med term semester one review
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
11 body systems
integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail
skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. Made up of bones and joints
muscular system
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat.
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
cardiovascular system
Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc. The heart pumps blood.
lymphatic system
Composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs. Provides defense against infection.
respiratory system
Brings oxygen into the body. Gets rid of carbon dioxide.
digestive system
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
urinary system
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water, electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood.
reproductive system
Reproduce offspring- produce male sex cells (sperm) and female sex cells (oocytes)
median plane/midsaggital plane
divides the body into equal left and right halves
frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back portions.
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right (dosent have to be even)
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
midline
An imaginary line drawn down the center of the body, dividing it into right and left halves.
medial
toward the midline
lateral
away from the midline
distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
superior
above
inferior
below
anterior/ventral
front of the body
posterior/dorsal
back of body
cranial cavity
contains the brain
dorsal cavity
includes the cranial and spinal cavities.
spinal cavity
contains the spinal cord
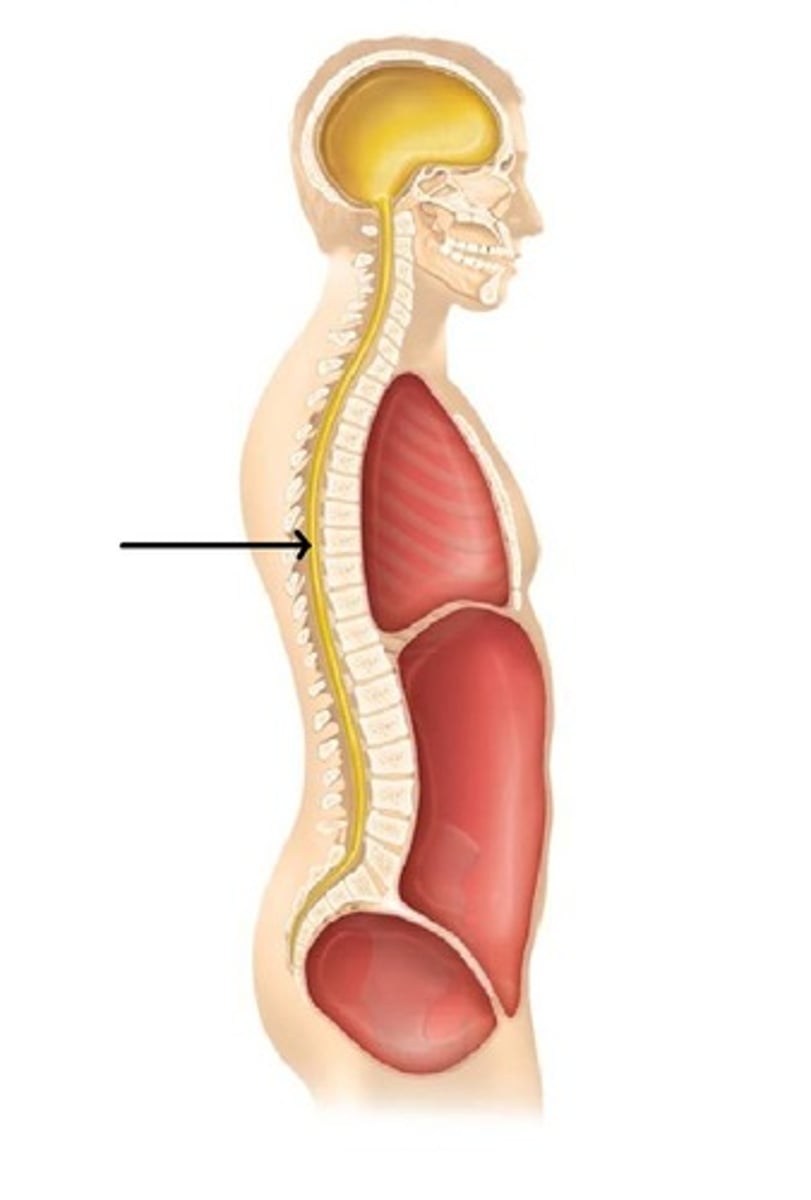
thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs
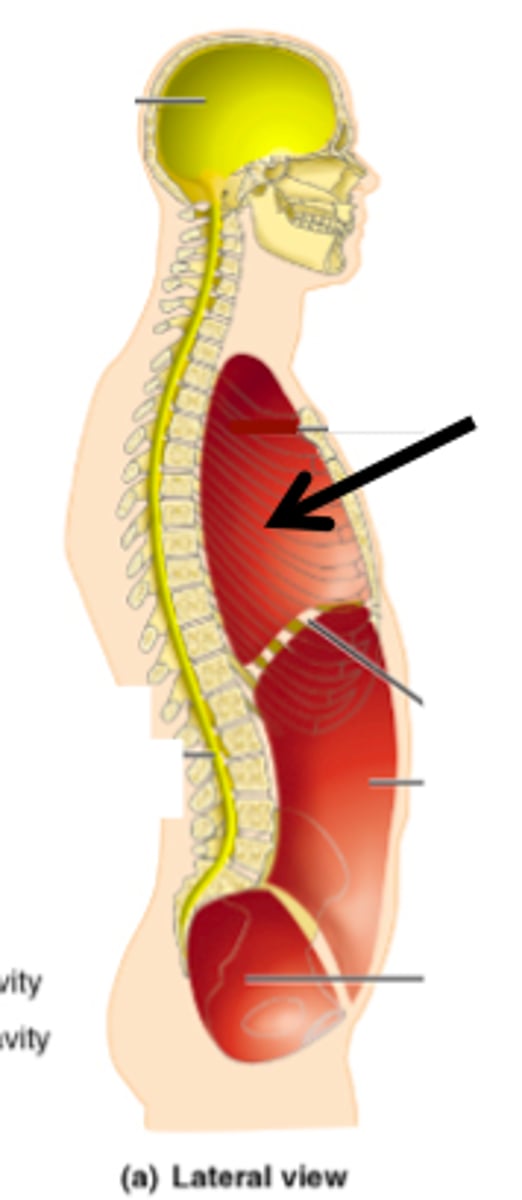
abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
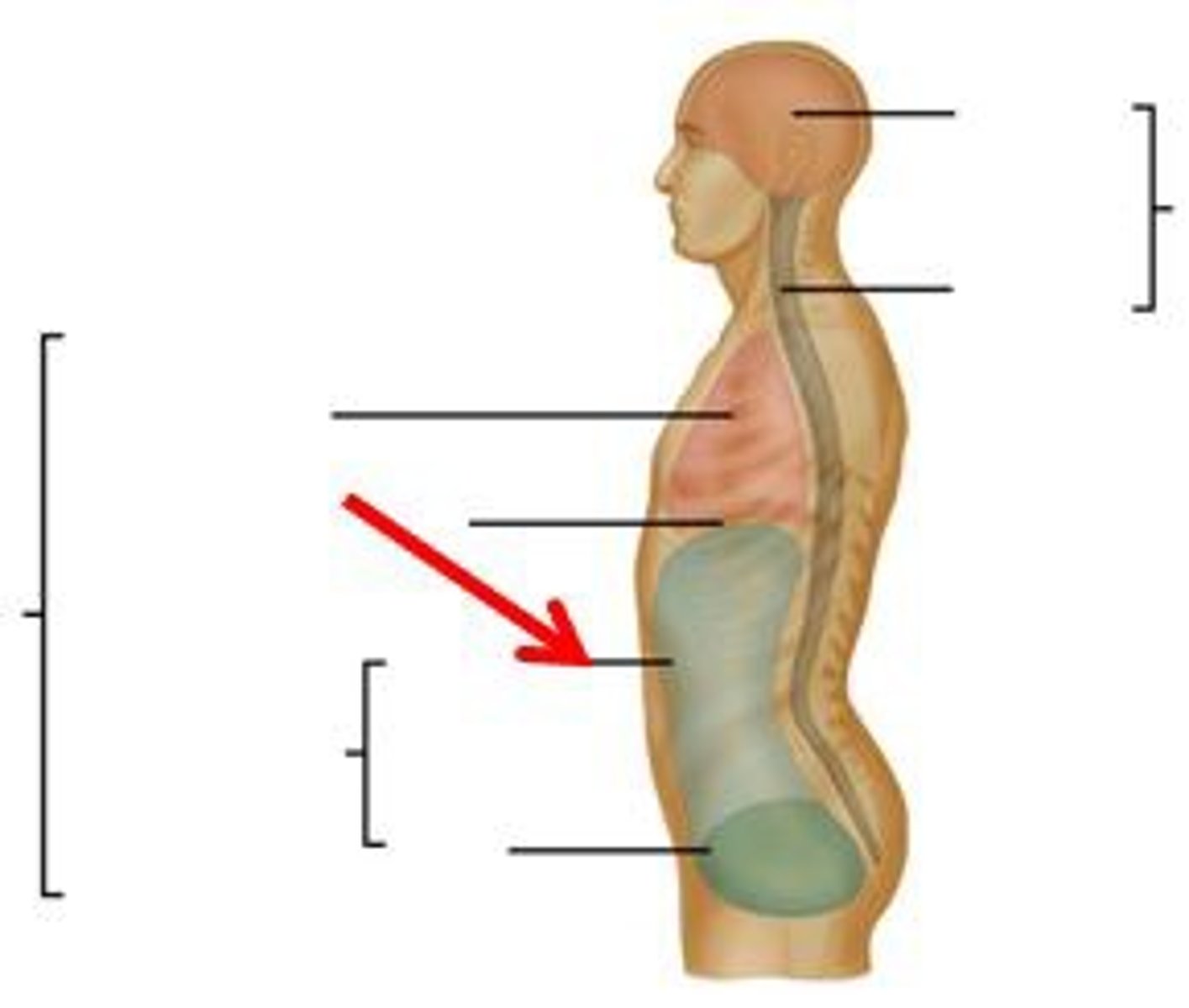
abdominopelvic cavity
abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
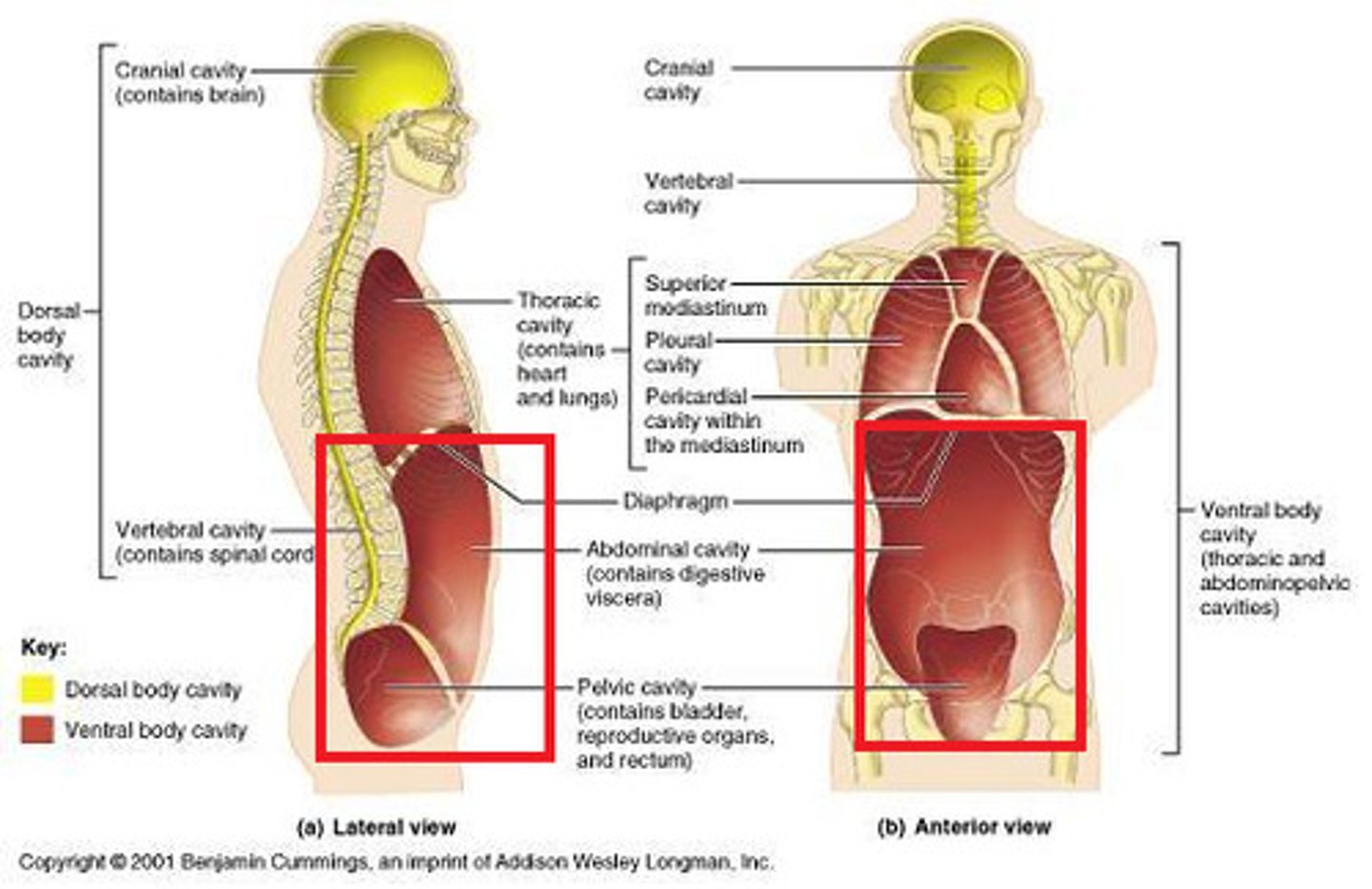
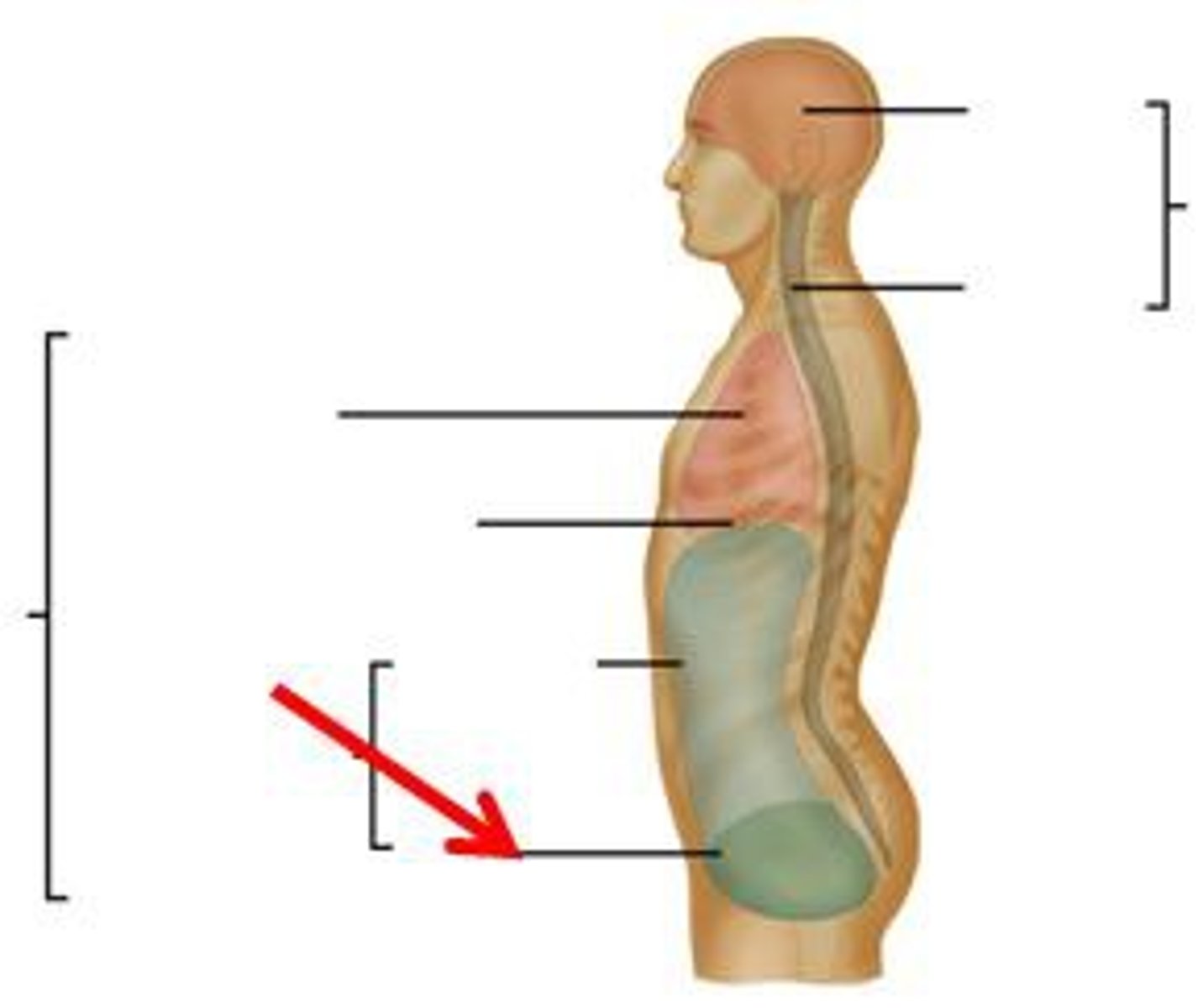
pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
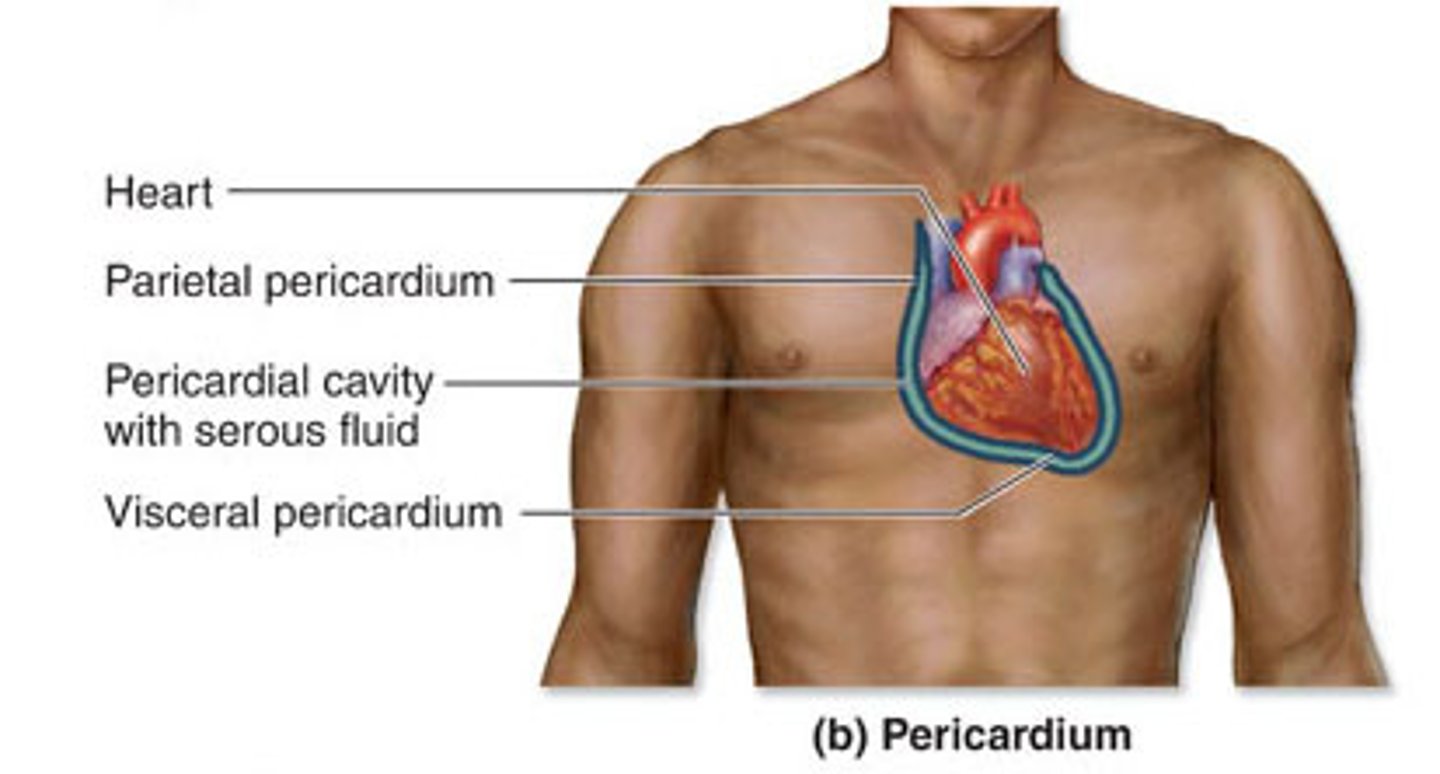
pericardial cavity
contains the heart
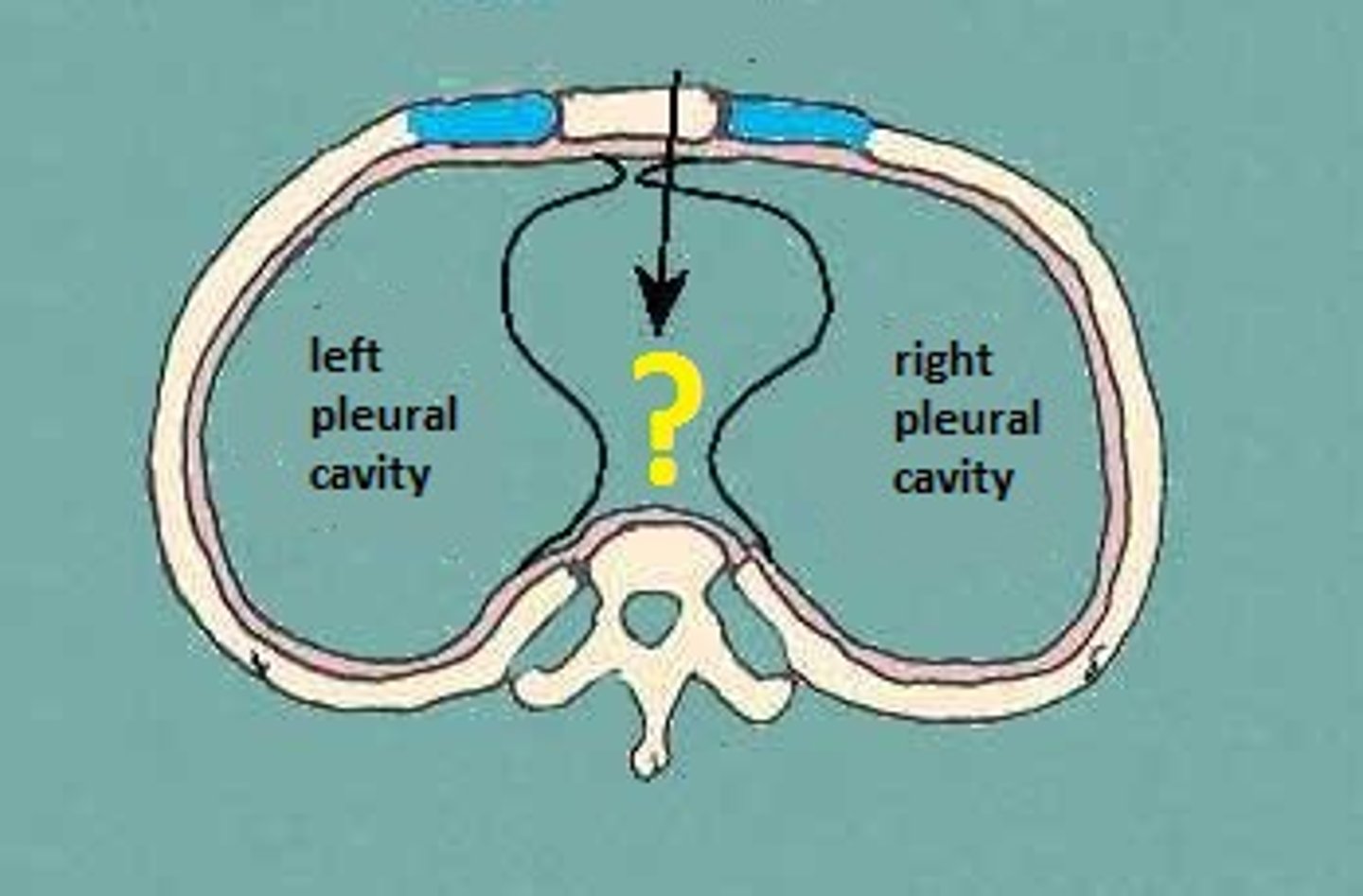
pleural cavity
contains the lungs
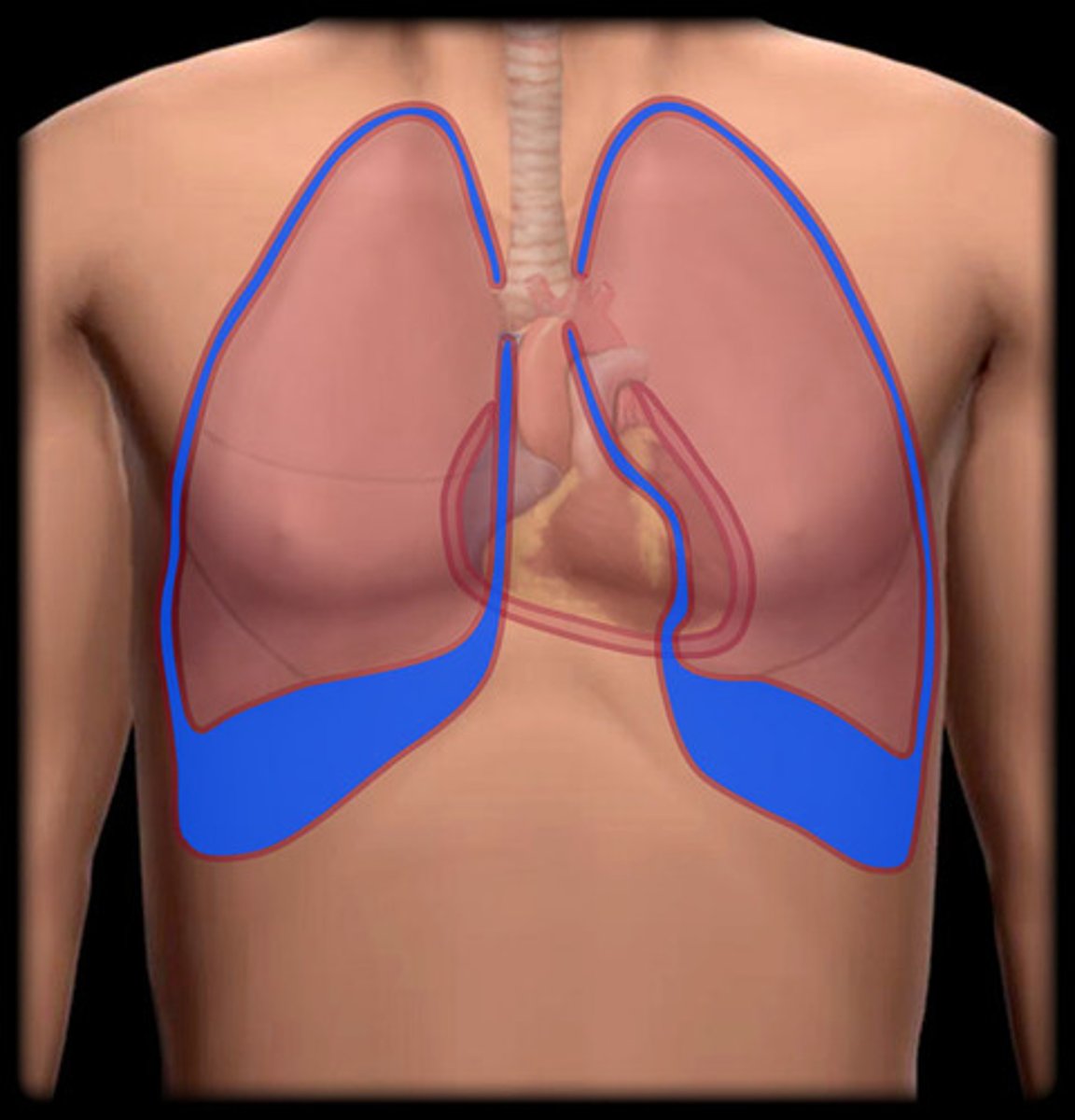
Mediastinum
space between the lungs
know anatomy and phsyiology
ok
ok
peri-
surrounding
-itis
inflammation
tatchy-
fast
brady-
slow
-logist
one who studies
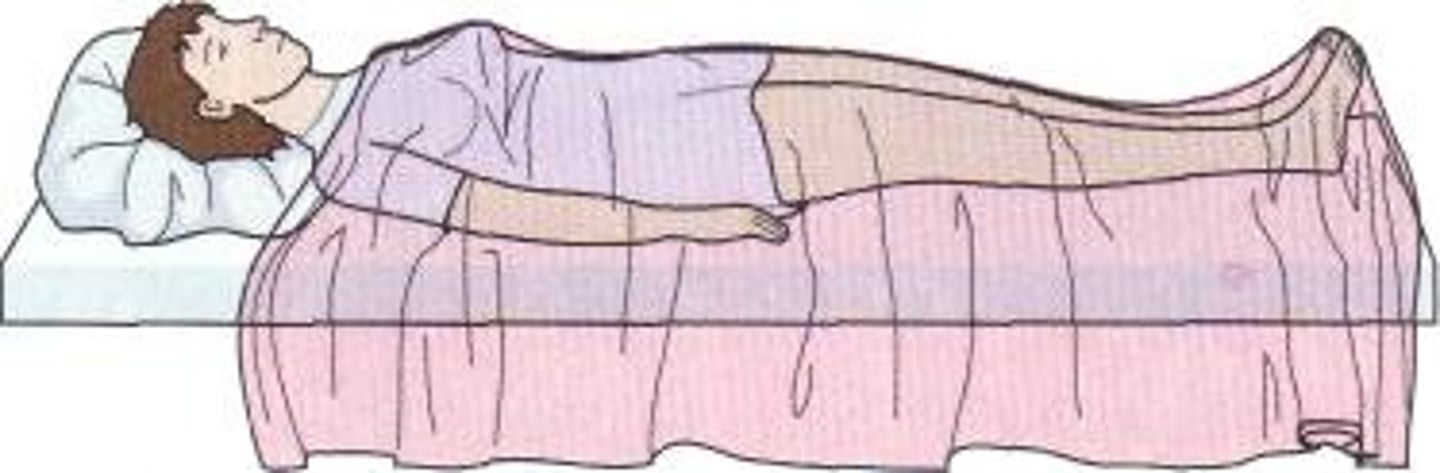
supine position
lying on back, facing upward
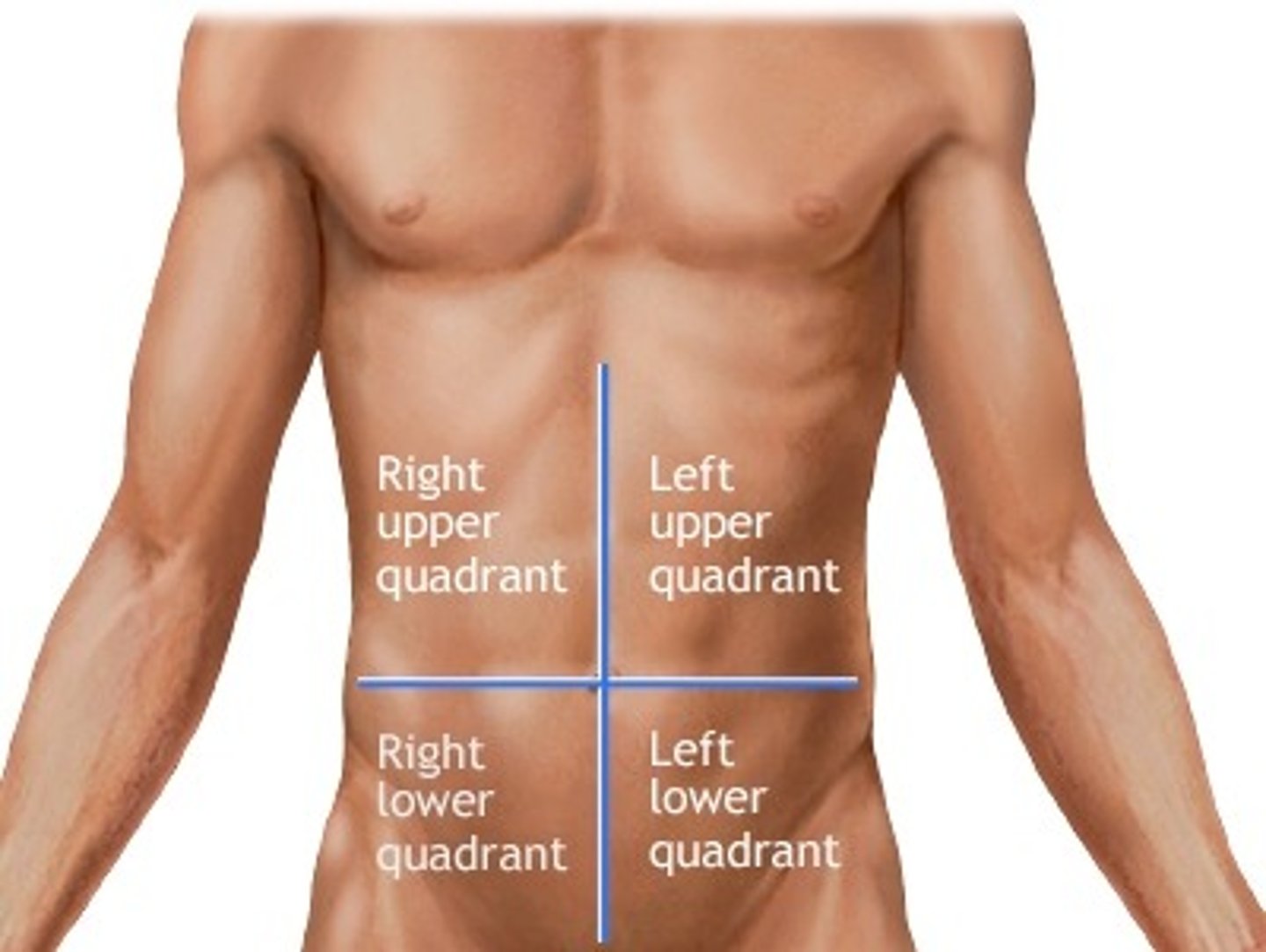
ruq, luq, llq, rlq
right upper quadrant, left upper quadrant, left lower quadrant, and right lower quadrant
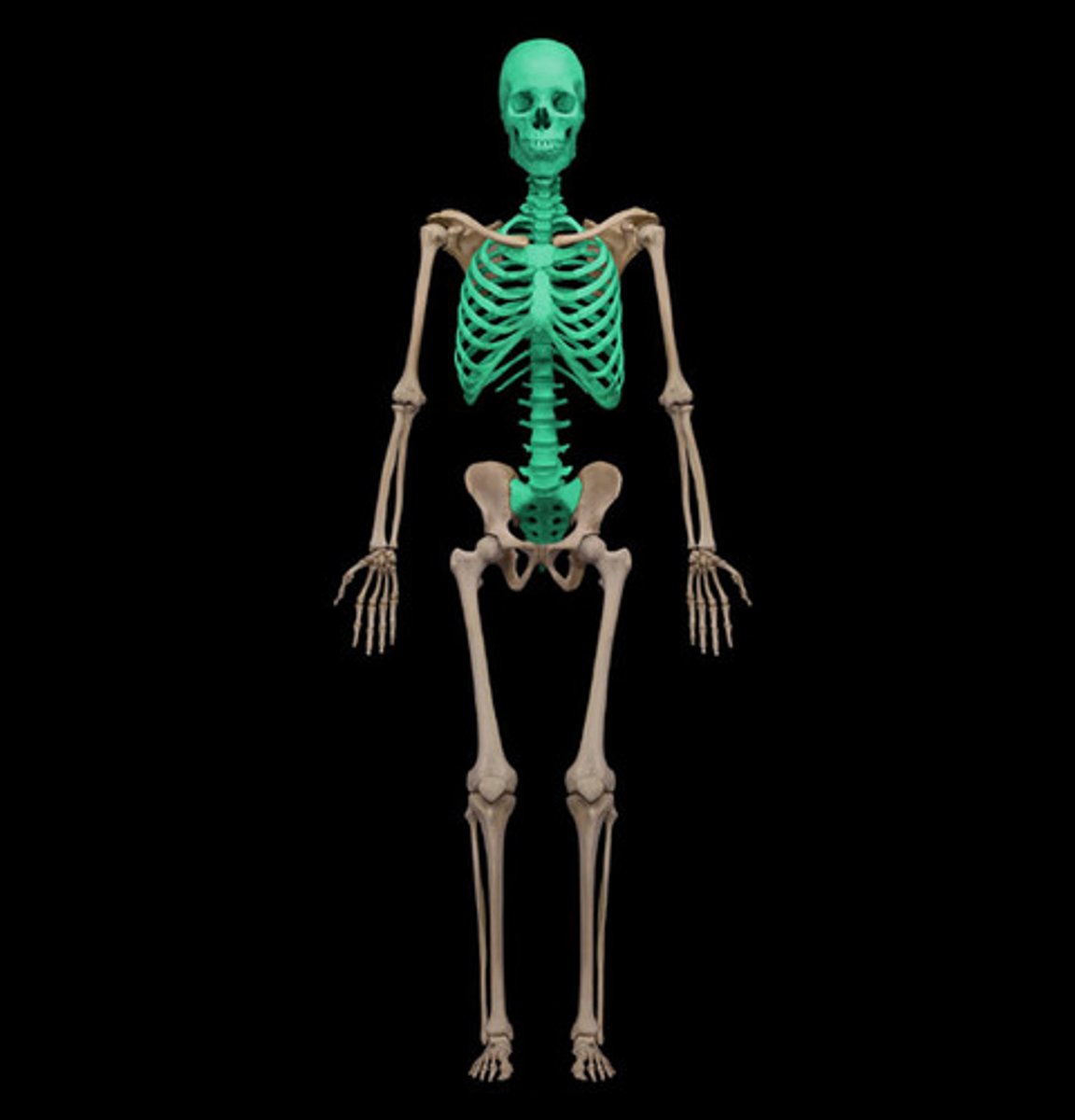
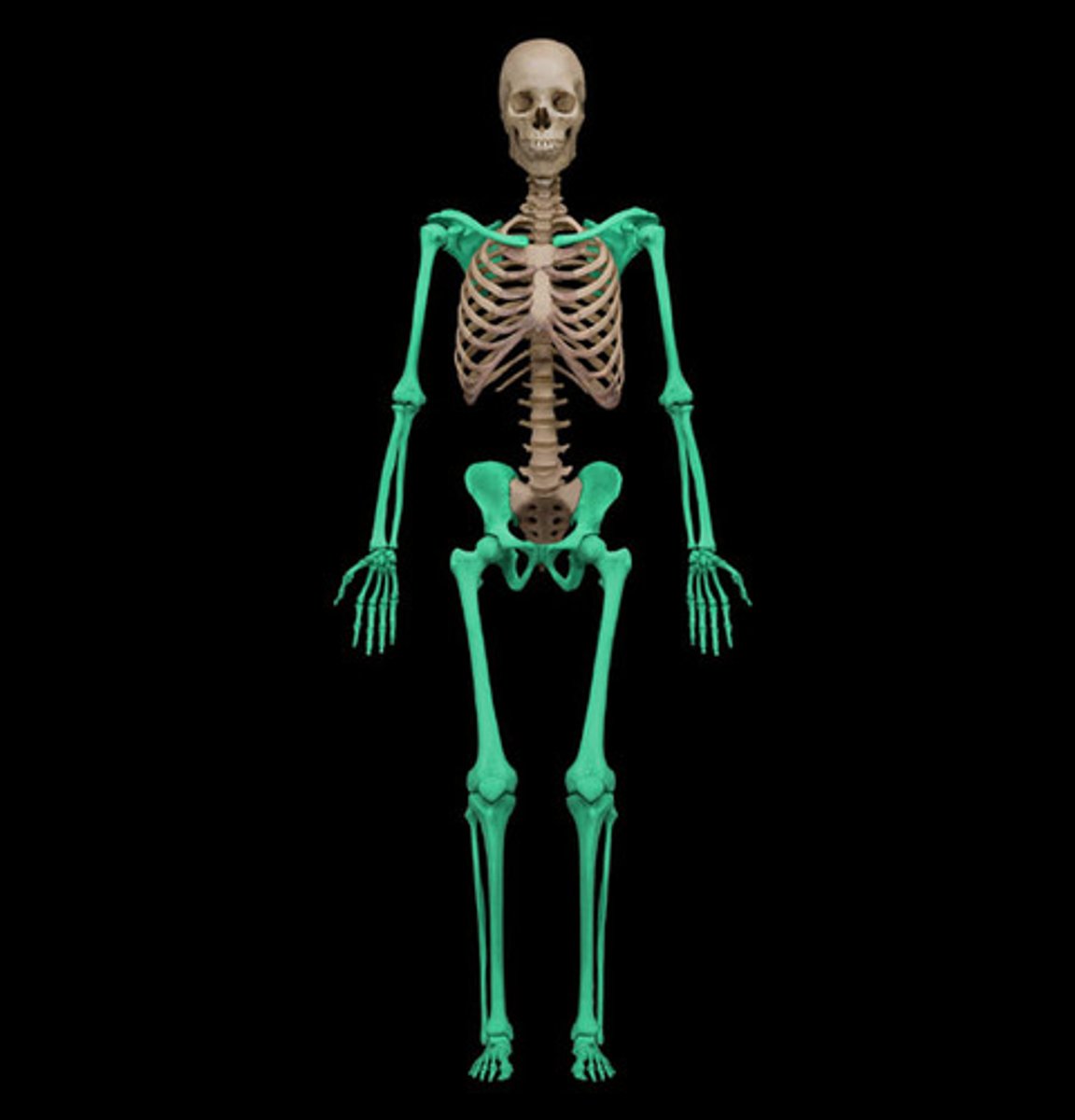
axial skeleton
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
tendons
Connect muscle to bone
ligaments
bone to bone
appendicular skeleton
Bones of the limbs and limb girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton
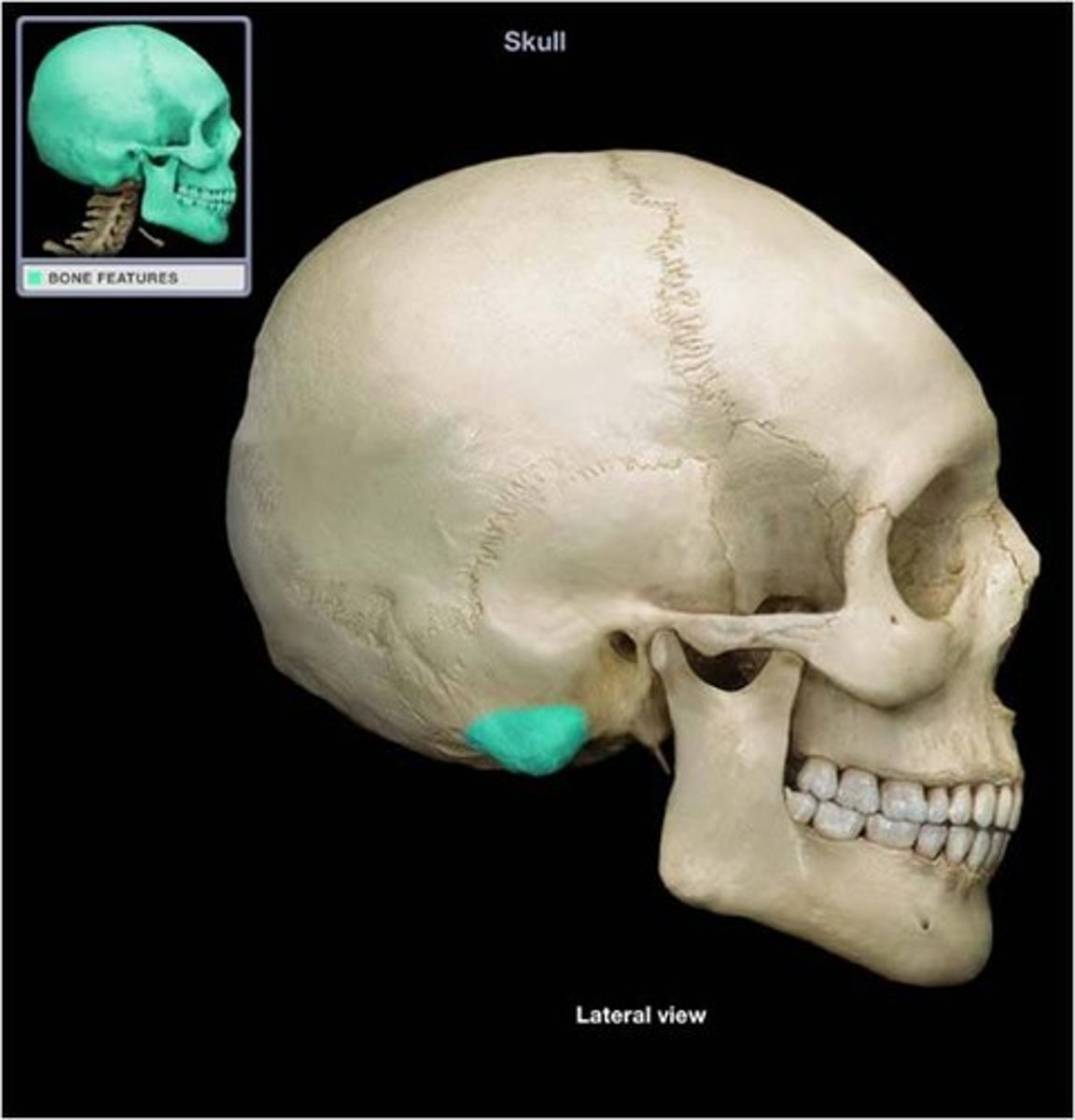
bone process
enlarged area that extends from bones as an attachment for muscles, tendons, and ligaments (dosent just apply to skull its everywhere !!)
brachi/o
arm
myel/o
spinal cord, bone marrow
osteo/o
bone
sarc/o
flesh, connective tissue
arthr/o
articulation, joint
use of a needle to puncure a joint space and remove fluid is what
Arthrocentesis
diagnostic tests that use electromagnetic field and radio waves
EMG (electromyography)
skull bones
cranium + jaw
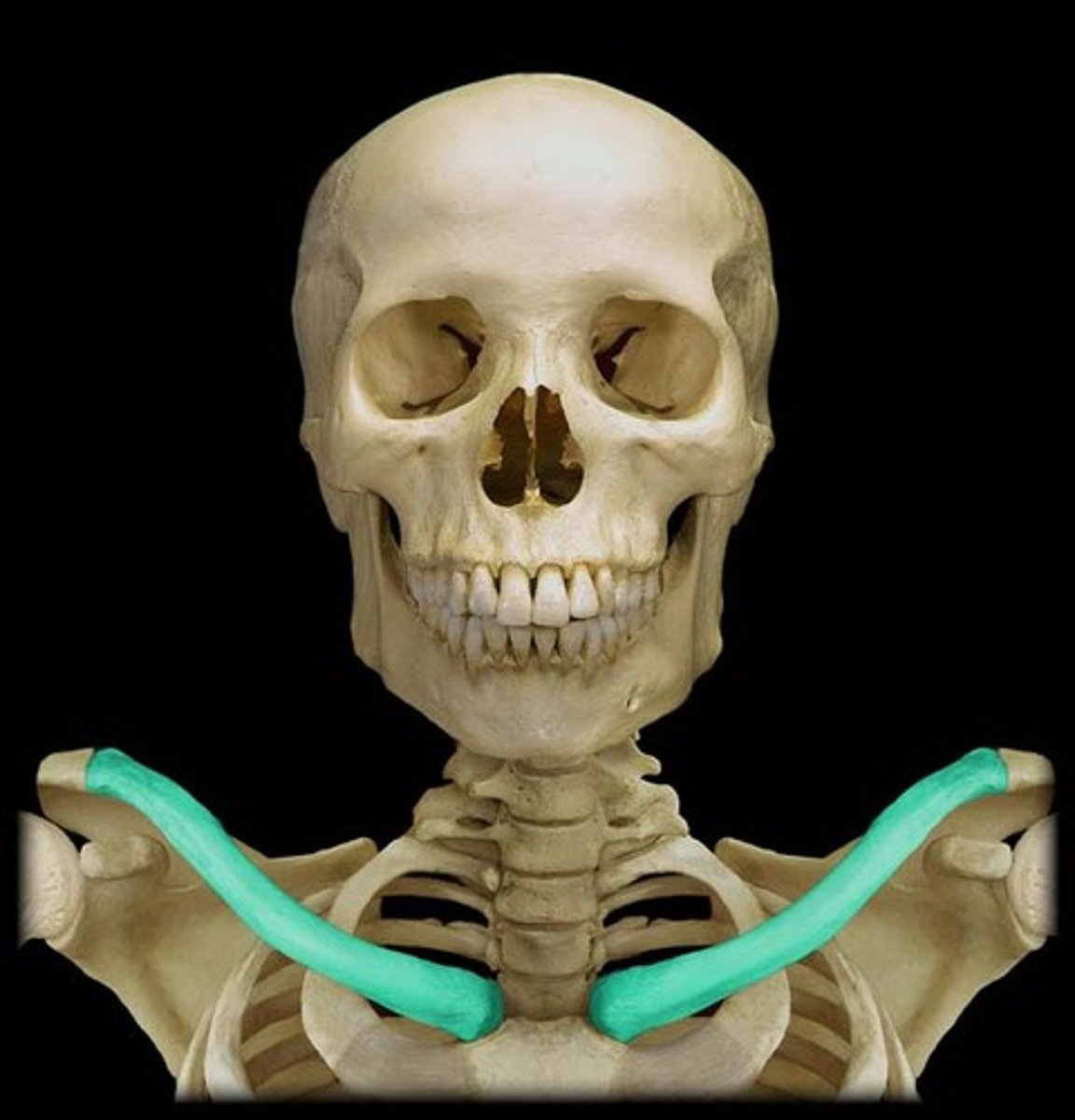
clavicle
collar bone
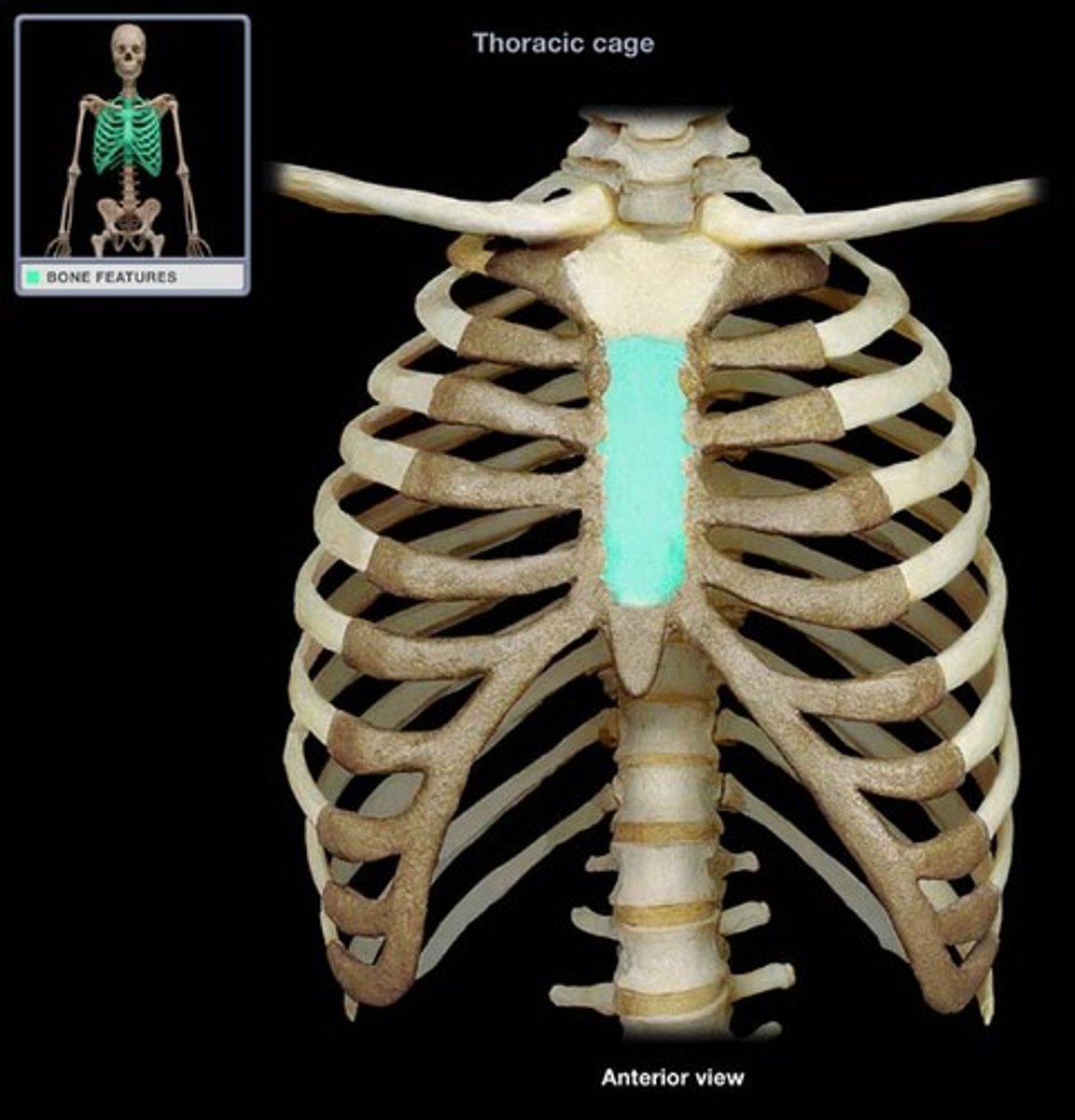
sternum is located where
Middle of the ribcage on the front
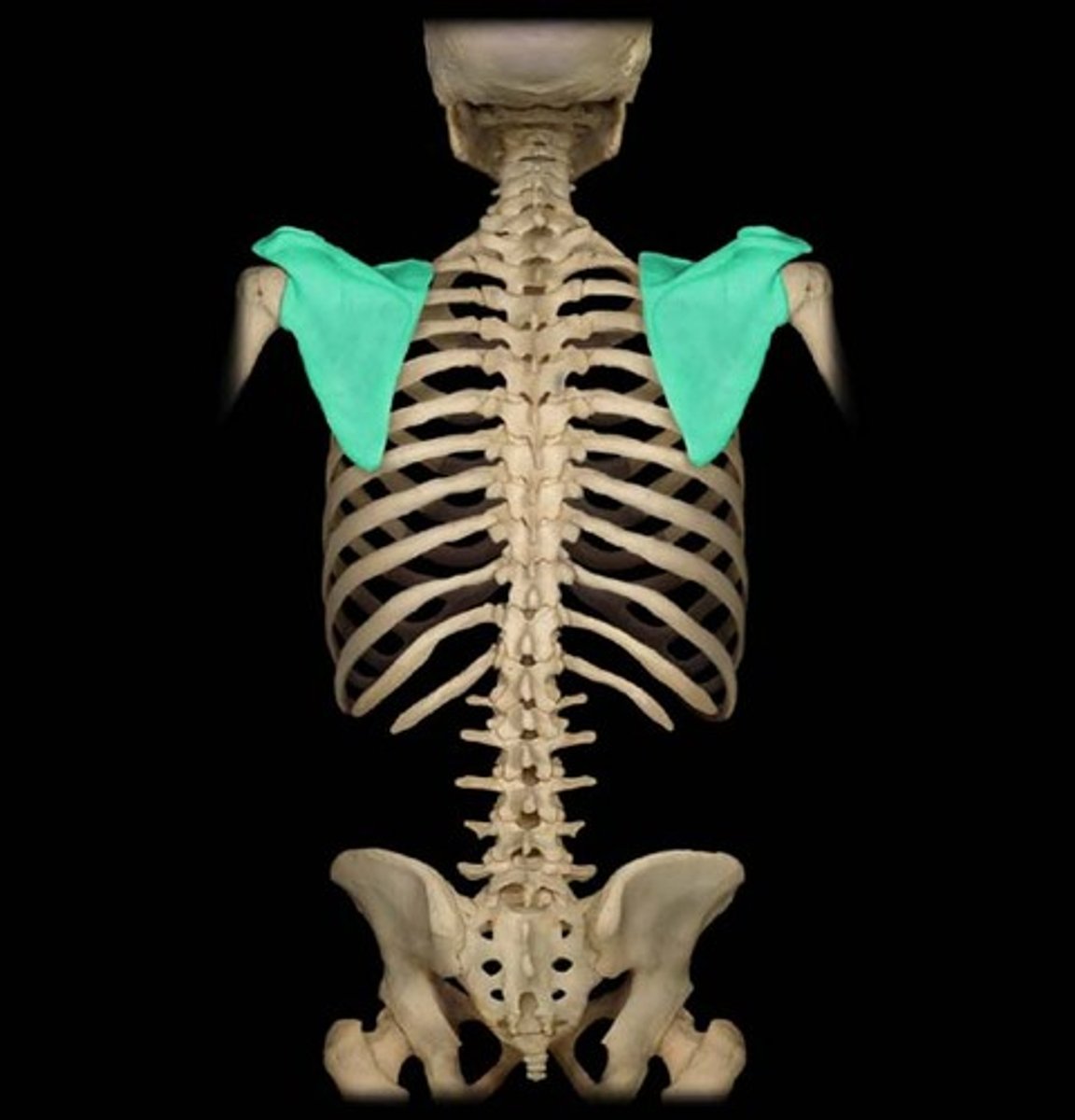
scapula
shoulder blade
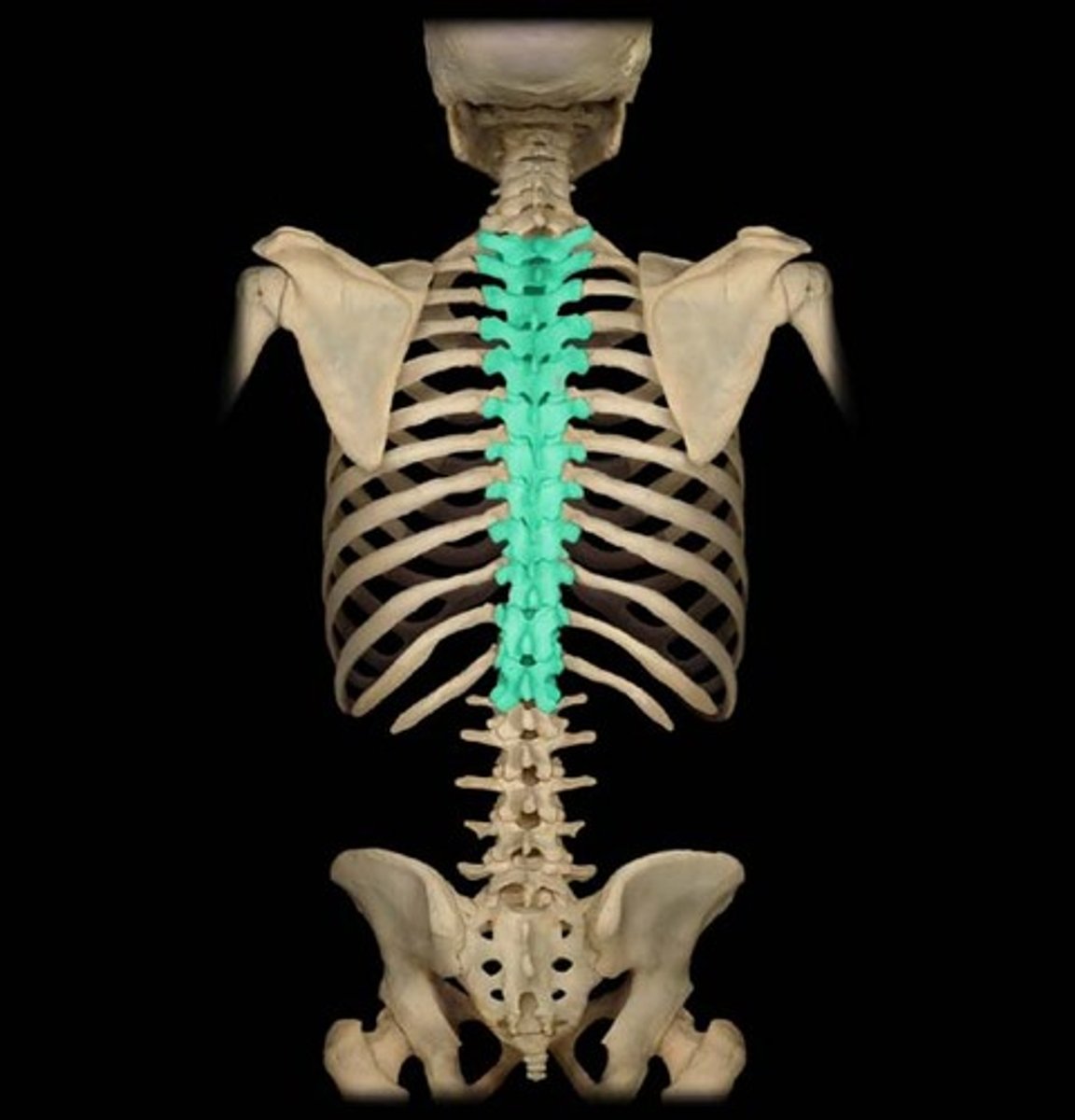
vertebrae
26 small bones that make up your backbone
the arm is made of which bones
humerus, radius, ulna
the hand is made of what bones
carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
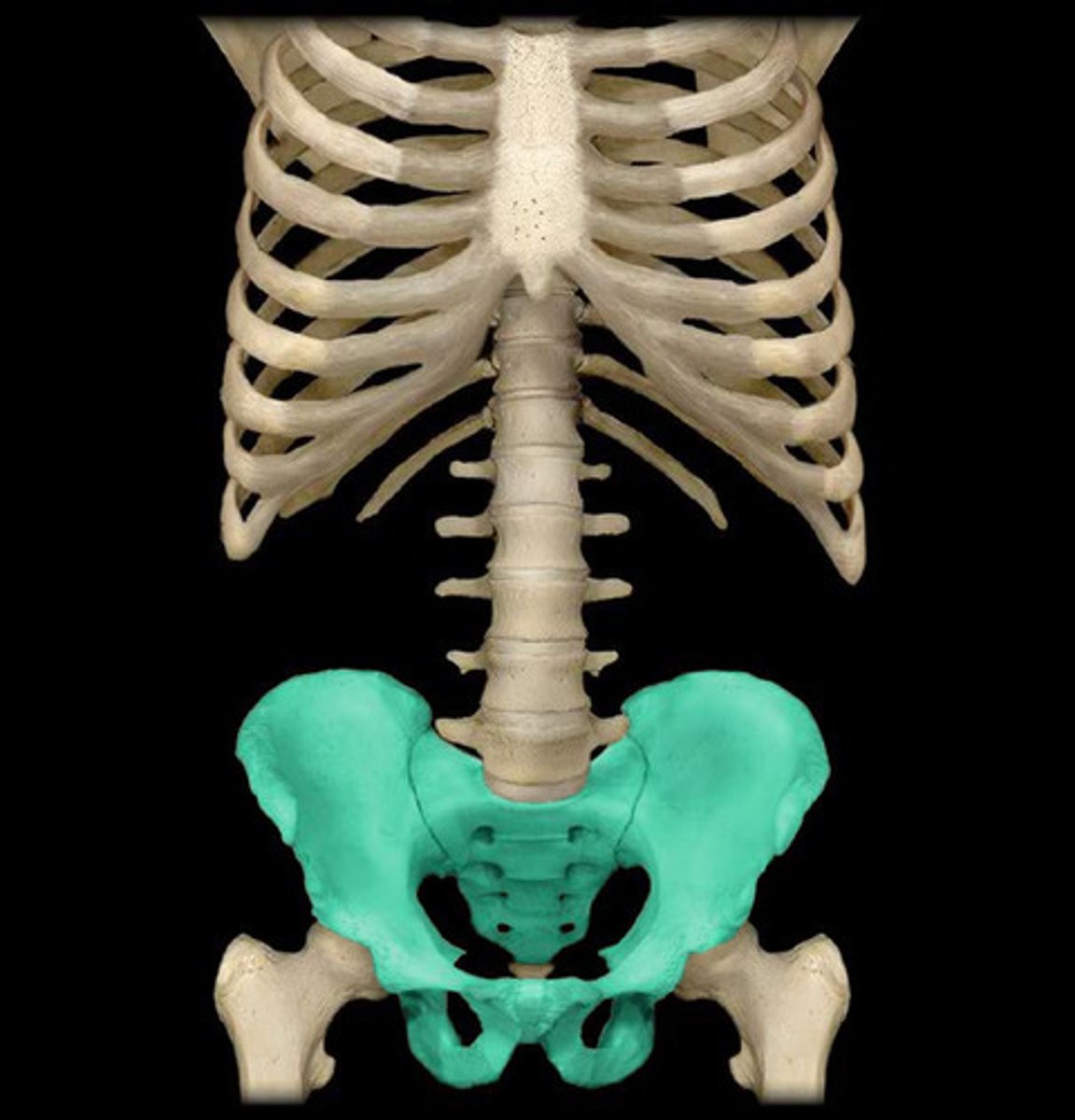
pelvis
hip bone
leg is made up of what bones
femur tibia fibula
femur
thigh bone
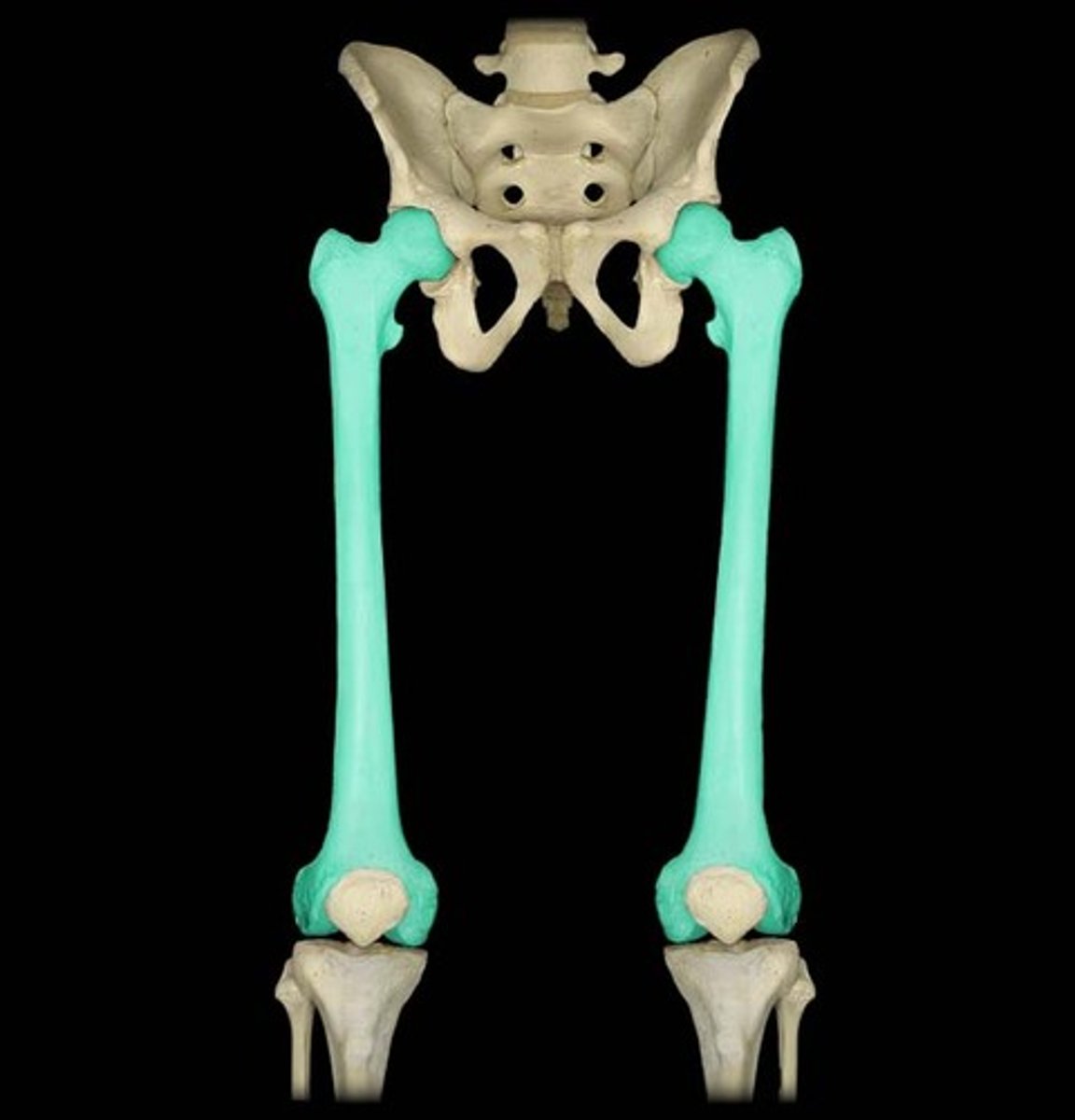
tibia
the medial and larger bone of the lower leg
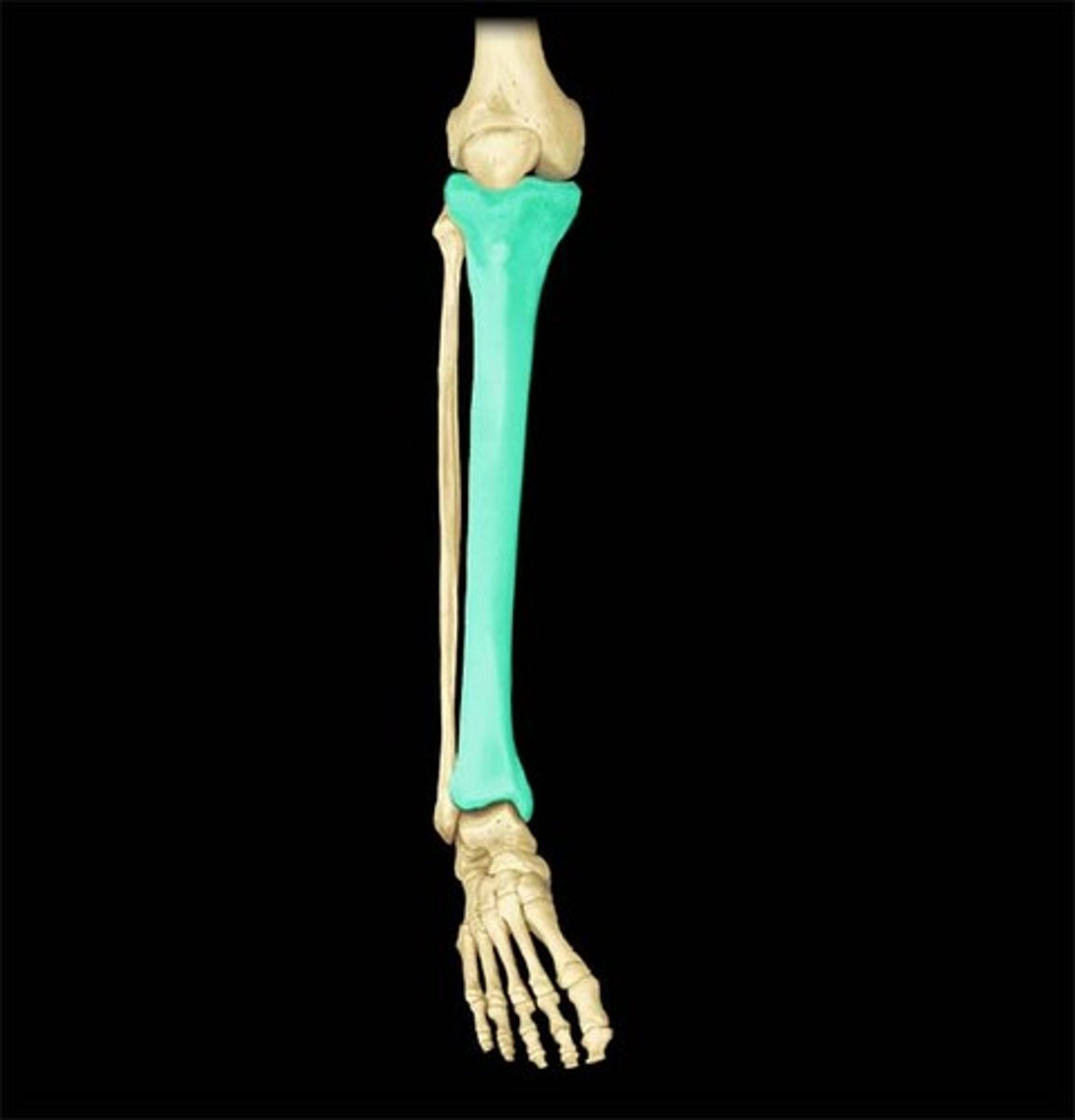
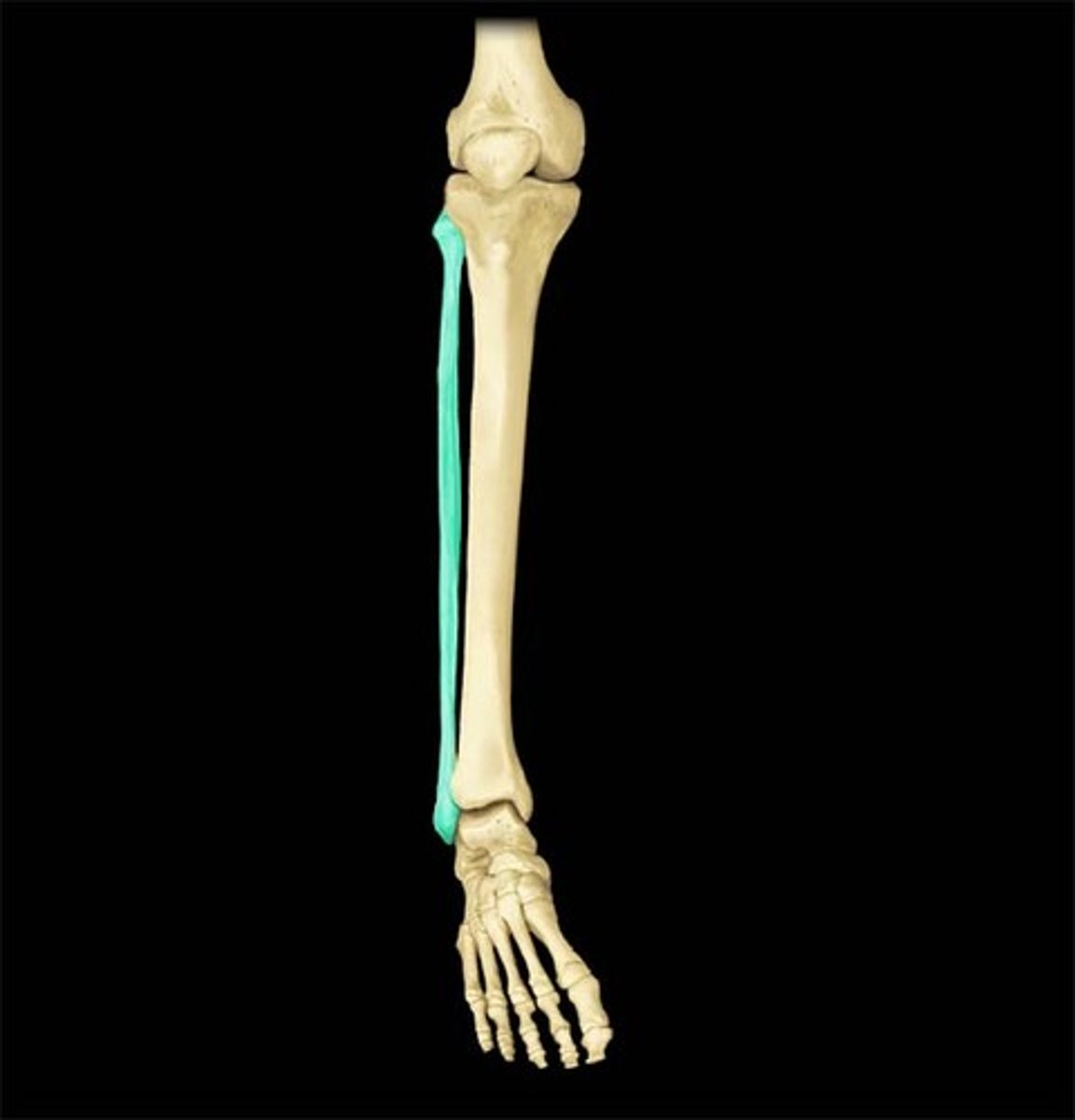
fibula
calf bone
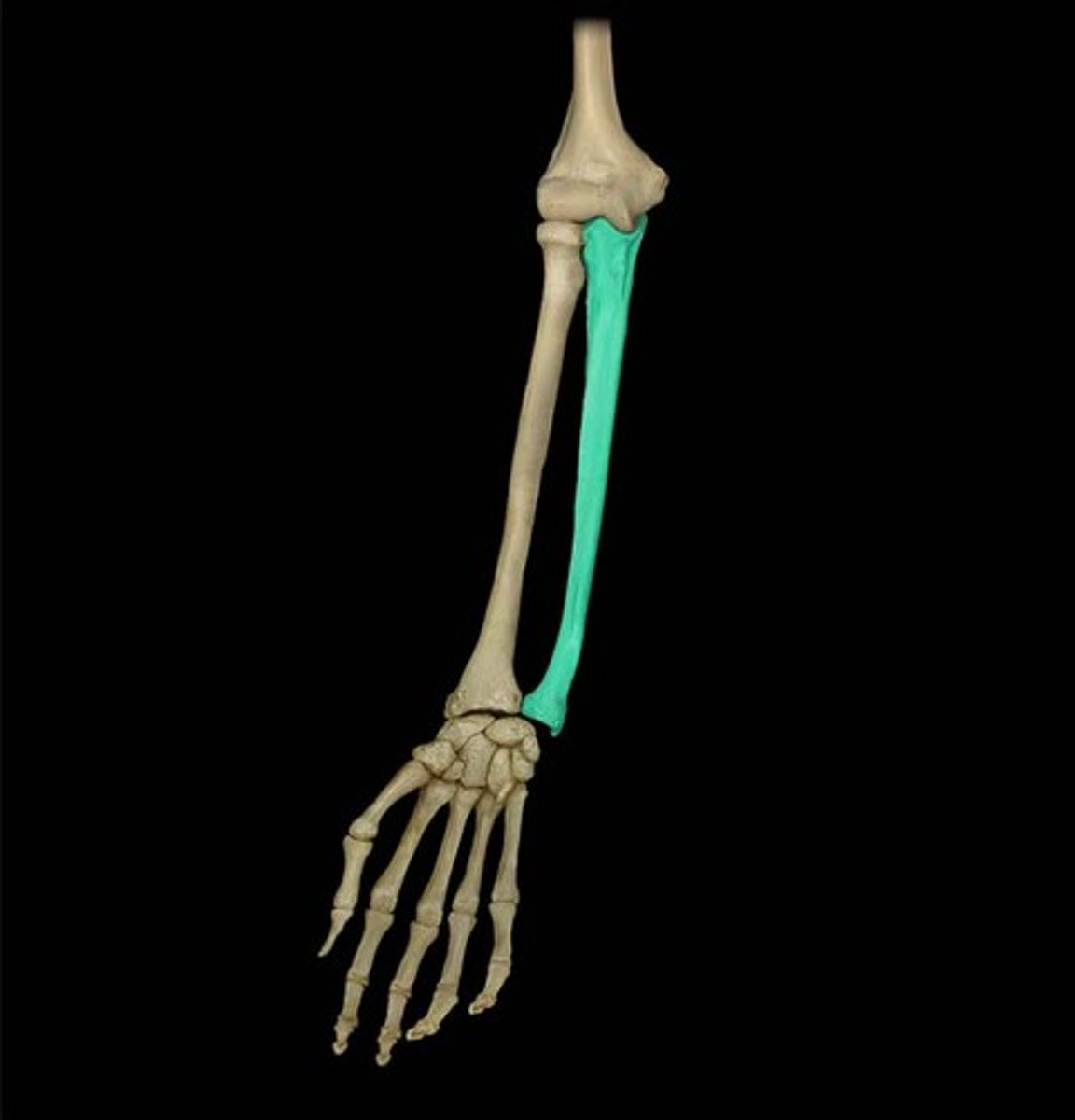
radius
lateral bone of the forearm
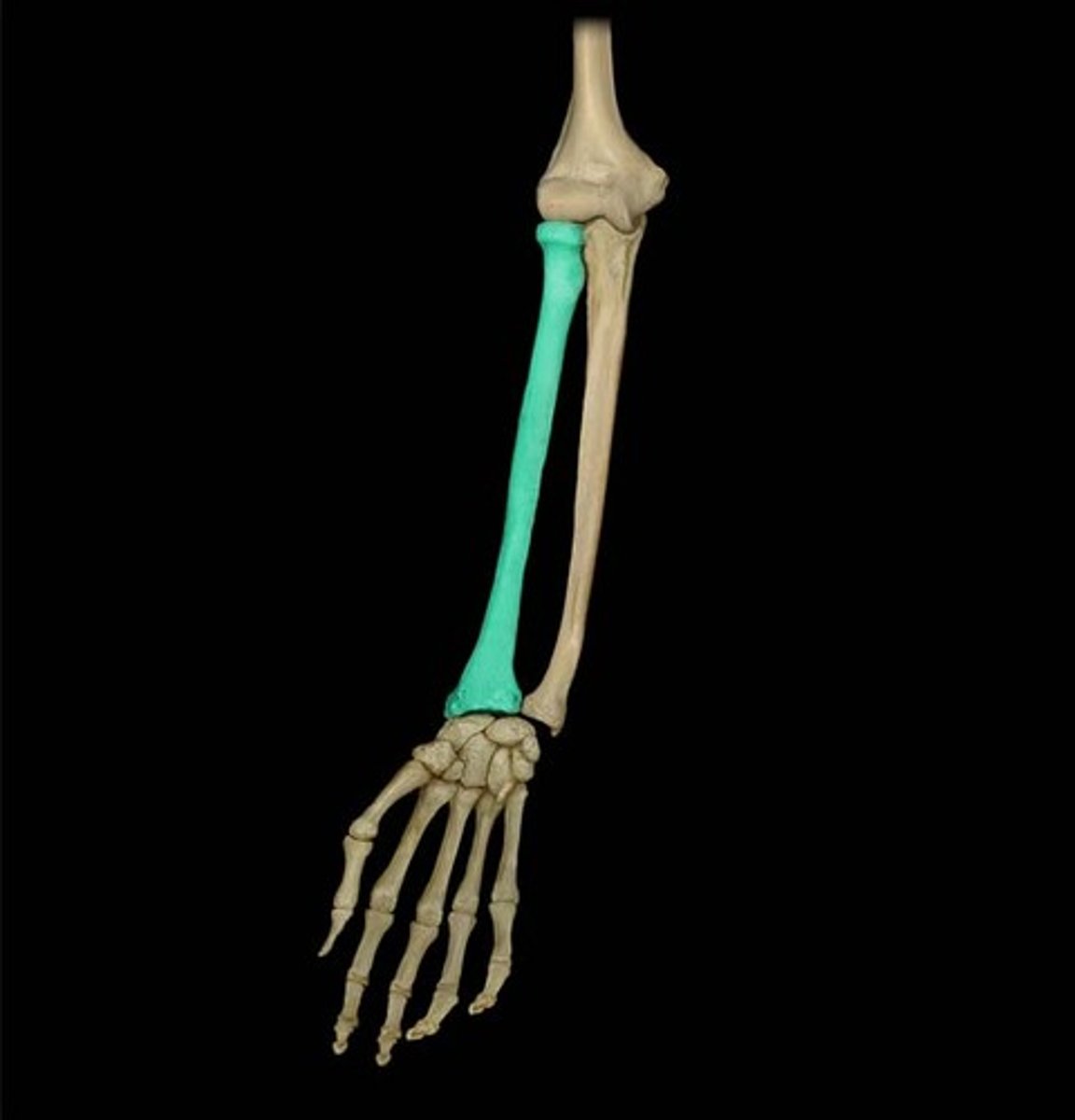
ulna
the inner and longer of the two bones of the human forearm
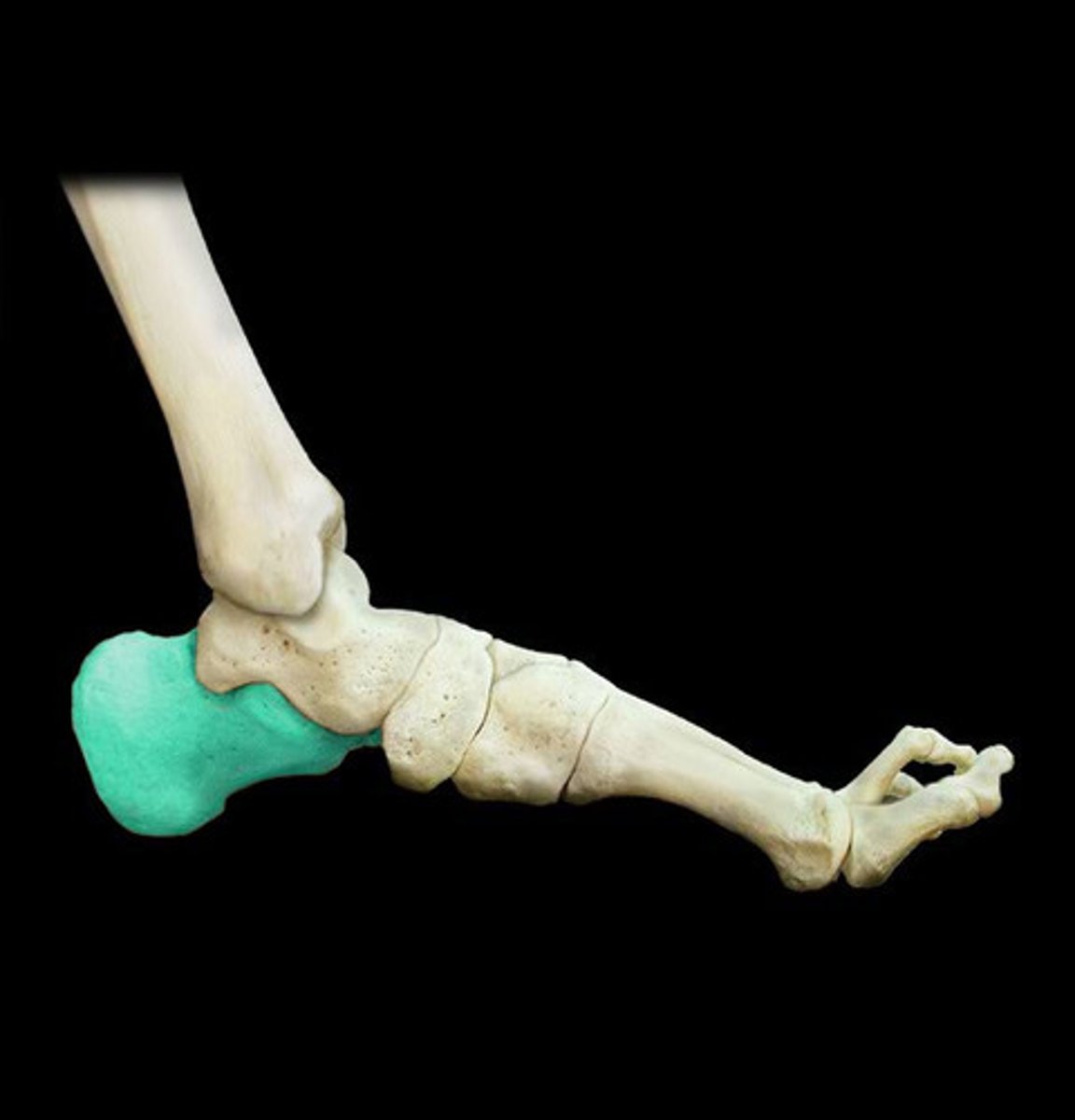
foot is made up of what bones
calcaneus, talus, tarsals, phalanges
calcaneus
heel bone
my.o
muscle
flex/o
bend
fasci/o
fascia, fibrous band
electromyogram
record of the electrical activity in a muscle
Hemiplegia
paralysis of one side of the body
frontalis
forehead
platysma
depresses mandible
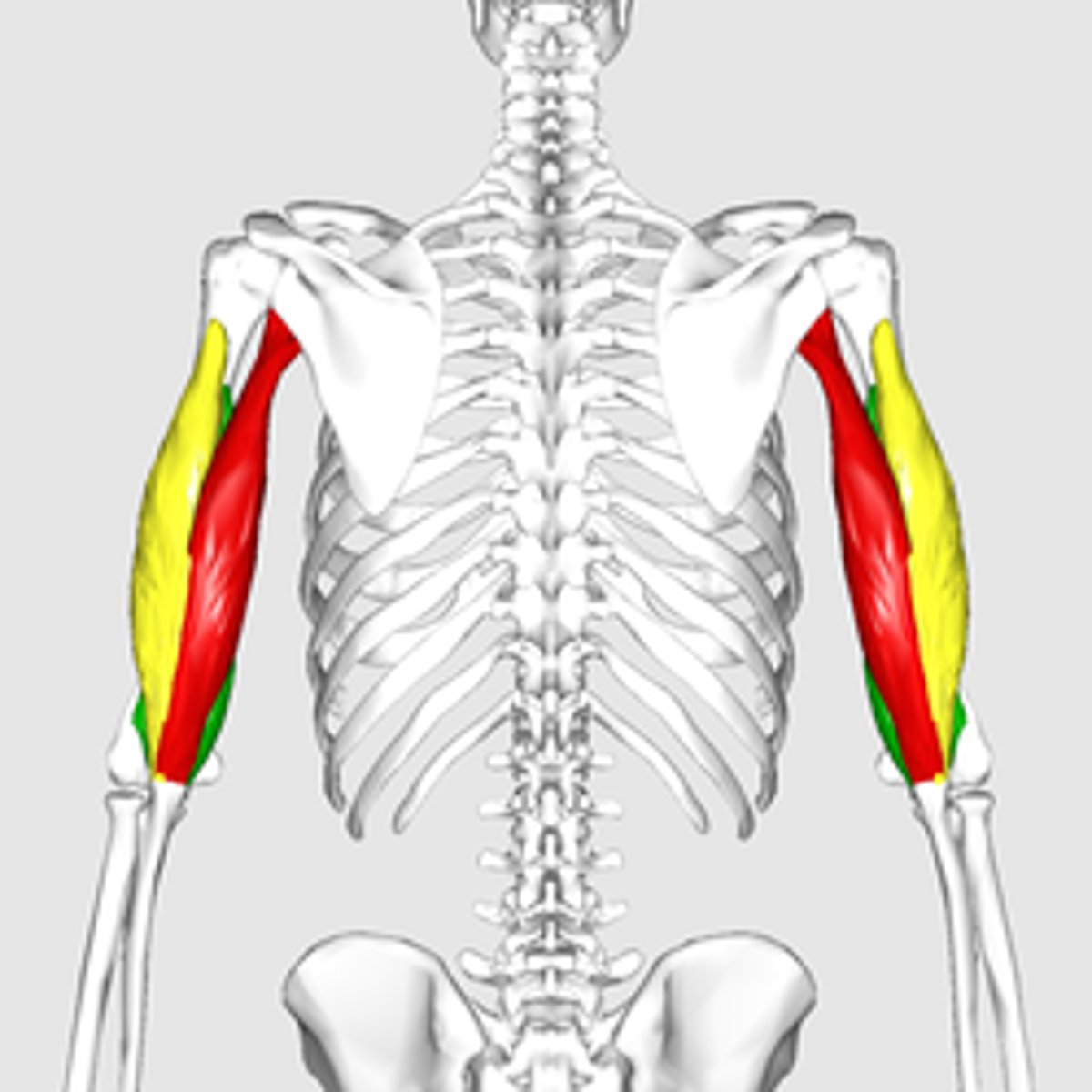
biceps
Front of upper arm
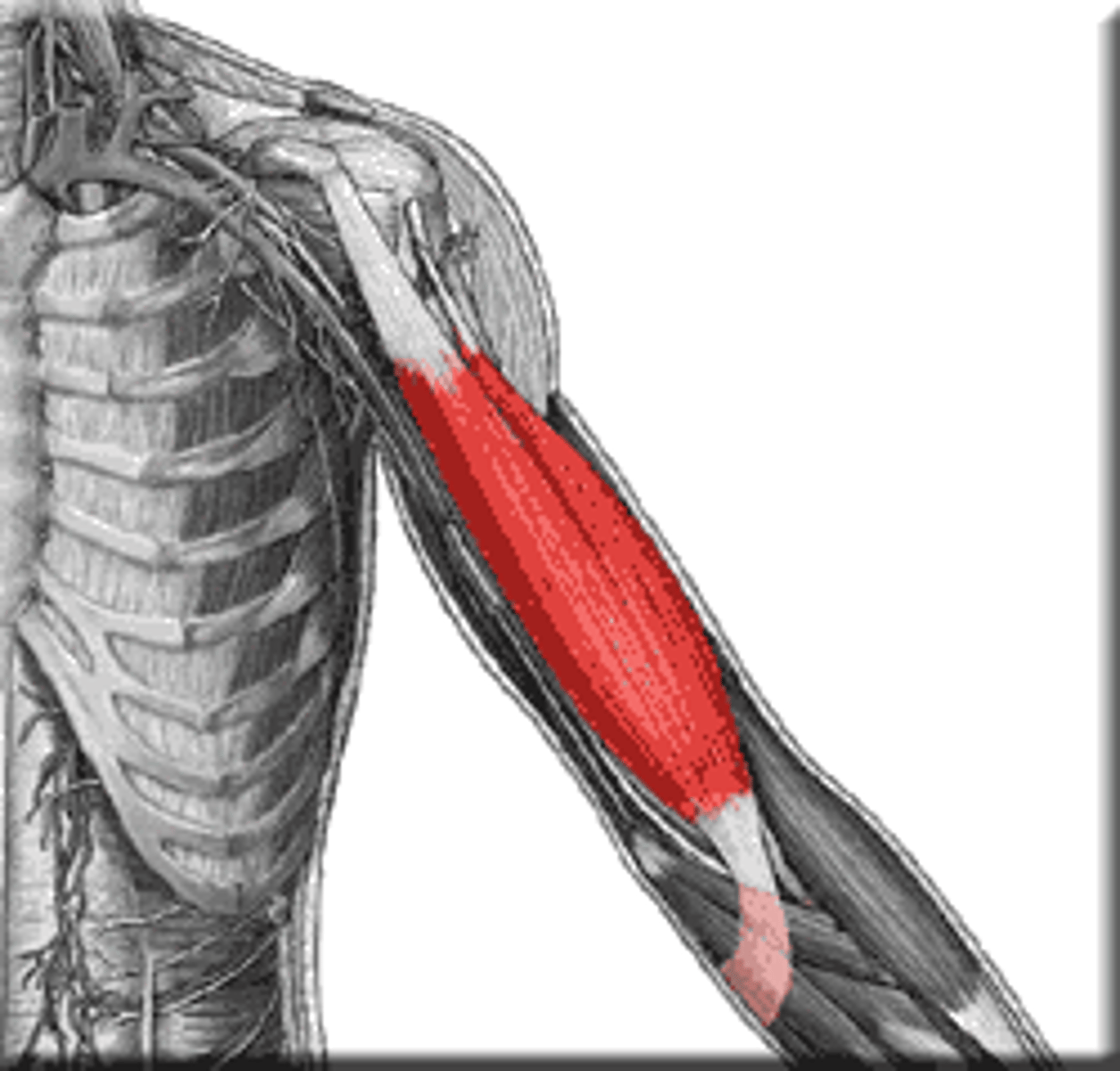
triceps
Back of upper arm
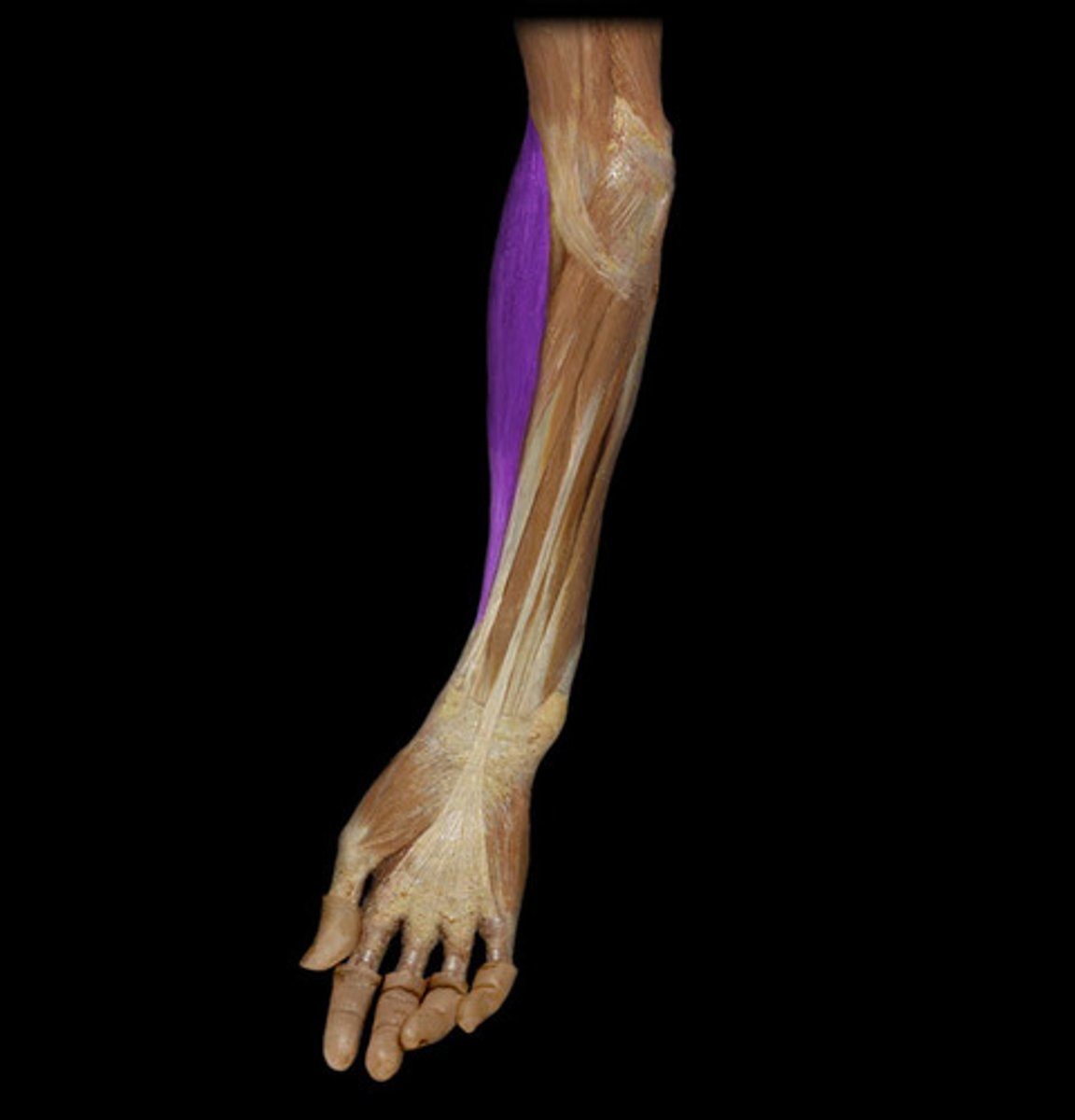
brachioradialis
flexes forearm at elbow
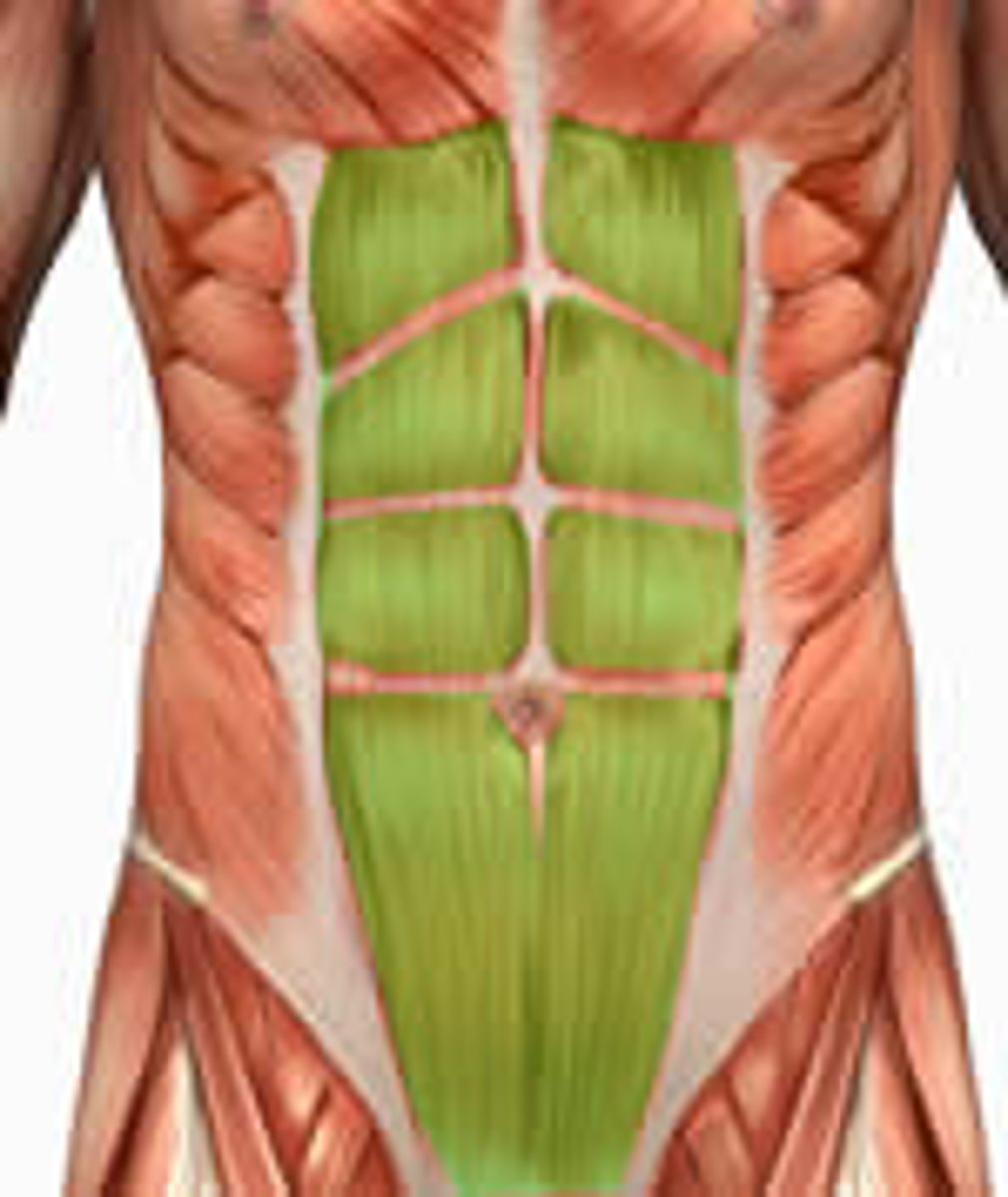
rectus abdominus
abs
quads
leg extension
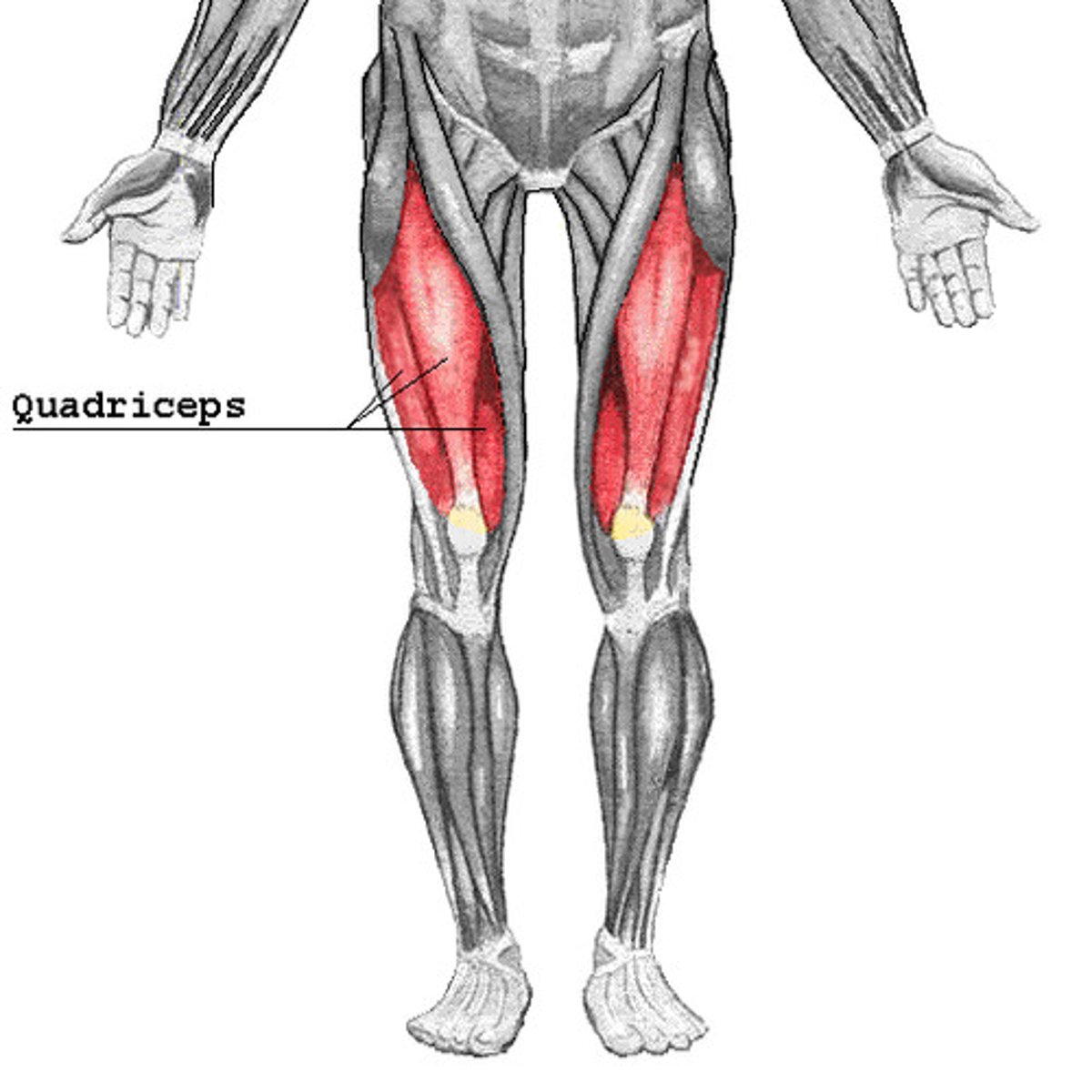
vastus medialis
extends knee
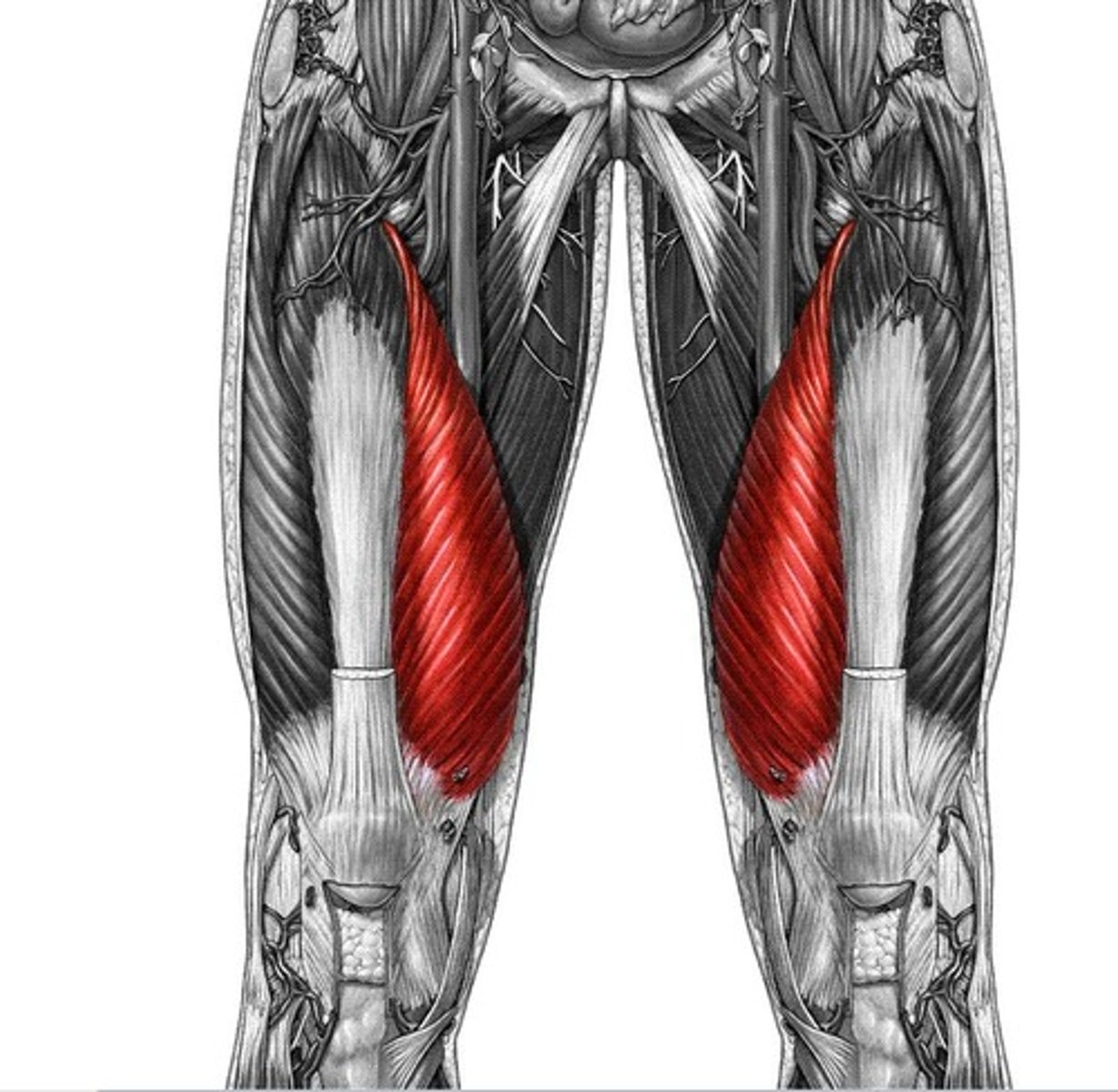
lateralis
toward the side
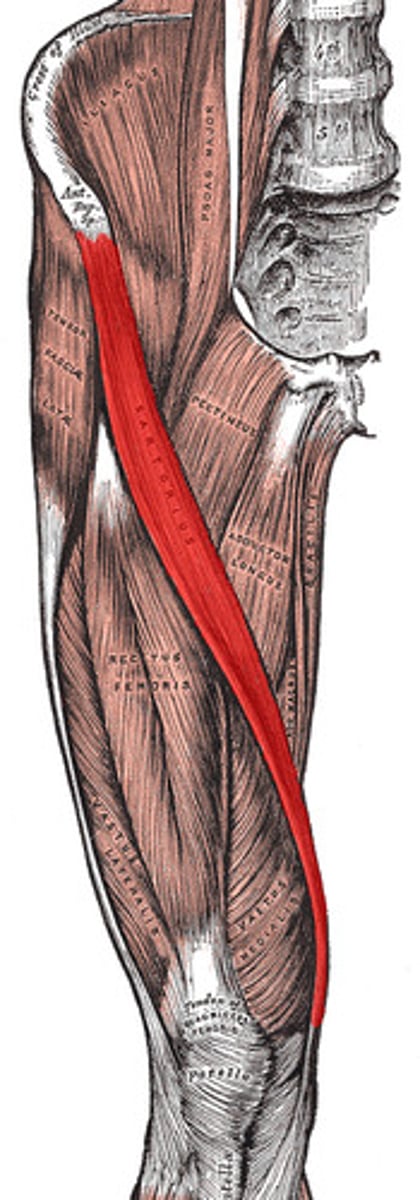
sartorius
Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates thigh at the hip; flexes knee
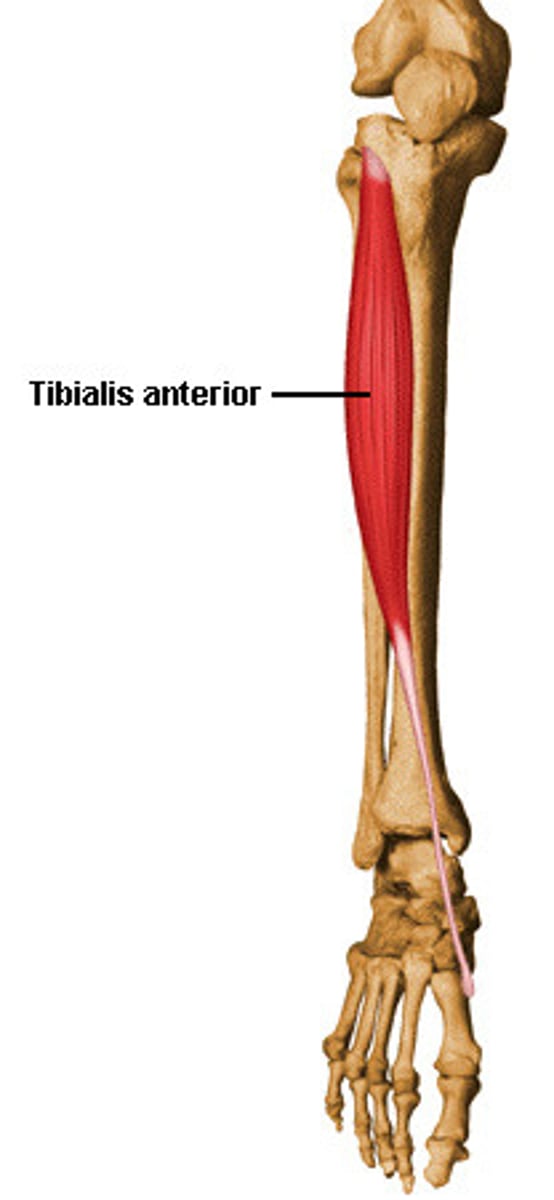
tibialis anterior
dorsiflexes and inverts foot
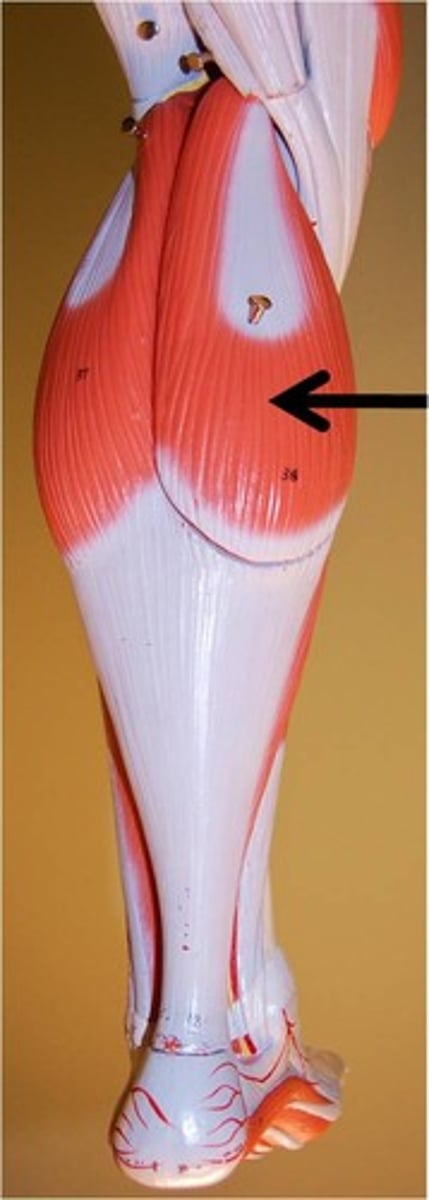
gastrocenmius
plantar flexion
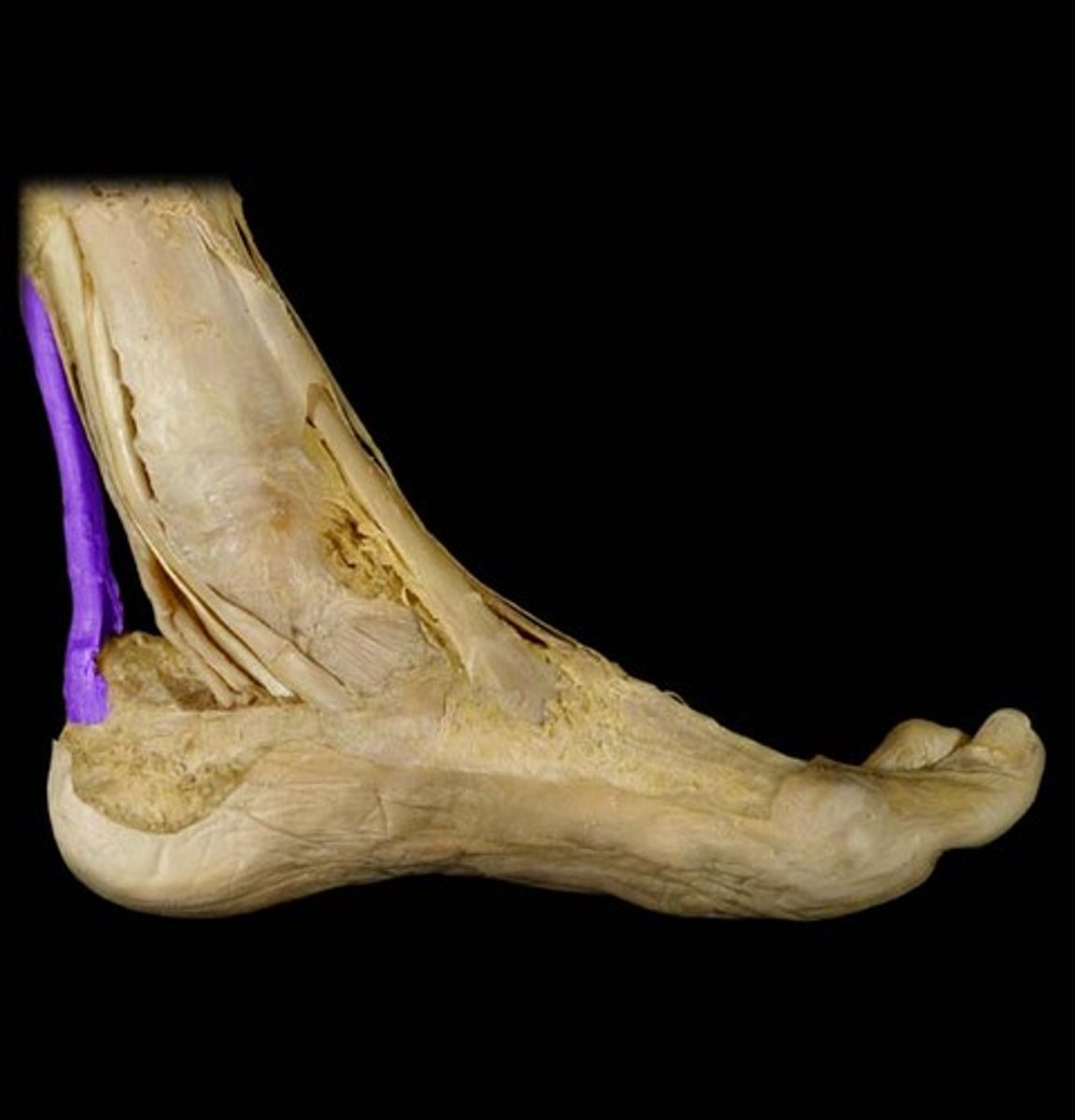
achilles tendon
attaches the gastrocnemius muscle to the heel bone
albinism
Absence of pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes
cyanosis
bluish discoloration of the skin
alopecia
hair loss
keloid
overgrowth of scar tissue
derm/o
skin
melan/o
black, dark
psor/o
itching
where are the skin follicles located
dermis
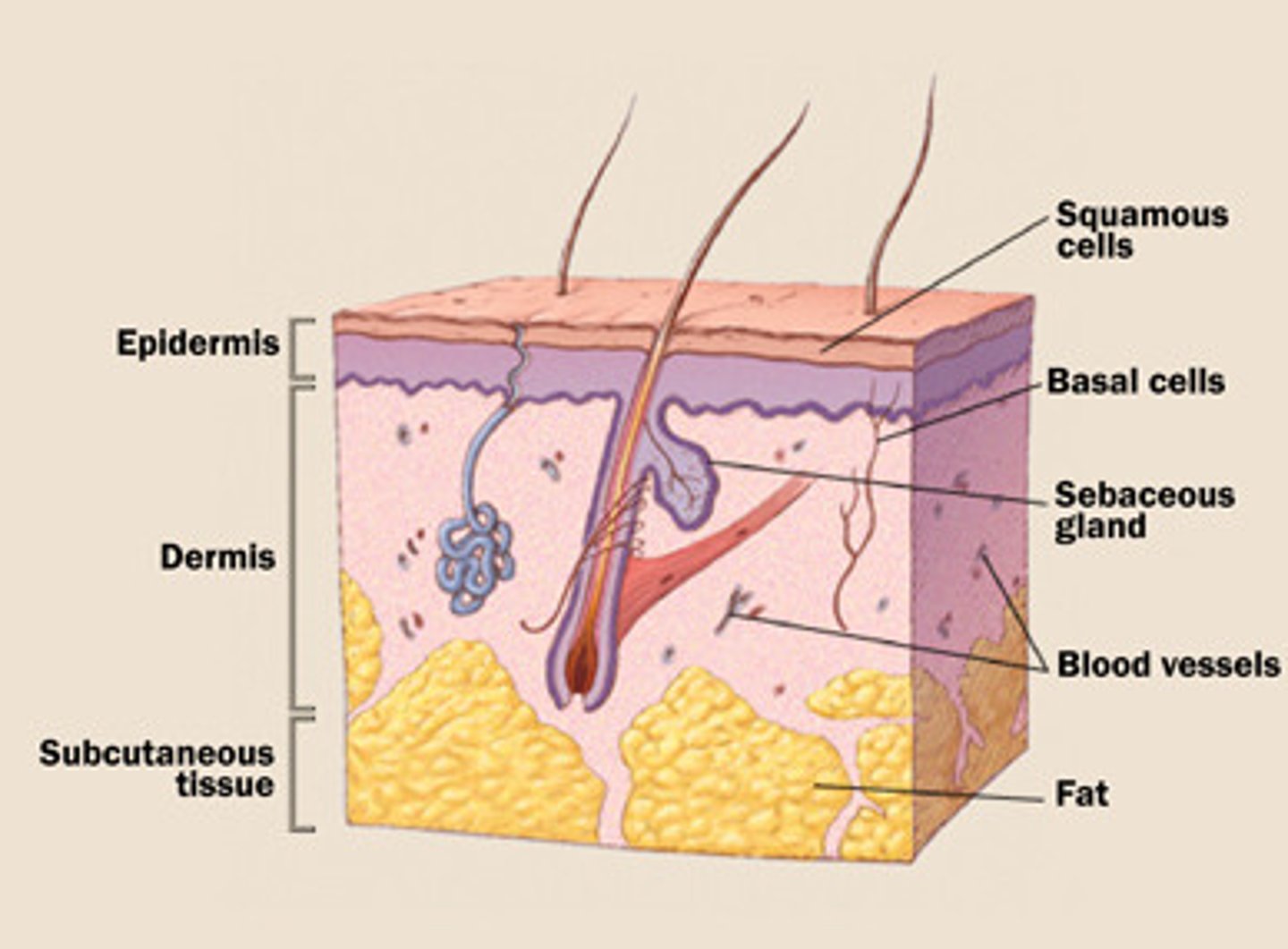
what is responsible for skin pigmentation
melanin/melanocytes
melanocytes vs melanin
produce melanin vs. pigment in hair and skin made by melanocytes
why do we do scratch tests/intradermal skin tests
allergies