W8: Scleral lenses
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10:00
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
WATCH LECTURE
Ability to quantify corneal shape and size, and pupil
Knows the methods for the CL correction of aphakia, high ametropia, keratoconus, post- surgical and post- refractive surgery
Contents
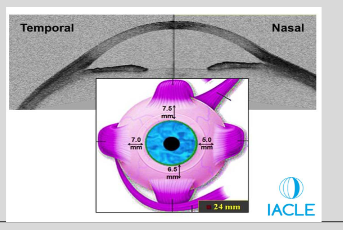
What anatomical features influence scleral shape?
Nasal sclera is flatter
Space from limbus to muscle insertion:
Temporal: 7.0 mm
Superior: 7.5 mm
Inferior: 6.5 mm
Nasal: only 5.0 mm
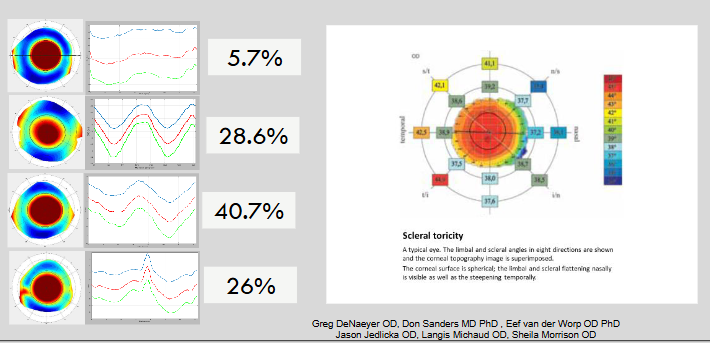
What do scleral profile measurements reveal about peripheral cornea and anterior sclera?
Avg peripheral corneal radius: 9.10 mm (range 7.80–10.80 mm)
Avg anterior scleral radius (nasal + temporal): 12.40 mm (range 10.10–16.60 mm)
Some peripheral corneal radii were actually flatter than some anterior scleras
Scleral toricity
Diagram shows amount of toricity in various meridians
3rd=40.7-signif diff btwn toricity in diff meridians
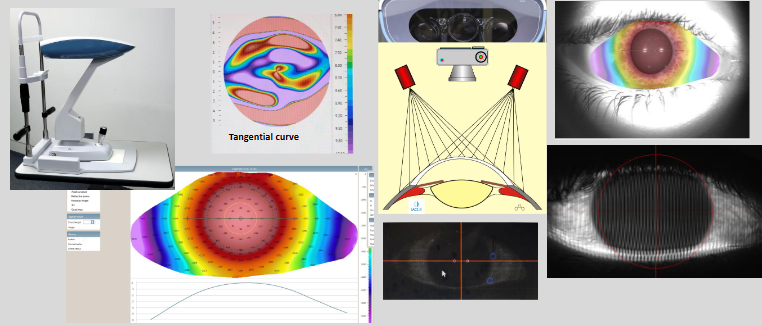
What is fourier transform profilometry?
Topographers: Corneo-scleral profile
Flashes vertical line patterns on the fluorescein-dyed tear film to map corneal & scleral topography
What does the limbal profile reveal about the corneal–scleral junction?
Traditional concept:
Smooth corneal–scleral junction
Reality shown:
Angled / tangential transition between cornea, limbus, and sclera
Reveals true asymmetry rather than a uniform junction
This asymmetry is clinically important for scleral lens fitting
What do sagittal height measurements show about horizontal and vertical asymmetry of the anterior segment?
Two sagittal sections measured on OCT:
Vertical and horizontal, from corneal apex to end of the anterior chamber (iris)
Sagittal heights:
Vertical ≈ 3,660 µm
Horizontal ≈ 3,490 µm
Difference ≈ 170 µm
Indicates horizontal ≠ vertical symmetry
Sectoral sagittal height pattern:
Inferior > Nasal > Temporal > Superior
Overall rules shown:
Nasal sag > Temporal sag
Inferior sag > Superior sag
Full order: I > N > T > S
Why is scleral lens fitting dependent on understanding ocular shape?
Scleral CLs interact with areas beyond the cornea, incl the limbus & sclera
Anterior eye= not a symmetrical solid
Lens + lens edges contact the nasal paralimbal zone before the temporal equivalent
→ leads to routine temporal decentration
Why do scleral lenses commonly show temporal decentration?
Scleral lenses tend to decentre temporally
During near tasks (e.g. reading), the eyes converge and the lens moves with the eye
There is limited space temporally between the corneal–limbal junction and extraocular muscle insertion
Reduced temporal space can cause the lens to knock into the canthus
This leads to rotation and temporal decentration
Effect is more pronounced with larger lenses, such as soft and scleral lenses
What material advancements have supported the resurgence of scleral lenses?
Newer scleral lens materials have higher O₂ permeability (Dk)
They do not rely on tear exchange beneath the CL
Prev Sceral lenses allowed for a lot of oedema bc reliance was not on materials perm but on tears to provide O2, like in a corneal GP
Result =improved corneal physiology during wear
What technological and manufacturing developments have improved scleral lens fitting?
Advancements and automation in lathing
Took a mold of eye
Greater understanding of ocular shape from:
Topography
Anterior segment OCT
Profilometry
Scheimpflug imaging
What are the primary visual indications for scleral lenses?
Irregular astigmatism
Post-traumatic irregularity
Penetrating Keratoplasty
Keratoconus
Pellucid Marginal Degeneration
Post-refractive surgery
Post herpetic infection
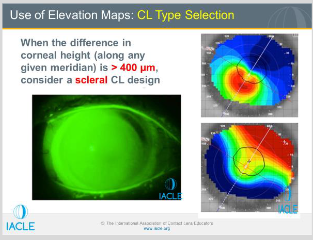
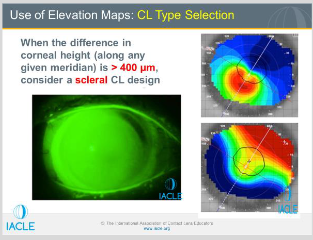
Describe the pic
Pt has PMD-kissing doves pattern
Difference map of the elevation of the eye presented in inferior pic measured in microns
Along the 1
What additional functional indications support the use of scleral lenses?
Athletes
Poor CL centration
Poor CL stability
Corneal GP CL intolerance
High scripts

What are the therapeutic indications for scleral lenses
Therapeutic indications
Chemical burns
Ocular pemphigoid
Stevens–Johnson syndrome
Symblepharon management
Graft vs host disease
Exposure keratitis
Neurotrophic keratopathy
Persistent epithelial defect(s)
Severe dry eye
Sjögren’s syndrome
Filamentary keratitis
Limbal stem cell deficiency
What does current evidence suggest about intra-ocular pressure (IOP) changes during scleral lens wear?
As measured using a non-standard transpalpebral IOP method, scleral lens wear may increase IOP by ~5 mmHg on average.
Regardless of scleral lens diameter.
Further research =req’d to det whether clinicians should exercise caution when fitting scleral lenses on patients at risk for glaucoma.

Scleral lens design
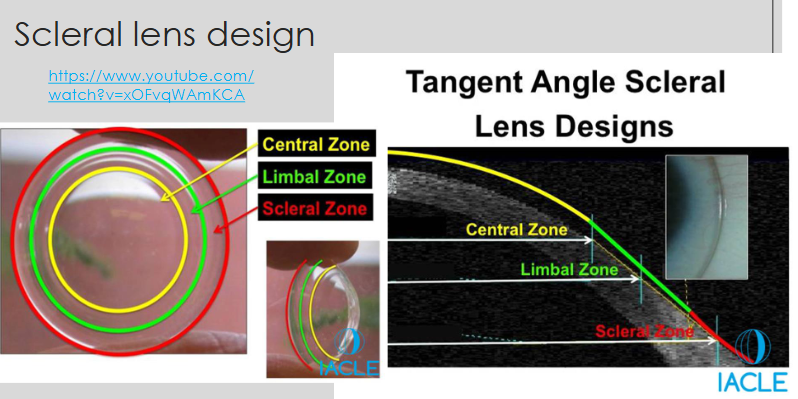
What are the key features of the central/optical zone in a scleral lens?
Front surface optics can be spherical or aspheric.
Back surface of the optical zone usually does not touch the cornea.
Post-lens fluid contributes optical power.
What is the role of the transition/mid-peripheral/limbal zone in a scleral lens?
Connects the end of the optical zone to the beginning of the landing zone going outwards
Sets the sagittal height of the lens.
In smaller designs:
Important to match the limbal shape.
Minimises mechanical pressure, as limbal clearance is typically absent (lens rests here).
Fenestration
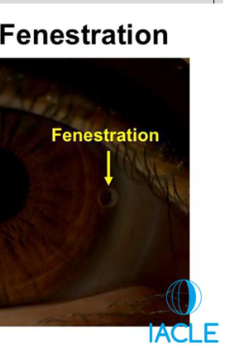
What are the characteristics of the landing/scleral/haptic zone in a scleral lens?
Region where the lens fits and makes contact with the eye.
Should be at least 3 mm wide for comfortable wear.
Defined as a flat curve or series of curves, often with radius 13.5–14.5 mm.
What are the main fitting goals for a scleral lens?
Clears (vaults) the central cornea
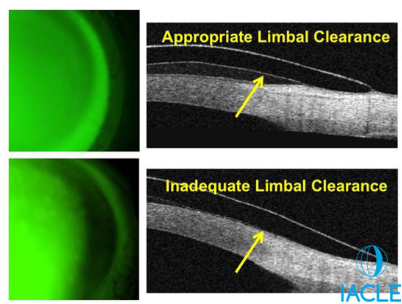
Increases limbal clearance
Visible as a bright ring of fluorescein above the limbus
Scleral alignment
All pressure, weight, and bearing of the lens should be on the sclera
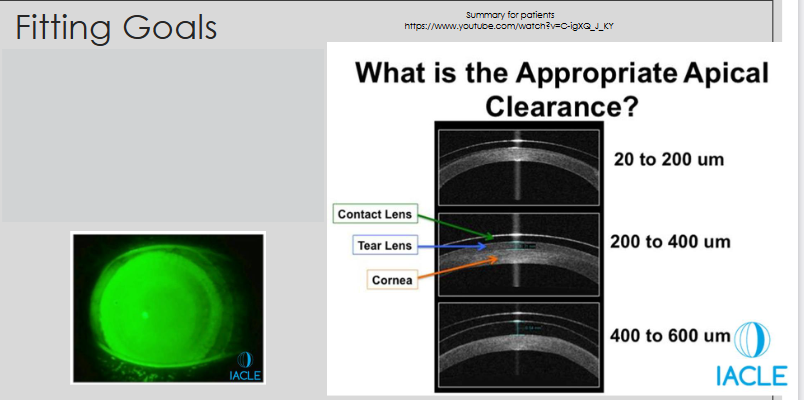
Apical Clearance
Limbal Clearance Zone
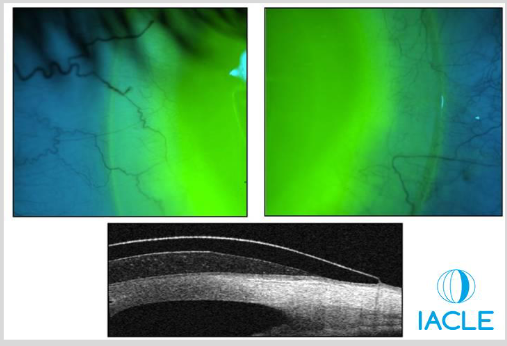
What are the characteristics of a flat landing zone fit in a scleral lens?
Ring of bearing on the inner part of the landing zone
Air bubbles may appear in the periphery of the lens
Possible frothing
What are the characteristics of a steep landing zone fit in a scleral lens?
Bearing occurs on the outer zone
Fluorescein pooling visible extending inward underneath the landing zone from the corneal clearance
Blanching
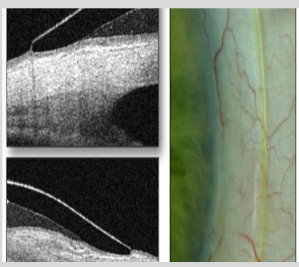
Landing: Impingement
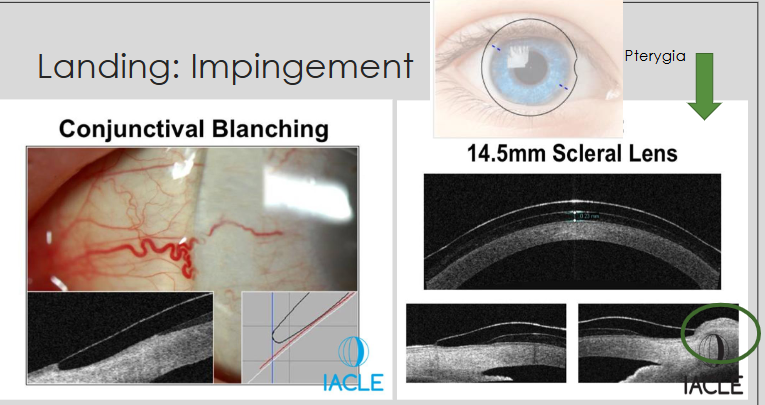
How is the sagittal height method used in scleral lens fitting?
Determine the anterior eye’s sagittal height for:
the chord length at 15.0 mm (for a 16.5 mm TD scleral lens)
Add 0.30 mm (300 μm) to that sagittal height to select the lens
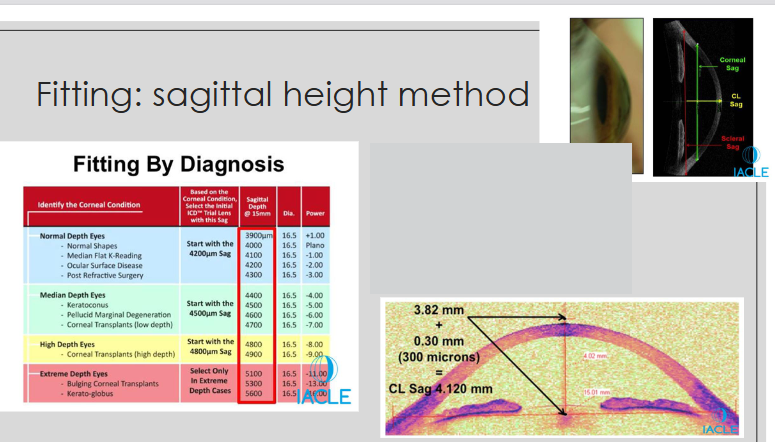
How is the sagittal height of a scleral contact lens calculated?
Eye’s total sagittal height = sag @ 10 mm + sag @ 15 mm
Example: 2100 μm + 1900 μm = 4000 μm
Initial diagnostic CL = 4000 μm sagittal height + 300 μm apical clearance = 4300 μm
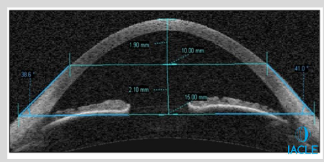
How is sagittal height assessed using corneal topography?
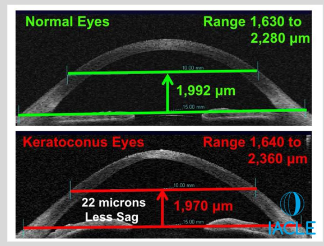
Topographers (e.g., Medmont) measure sag heights within 10.0 mm chord lengths
Avg sag height btwn 10.0 mm and 15.0 mm chord ≈ 2,000 μm
Similar sag heights found in normal + keratoconic eyes
Sag from 10 to 15 mm chords is unaffected by rCorneal Apex
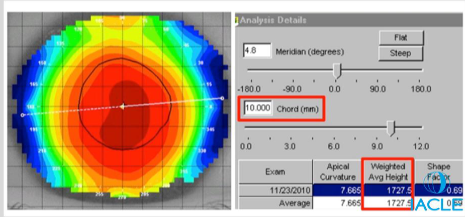
How is the sagittal height for a scleral contact lens calculated?
Cornea/Sclera Sag: 2,000 μm
Corneal Sag: 1,727 μm
Corneal Clearance: 300 μm
Total Sag: 4,027 μm
Lenses are ordered by sag (e.g., 4.0 Sag = 4,000 μm)
How can adjustments to the limbal zone affect the sagittal depth of a scleral contact lens?
Most scleral CL designs allow independent parameter adjustments for different portions of the lens.
Increasing the rise of the limbal zone by 5° will increase the overall sagittal depth of the lens by 125 μm
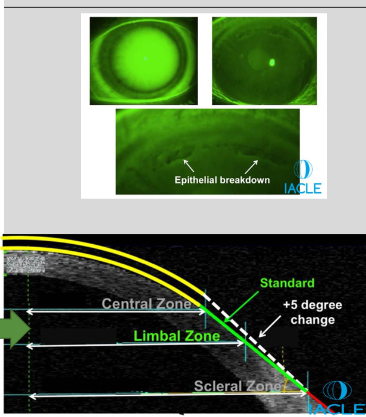
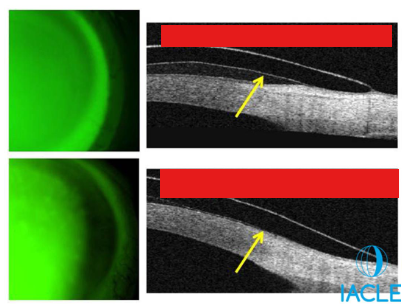
Label:
_____________ limbal clearance
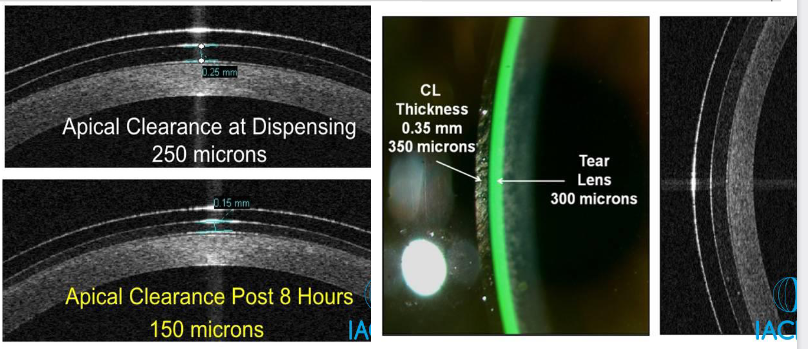
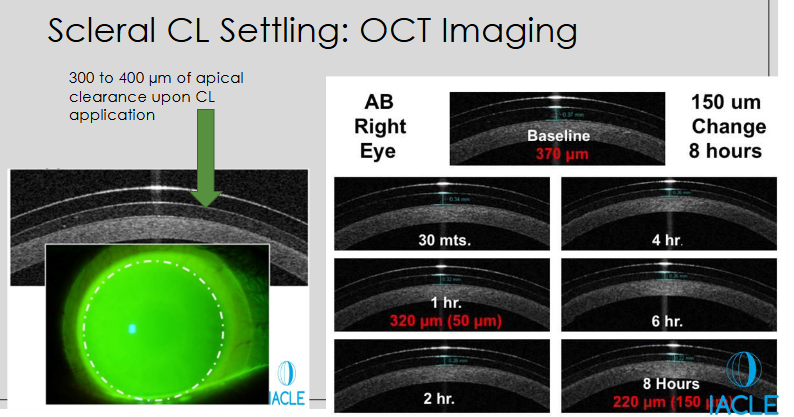
What does OCT imaging reveal about scleral CL settling over time?
Initial apical clearance upon application: 300–400 μm
Clearance reduces over time as the lens settles on the eye
Example (Right Eye, baseline 370 μm):
1 hr: 320 μm (50 μm reduction)
2 hr: 310 μm
4 hr: 295 μm
6 hr: 280 μm
8 hr: 220 μm (150 μm total reduction)
What factors contribute to the presence of bubbles under a scleral lens?
Bubbles can arise from:
Insertion technique
Lens fit (more frequent)
Observe their location to det cause
What is the clinical significance of bubble location under a scleral lens?
Central bubbles → central sagittal height too large, needs lowering.
Small bubbles that move behind the lens may be acceptable if they do not cross the pupil margin.
Large stationary bubbles → not acceptable.
Limbal area bubbles → too much limbal clearance; may req:
Steepening the BC
Dec’ng the limbal shape profile, depending on lens design.
How can air bubbles be managed or minimized when fitting scleral lenses?
Not always preventable, esp w/ non-uniform tear reservoir (e.g., corneal ectasia).
Consistent air bubbles may be reduced by using a more viscous solution for lens insertion.
Asphericity and quadrant specific
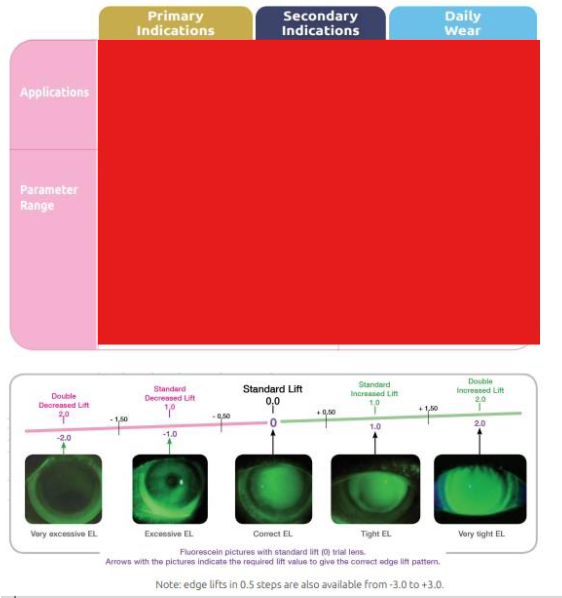
Fill in the table:
Semi scleral lenses
Fill in the table:
Semi scleral lenses
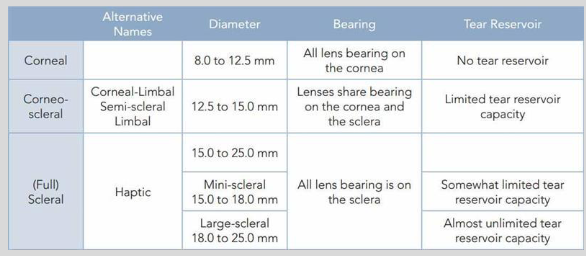
Full scleral*

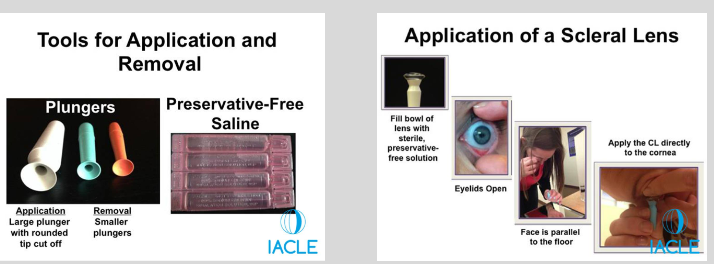
Application
How would you assess the fit of scleral lenses using a slit lamp?
White light
Use optic section to assess tear film clearance:
Centrally
Laterally
Vertically
Over the limbus all around
Assess the edge fit:
Heel → pressure on inside of edge curve
Toe → pressure on outer side of edge curve
What are the limitations of white light slit lamp assessment for scleral lenses?
Less accurate than OCT
Ideally, lens thickness should be known; if not, a 1:1 ratio is accepted
Corneal thickness is not always uniform, which can affect assessment
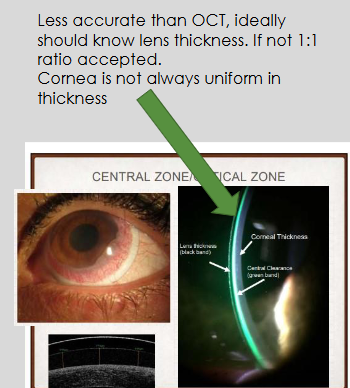
How would you assess the fit of scleral lenses using a slit lamp?
Blue light
Use blue light for overall view of limbal clearance
Easy to detect bubbles or bearing
Easy to observe decentration, often caused by lens gravity
Lift the top lid to check for superior limbal tissue bearing
What is the expected scleral lens settling pattern and related patient education?
Settling time: allow 20–30 minutes for the lens to sink in
Initial drop: 50–80 microns
Further drop after 6–8 hours wear: 50–100 microns
Check tear film
Educate pt that tear debris is normal in nearly 30% of scleral wearers
Reinsertion throughout the day may be needed to remove debris
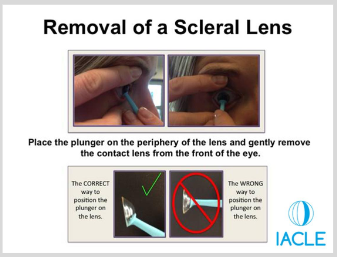
What is the correct technique for removing a scleral lens with a plunger?
1. Aim for the lower half of the lens with the plunger.
2. Once the plunger is sucked on, make a movement away from the eye, and upward. This will break the seal and the lens can easily be removed.
3. Lift the lens edge from the eye
Lens care

Scleral CLs: Is Saline Appropriate?
