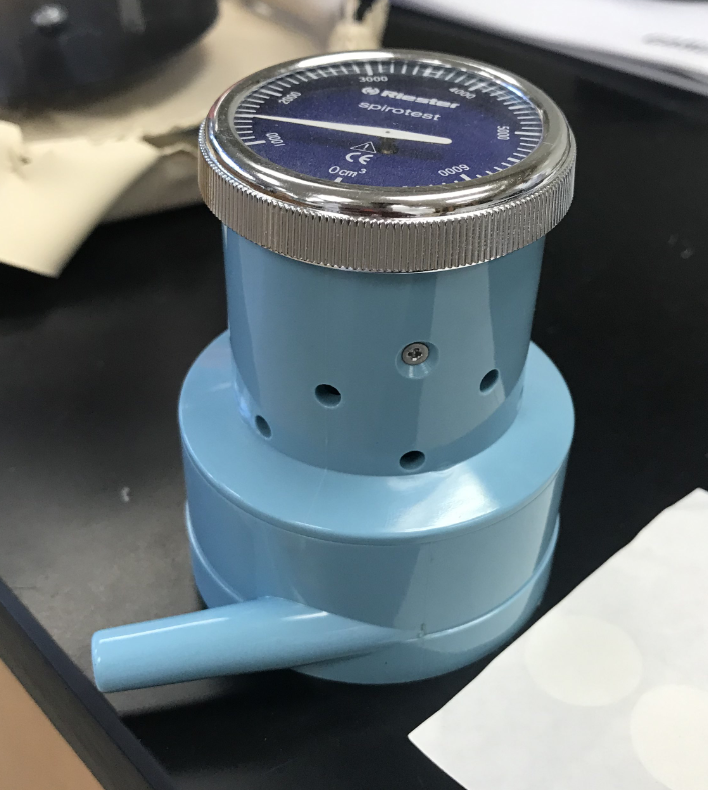

what is this
spirometer
what does a spirometer measure
respiratory volume
when the rubber membrane is pulled down (diaphragm, contracting) what happens to the balloons (lungs)
inflates
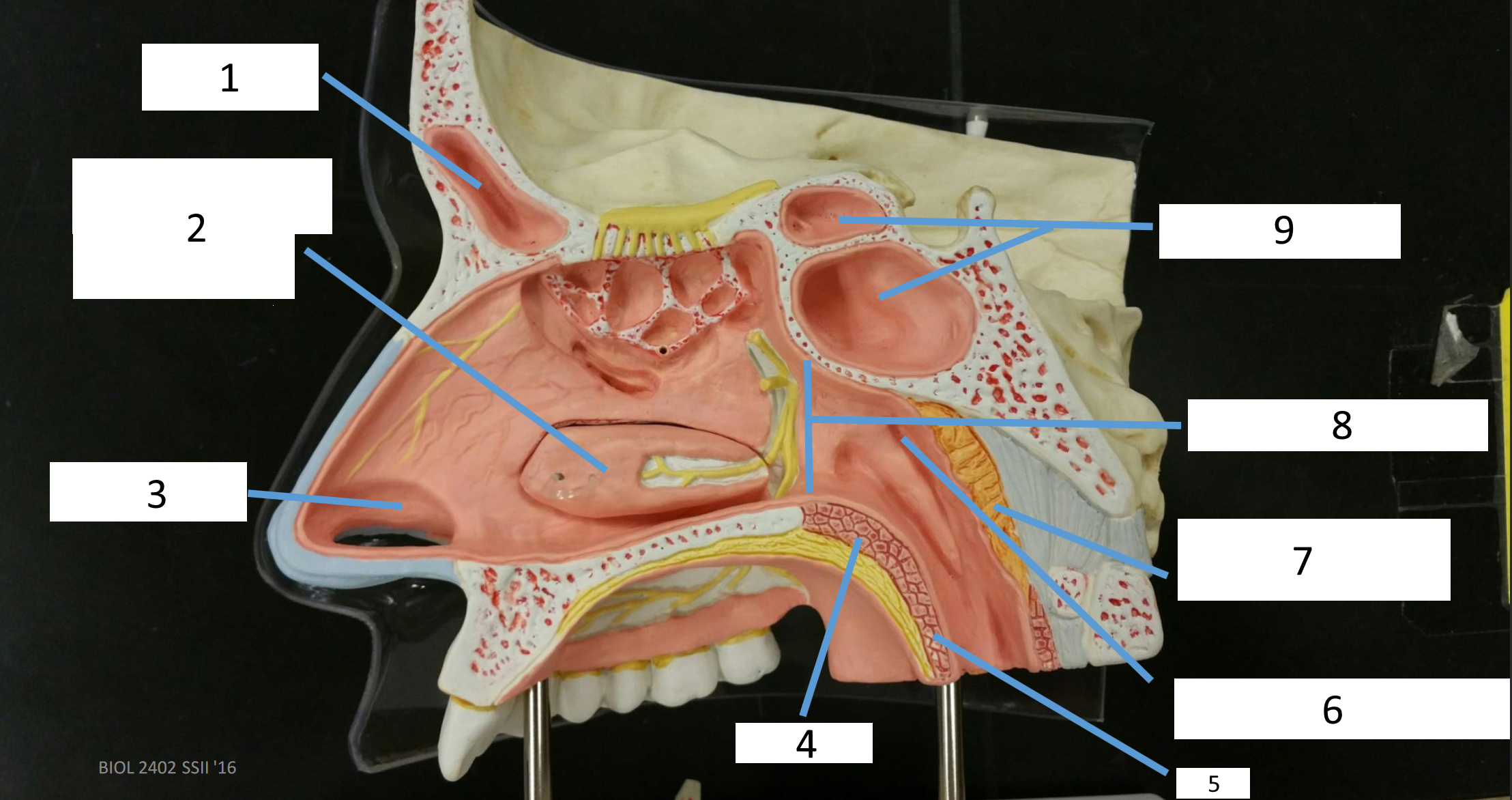
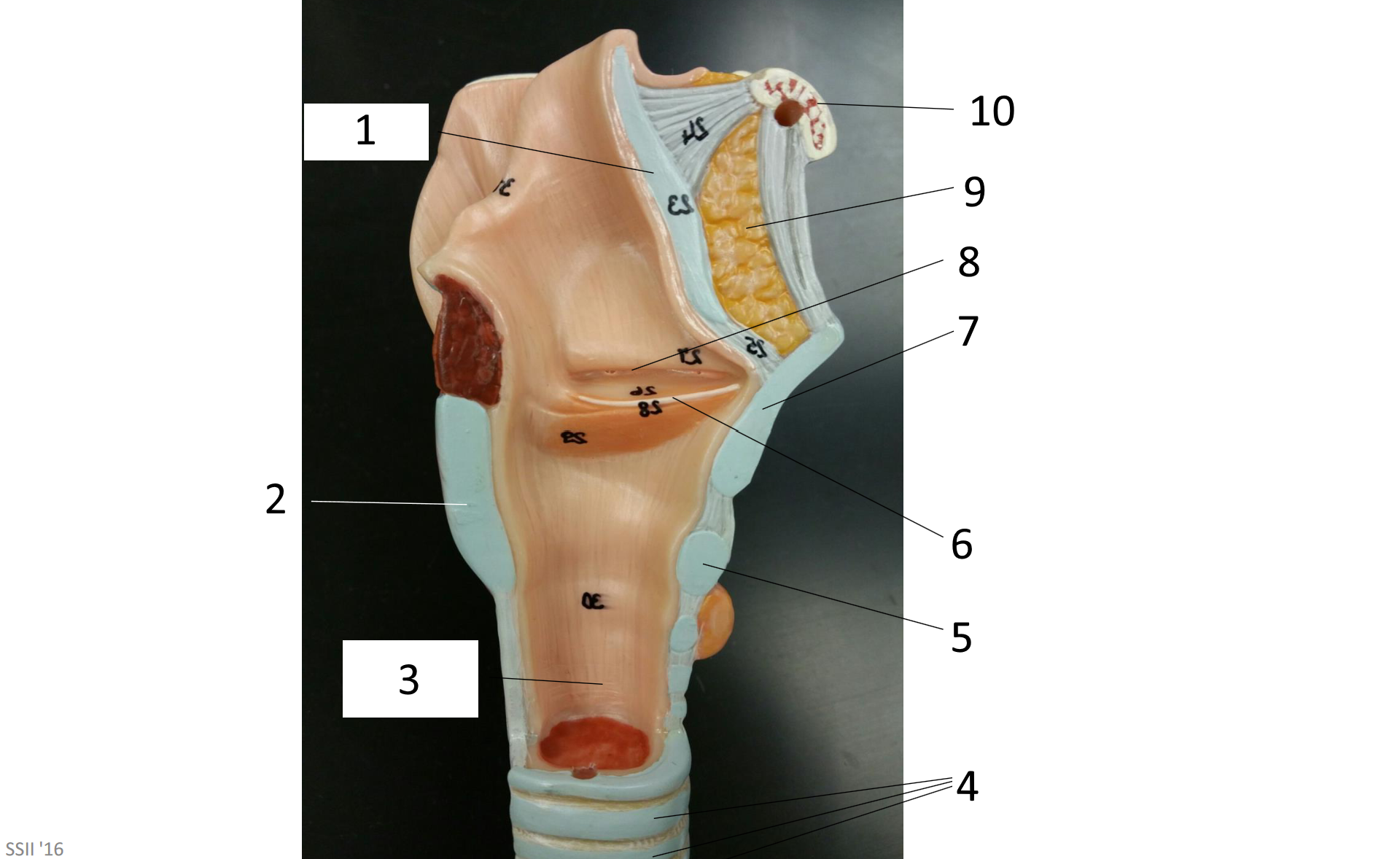
1
frontal sinus
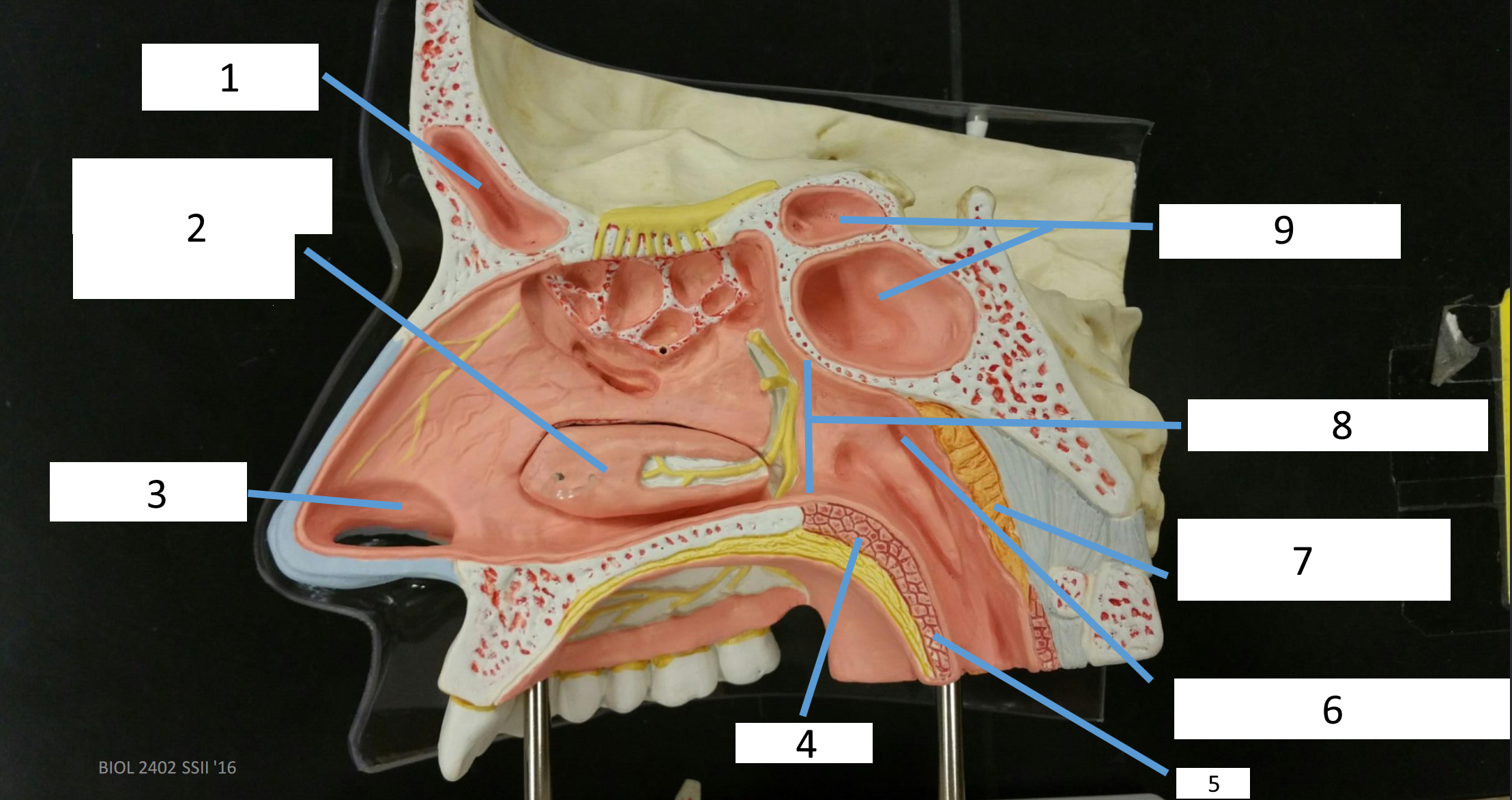
2
inferior nasal concha
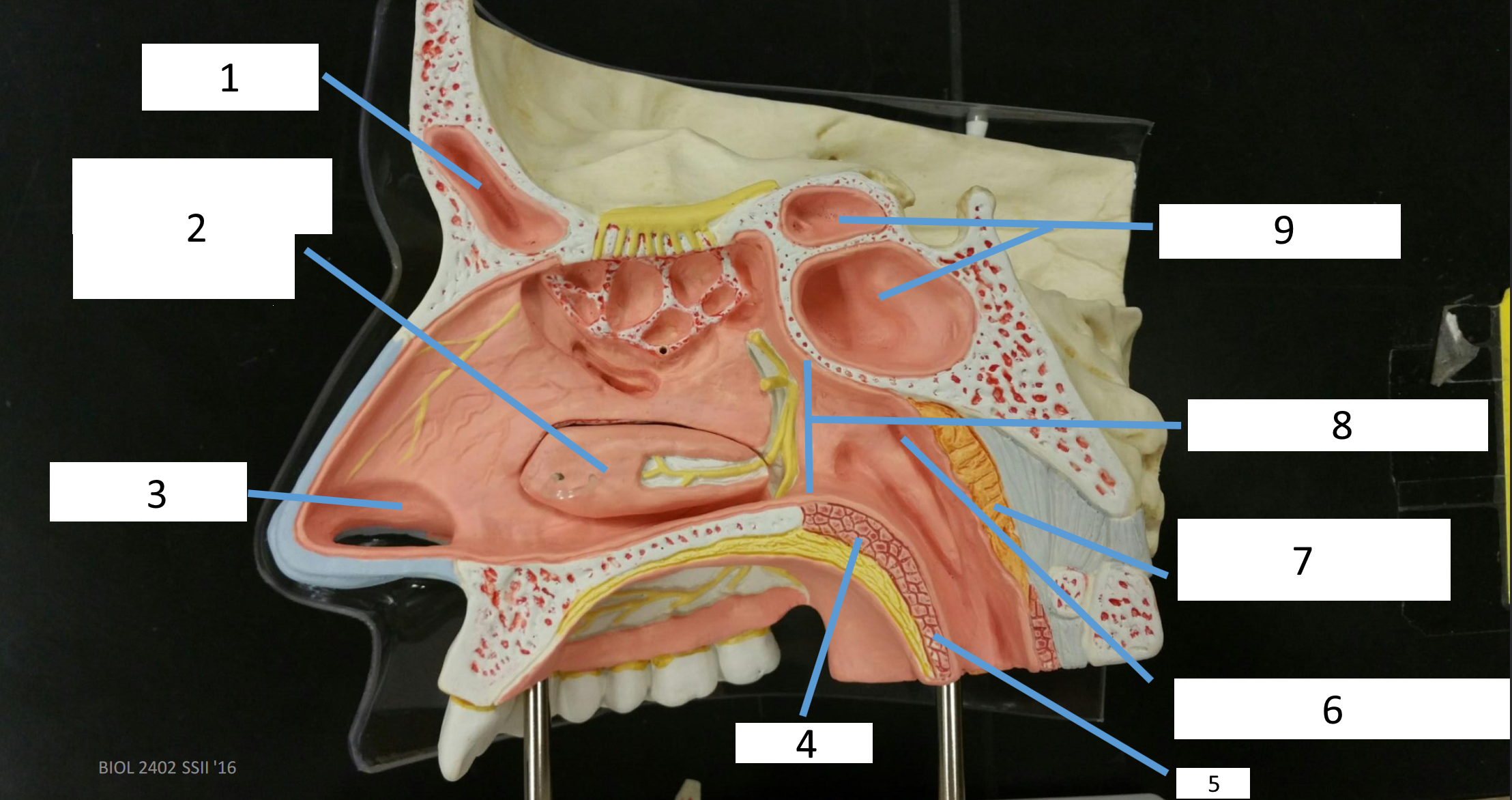
3
nasal vestibule
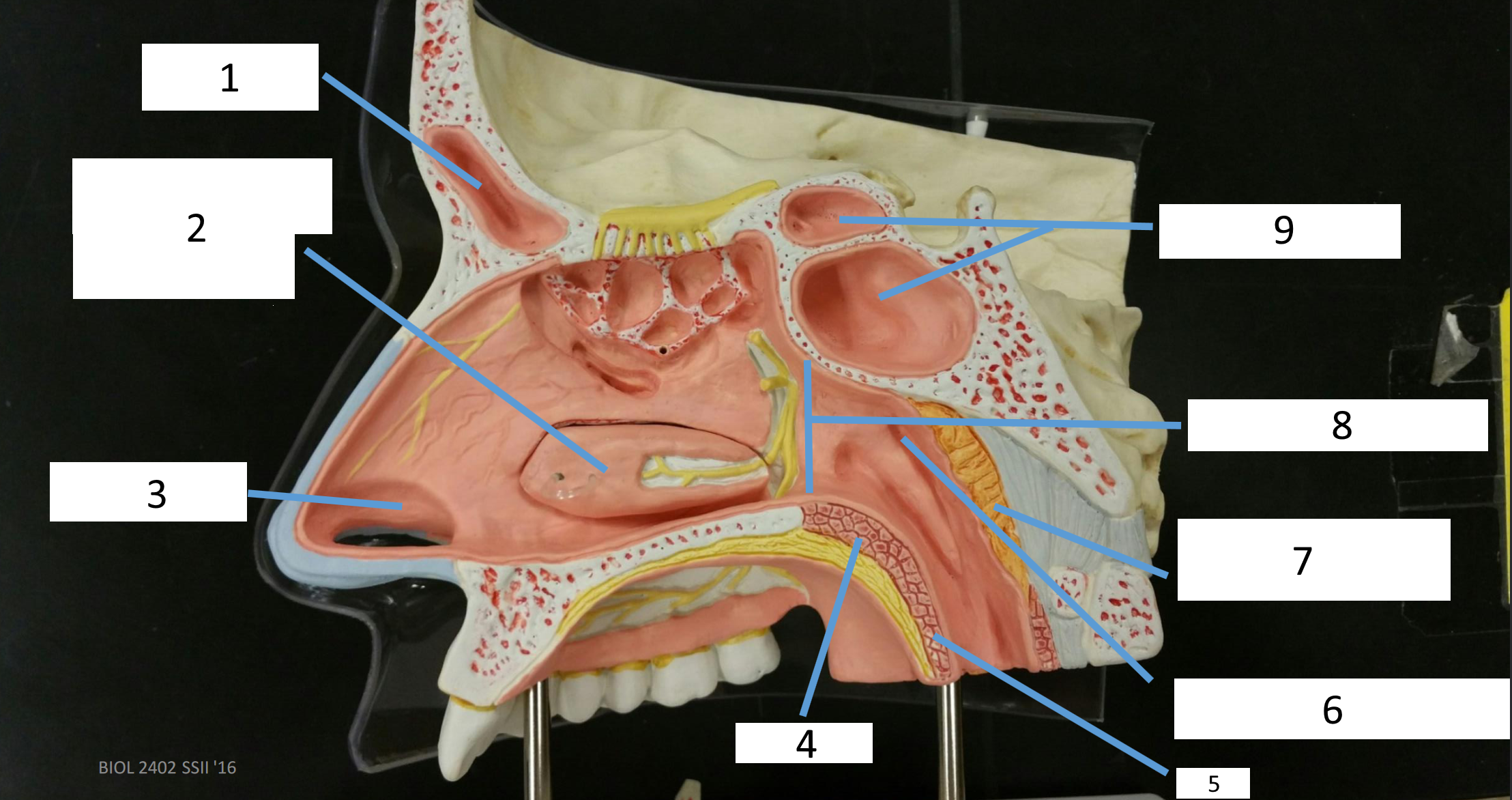
4
soft palate
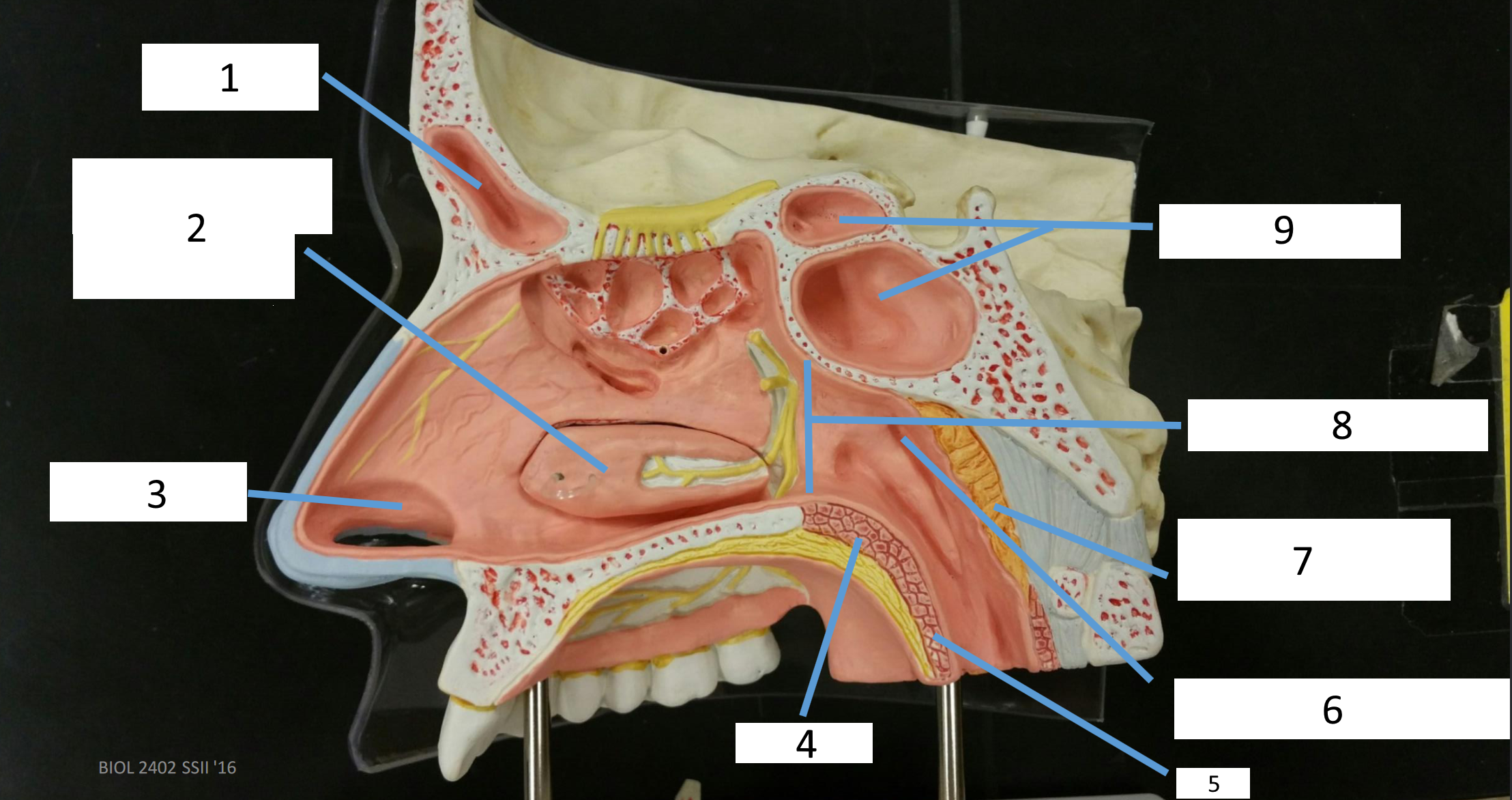
5
uvula
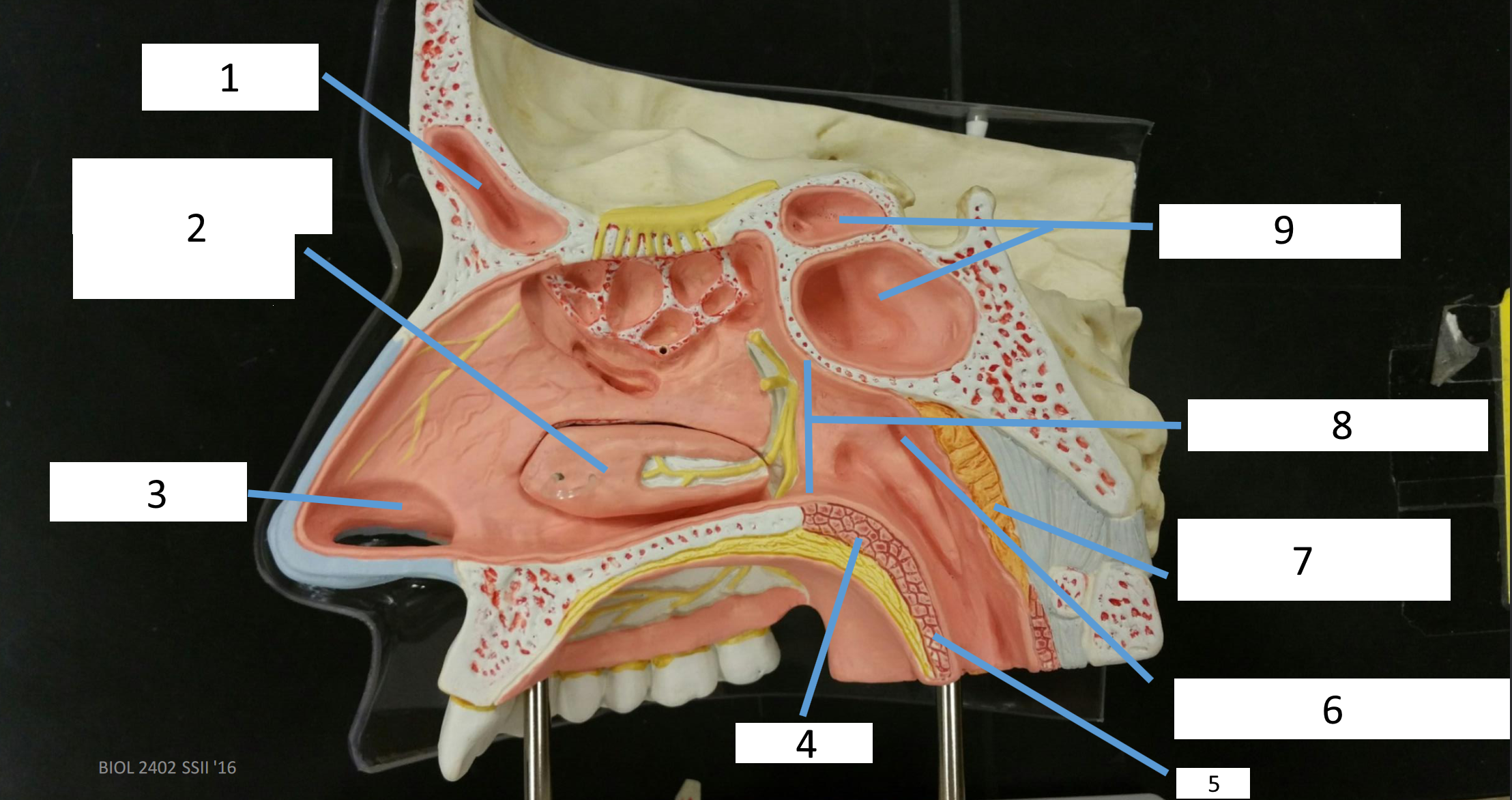
6
opening of pharyngotympanic tube
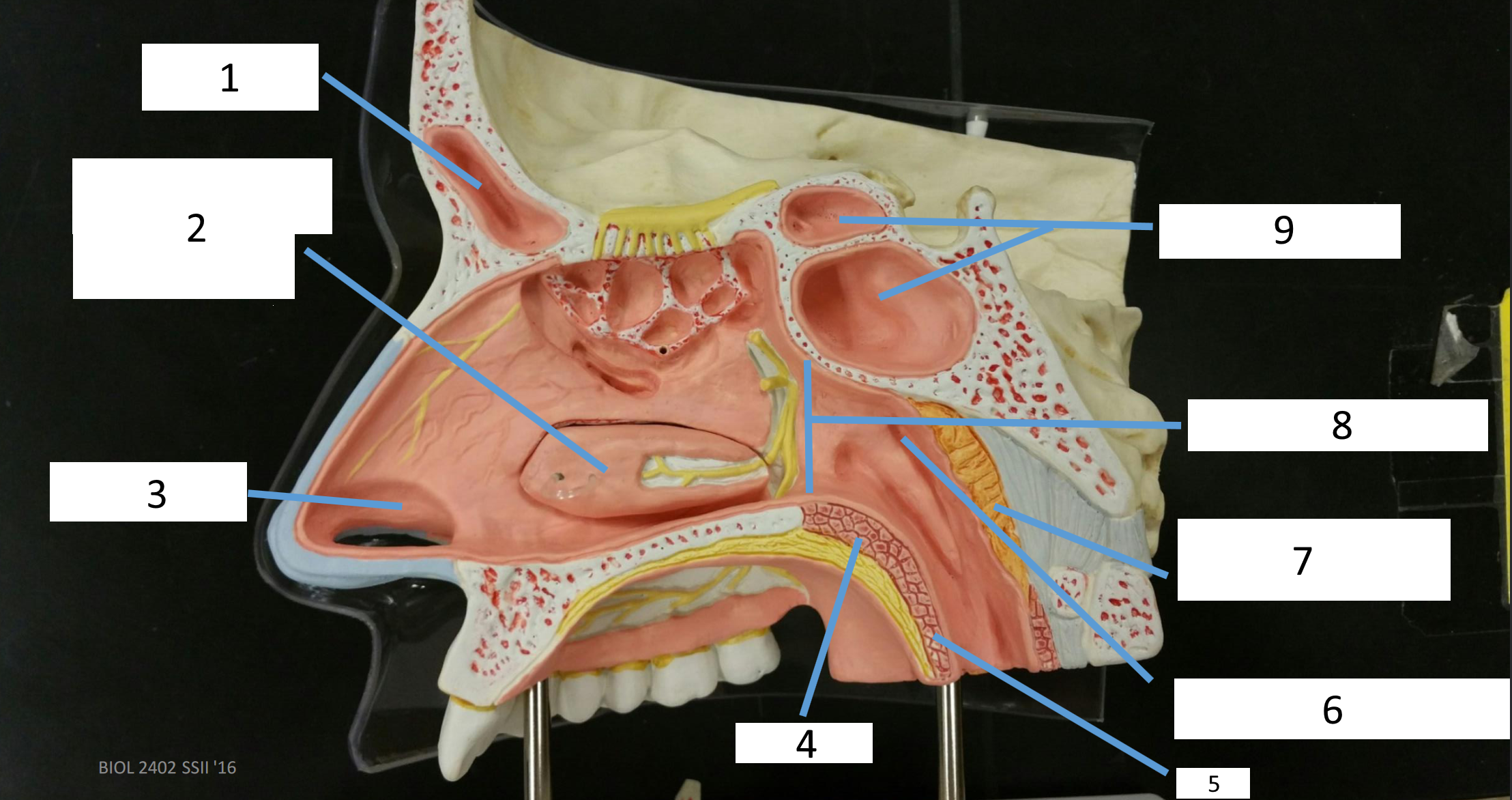
7
nasopharynx pharyngeal tonsil
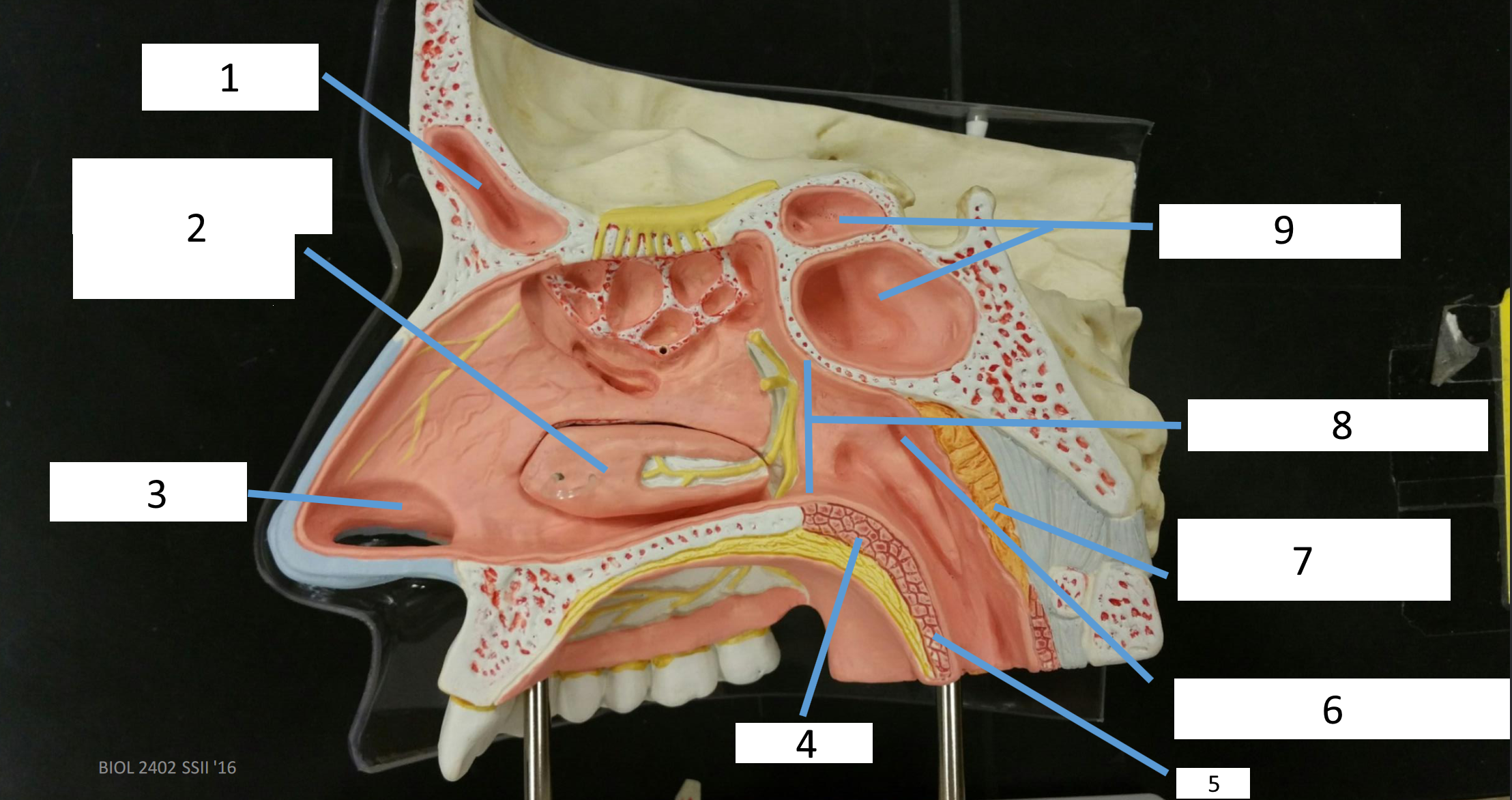
8
posterior nasal aperture
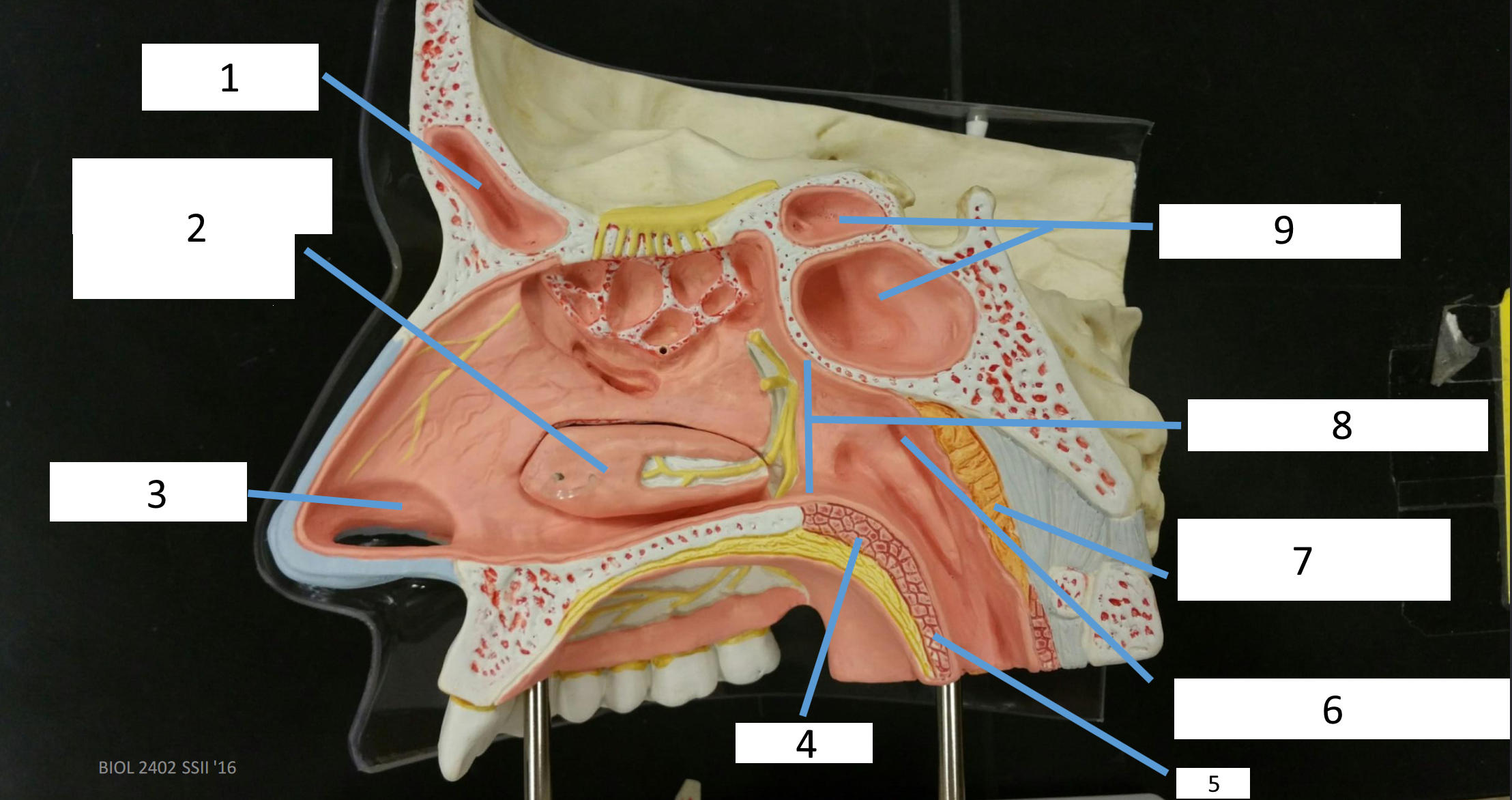
9
sphenoidal sinuses
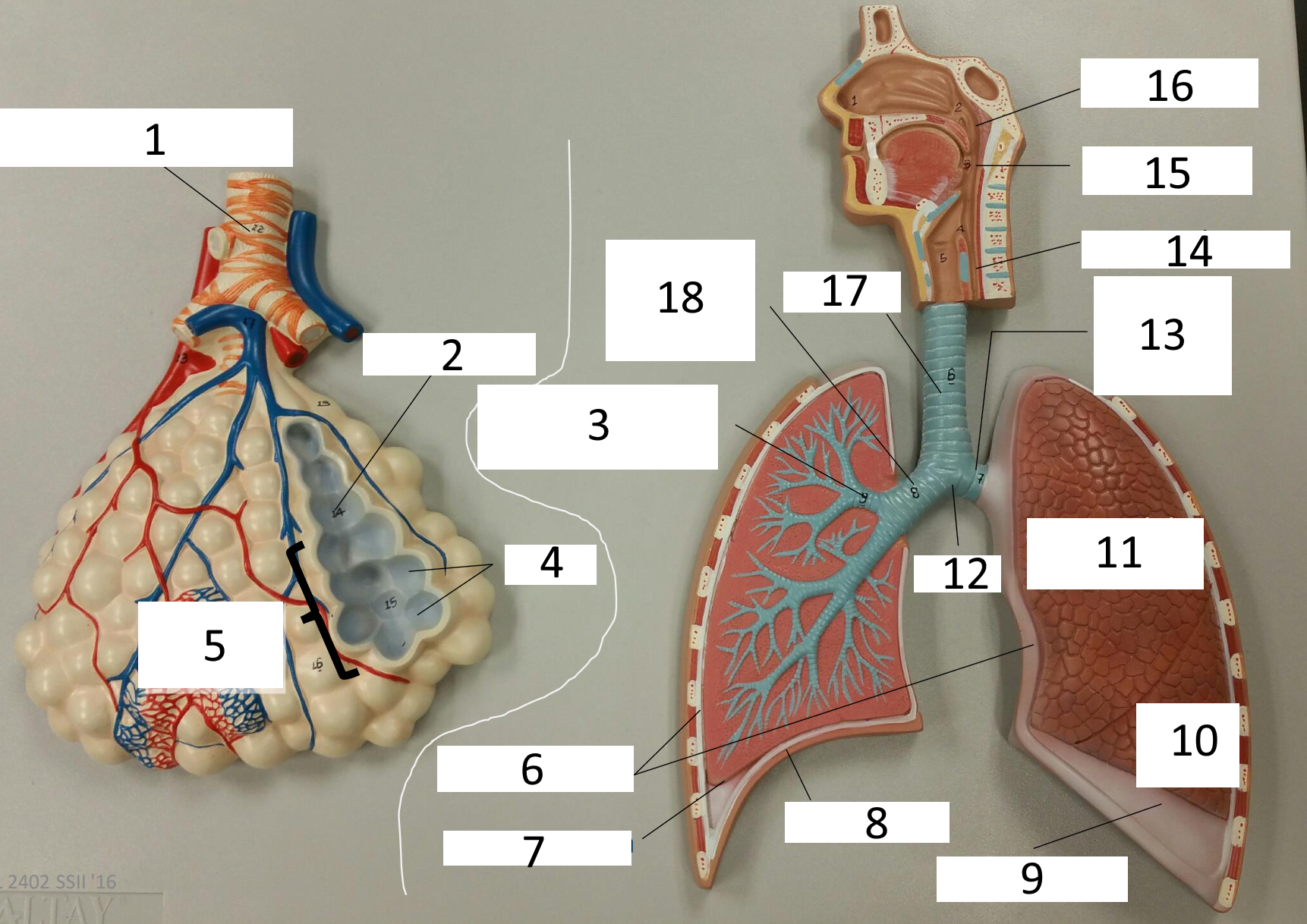
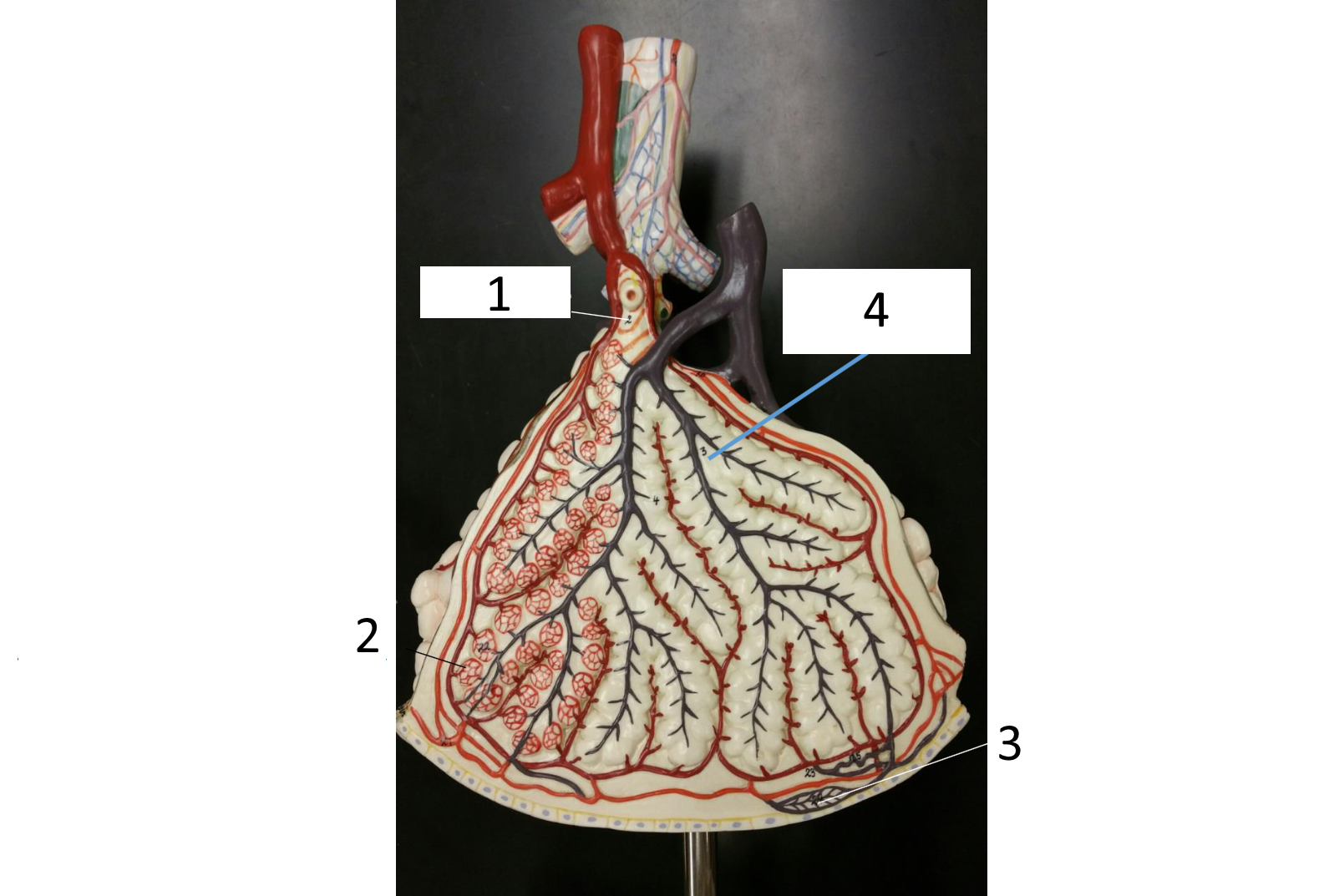
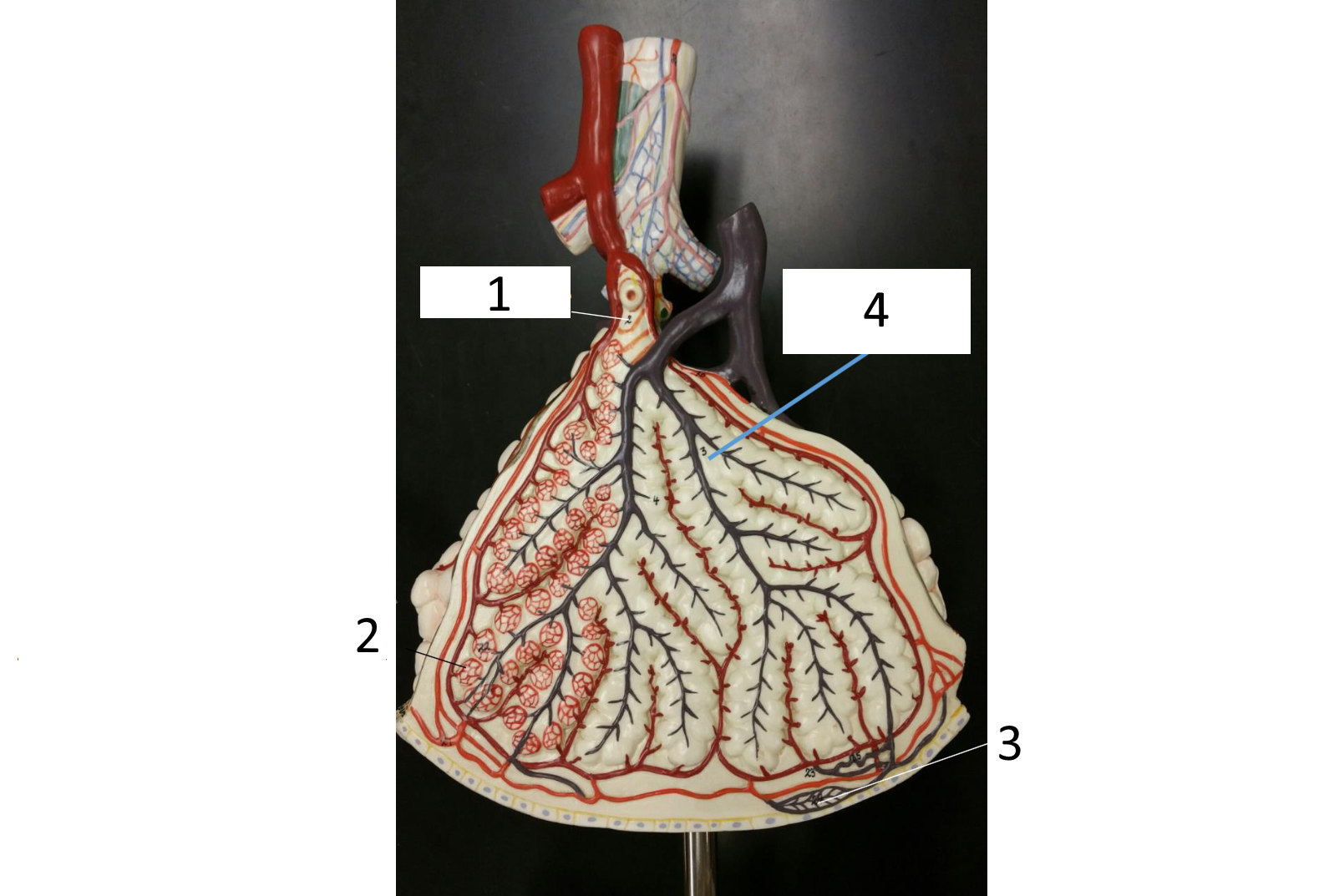
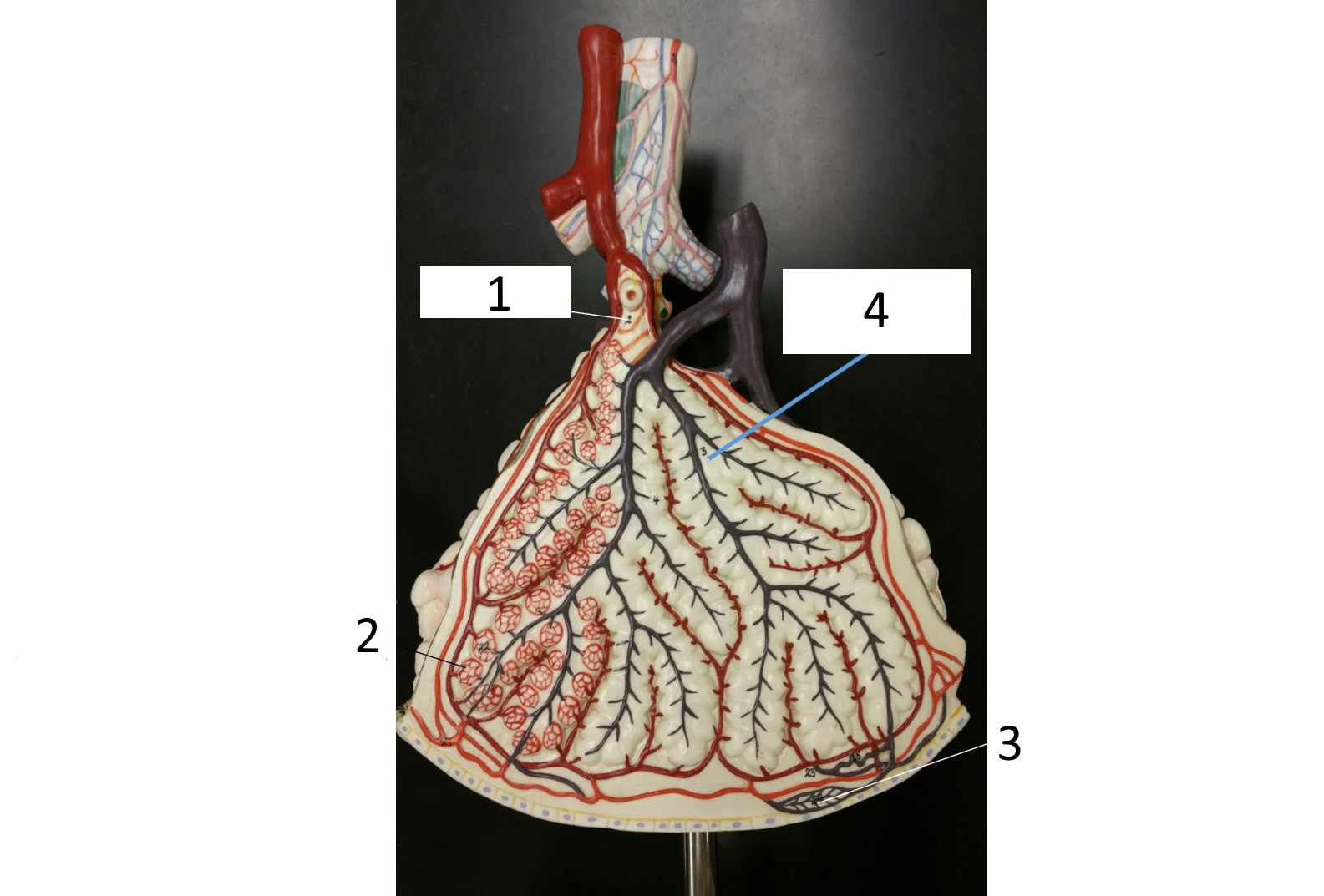
1
respiratory bronchiole
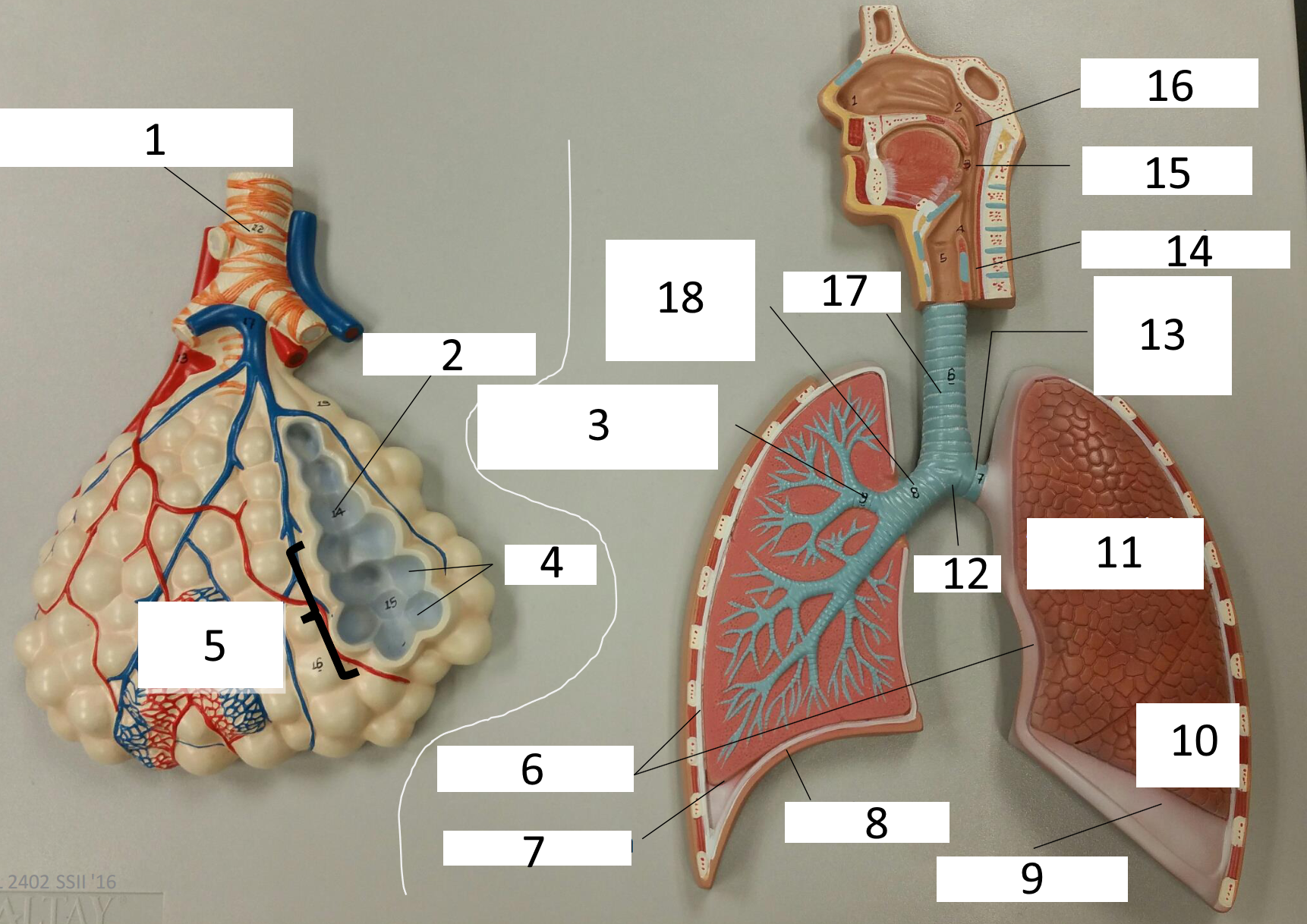
2
alveolar duct
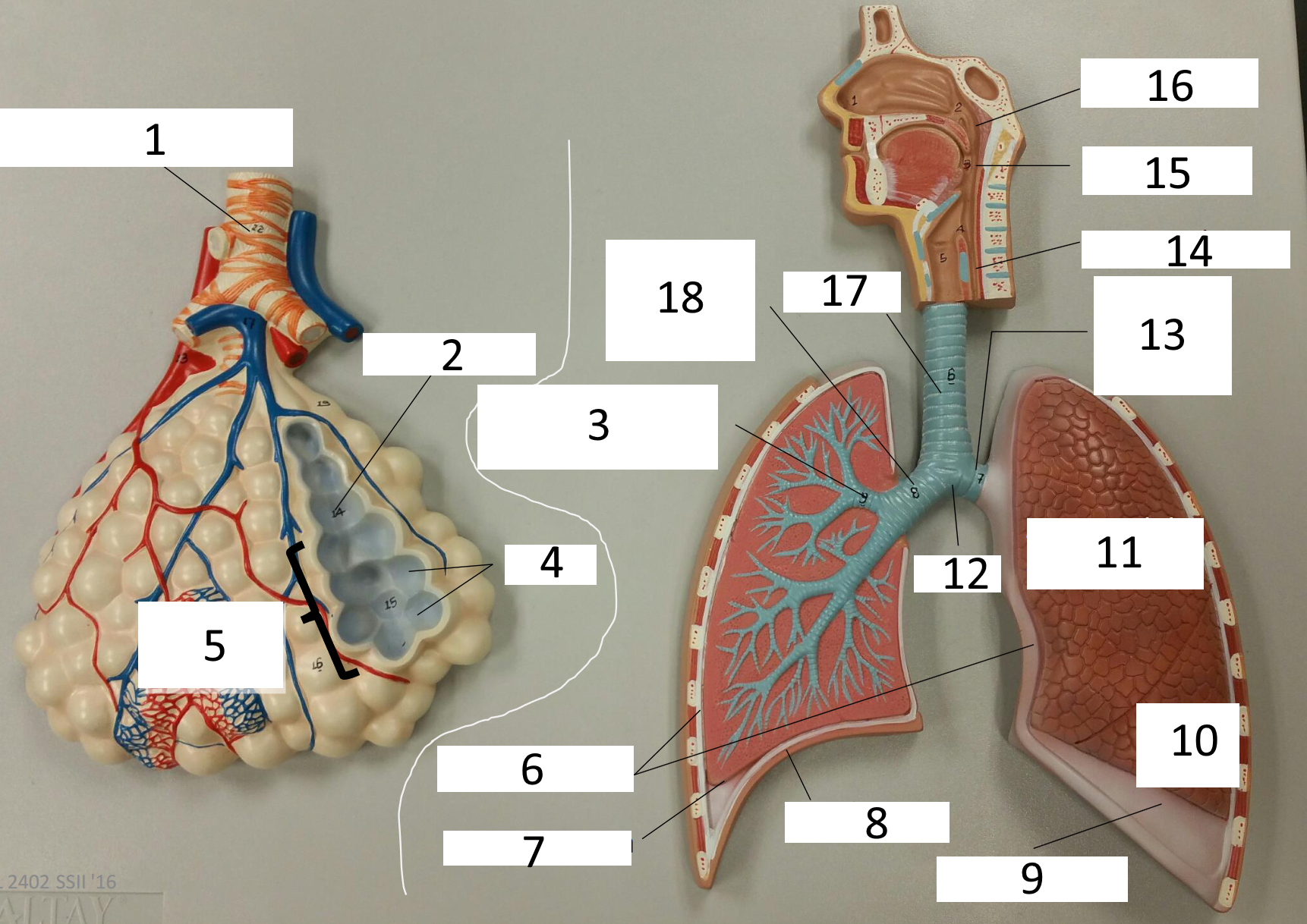
3
lobar (secondary) bronchus
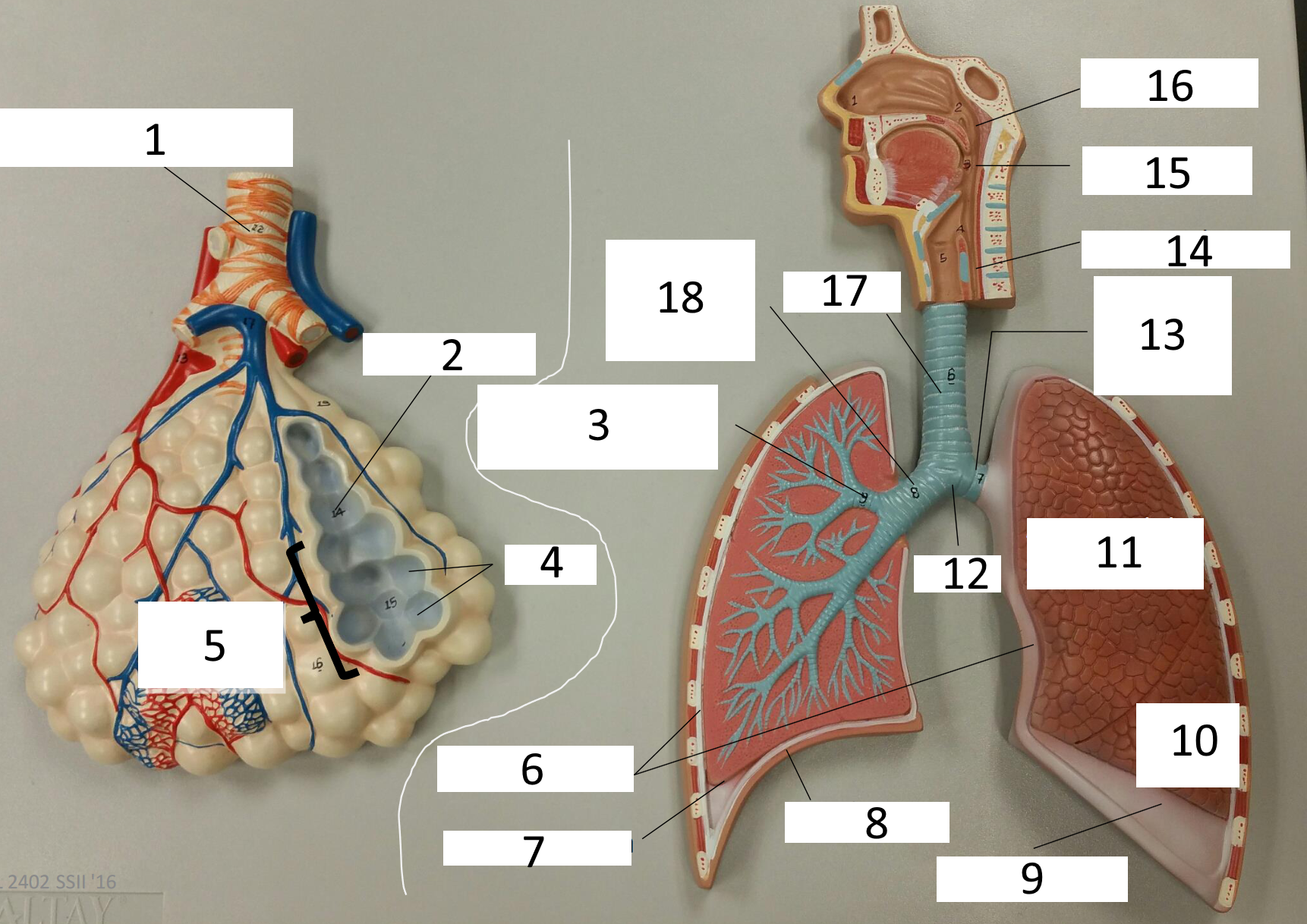
4
alveoli
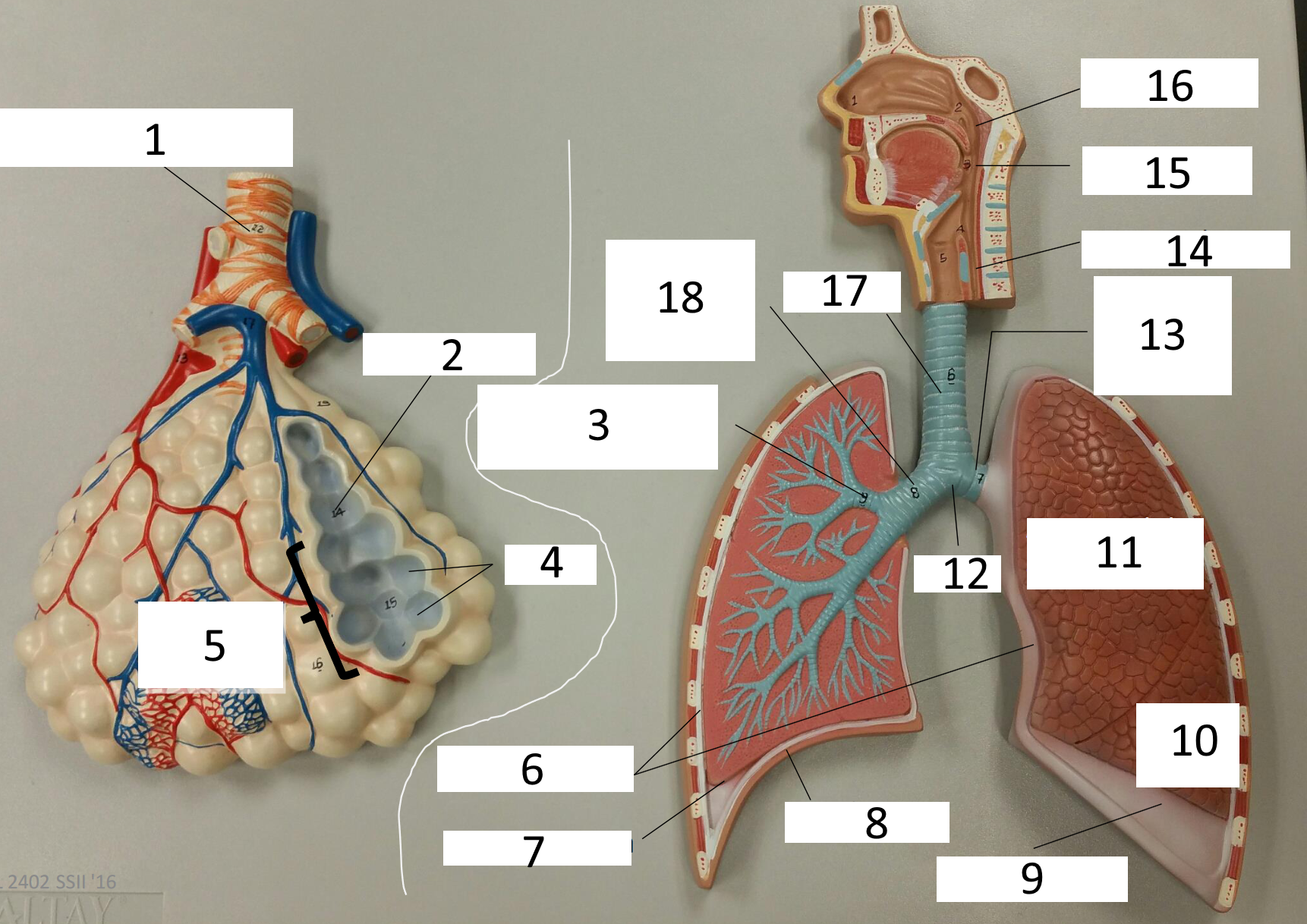
5
alveolar sac
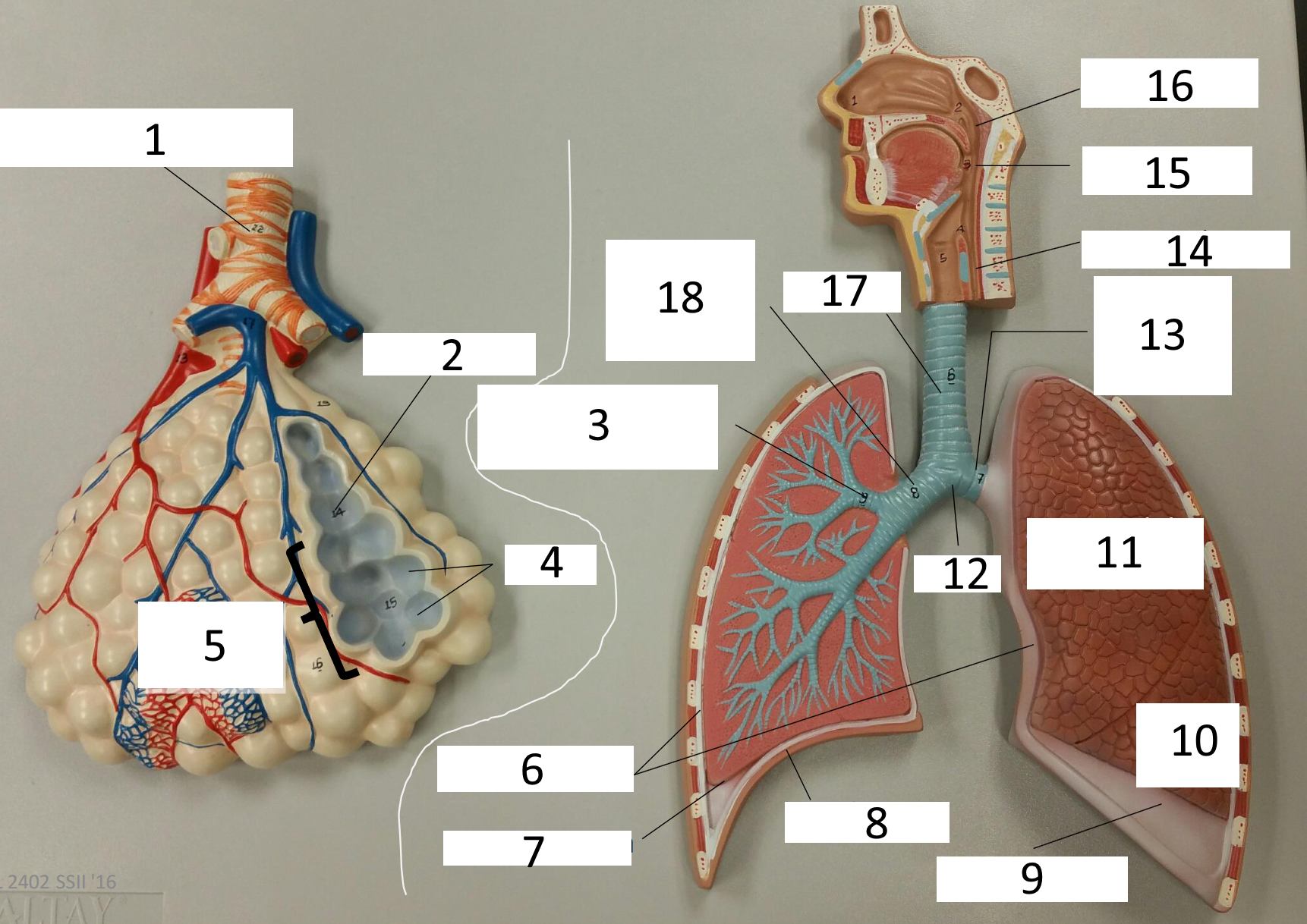
6
parietal pleura
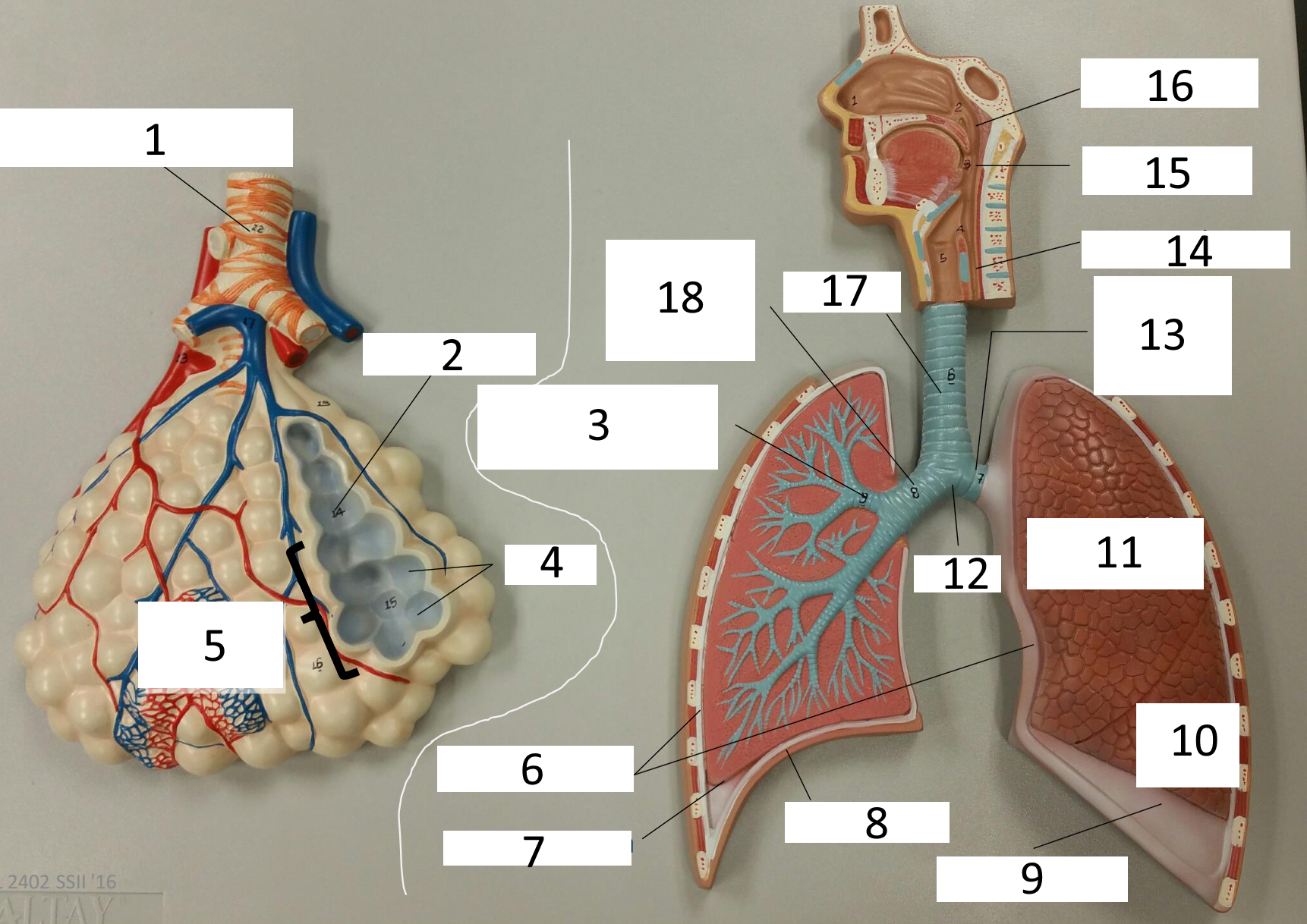
7
visceral pleura
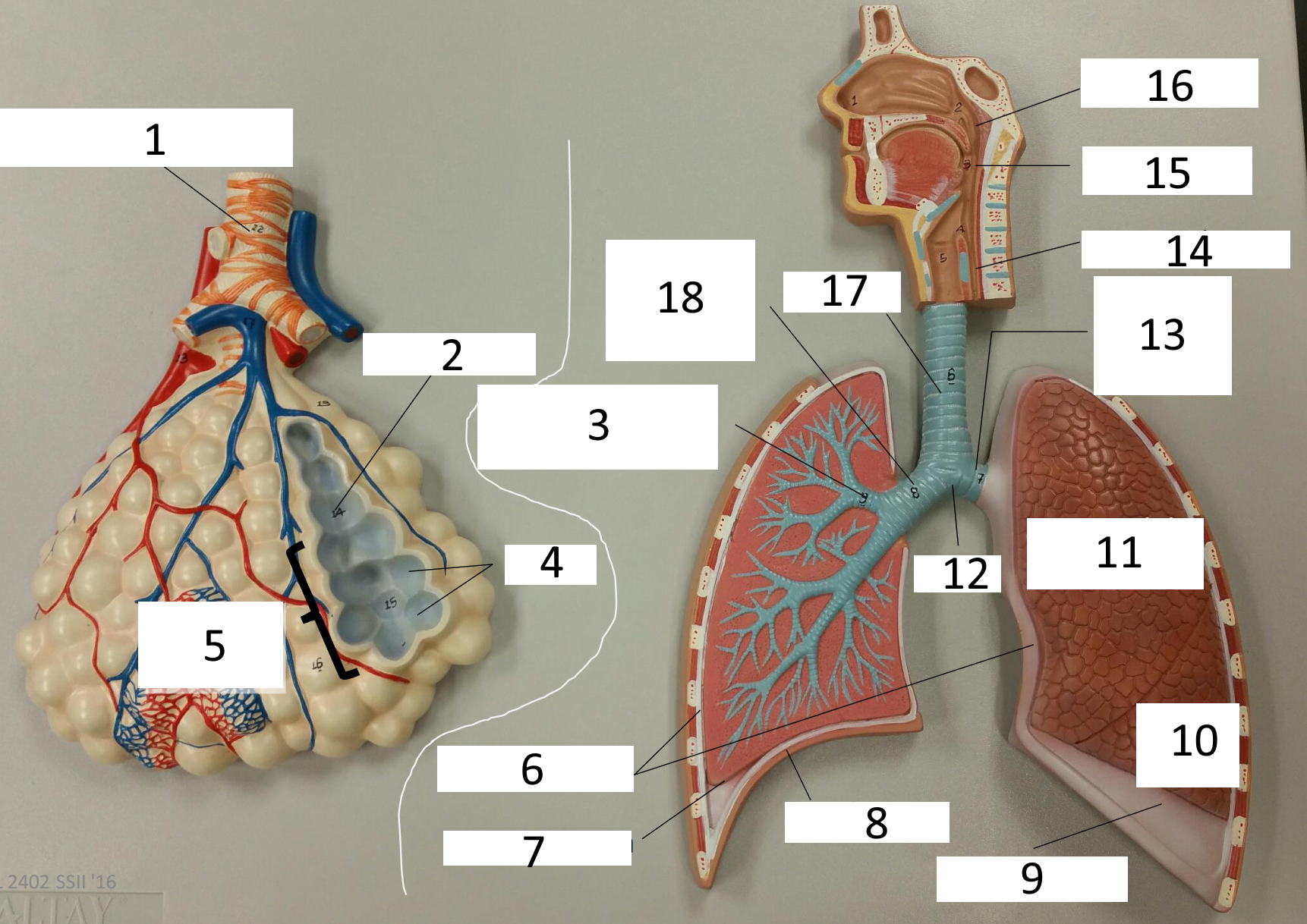
8
diaphragm
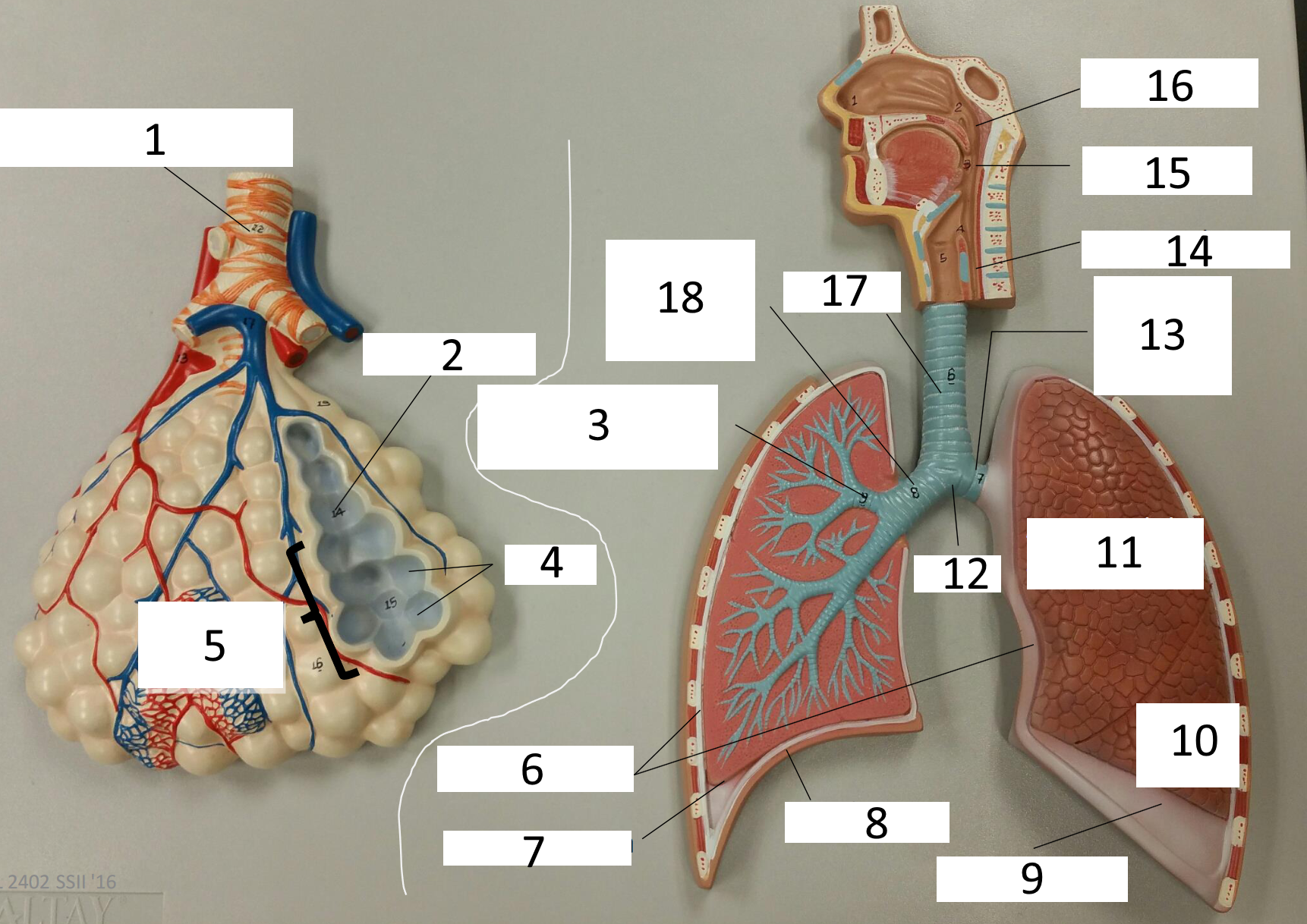
9
pleural cavity
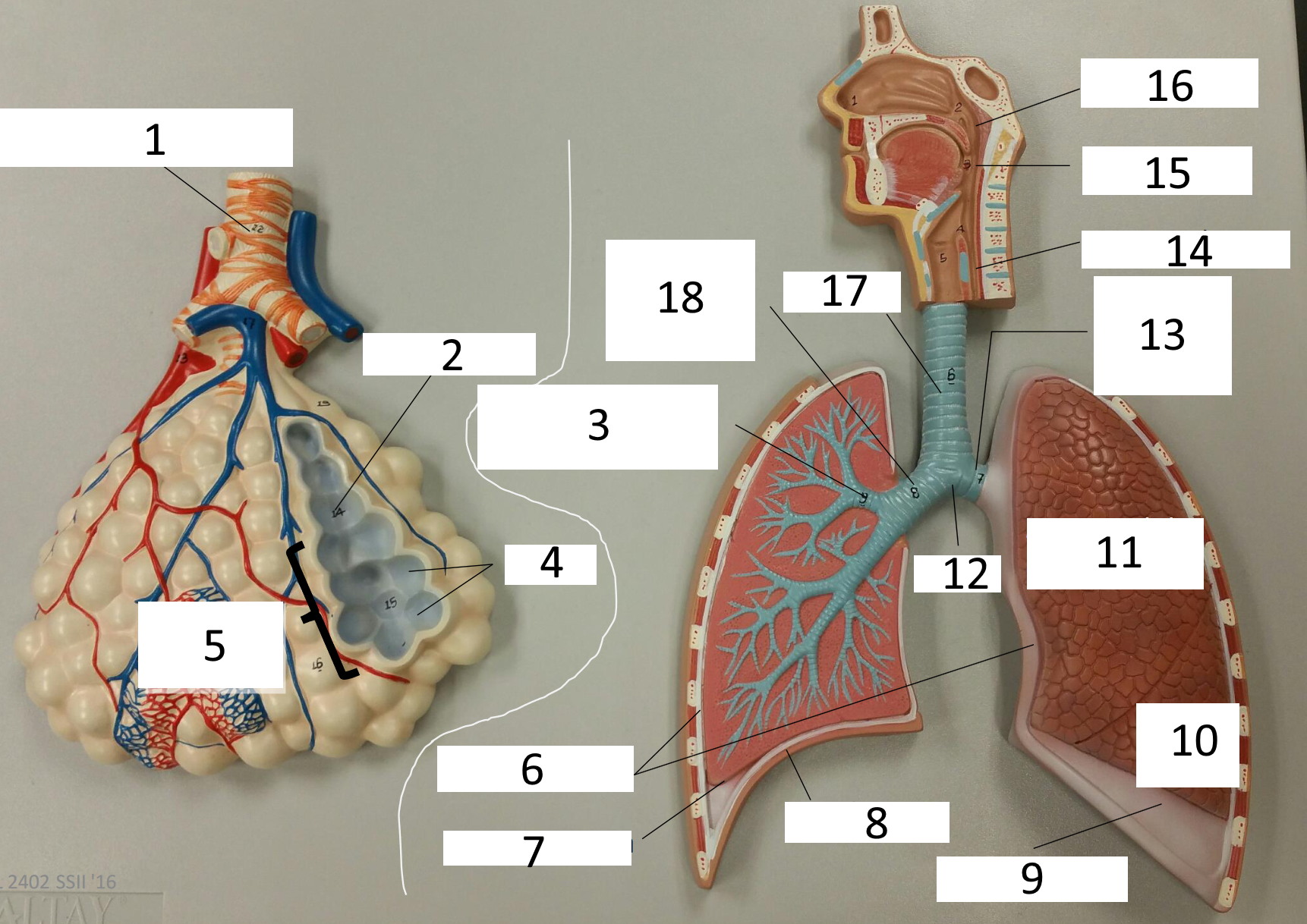
10
inferior lobe
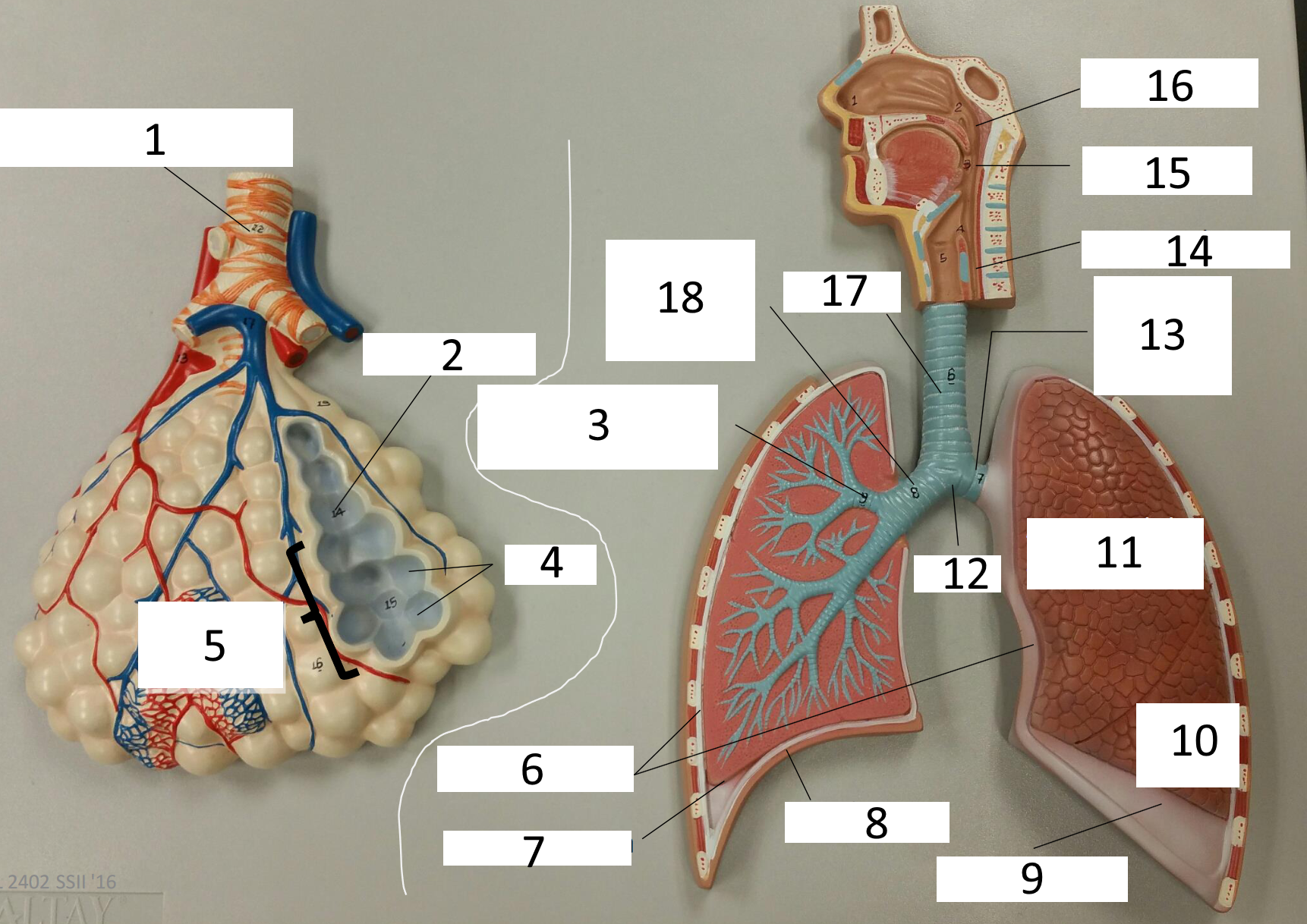
11
superior lobe
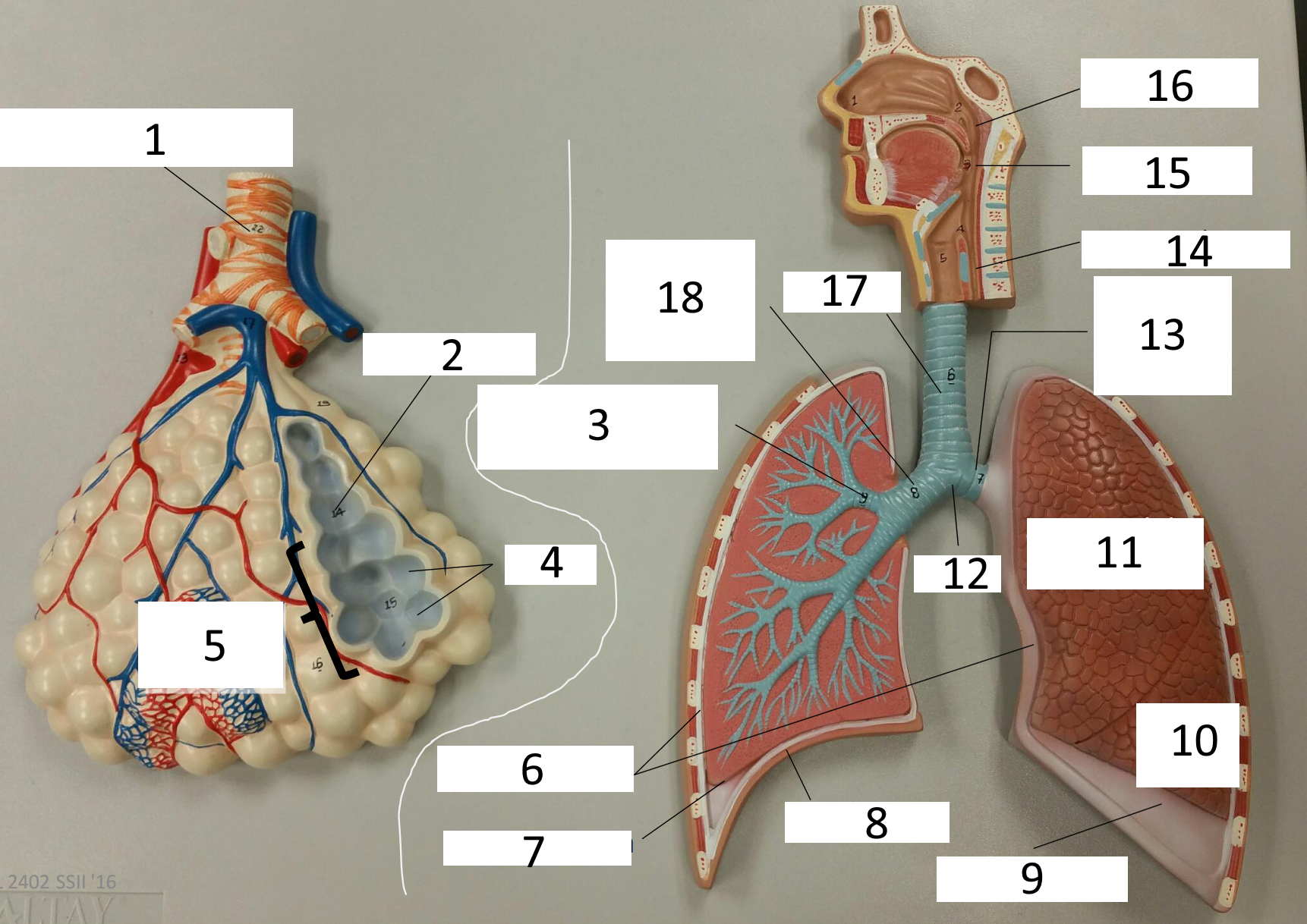
12
carina
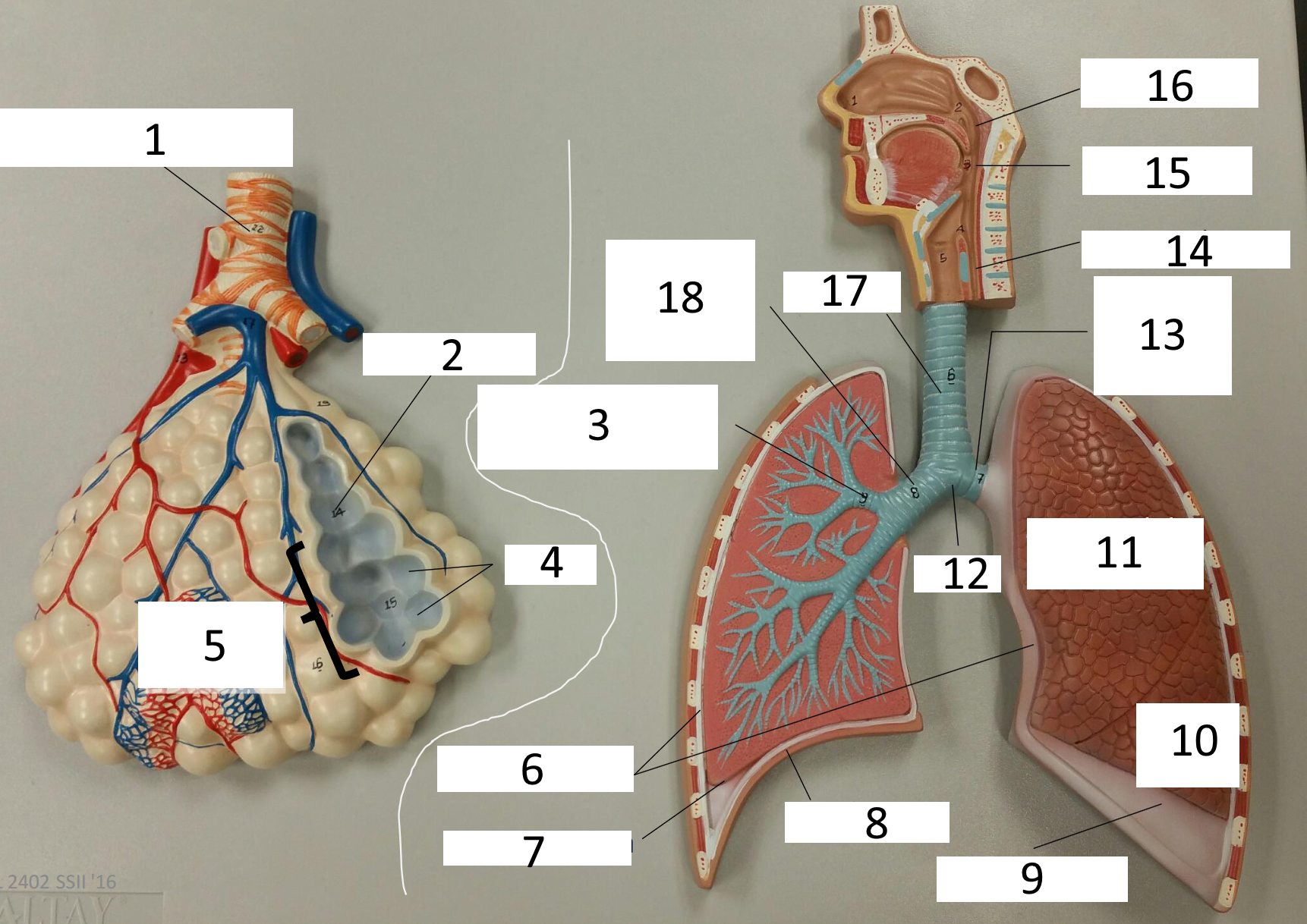
13
left main (primary) bronchus
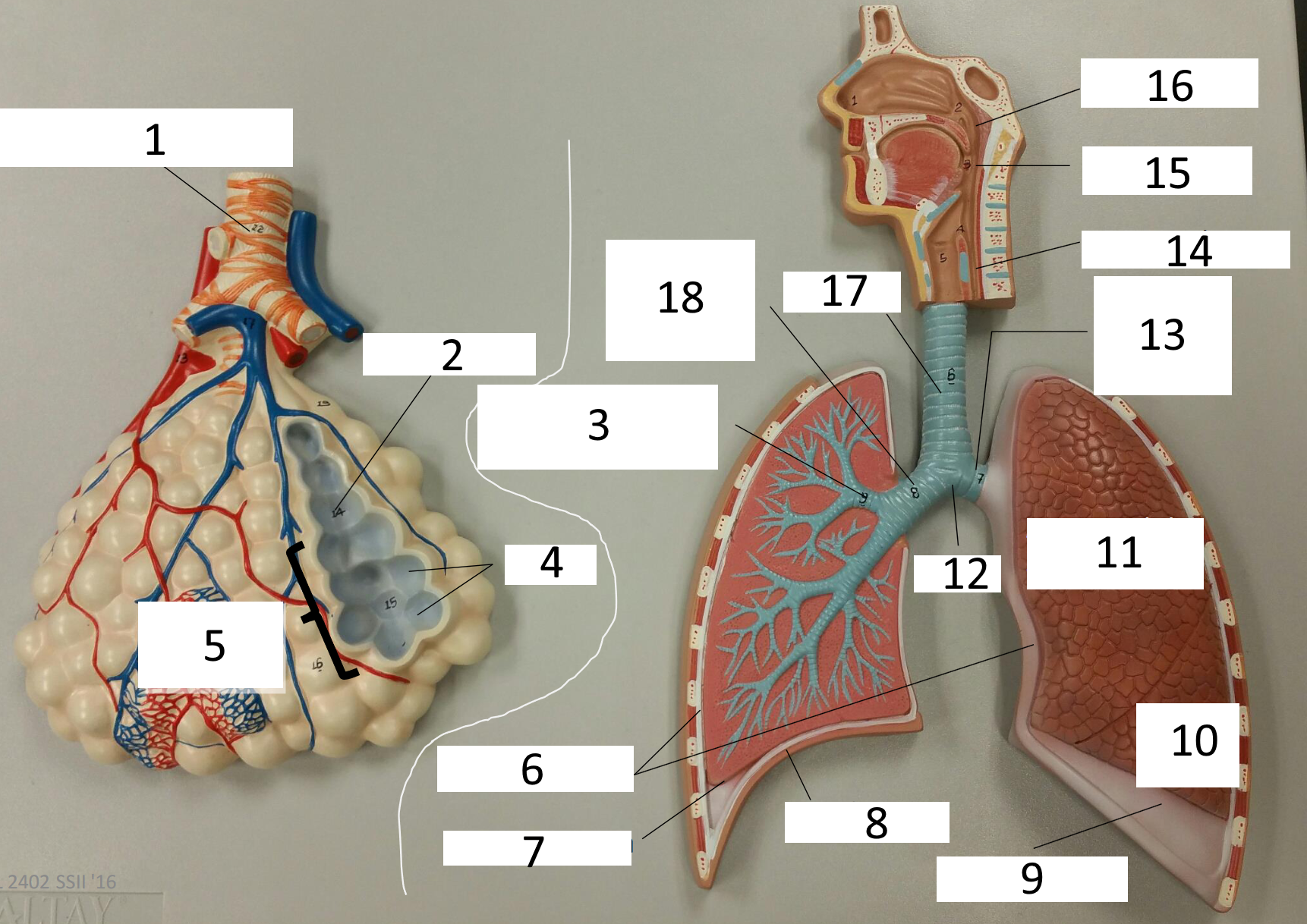
14
laryngopharynx
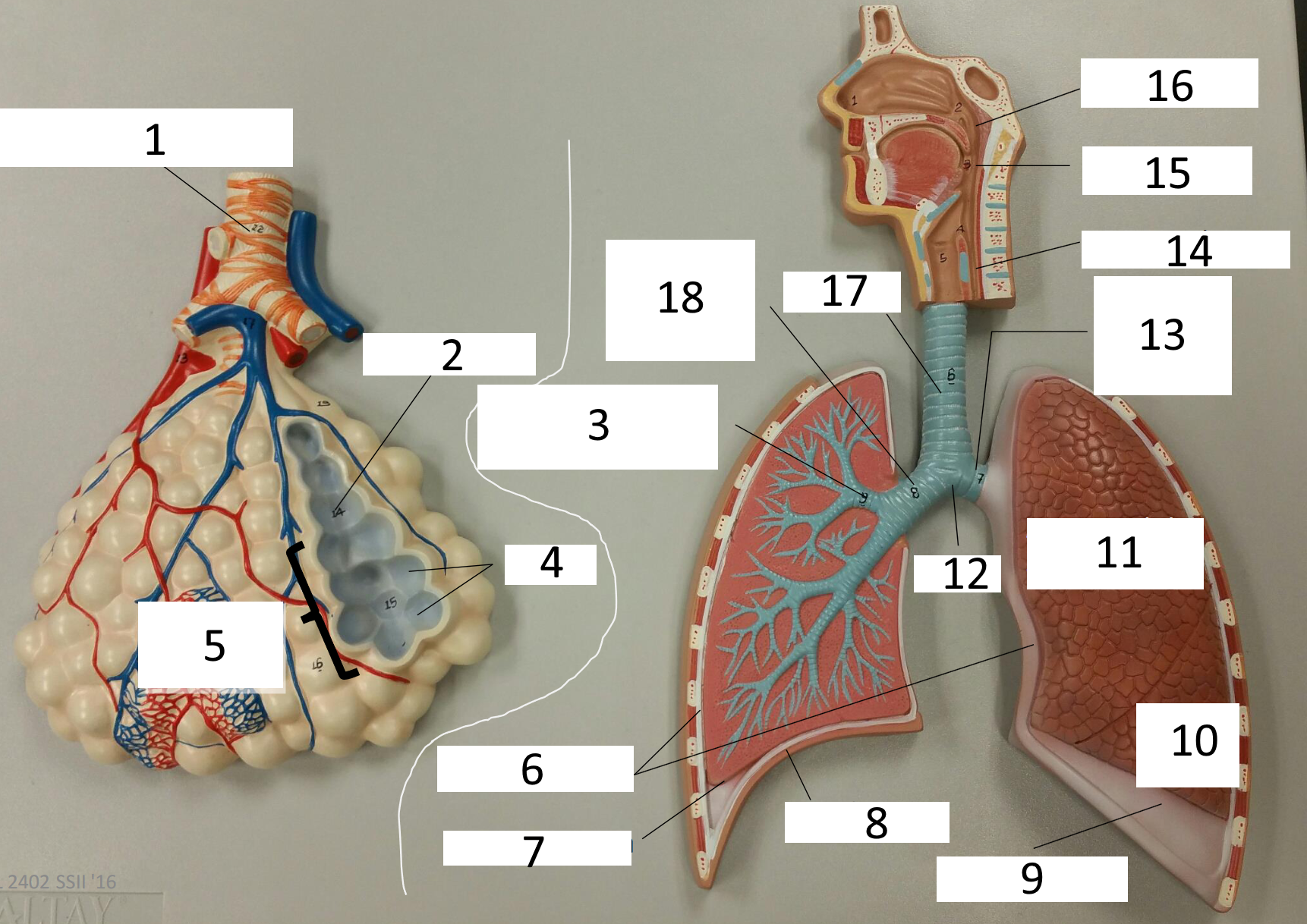
15
oropharynx
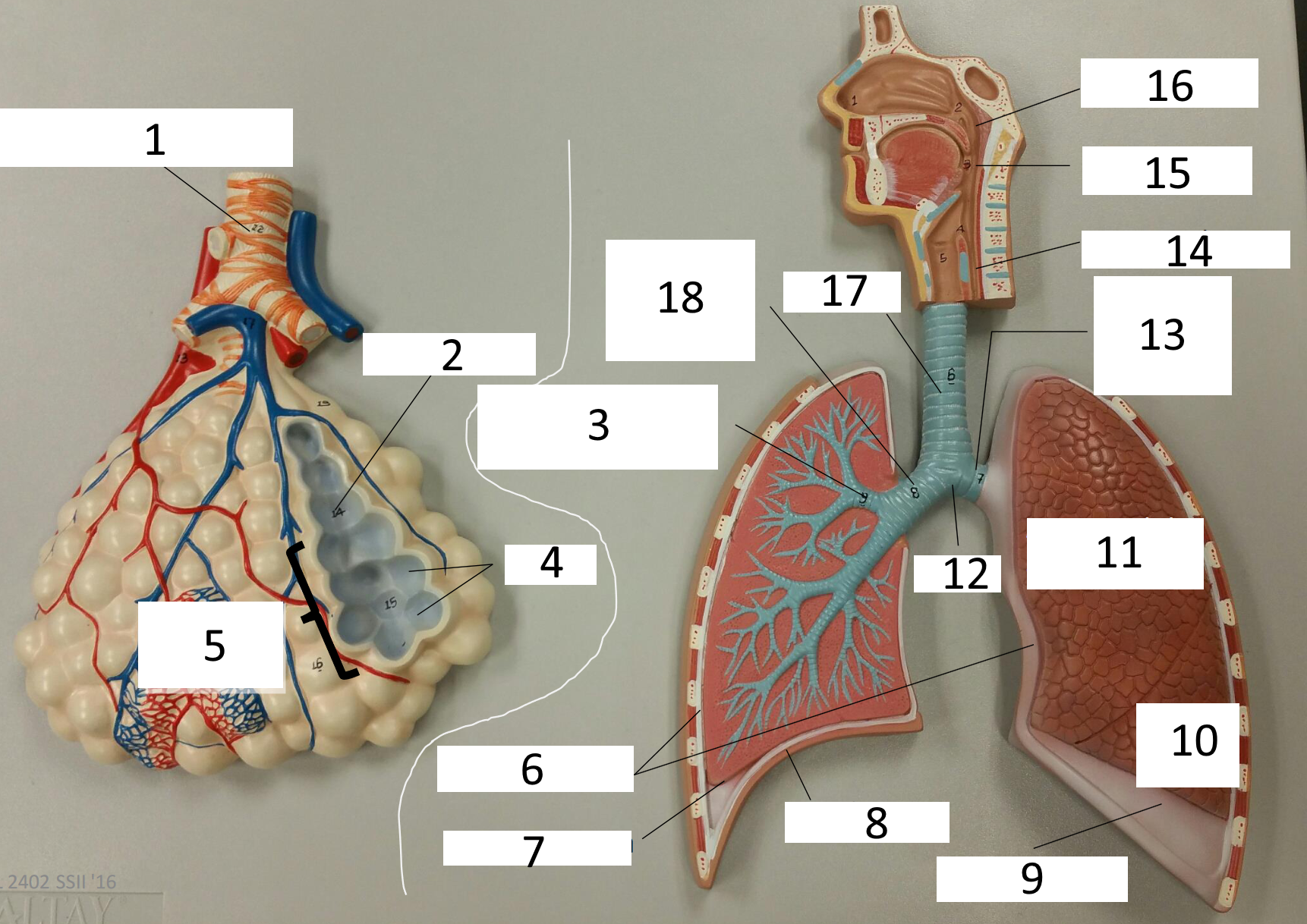
16
nasopharynx
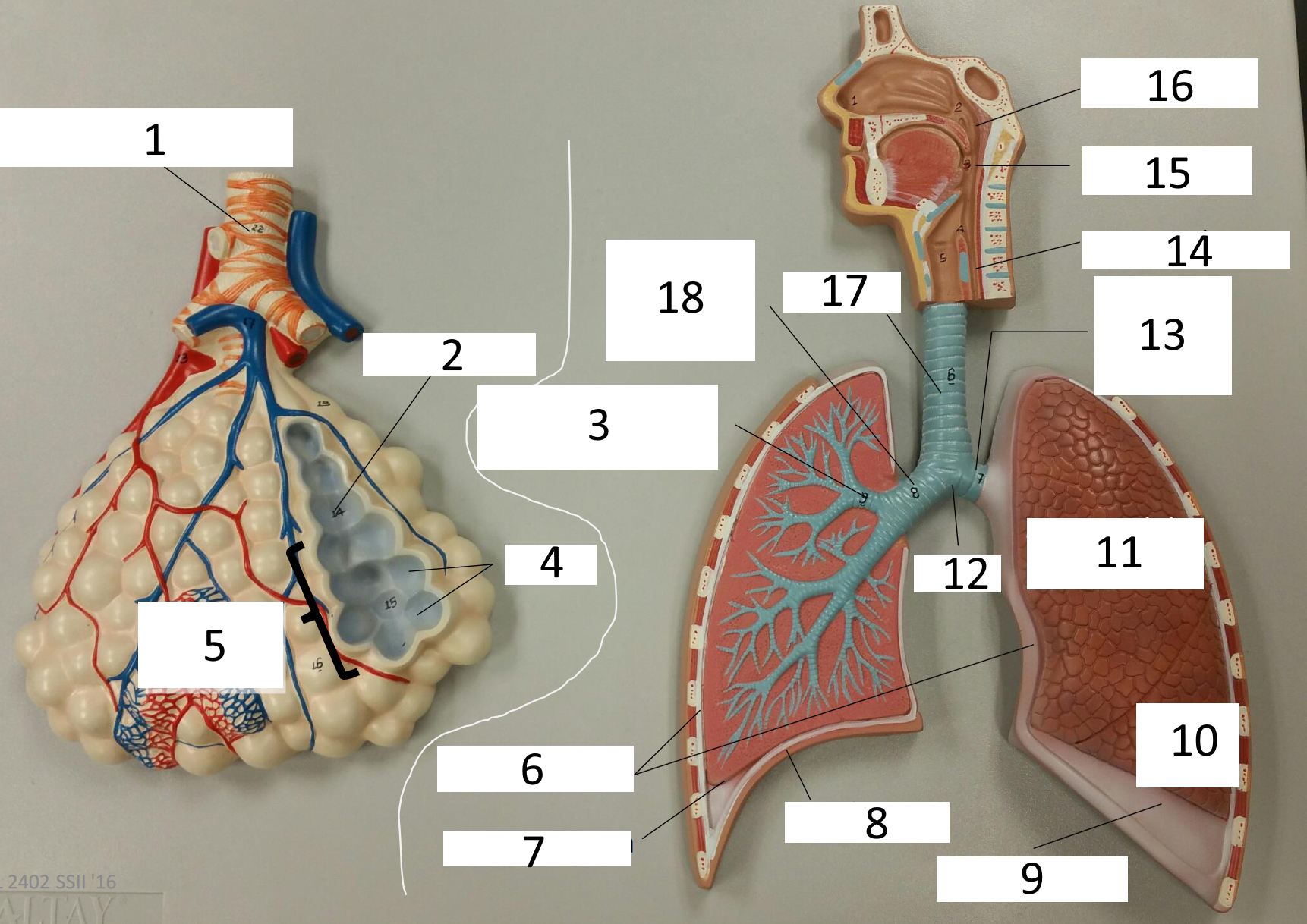
17
trachea
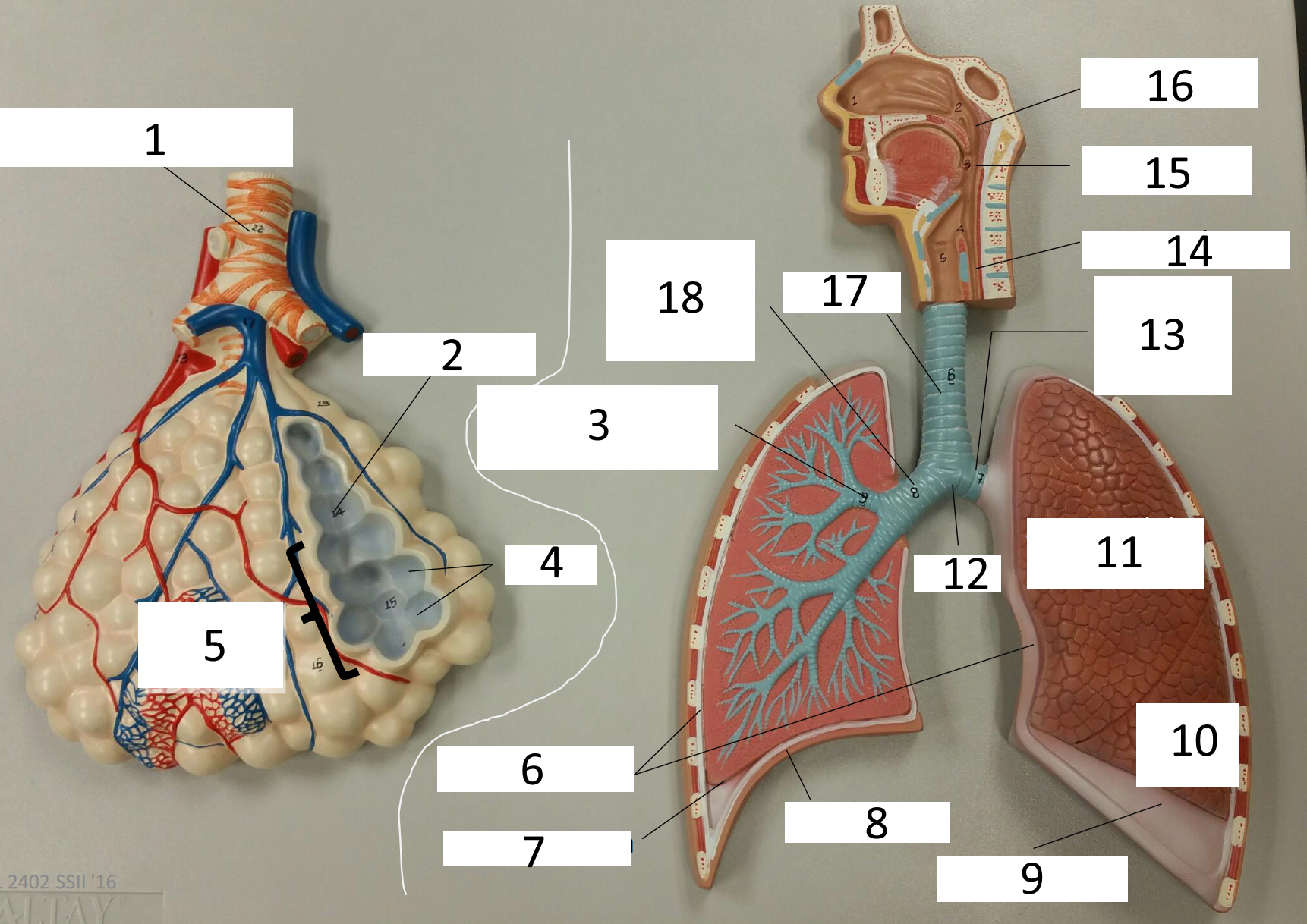
18
right main (primary) bronchus
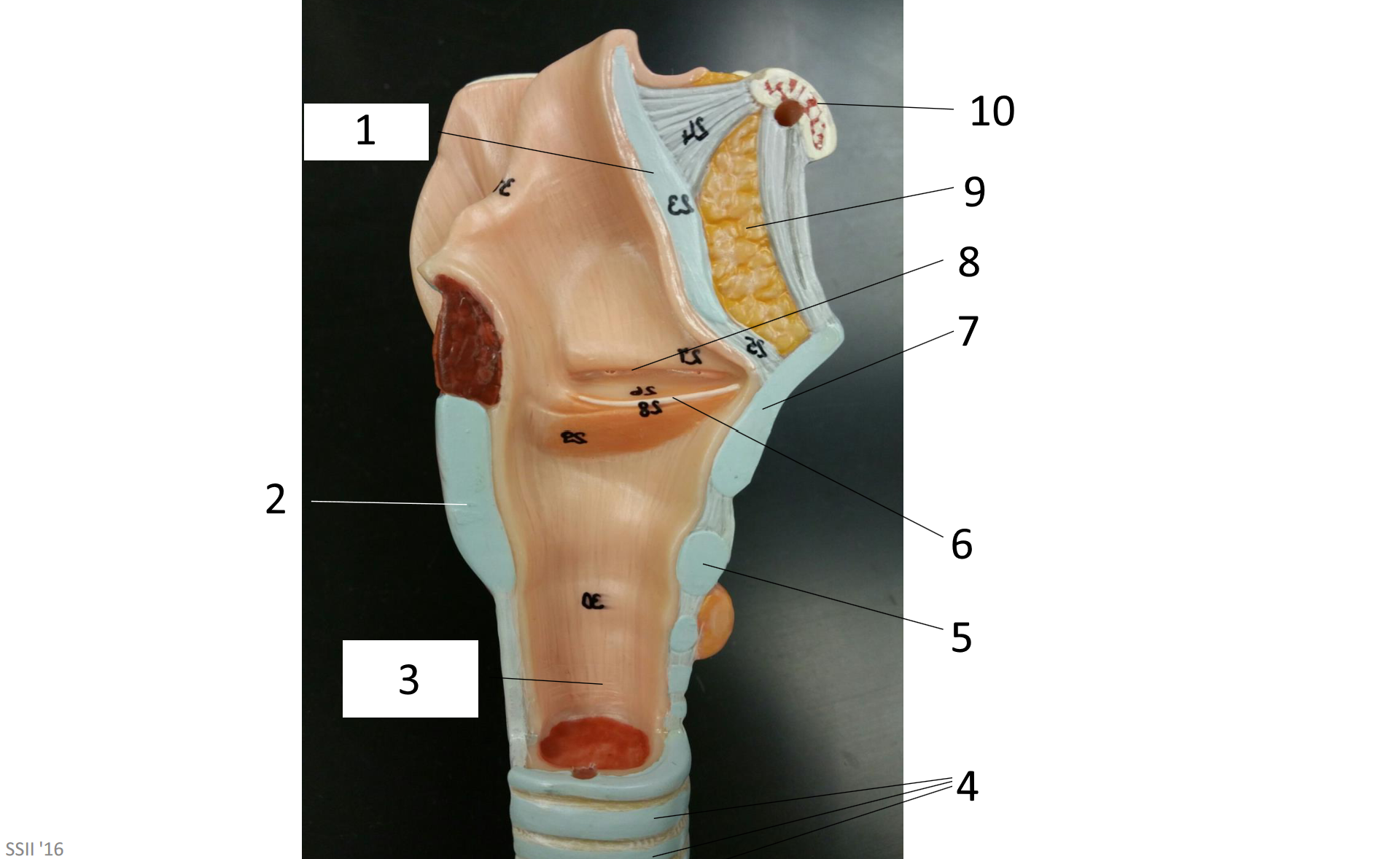
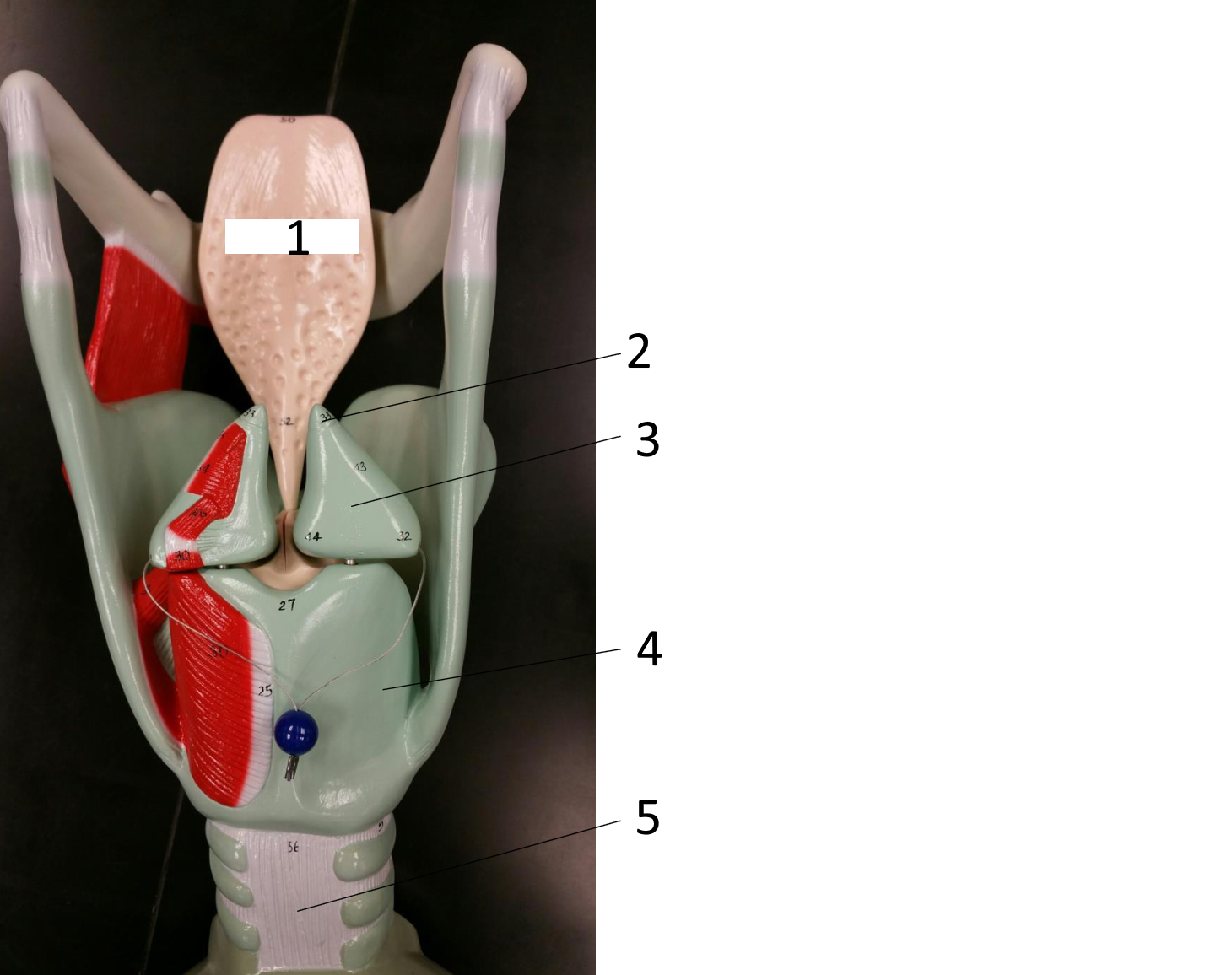
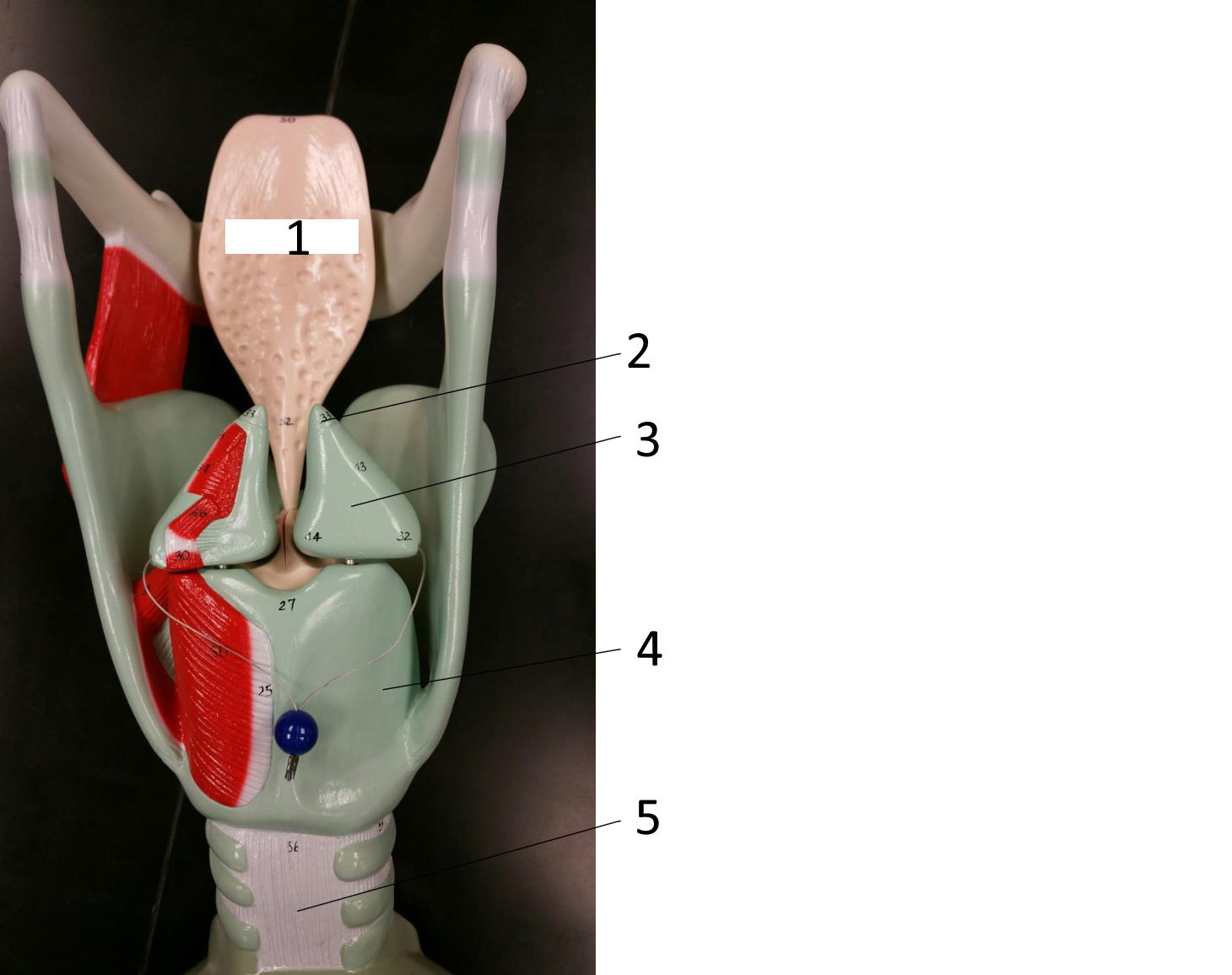
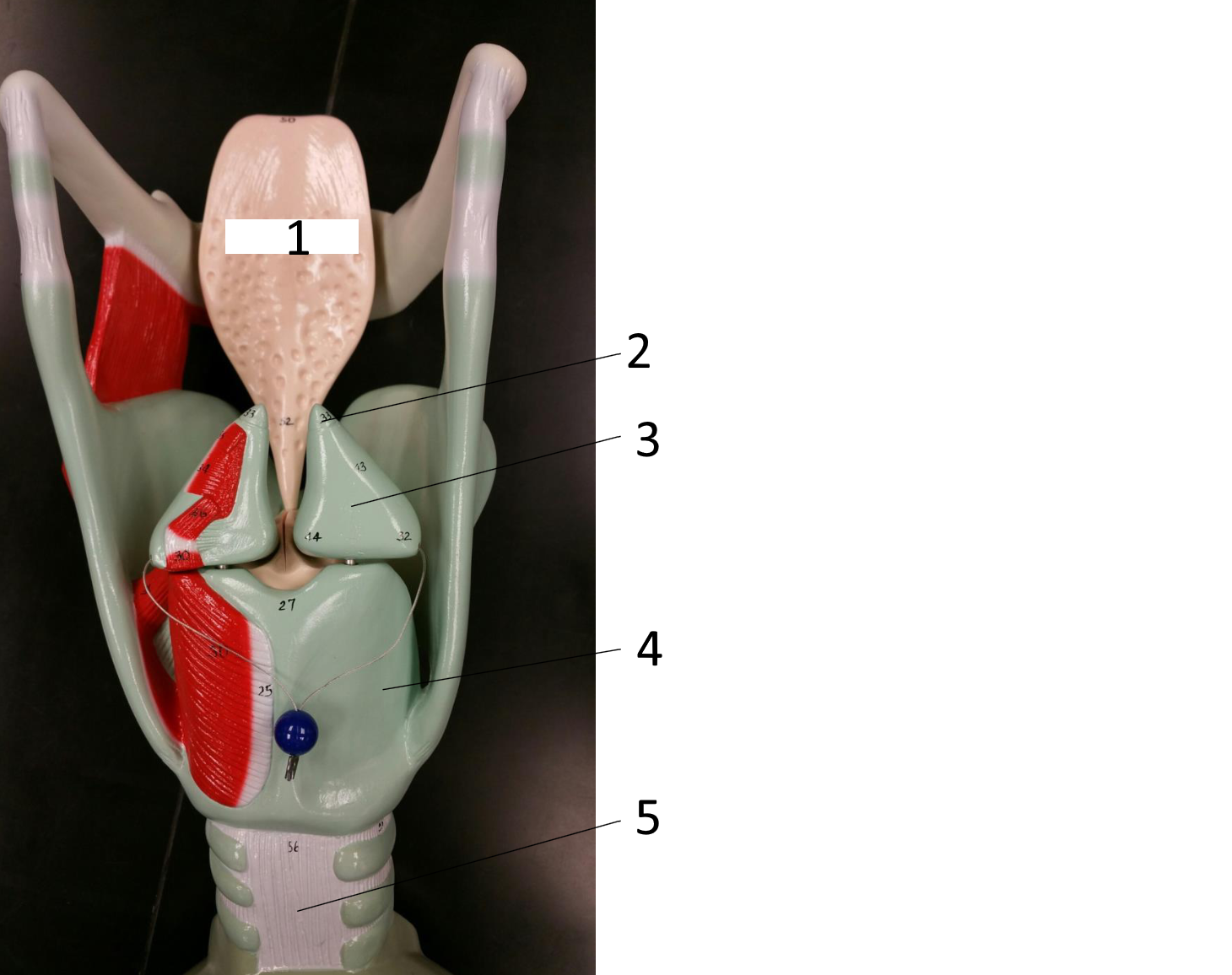
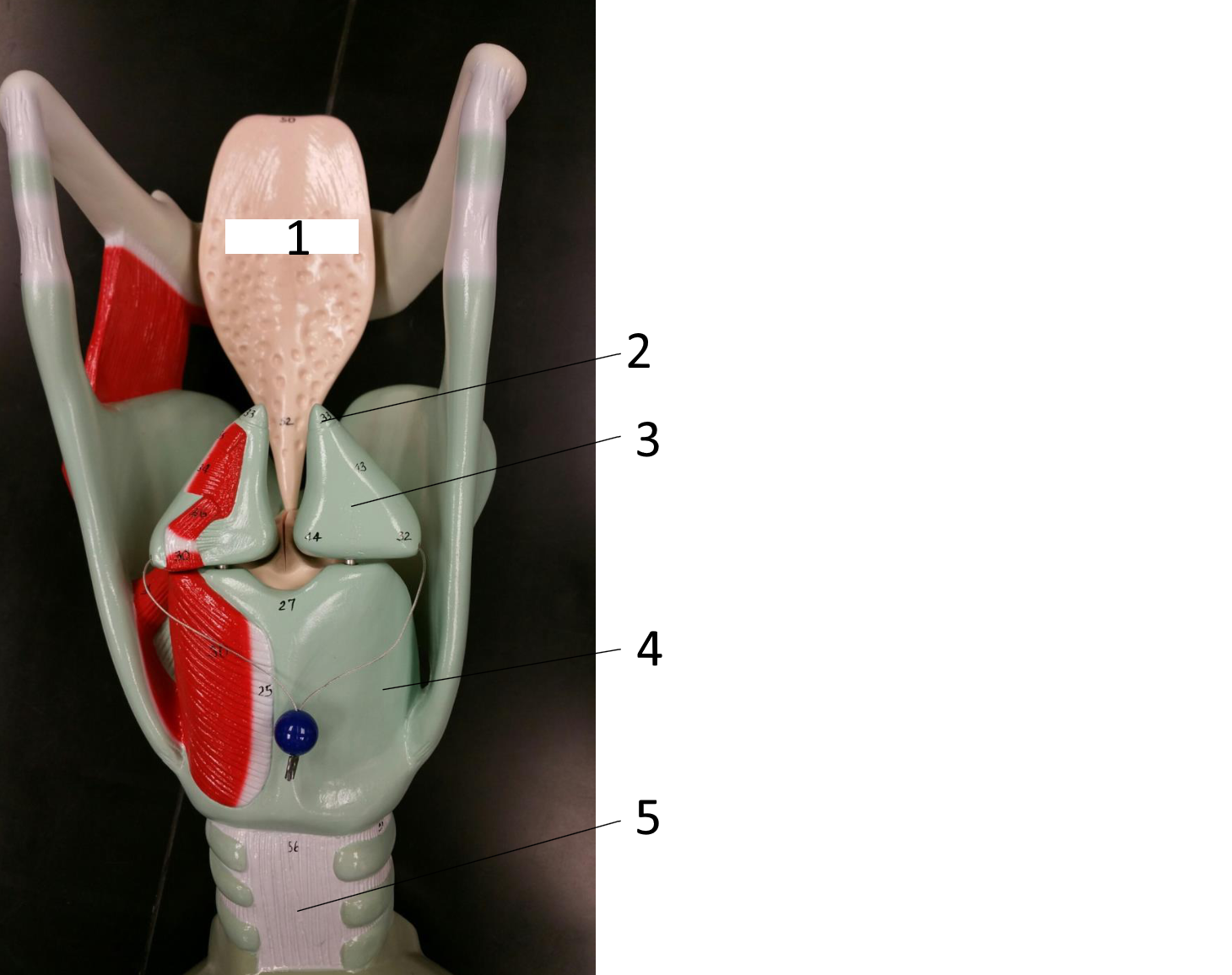
1
epiglottis
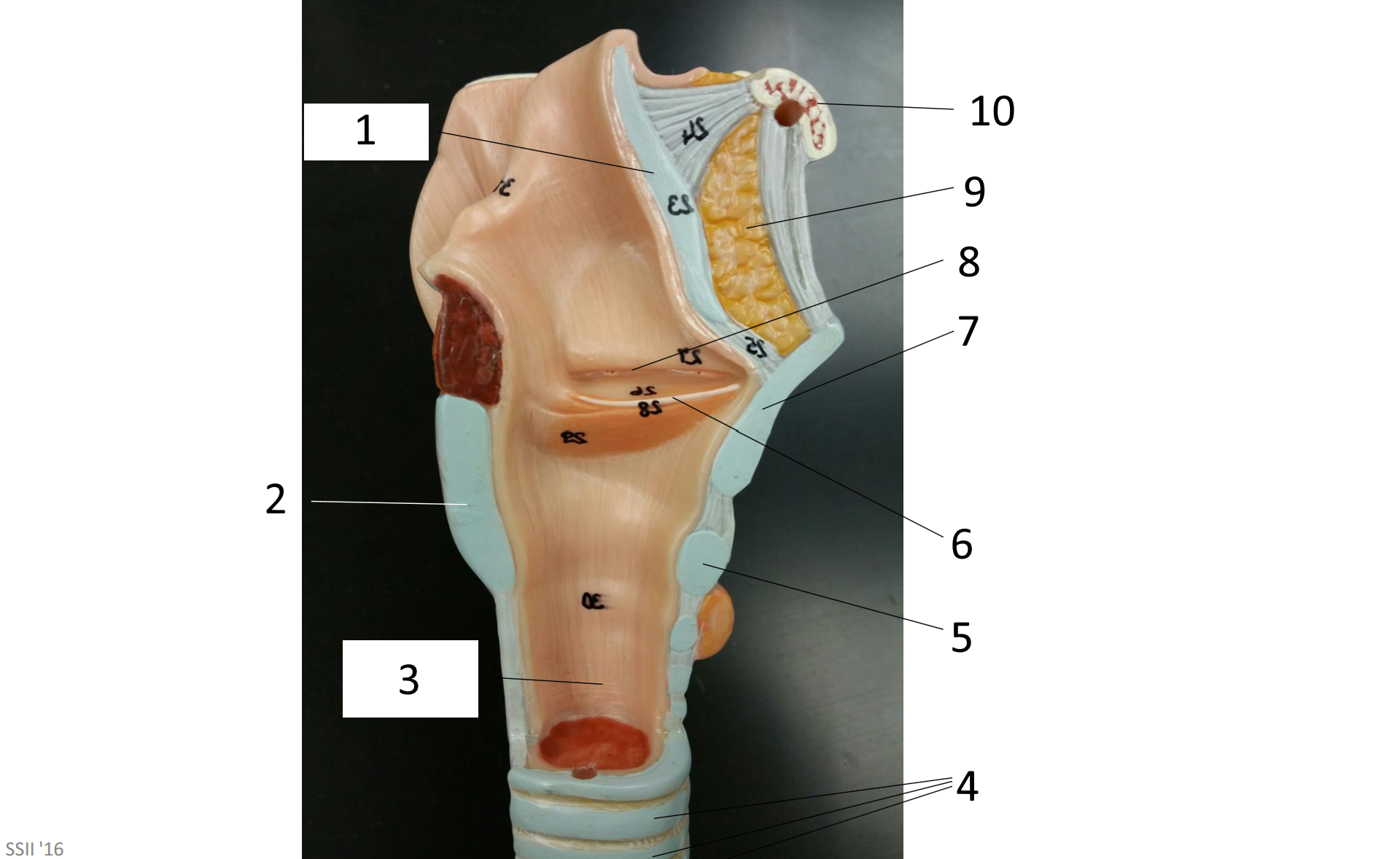
2
cricoid cartilage
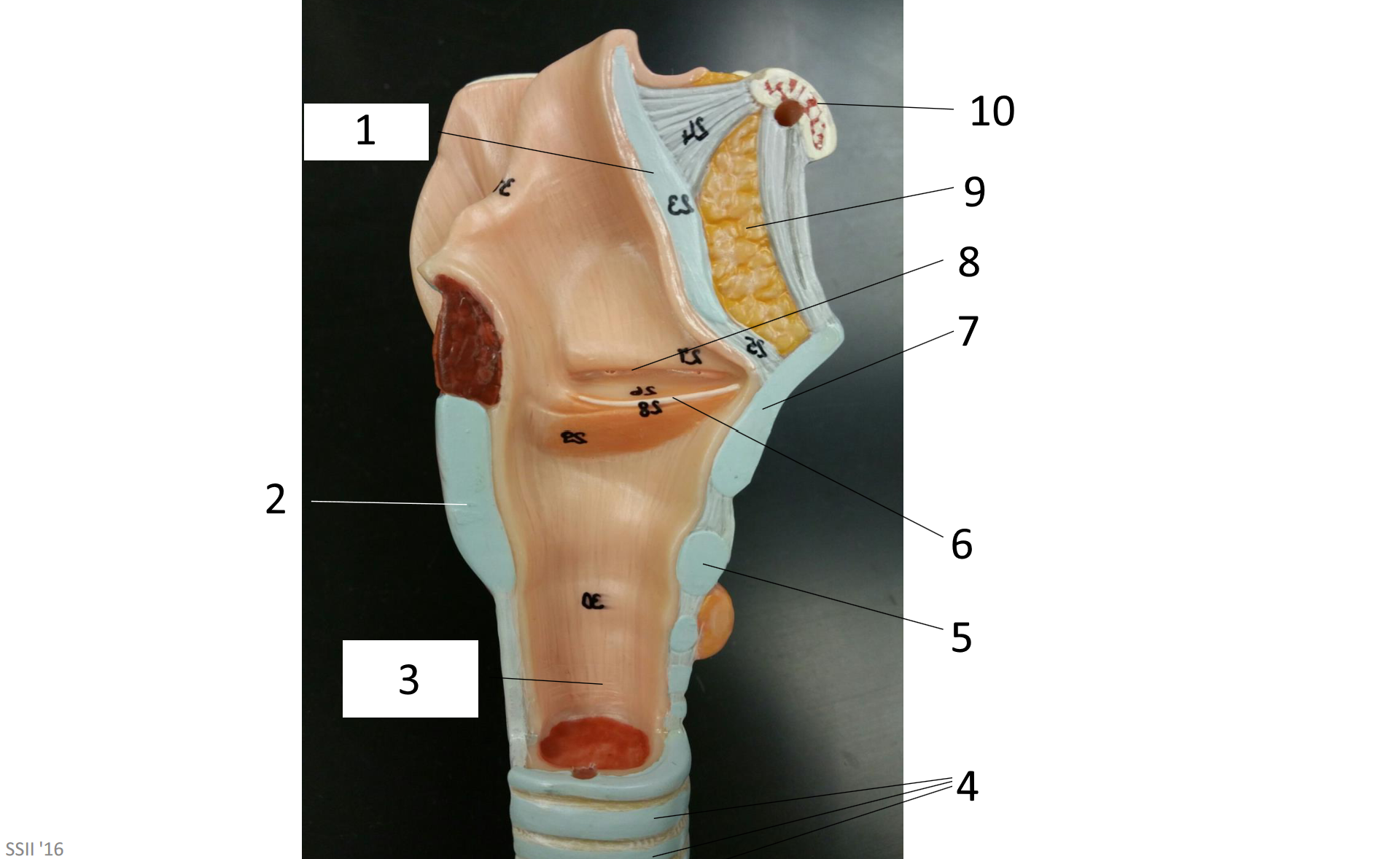
3
lumen of trachea
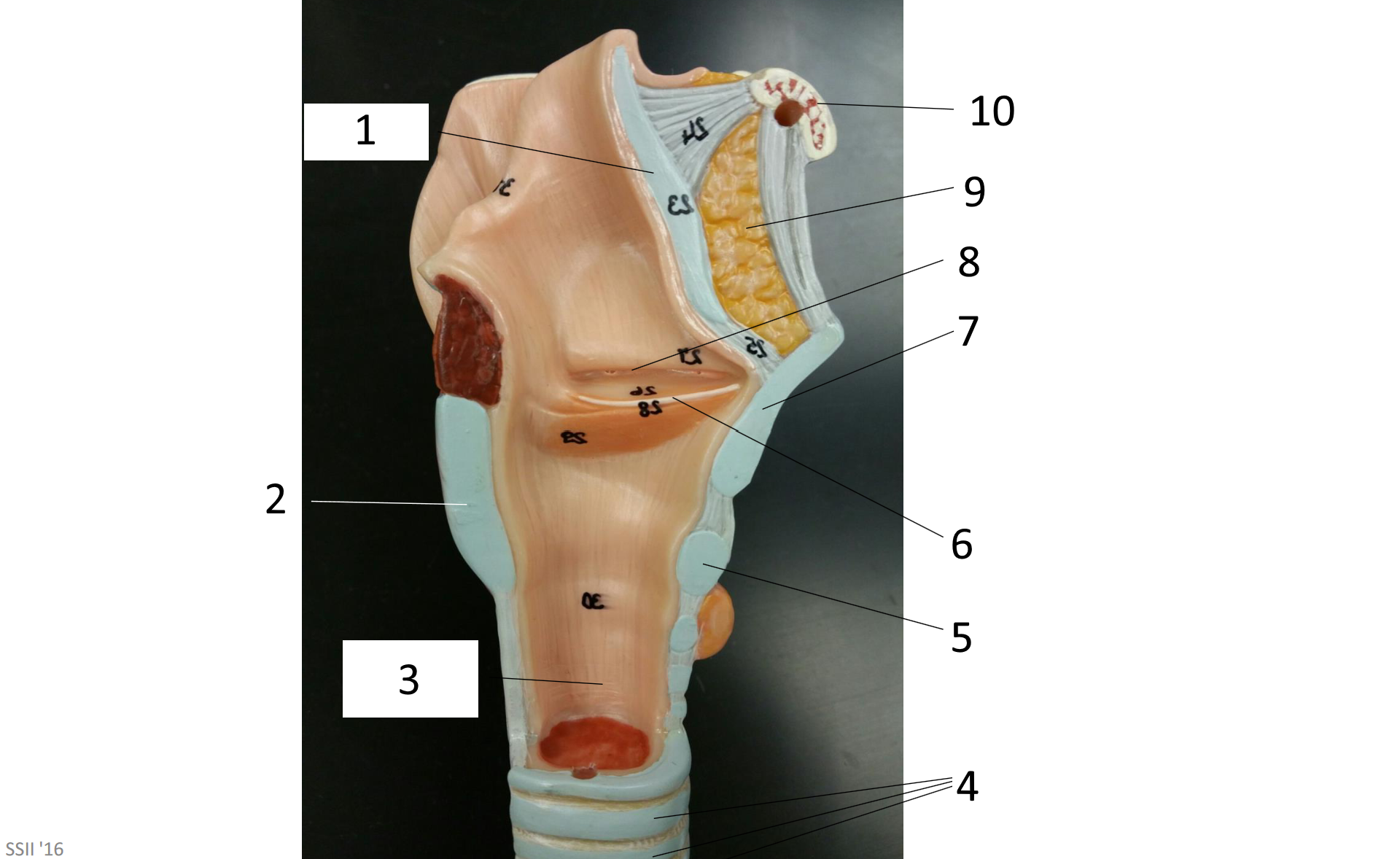
4
tracheal cartilages
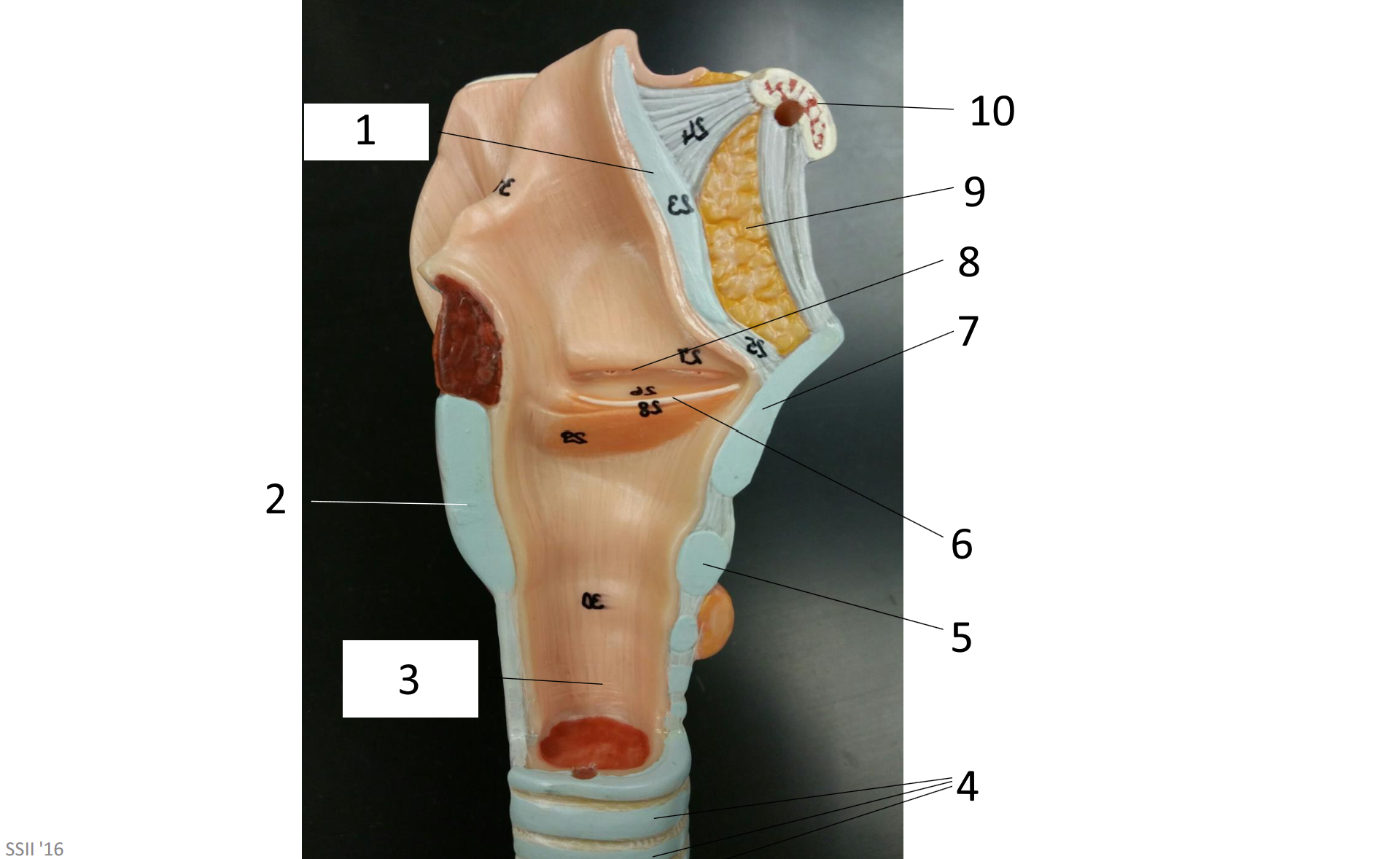
5
cricoid cartilage
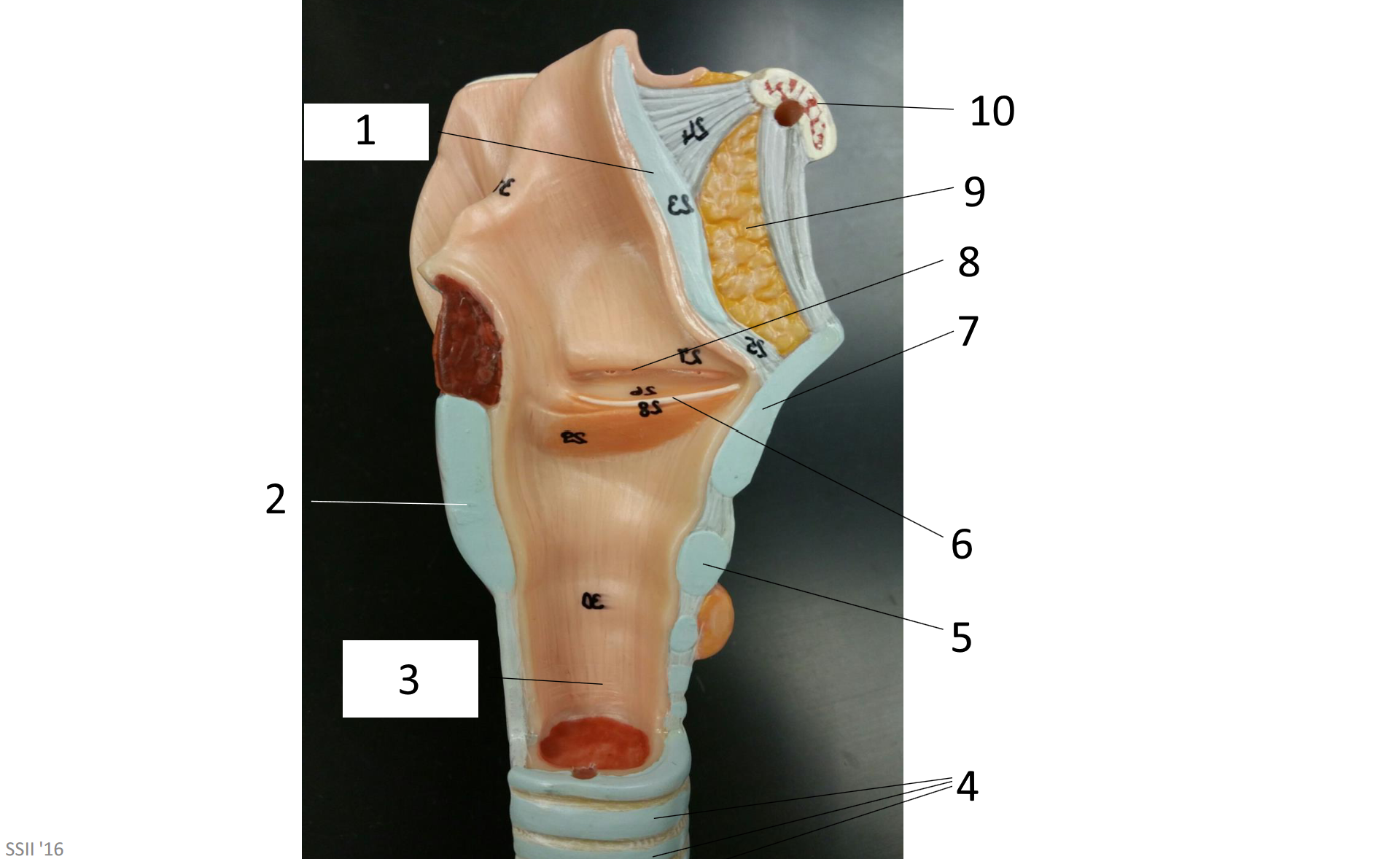
6
vocal fold
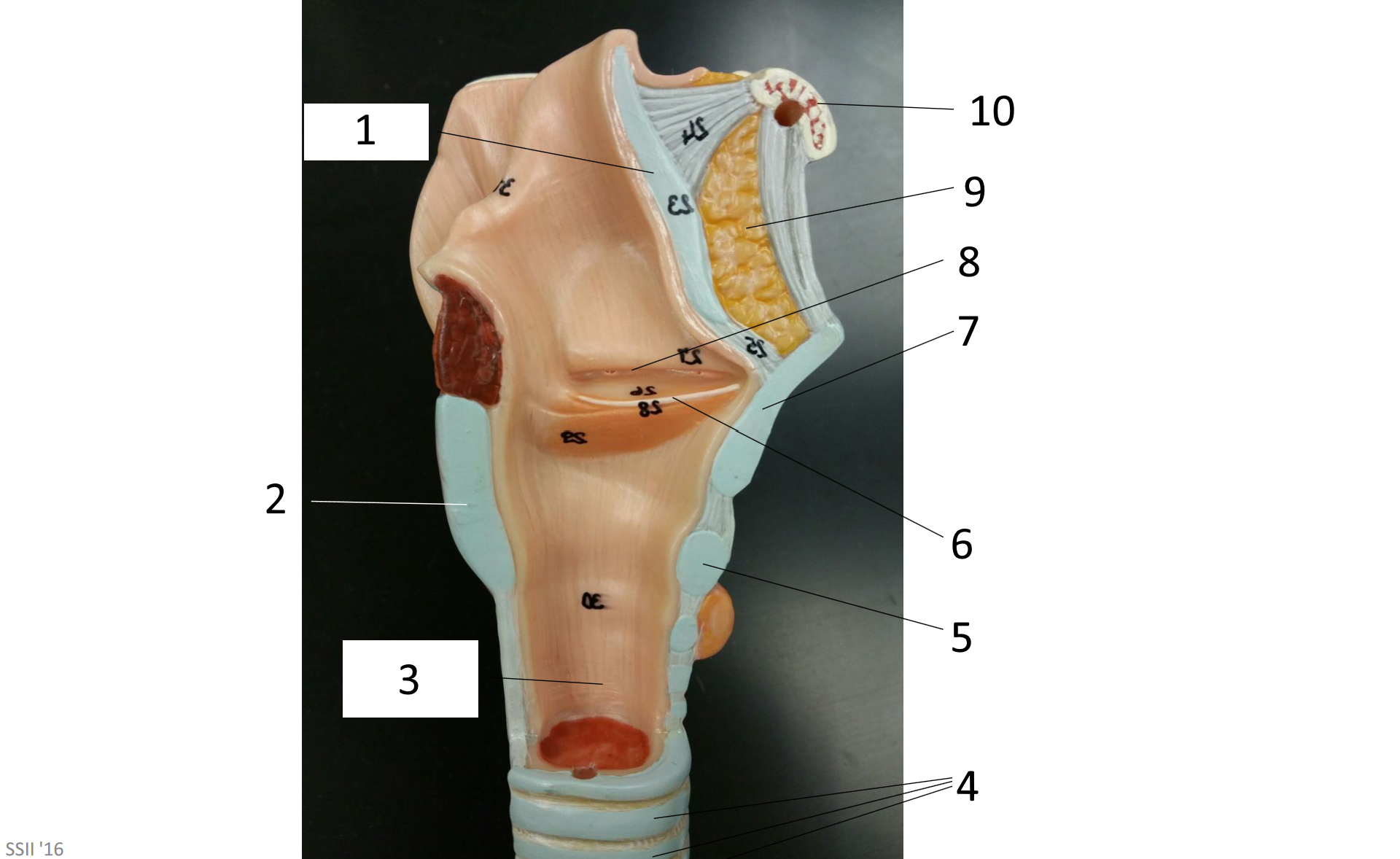
7
thyroid cartilage
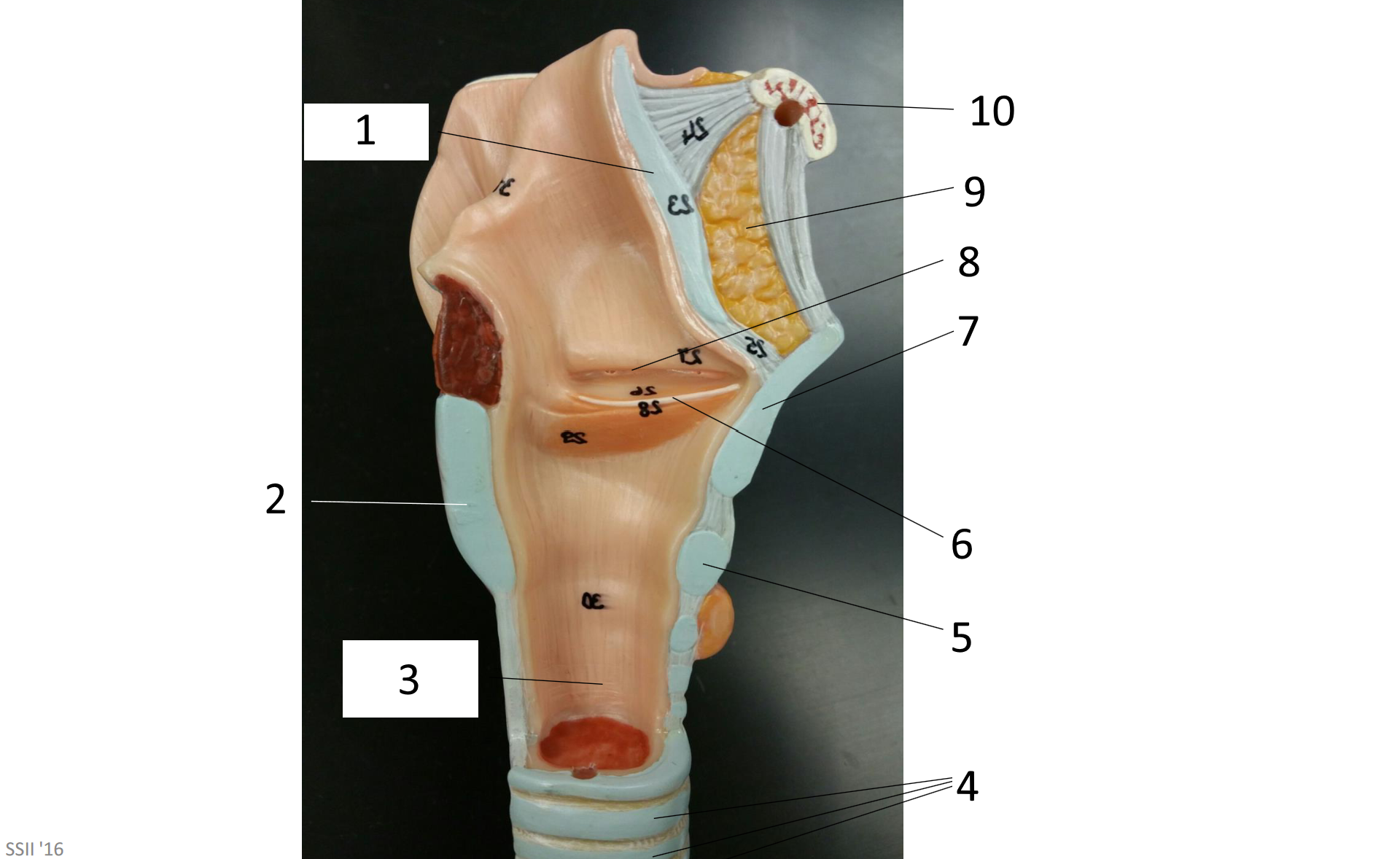
8
vestibular fold
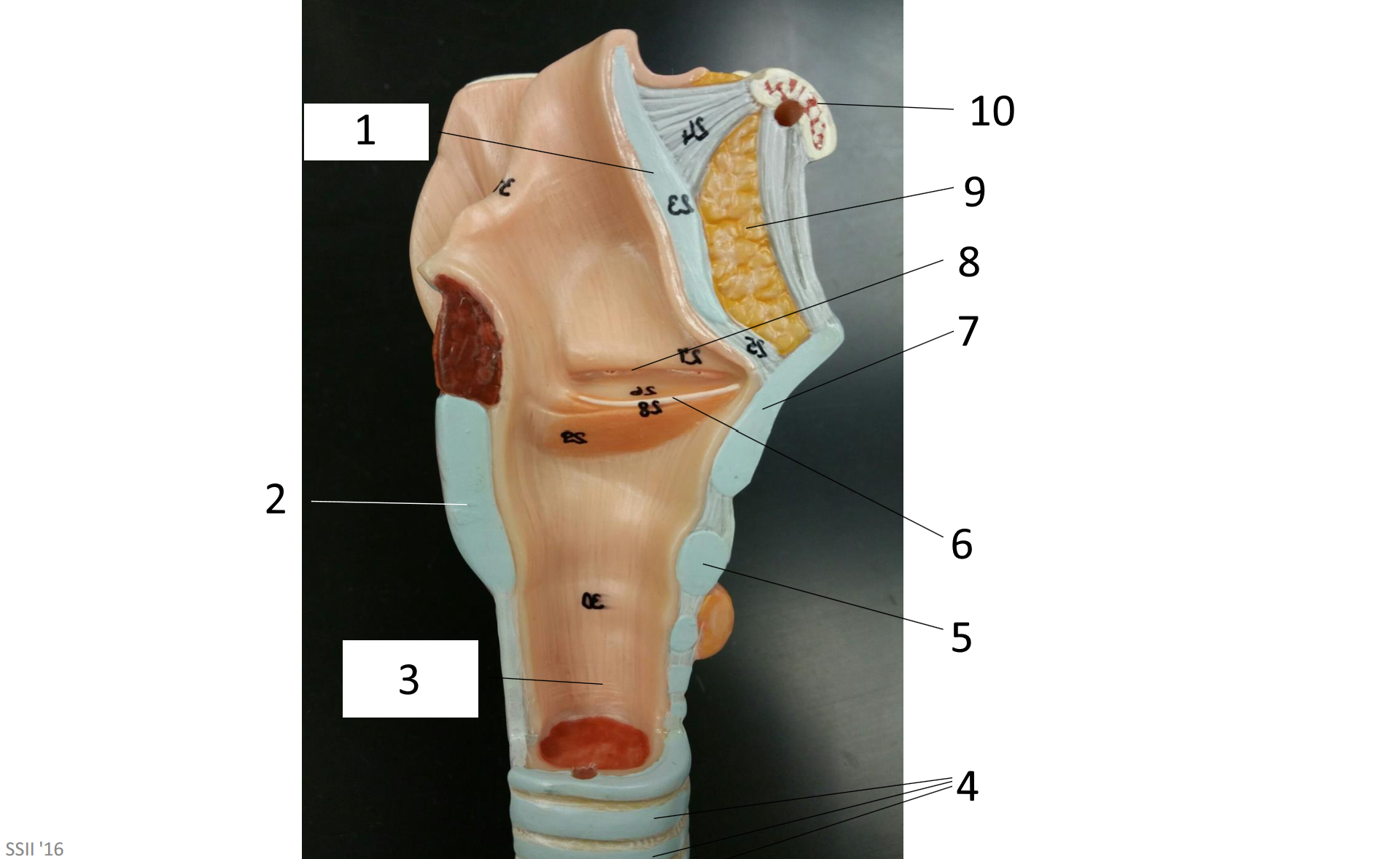
9
adipose tissue
10
hyoid bone
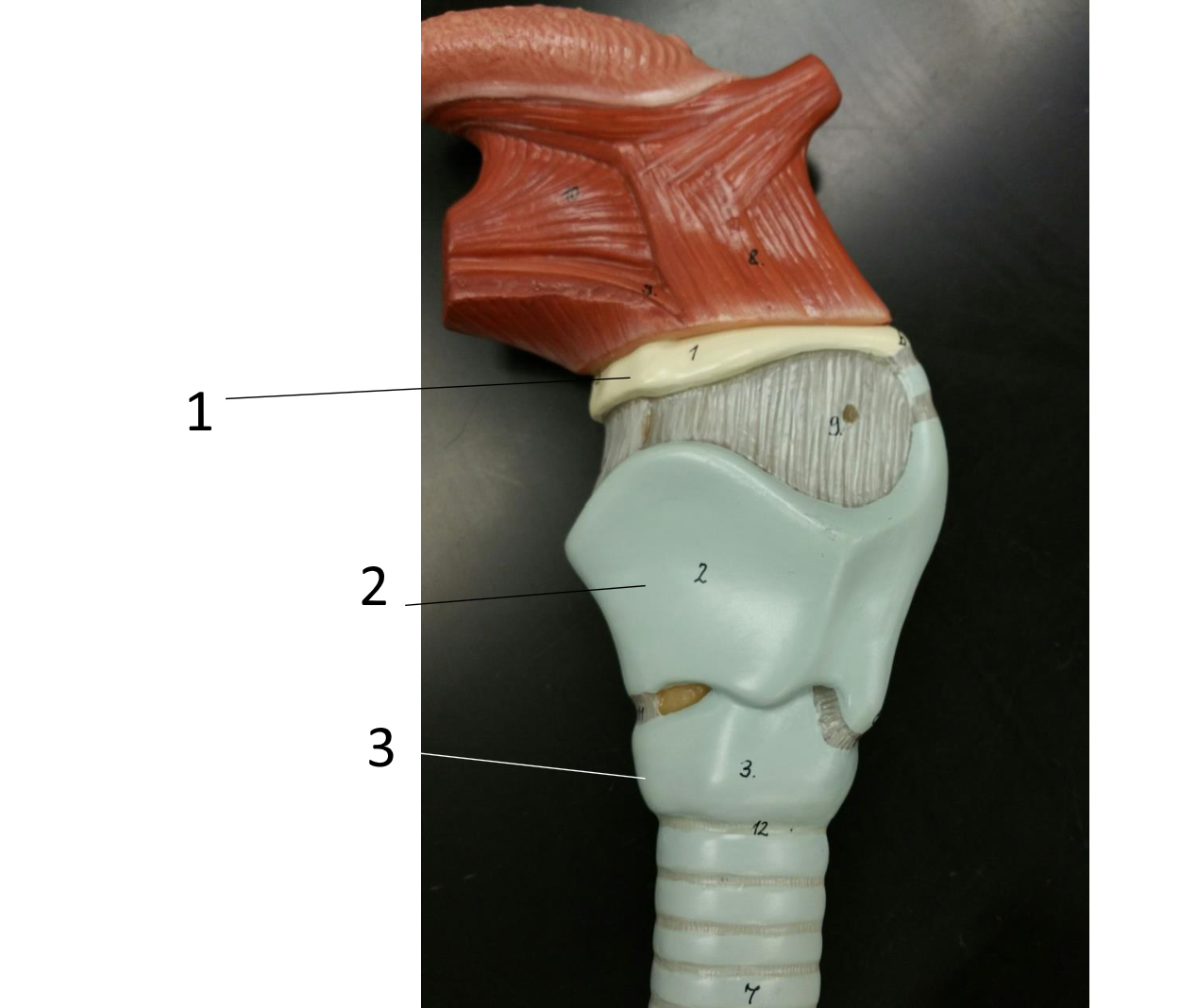
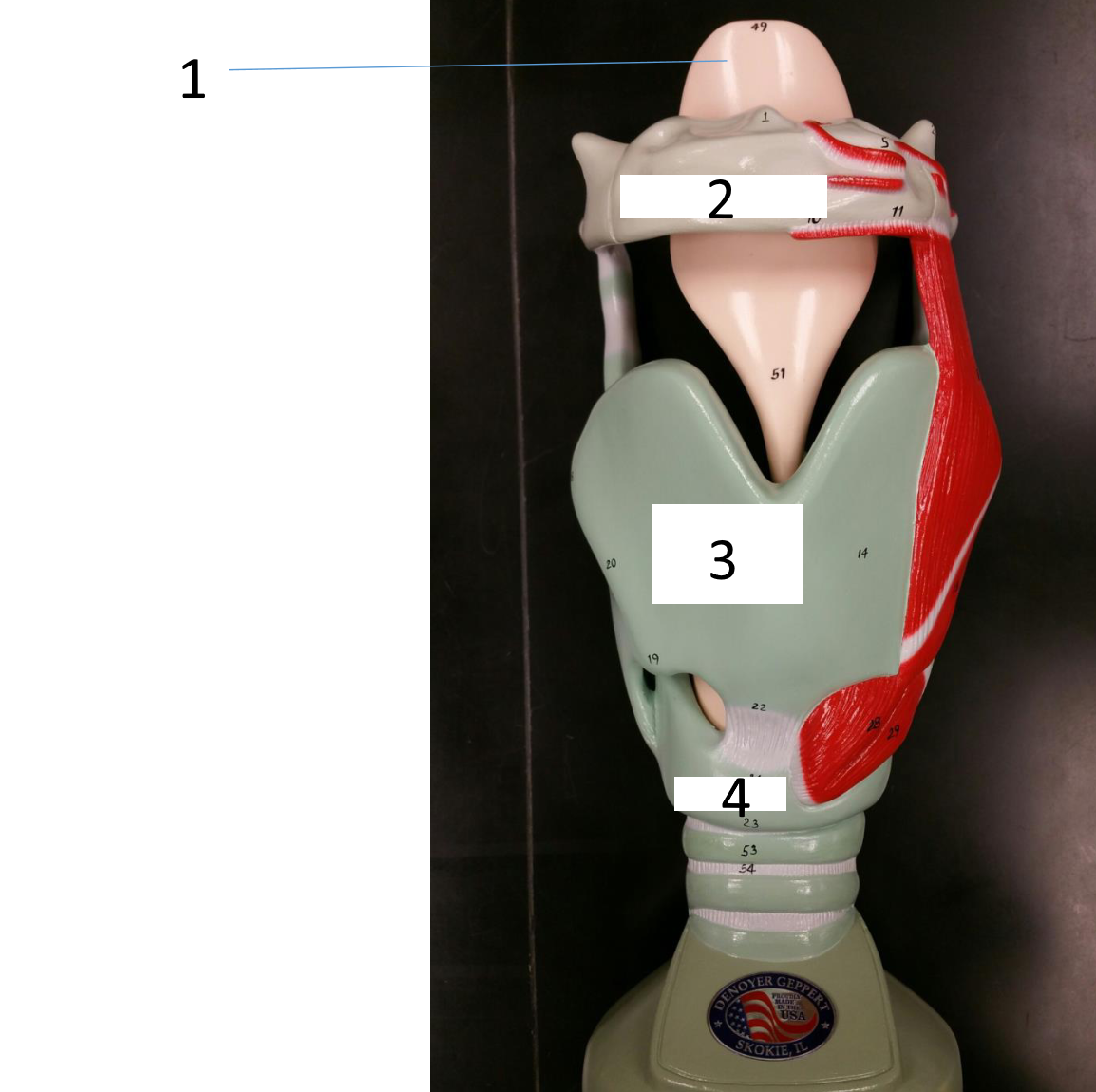
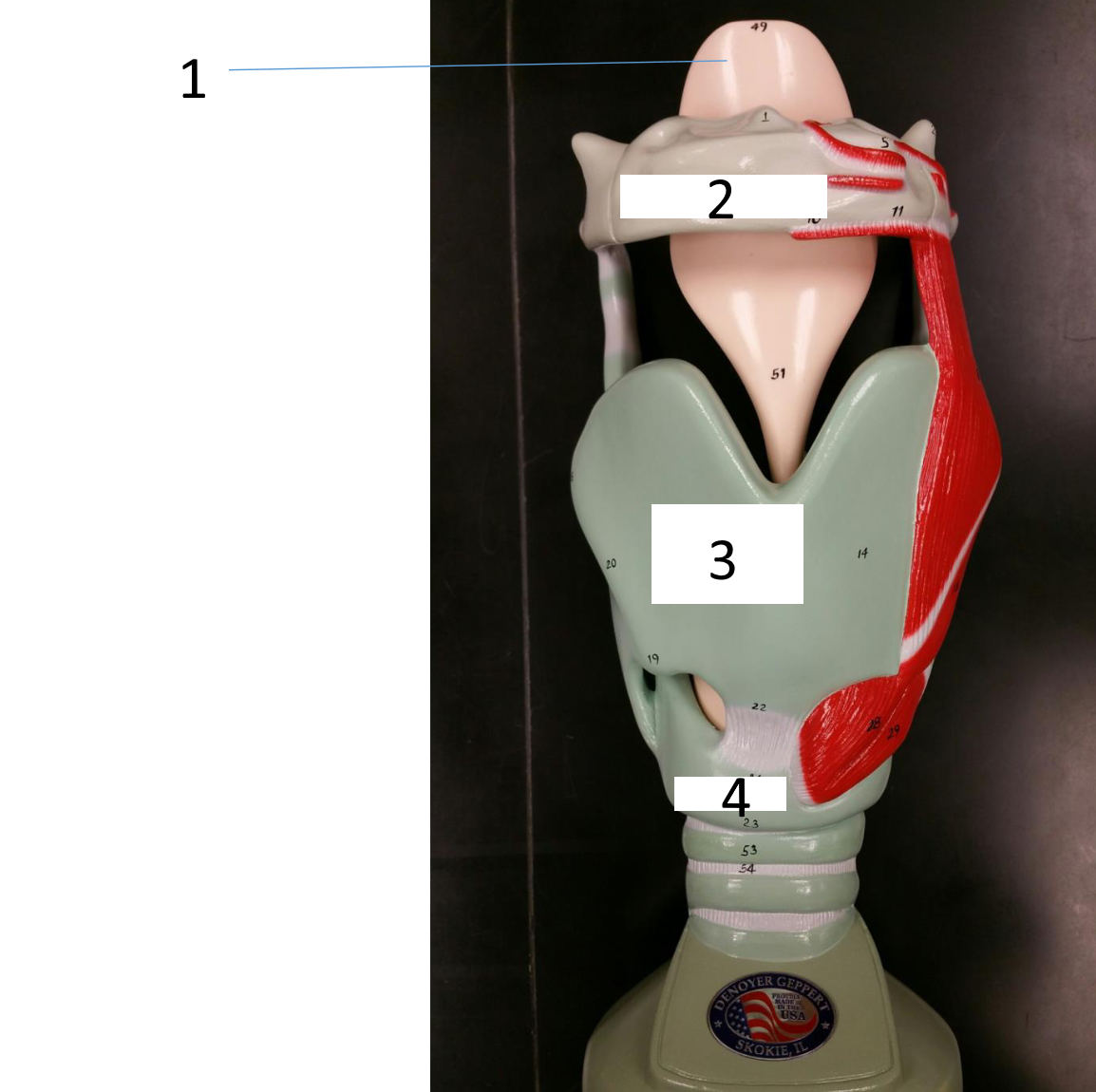
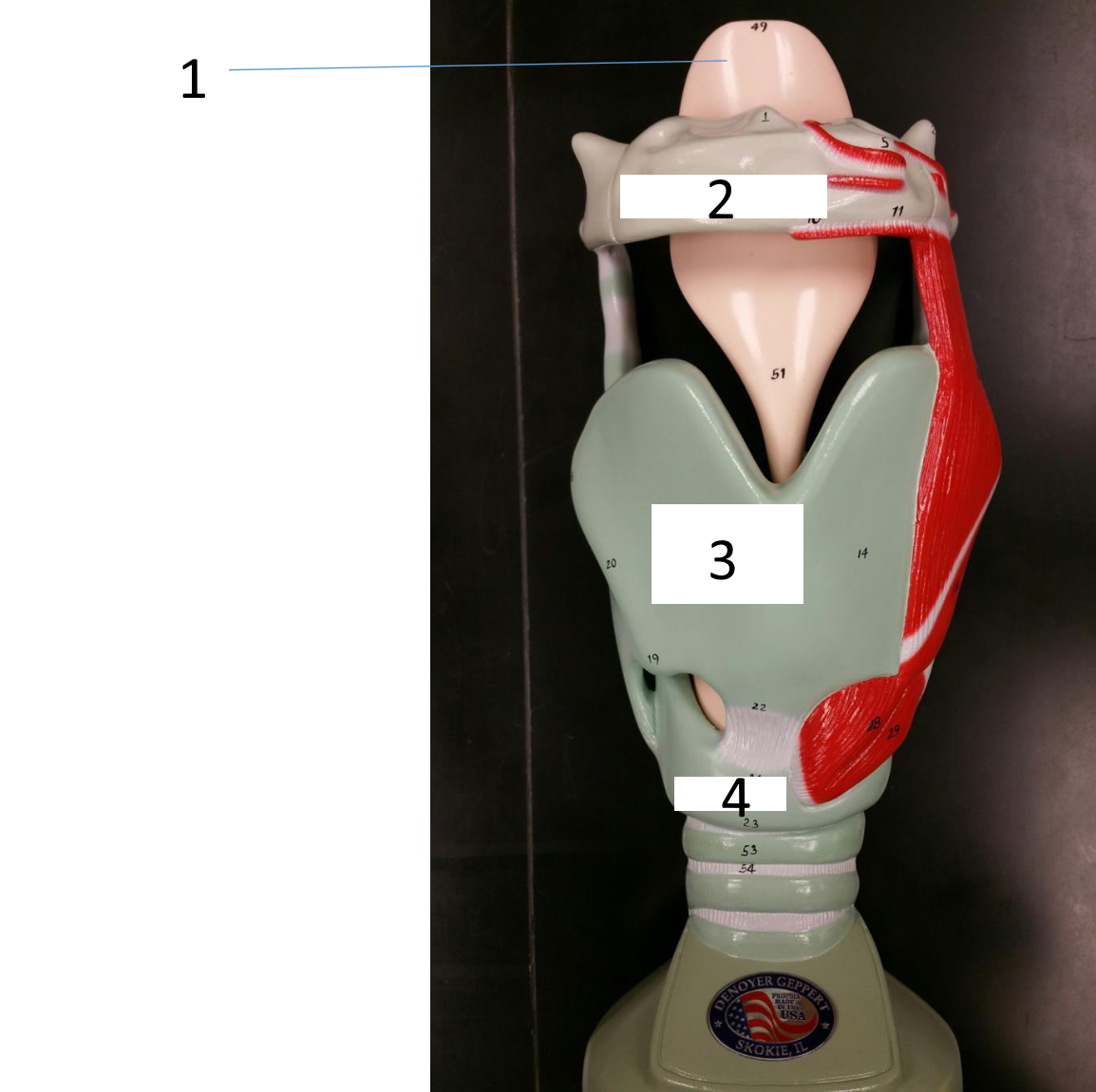
1
hyoid bone
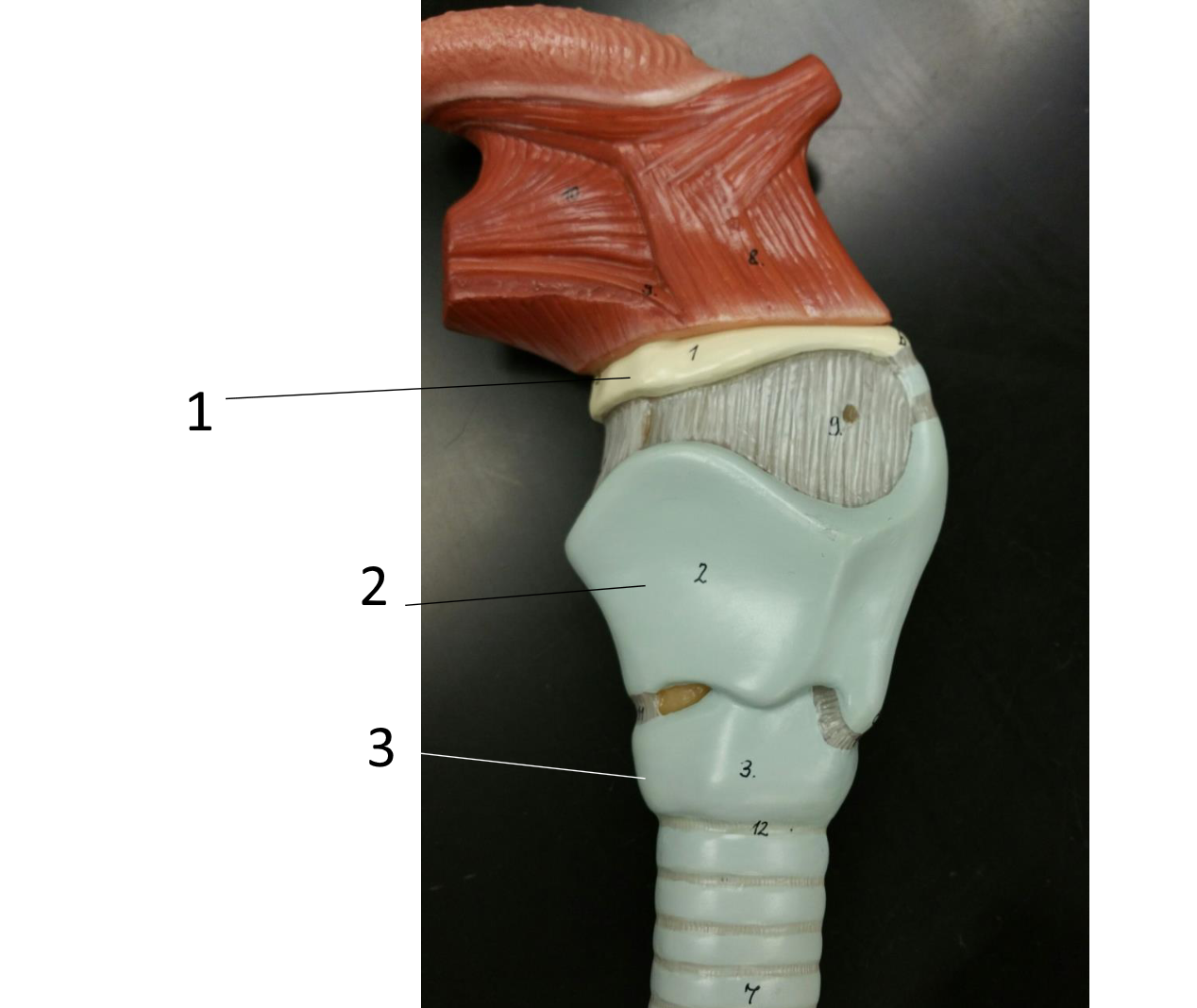
2
thyroid cartilage
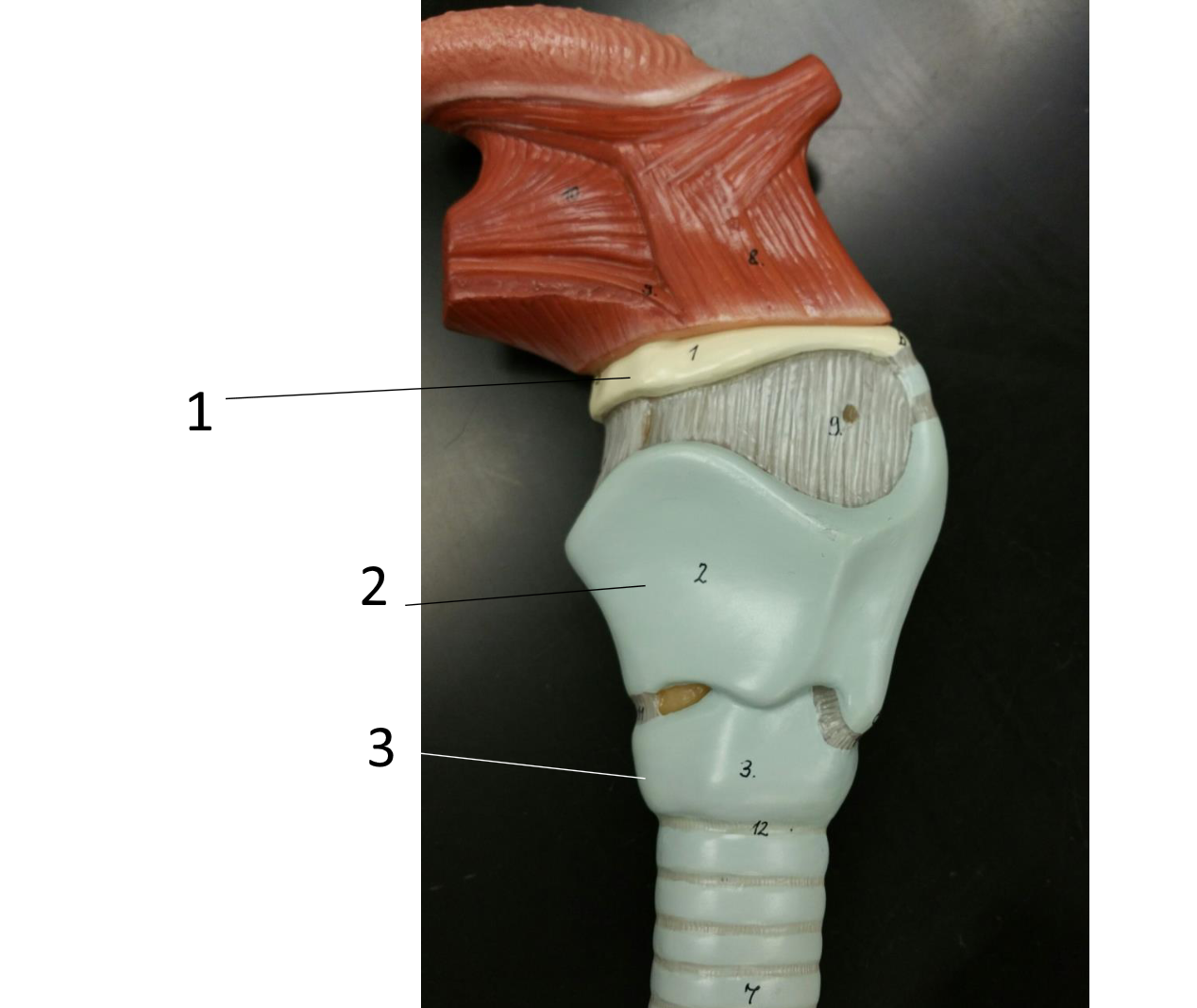
3
cricoid cartilage
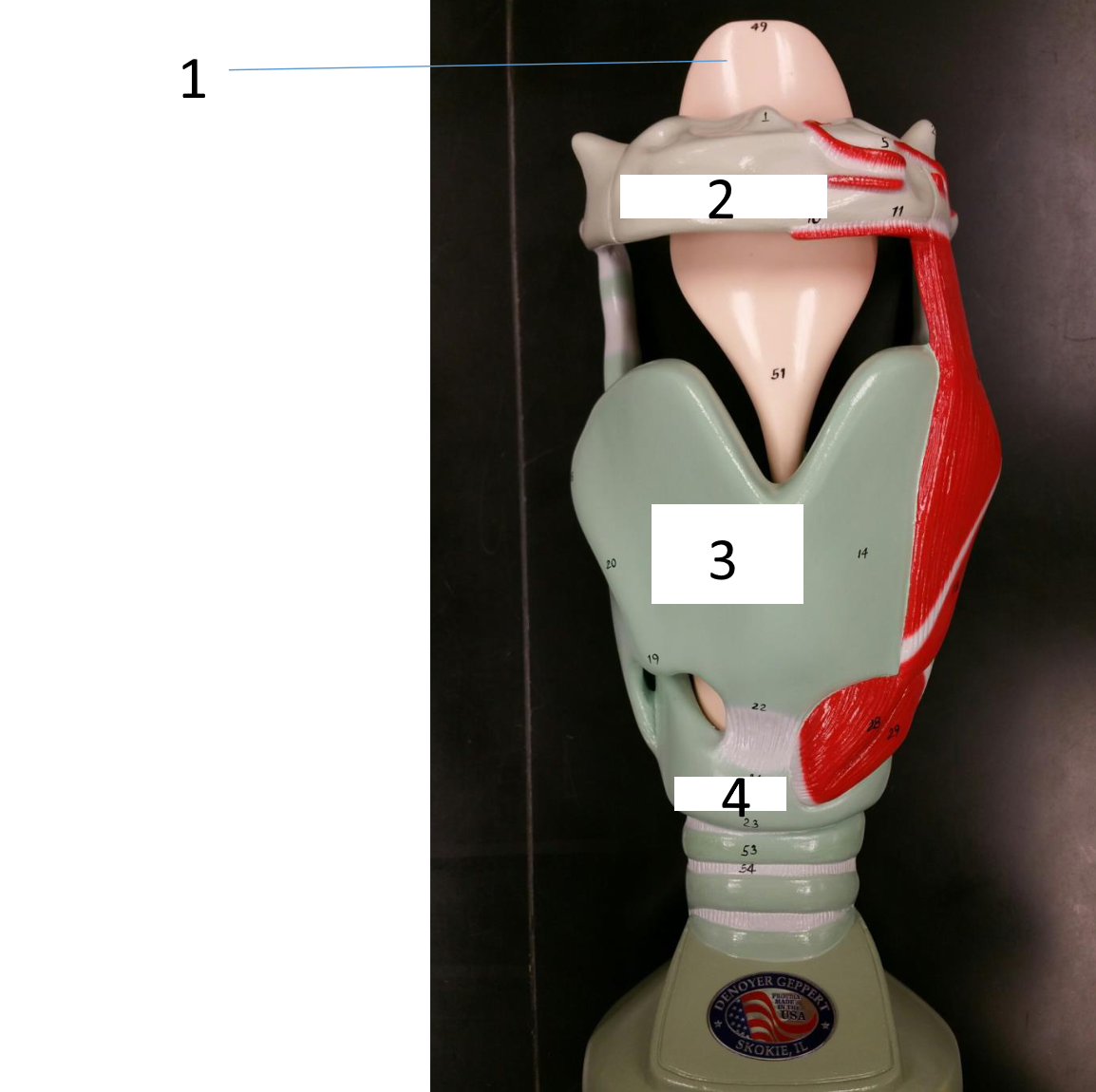

1
epiglottis

2
hyoid bone

3
thyroid cartilage

4
cricoid
1
epiglottis
2
corniculate cartilage
3
artyenoid cartilage
4
cricoid cartilage
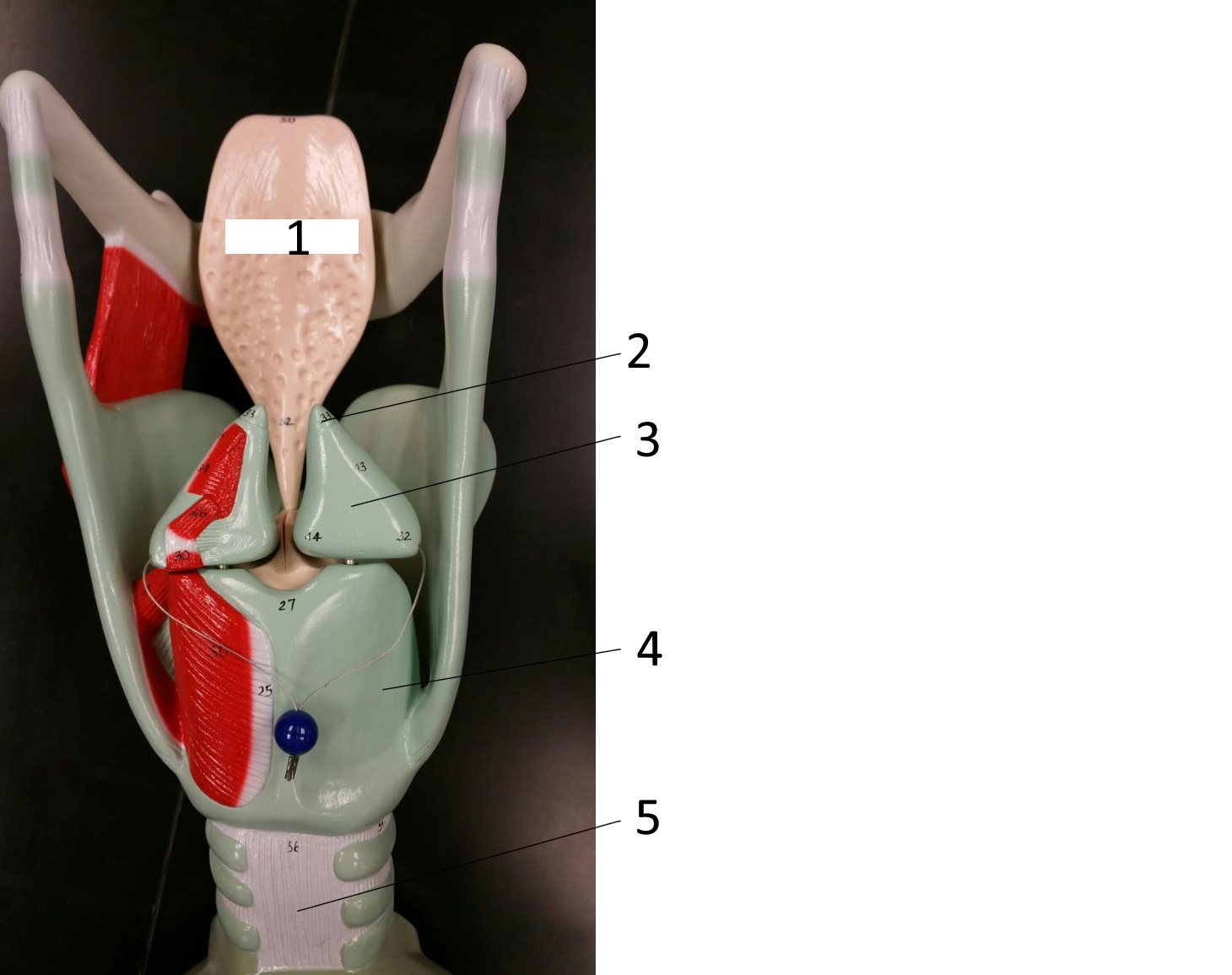
5
posterior membranous wall of trachea
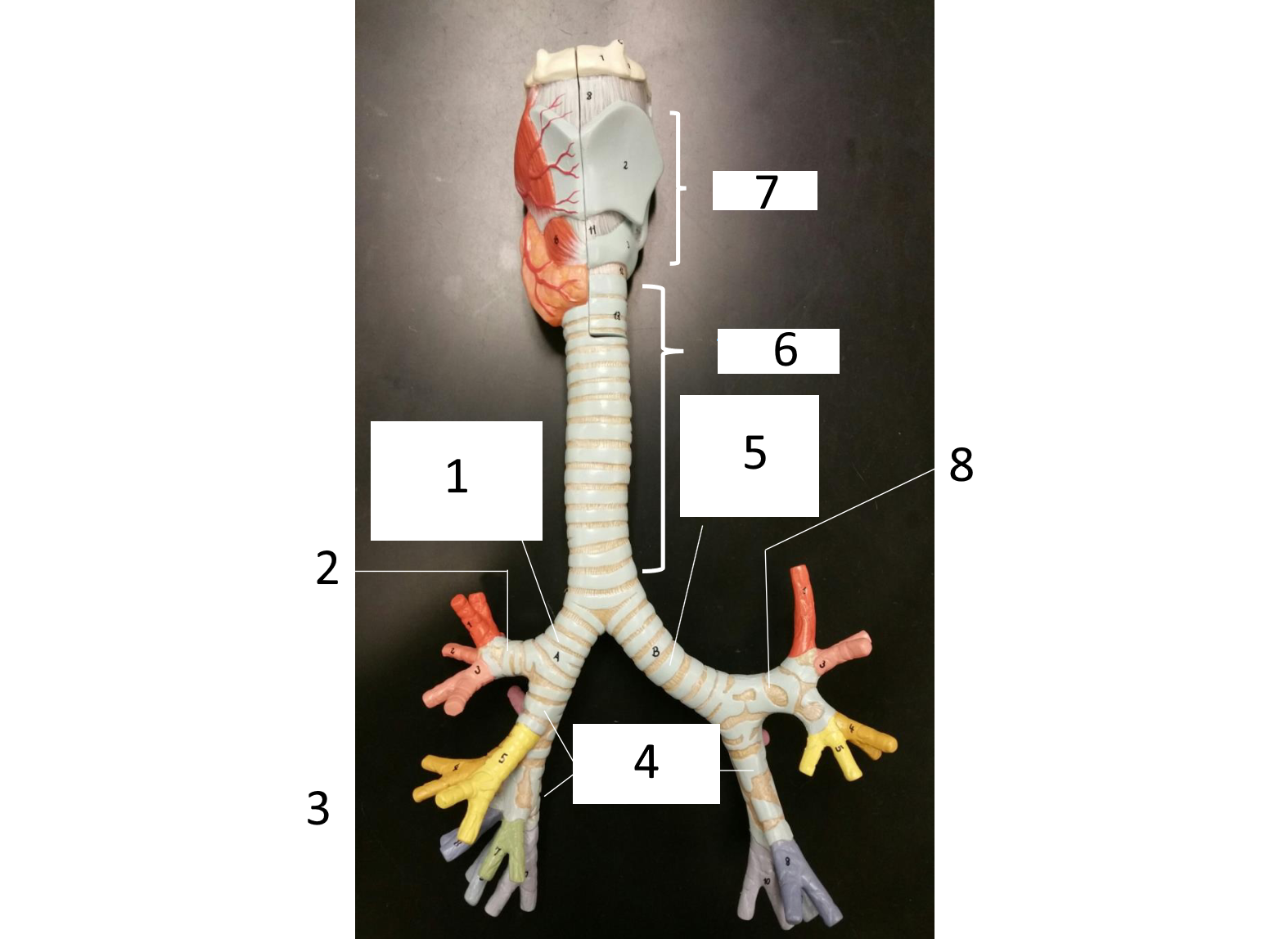
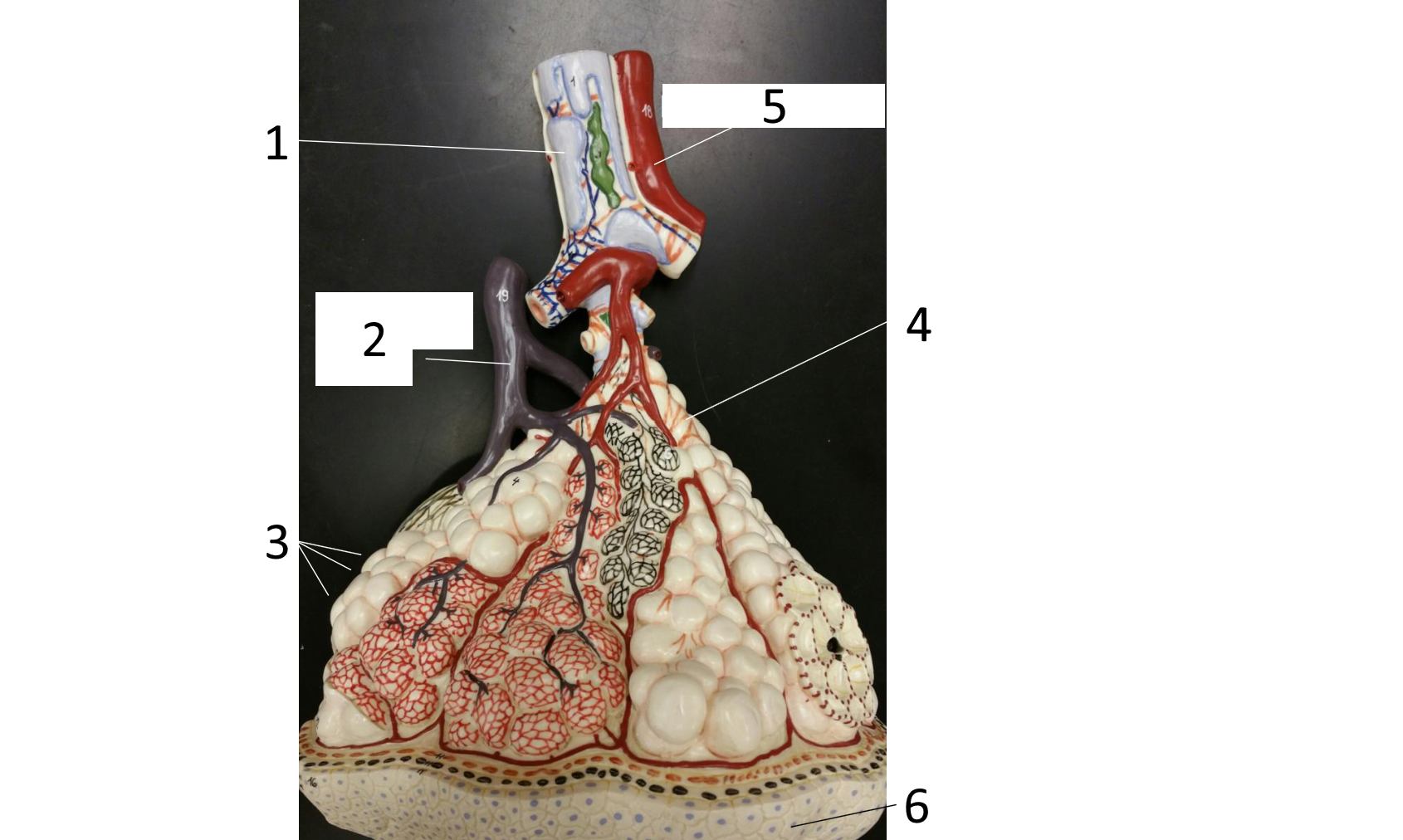
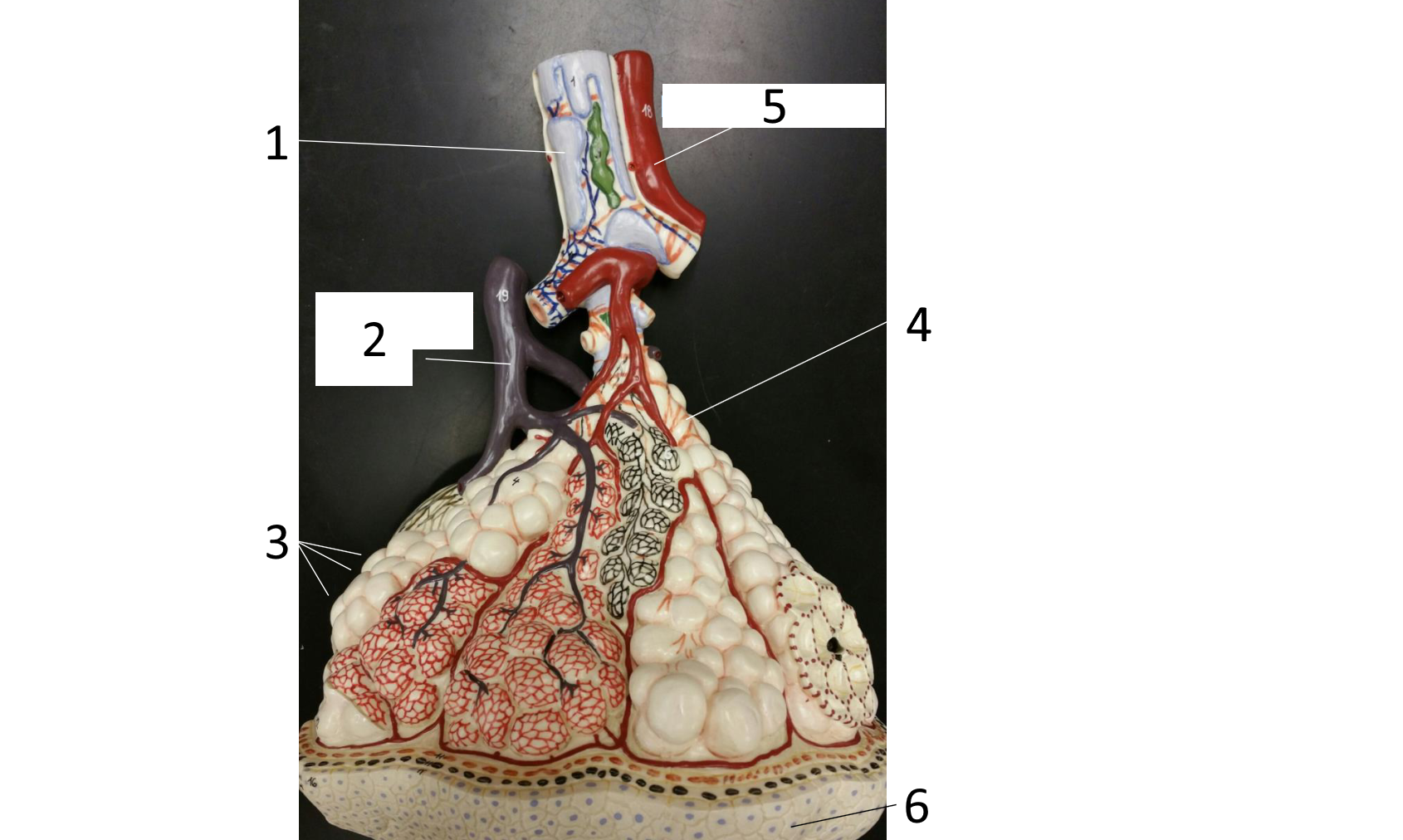
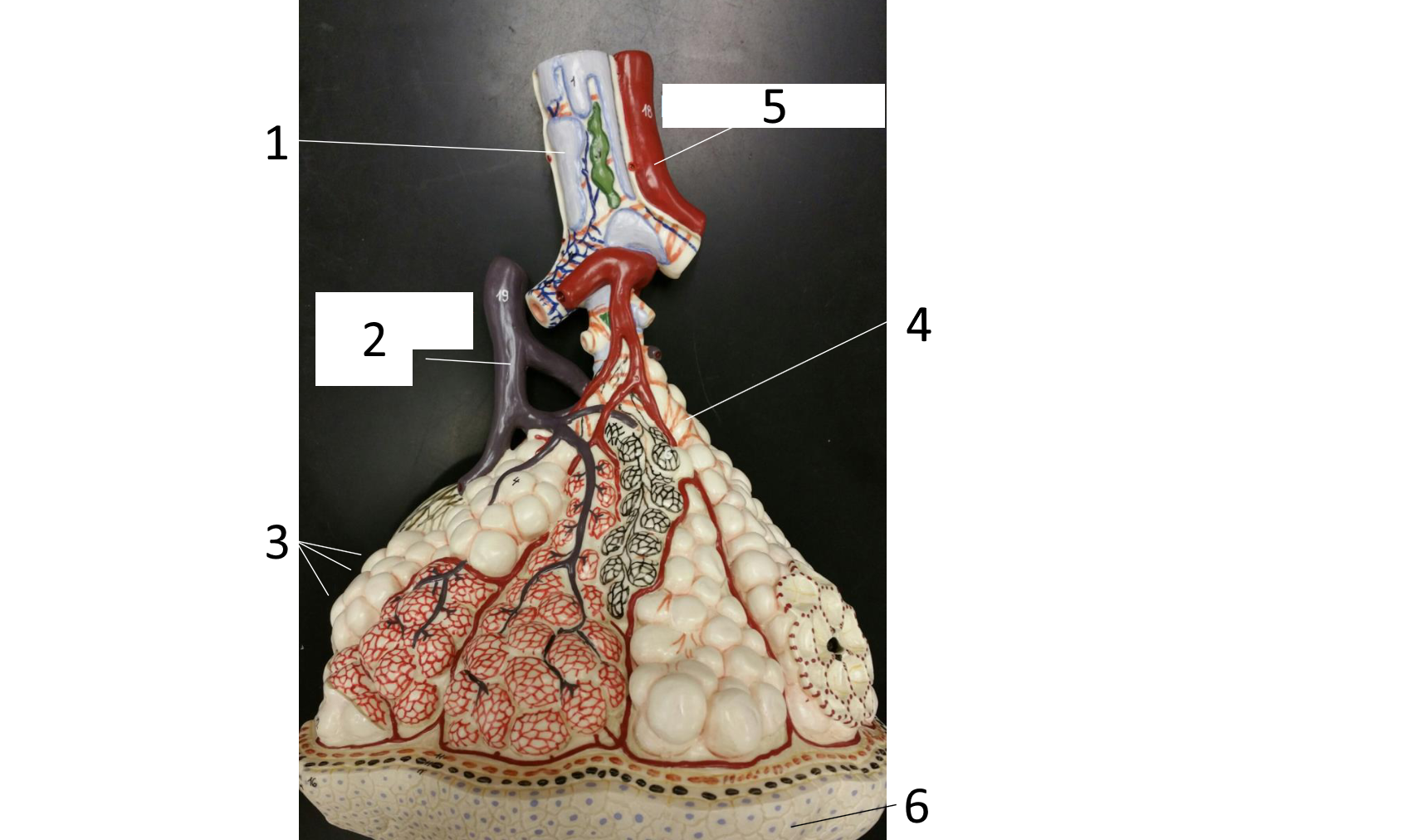
1
right main (primary) bronchus
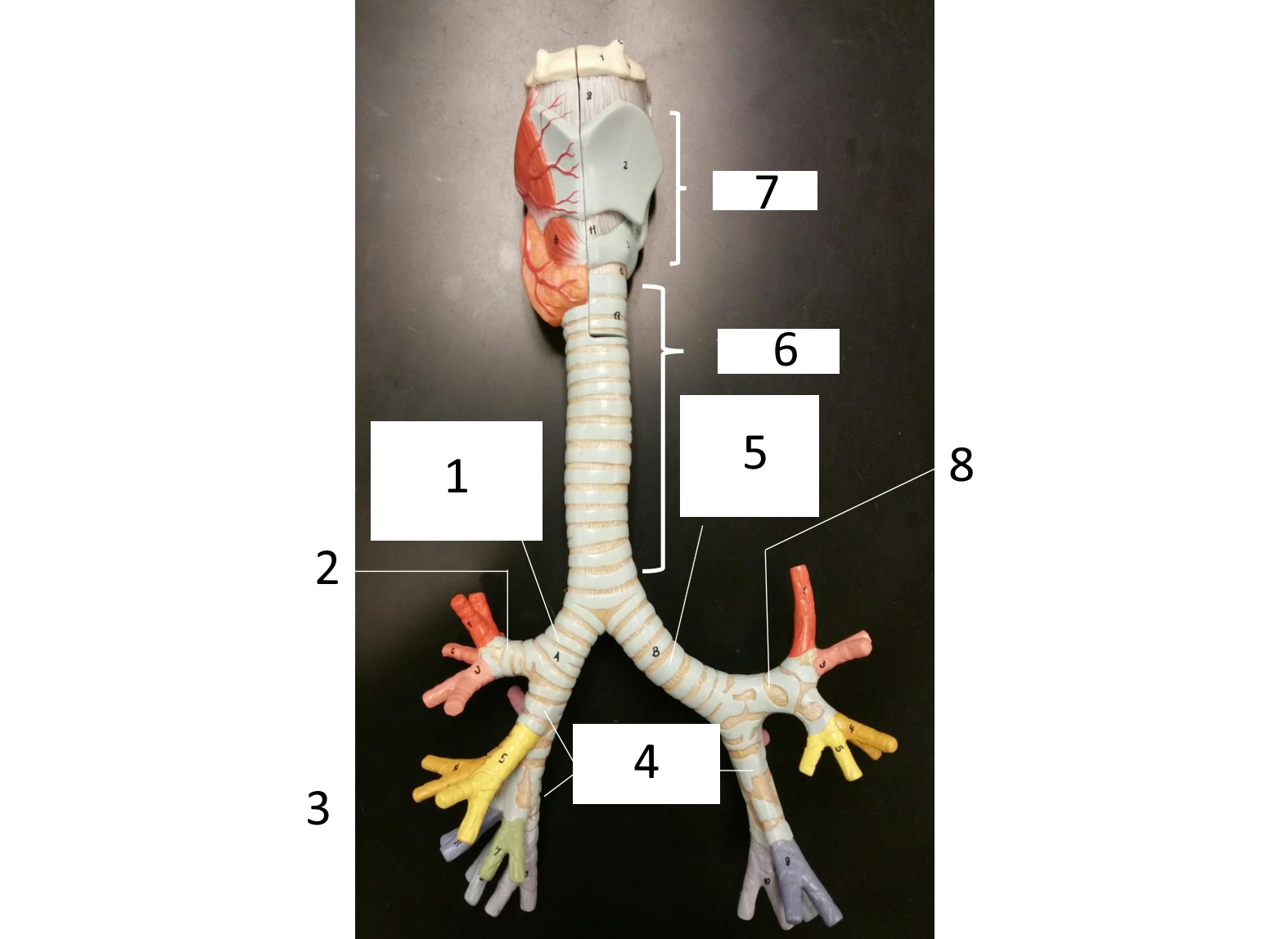
2
secondary bronchus
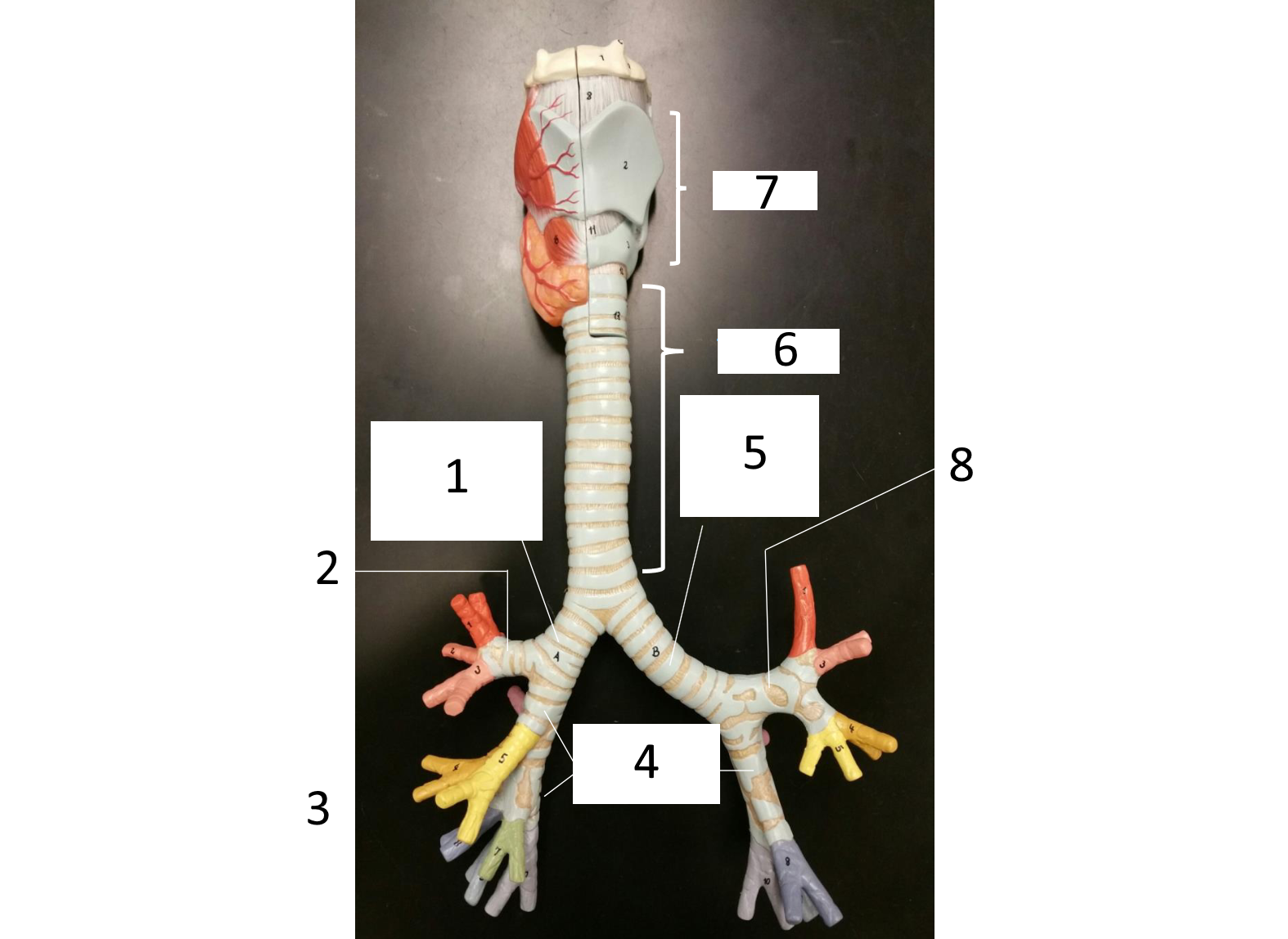
3 (in various colors)
tertiary bronchi
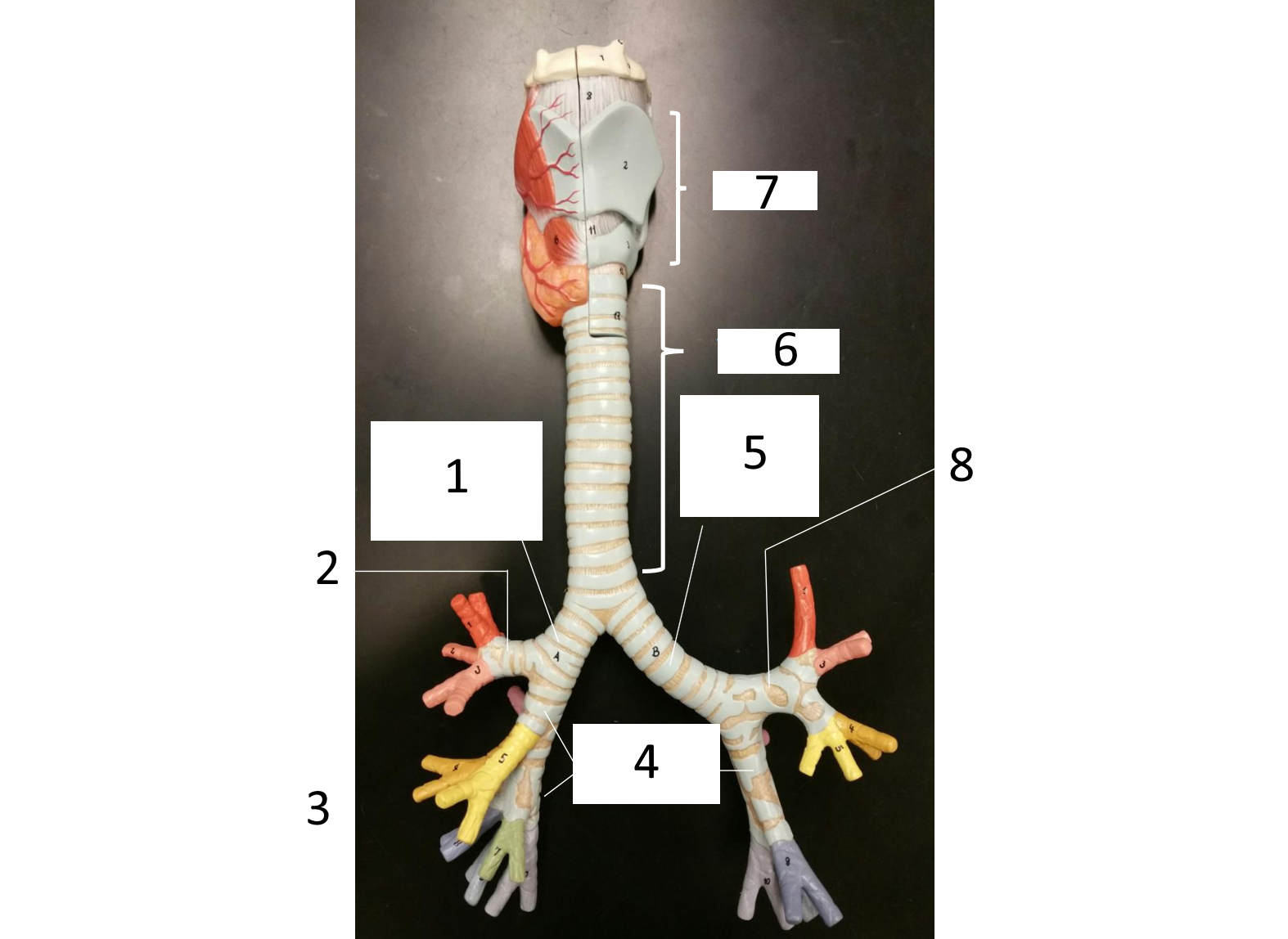
4
secondary bronchi
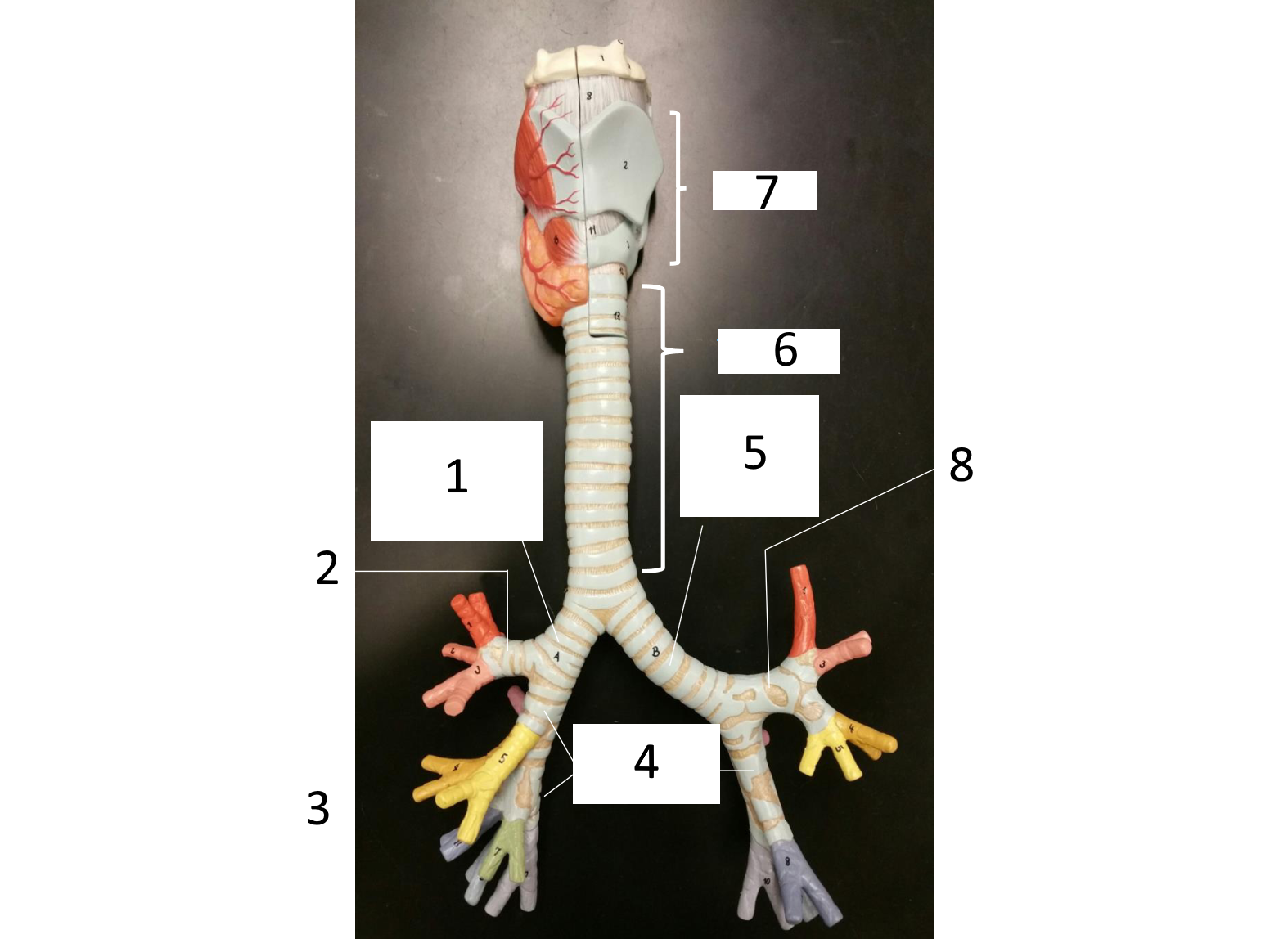
5
left main (primary) bronchus
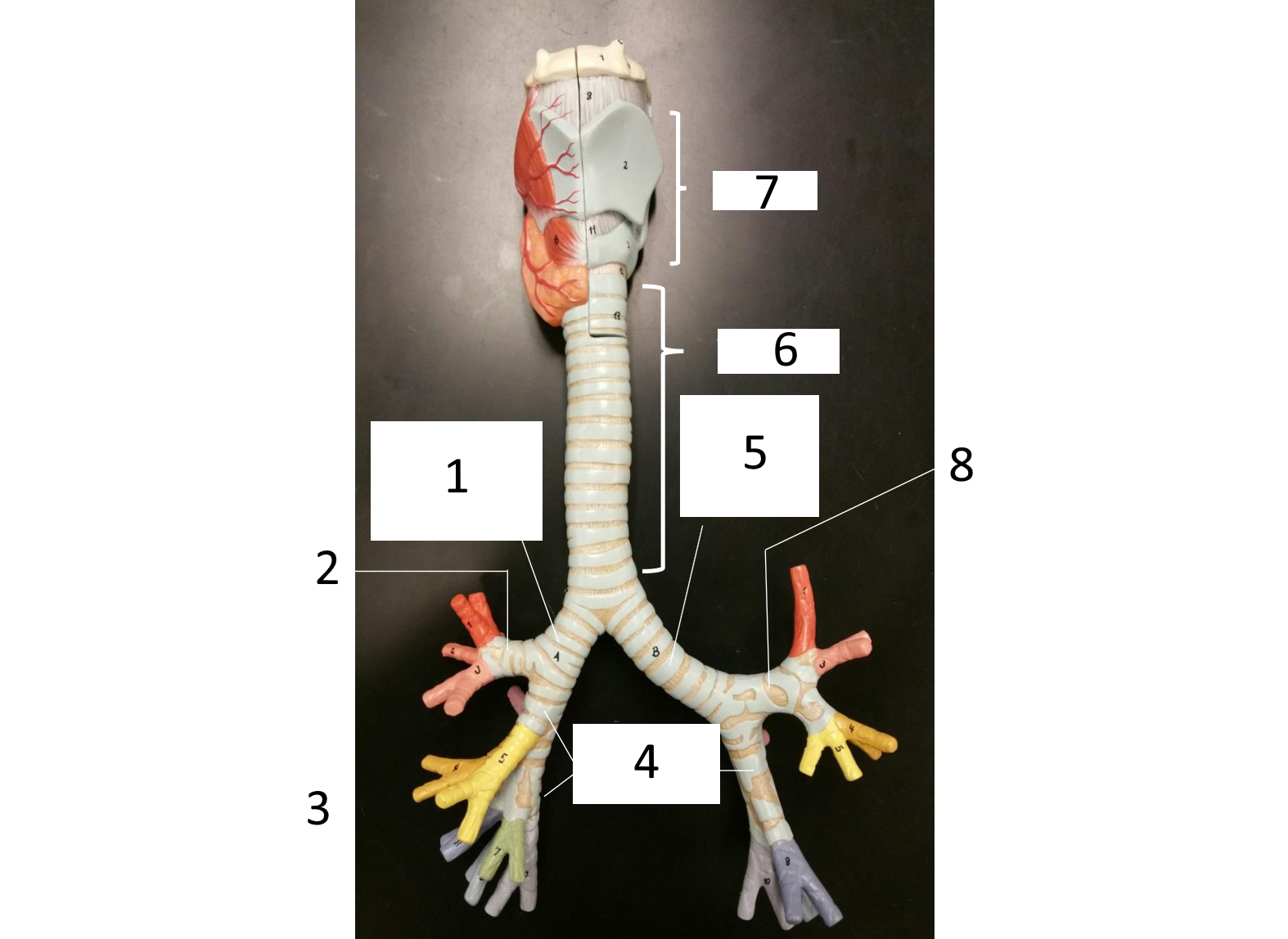
6
trachea
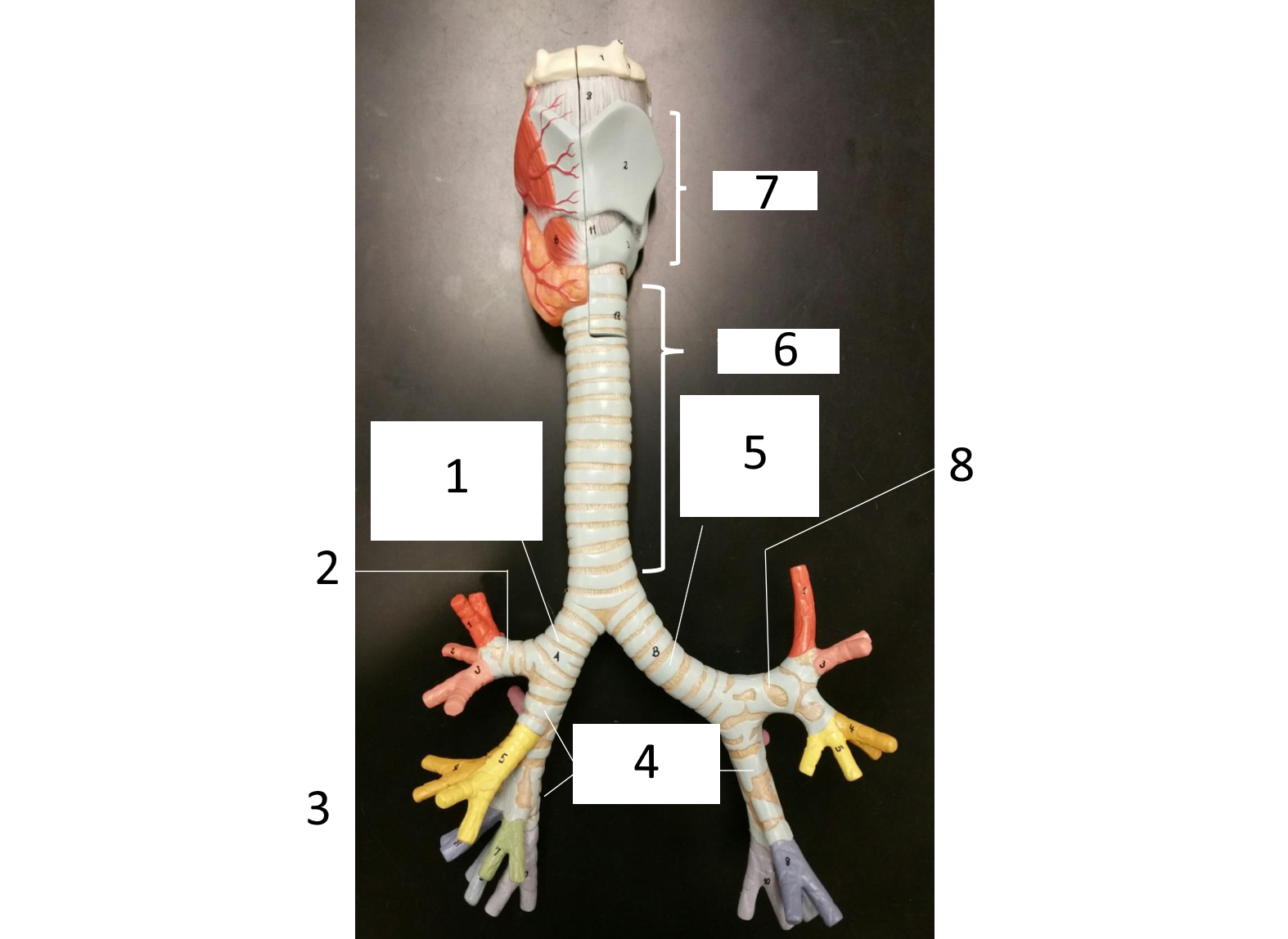
7
larynx
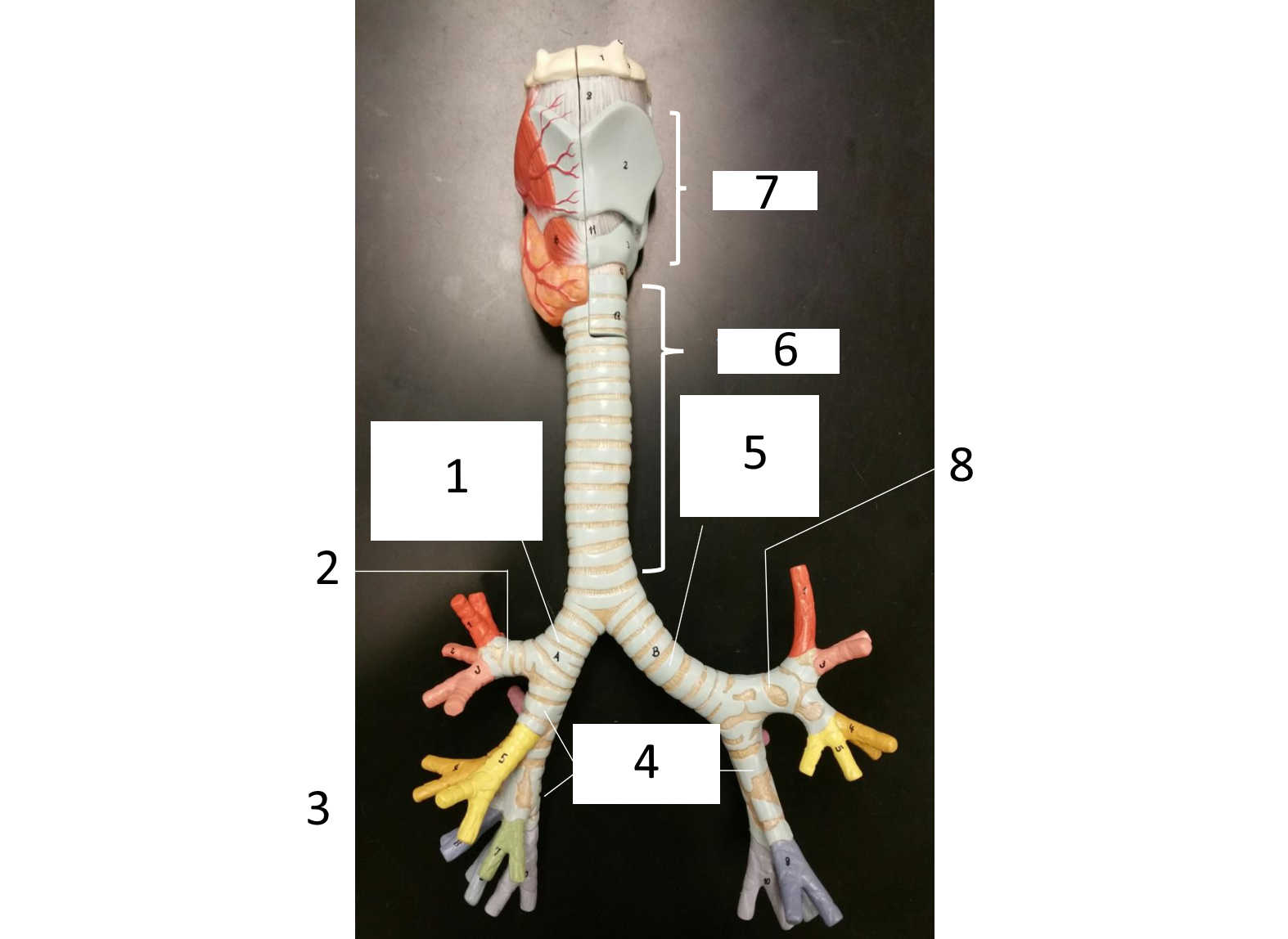
8
secondary bronchus
which lung has 3 lobes
right
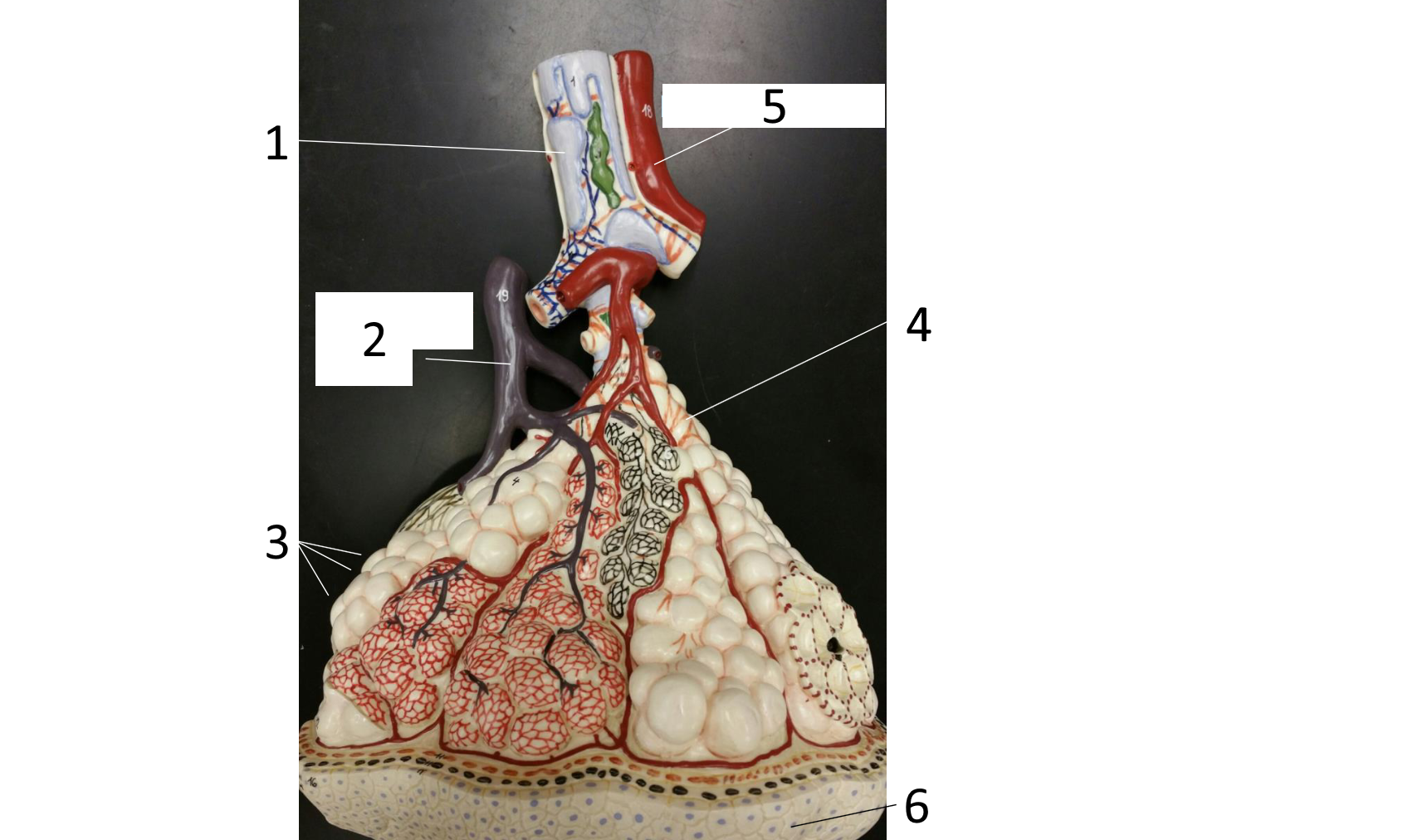
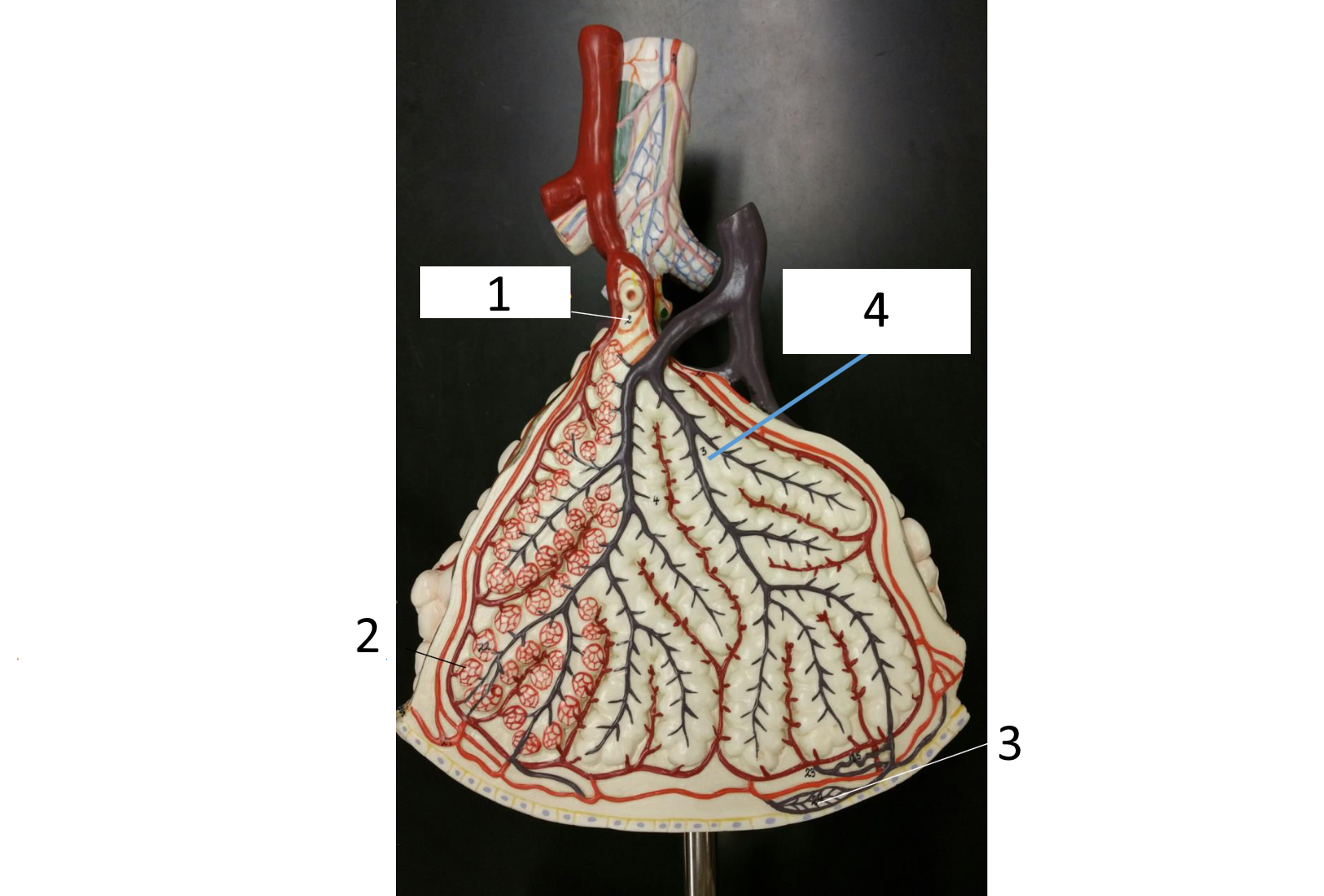
1
cartilaginous plate of smaller bronchi
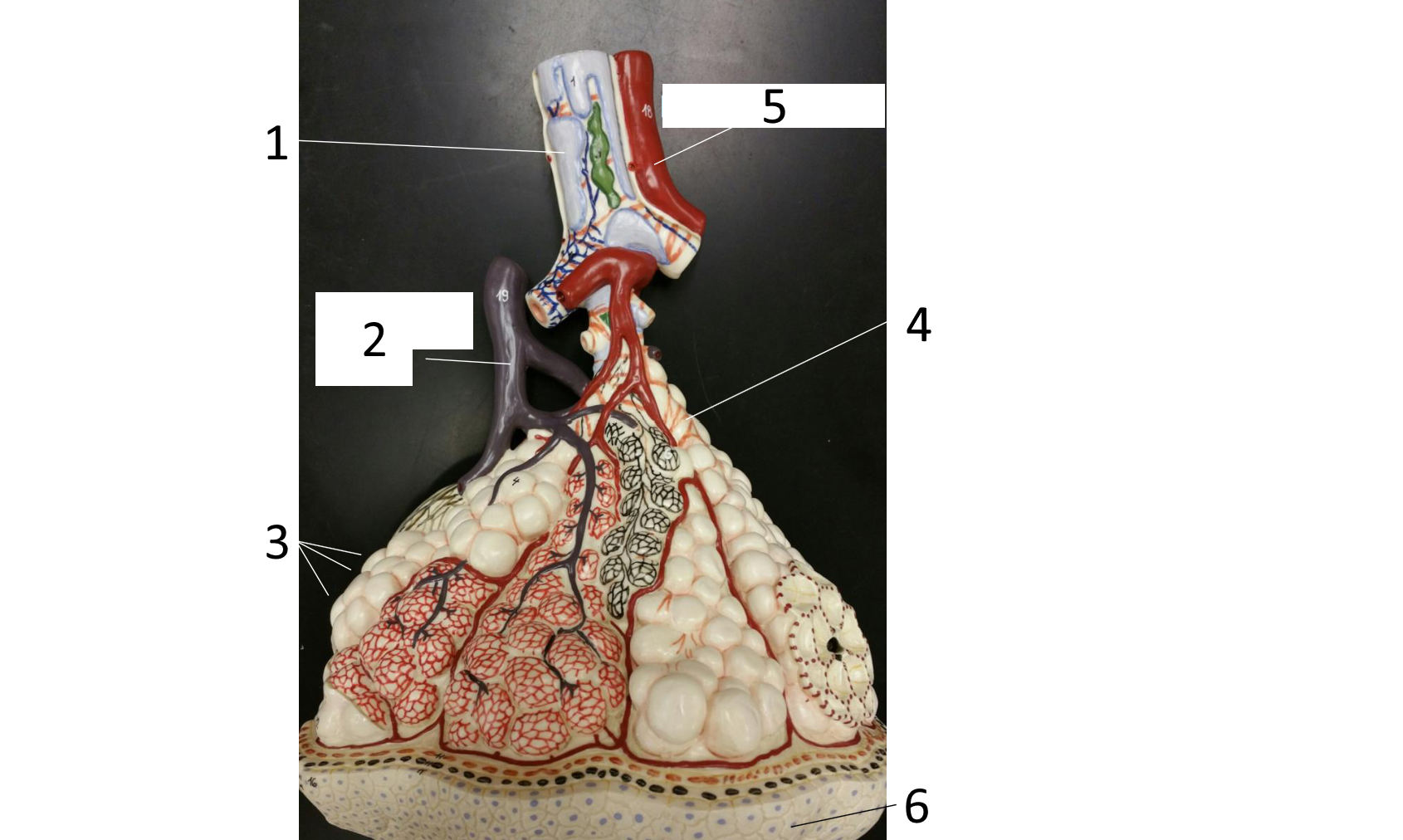
2
pulmonary artery
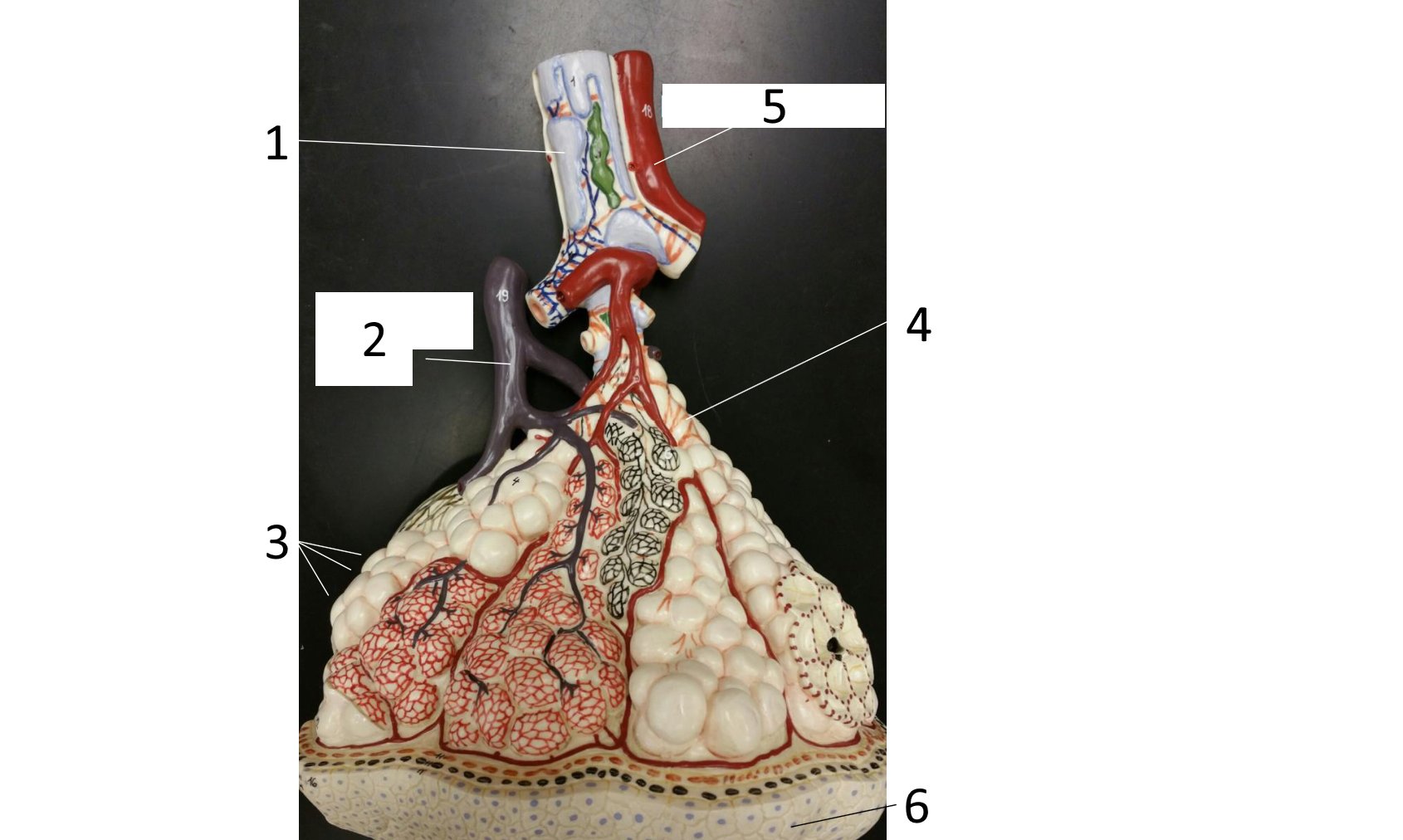
3
alveoli
4 (brown)
smooth muscle
5
pulmonary vein
6
simple squamous epithelium
1
bronchiole
2
alveolar capillary network
3
capillary network
4
respiratory bronchiole
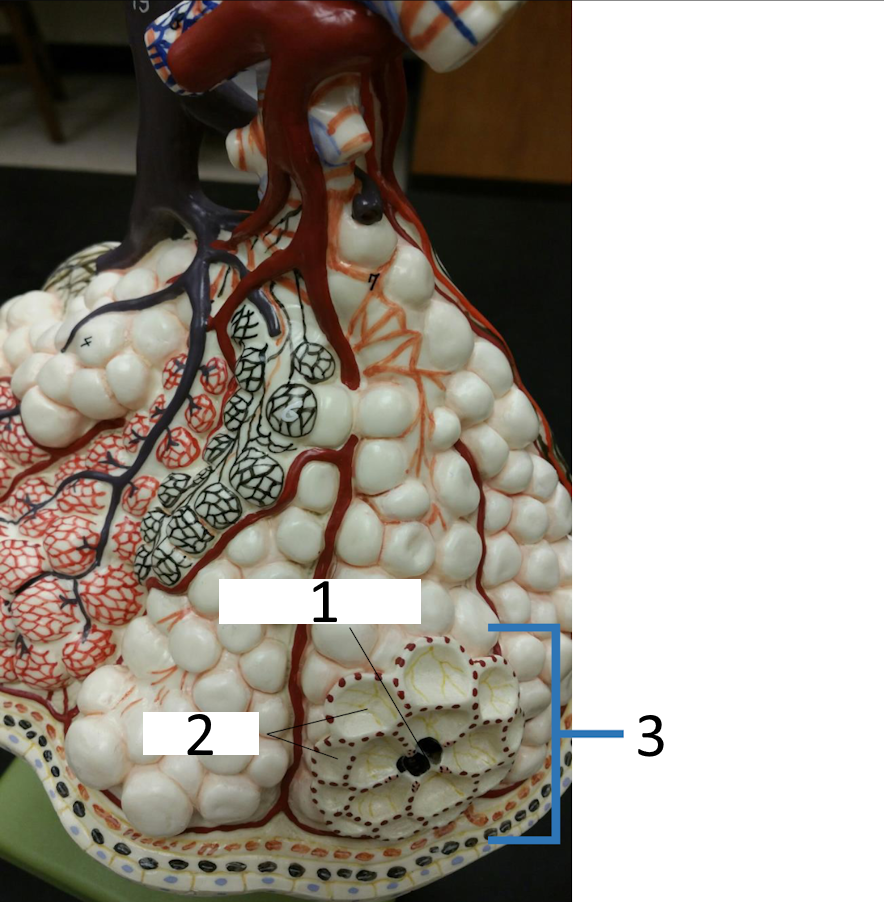
1
alveolar pore
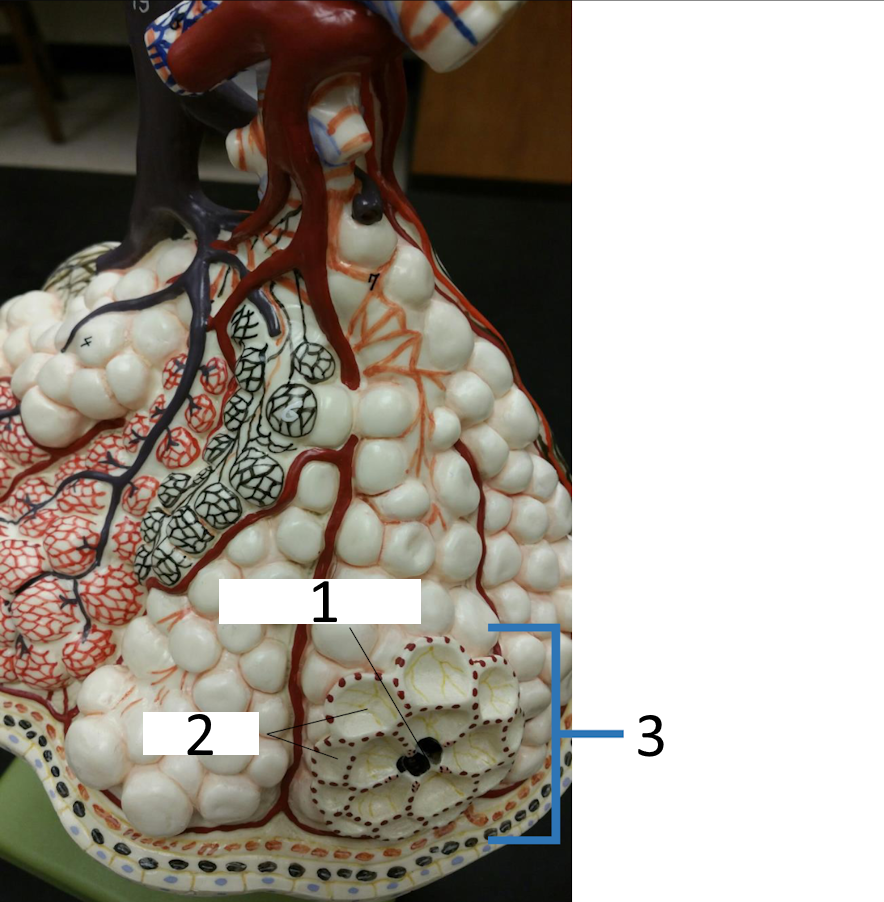
2
alveoli
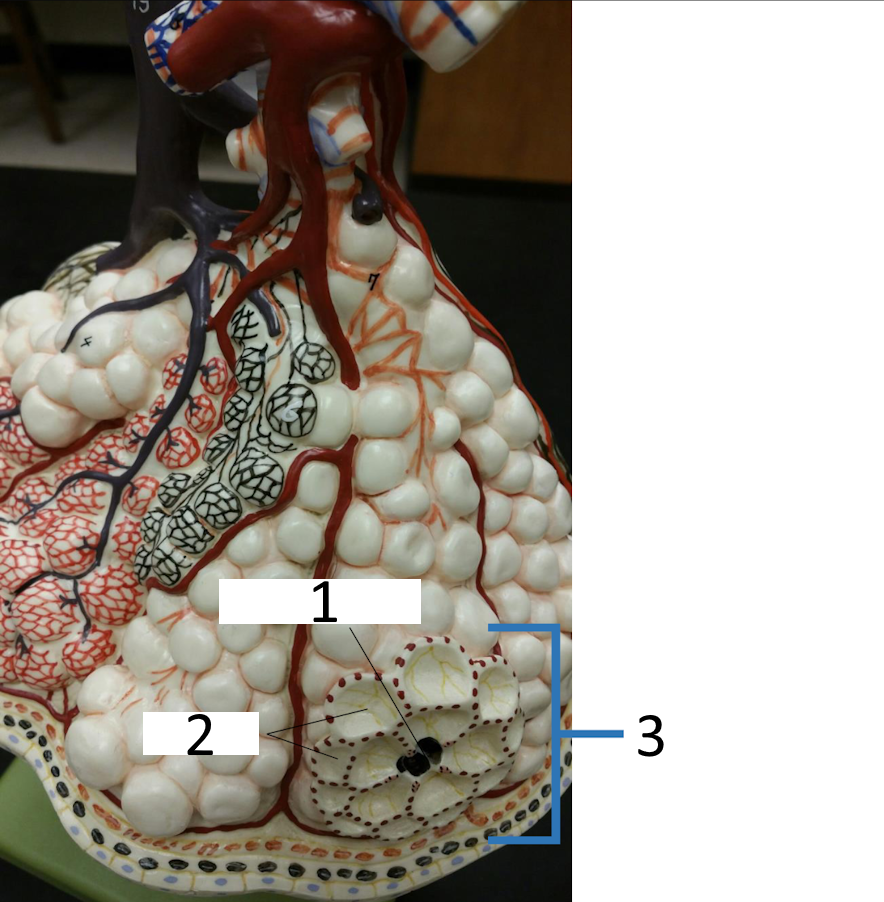
3
alveolar sac
what is movement of air into and out of the lungs which results in exchange of gases in the alveoli of the lungs (aka breathing)
pulmonary ventilation
what is the gas exchange between the blood and the air-filled chambers of the lungs
external respiration
what is the exchange of gases between systemic blood and tissue cells
internal respiration
what is movement into the blood called
loading
what is movement out of the blood called
unloading
what is loaded in external respiration
oxygen
what is unloaded in external respiration
co2
what are these structures apart of:
nasal cavity, nostril, oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, carina of the trachea, left primary bronchus, right primary bronchus
conduction zone
what are these structures apart of:
superior lobe of the right lung, middle lobe of the right lung, inferior lobe of the right lung, superior lobe of the left lung, inferior lobe of the left lung,
respiratory zone
what does the left lobe have
2 lobes and cardiac notch
what is the outer layer that covers the thoracic wall and superior face of the diaphragm
parietal pleura
what is the inner layer that covers the external lung surface dipping into and lining its fissures
visceral pleura
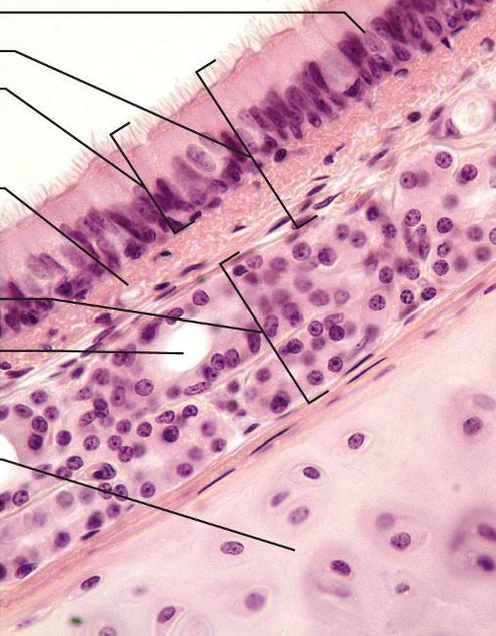
what is this
tracheal wall
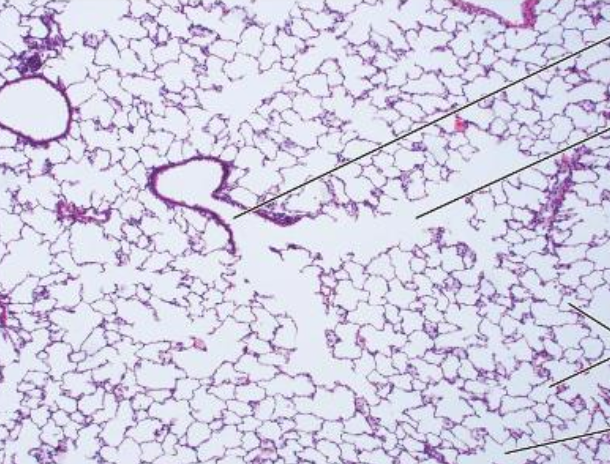
what is this
lung
what is the white space in this slide
alveoli
what is the phase which air is taken into the lungs
inspiration
what is the phase which air passes out of the lungs
expiration
what is normal quiet breathing (~500ml)
tidal volume
what is total amount of exchangeable air (~4800ml)
vital capacity
what is amount of air that can be expelled from the lungs after a normal tidal volume expiration (~1200 ml)
expiratory reserve volume
what is amount of air that can be inspired forcibly beyond the tidal volume (~3200 ml)
inspiratory reserve volume
what is the air that remains in the lungs which helps to keep the alveoli open and prevent lung collapse
residual volume