Injury, Inflammation, and Healing in Physical Therapy
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
Heat, pain, redness, swelling, and decreased function.
Reversible Cell Injury
Transient injury allowing cellular adaptation and recovery.
Chronic Cell Injury
Sustained stress leading to stable cellular adaptation.
Intracellular Accumulations
Increased lipids, proteins, or pigments due to overload.
Irreversible Cell Injury
Cell death via apoptosis or necrosis.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death, genetically mediated.
Necrosis
Pathological cell death, often resulting in gangrene.
Acute Inflammation
Sudden onset, short duration response to injury.
Inflammatory Process
Removes injurious agents and initiates healing.
Healing Process
Includes regeneration, repair, or combination of both.
Regeneration
Regrowth of original tissue after injury.
Repair
Formation of connective tissue scar after injury.
Outcome of Inflammation
Determined by degree and persistence of inflammation.
Physical Therapy Implications
Understanding injury essential for managing patient recovery.
Acute Inflammation Triggers
Infections, tissue necrosis, foreign bodies, immune reactions.
Swelling in Inflammation
Caused by exudation and leukocyte infiltration.
Increased Temperature in Inflammation
Due to arteriolar vasodilation during acute response.
Pain in Inflammation
Pressure from edema on peripheral nerves.
Decreased Function in Inflammation
Result of pressure from edema on nerves.
Termination of Inflammation
Occurs when injurious agent is removed.
Impact on Physical Therapy
Influences management across various healthcare settings.
Tonsillitis
Inflammation of the tonsils, often due to infection.
Myositis
Inflammation of muscle tissue, causing pain.
Epicondylitis
Inflammation of the tendons at the elbow.
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels to increase blood flow.
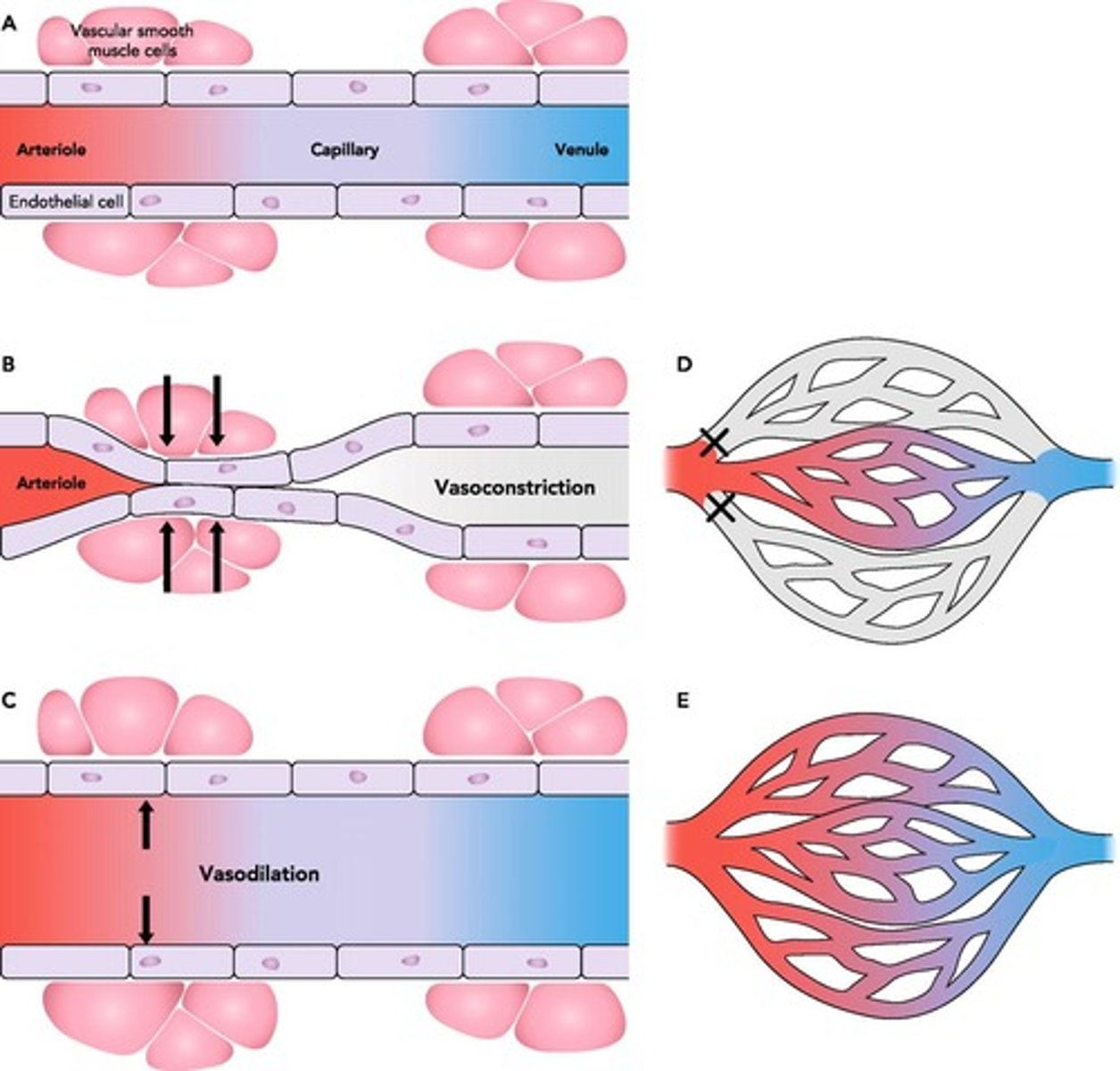
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels to reduce blood flow.
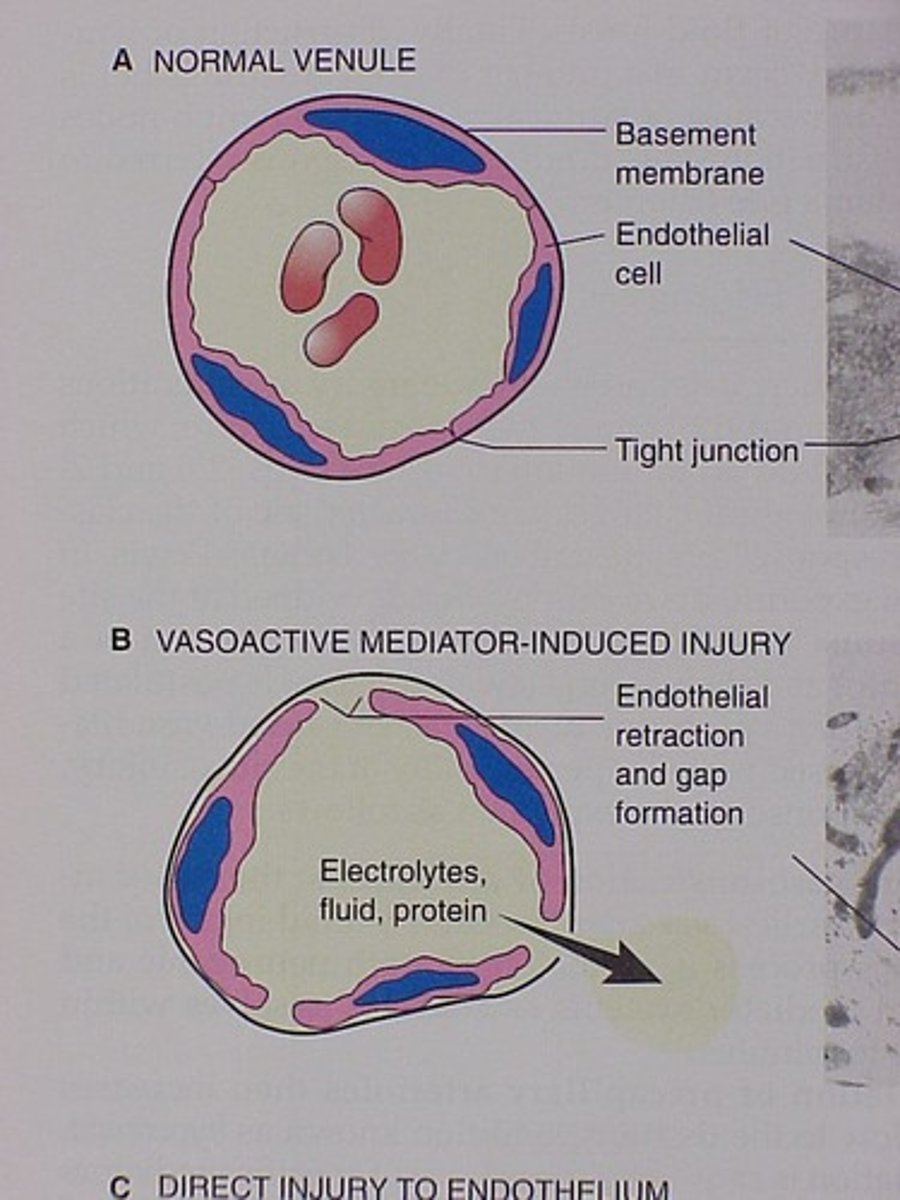
Endothelial cells
Cells lining all blood vessels, regulating permeability.
Serum
Clear fluid remaining after blood coagulation.
Plasma
Liquid component of blood, includes serum and proteins.
WBC
White blood cells, key players in immune response.
RBC
Red blood cells, responsible for oxygen transport.
Platelets
Cell fragments aiding in blood clotting.
Laminar blood flow
Smooth, layered flow of blood in vessels.
Hyperemia
Increased blood content in tissues, causing redness.
Fluid Exudate
Plasma leaking into tissues due to inflammation.
Stasis
Slowed blood flow and pooling in small vessels.
Pavementation
WBCs adhering to endothelial cells during inflammation.
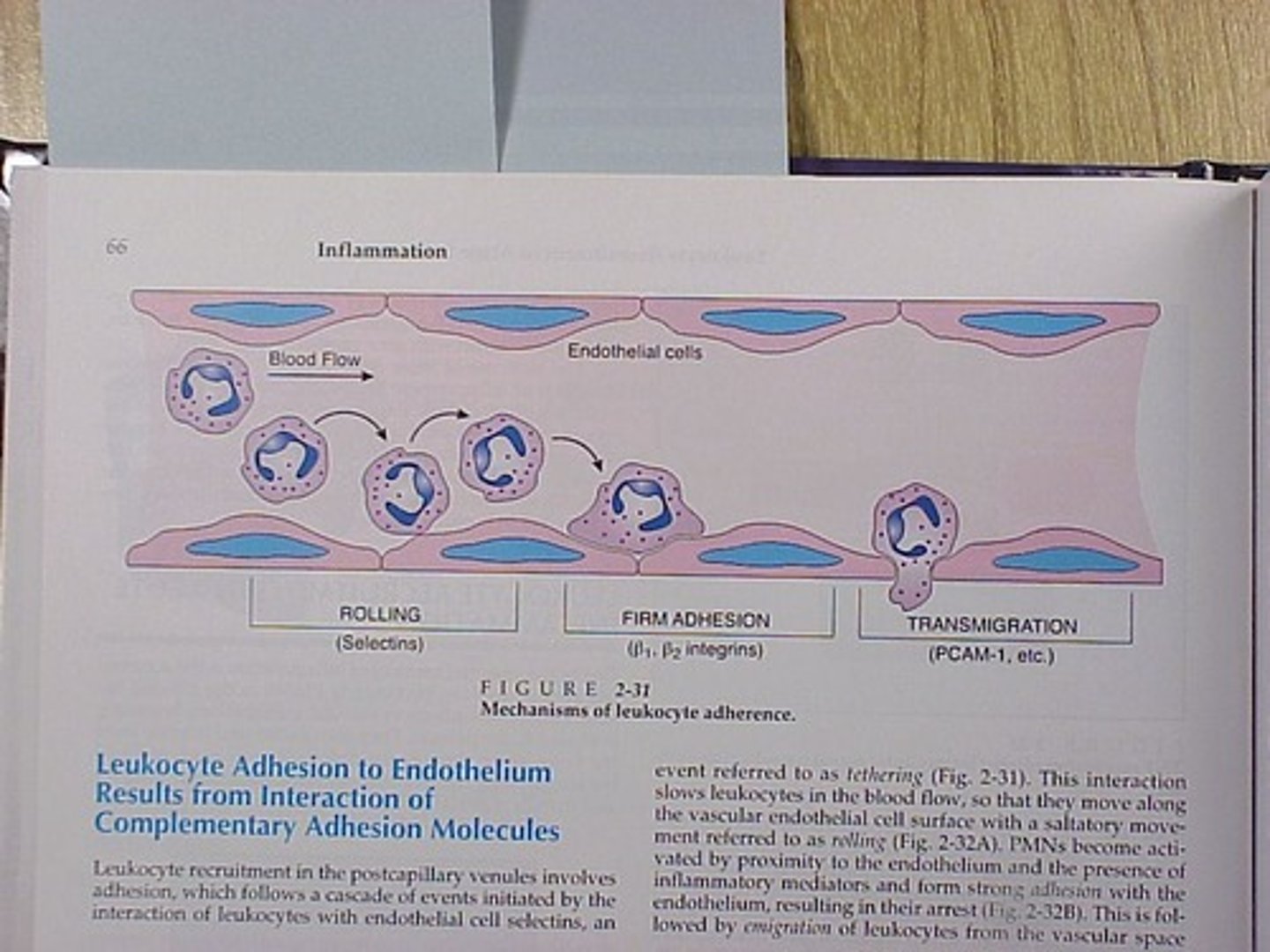
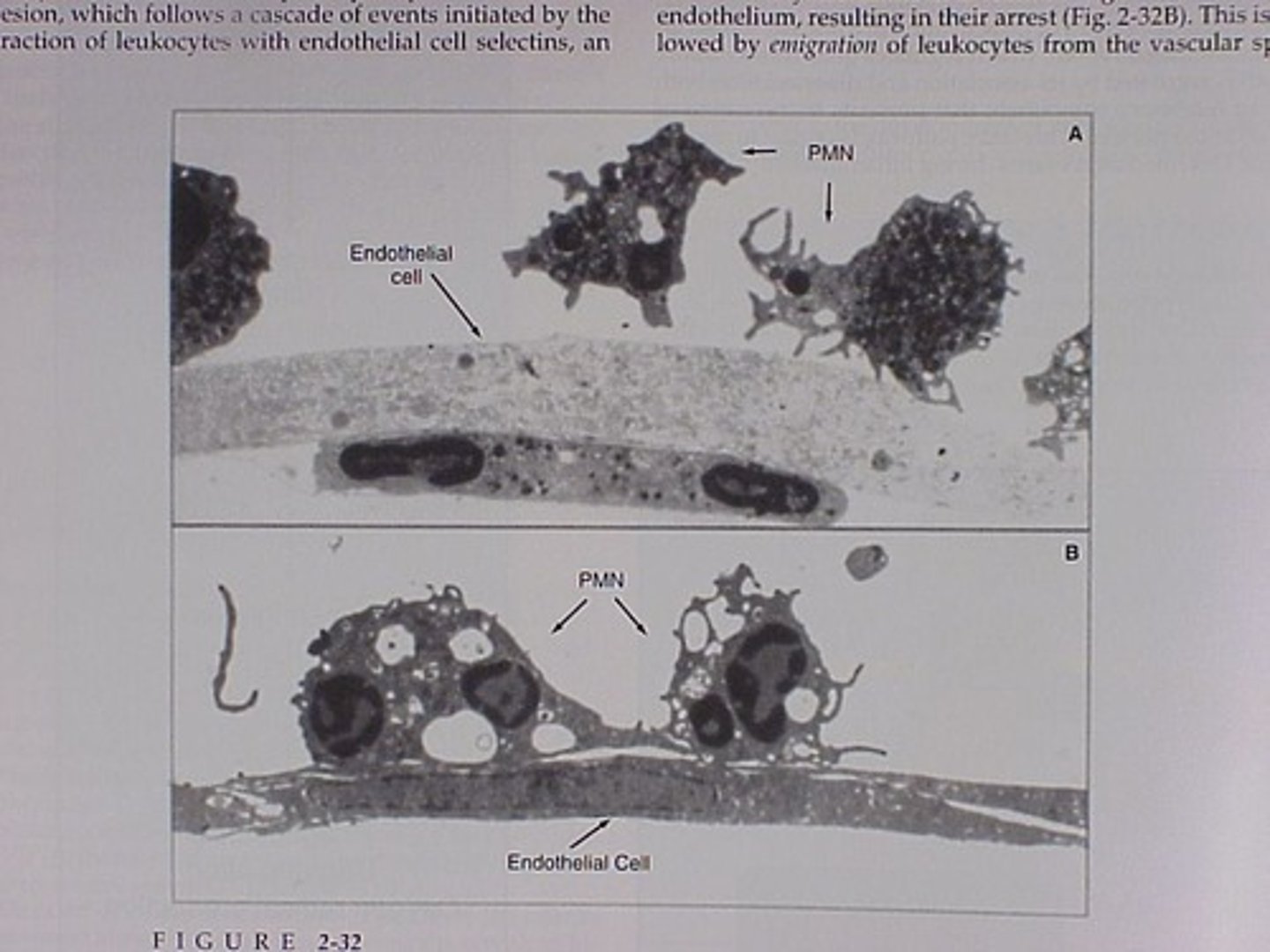
Diapedesis
Migration of WBCs out of blood vessels.
Resolution
Removal of fluid and cells by lymphatics.
Histamine
Chemical mediator causing vasodilation and permeability.
Bradykinin
Induces blood vessel dilation and pain sensation.
Prostaglandins
Mediators of inflammation, pain, and fever.
Lactic acid
Byproduct of metabolism, accumulates during inflammation.
Acute Inflammation
Body's immediate response to injury or infection.
Protection
First line of defense against harmful agents.
Fluid Exudate
Fluid accumulation at injury site for healing.
Cellular Exudate
White blood cells involved in immune response.
Swelling
Result of fluid accumulation in tissues.
Serum
Liquid component of blood, aids in healing.
Antibodies
Proteins that provide immunity against pathogens.
Fibrin
Protein that forms clots to prevent damage spread.
Opsonins
Substances that enhance phagocytosis of pathogens.
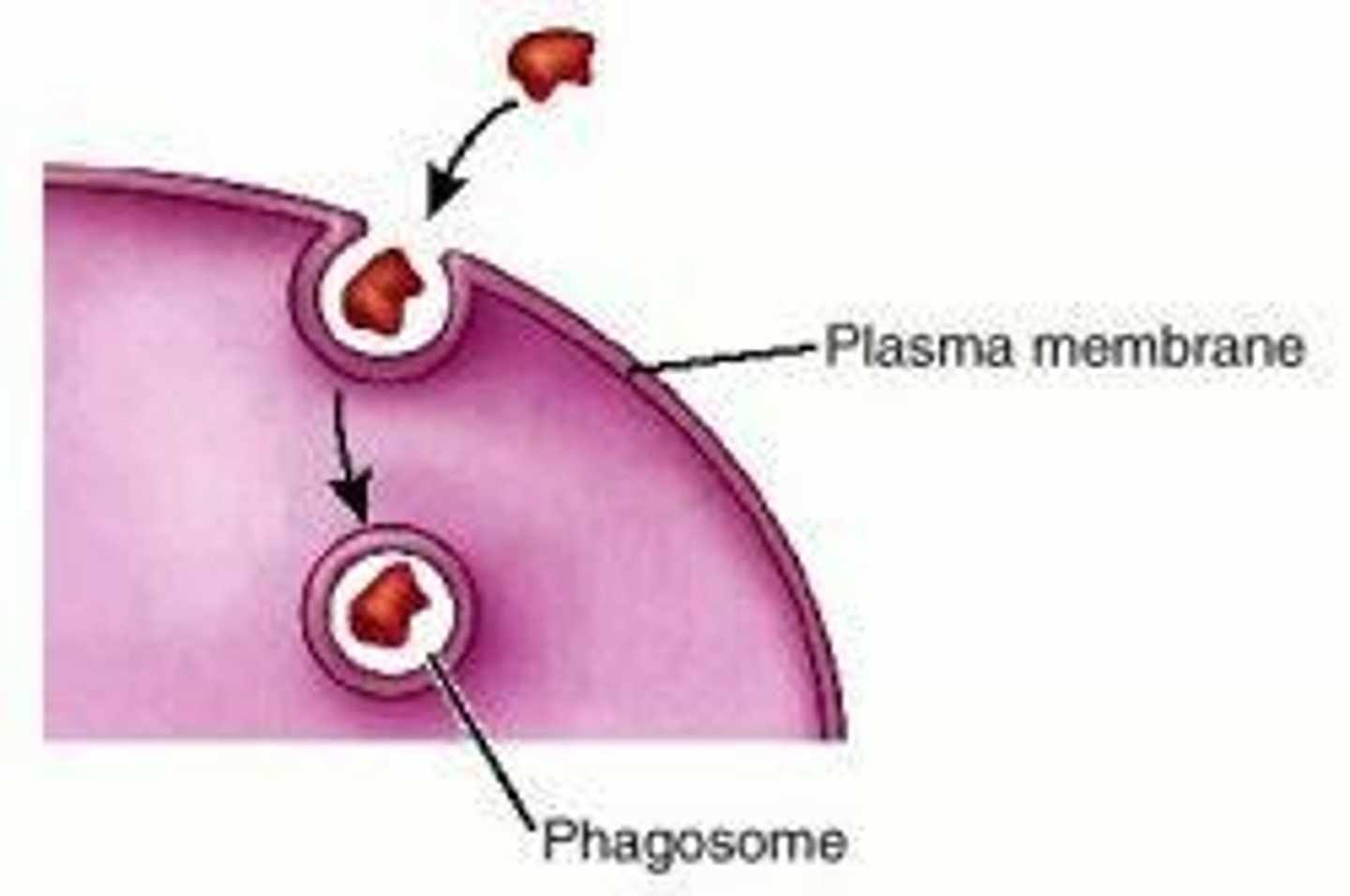
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing and digesting foreign materials.
Pyrogens
Substances that induce fever during inflammation.
Immune Response
Body's defense mechanism against infections.
Serous Inflammation
Clear fluid exudate, often seen in blisters.
Fibrinous Inflammation
Characterized by fibrin formation, seen in pericarditis.
Hemorrhagic Inflammation
Presence of red blood cells in exudate.
Catarrhal Inflammation
Inflammation of mucous membranes with clear mucus.
Pseudomembranous Inflammation
Necrotic tissue with exudate, appears as coating.
Gangrenous Inflammation
Infection of dead tissue, leading to necrosis.
Suppurative Inflammation
Presence of pus due to infection.
Abscess
Localized collection of pus surrounded by tissue.
Chronic Inflammation
Prolonged inflammation that can cause tissue damage.
Healing Process
Restoration of tissue integrity following inflammation.
Inflammation Agent Removal
If removed, inflammation resolves and healing occurs.
Persistent Inflammation
If not removed, inflammation can become chronic.
Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
Pain, heat, swelling, redness, loss of function.
Pain Measurement
Utilizes pain scales to assess severity.
Heat Assessment
Compare temperature between affected sides.
Swelling Measurement
Use tape measure and volumetrics for assessment.
Redness Evaluation
Compare color changes between affected sides.
Loss of Function Assessment
Evaluate weight bearing and goniometry.
RICED Protocol
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation, Drugs for treatment.
Rest in RICED
Allows tissue healing without complete inactivity.
Ice Application
Reduces hyperemia through vasoconstriction.
Compression Techniques
Controls fluid formation and increases tissue tension.
Elevation Purpose
Facilitates drainage and reduces swelling via gravity.
Drugs in RICED
Includes anti-inflammatories like aspirin and ibuprofen.
Wound Healing Process
Involves contraction and complex tissue repair mechanisms.
Local Factors in Healing
Blood supply and tissue breakdown influence recovery.
Patient Factors in Healing
Age, nutrition, and genetics affect healing outcomes.
Chronic Inflammation Characteristics
May follow acute inflammation and cause scar tissue.
Chronic Inflammation Treatment
Heat application is typically contraindicated.
Chronic Inflammation
Persistent inflammation that does not resolve over time.
Necrosis
Cell death due to injury or disease.
Fluid Exudate
Fluid that leaks from blood vessels during inflammation.
Cellular Exudate
Accumulation of immune cells at inflammation site.
Myofibroblasts
Cells that aid in wound healing and tissue repair.
Chronic Suppurative Inflammation
Inflammation characterized by pus formation.
Pyogenic Agent
Bacteria that produce pus during infection.
Granulomatous Inflammation
Inflammation with heavy macrophage infiltration.
Tuberculosis
Infectious disease causing granulomatous inflammation.
Hansen's Disease
Also known as Leprosy, causes chronic inflammation.
Crohn's Disease
Chronic inflammatory bowel disease with granulomas.
Chronic Peptic Ulcer
Ulceration in the stomach or duodenum due to inflammation.
Hemoptysis
Coughing up blood from bronchial tubes.
Chronic Fibrosis
Excessive connective tissue formation in chronic inflammation.
Stenosis
Narrowing of a bodily passage or opening.
Delayed Wound Healing
Prolonged recovery time for tissue repair.