Lect. 8 MRI/FMRI
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is the difference between structural and functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)?
Structural MRI is based on the fact that different types of tissue have different physical properties. This gives us a static map of the brain.
Functional MRI is based on the assumption that neural activity is associated with physiological changes. This gives us a dynamic map of physiological changes (oxygen in the blood, the BOLD signal) in response to a stimulus or task.
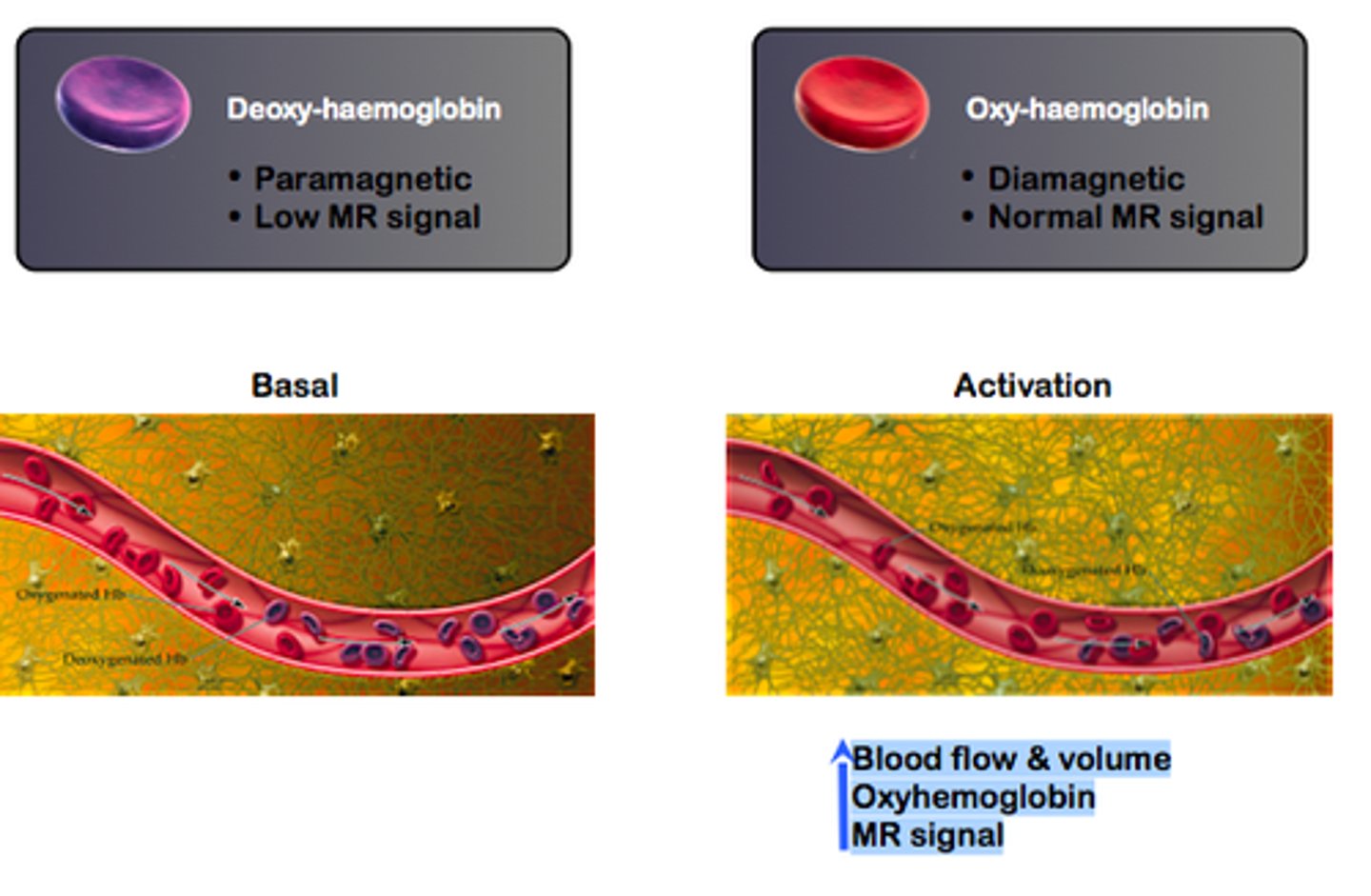
What is BOLD signal?
BOLD: Blood Oxygen Level Dependent
- An indirect measure of neural activity
- When neurons are active, the oxygen level in that part of the brain increases and so does the BOLD signal.
- Signal measured with fMRI (and fNIRS)
What are advantages of structural MRI?
- High spatial resolution
- non invasive
What are disadvantages of structural MRI?
- low temporal resolution
- expensive
- several contraindications, e.g. can't be used with metal implants
- participant must be able to lie very still
What is Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)?
An imaging method based on diffusion of water molecules in the brain. Commonly used to study white matter tracts.
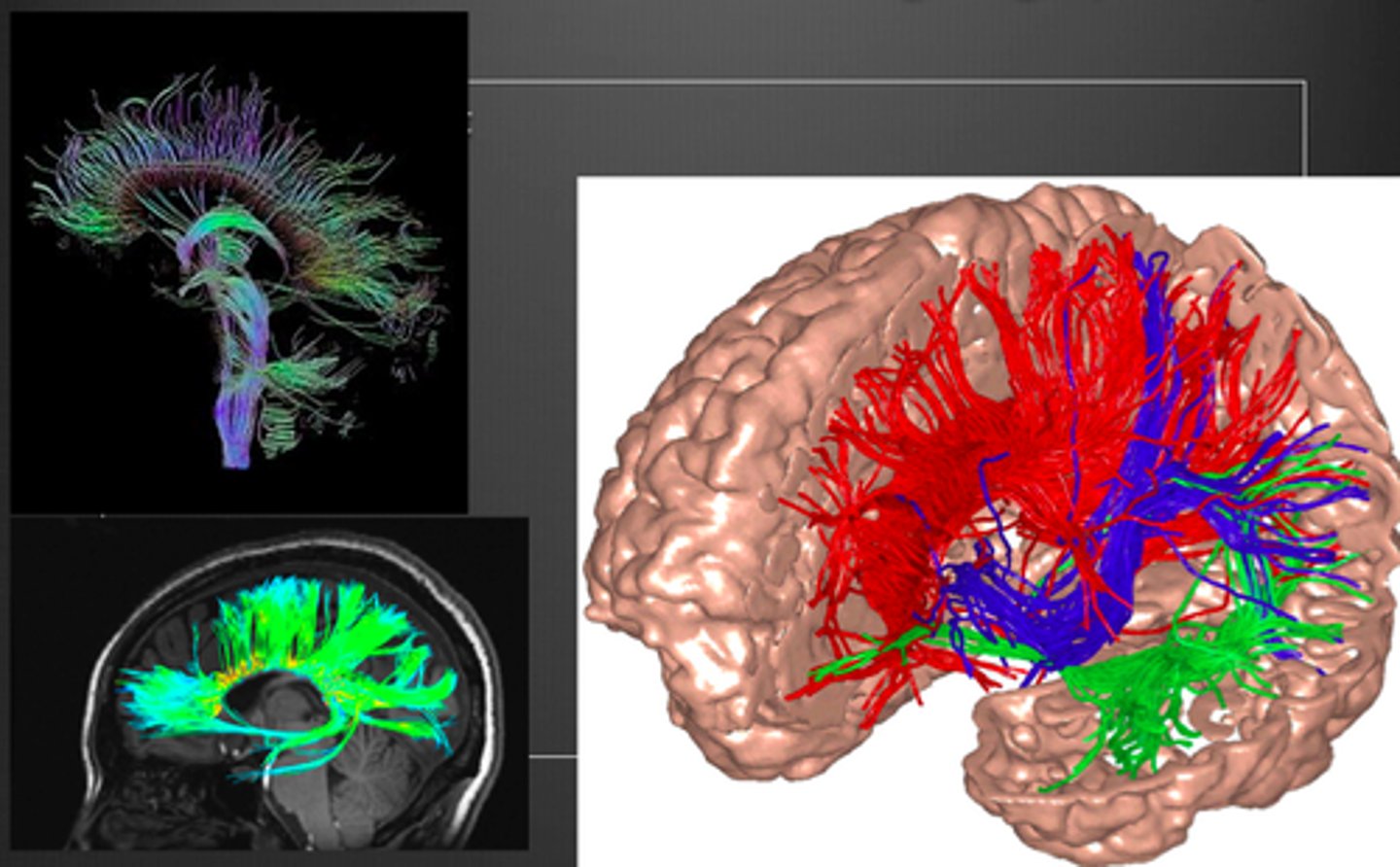
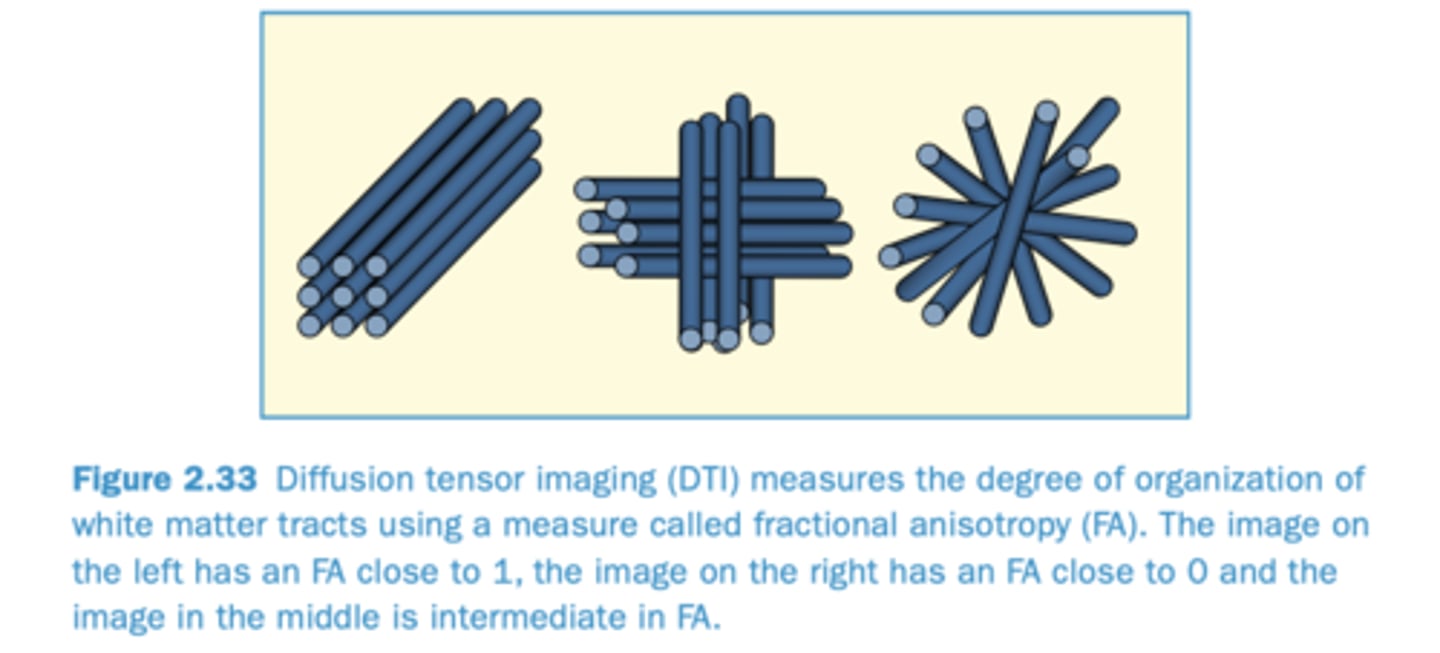
What is fractional anisotropy (FA)?
A measure of the extent to which diffusion takes place in one directions more than others
*better alignment (FA = 1) leads to a stronger signal
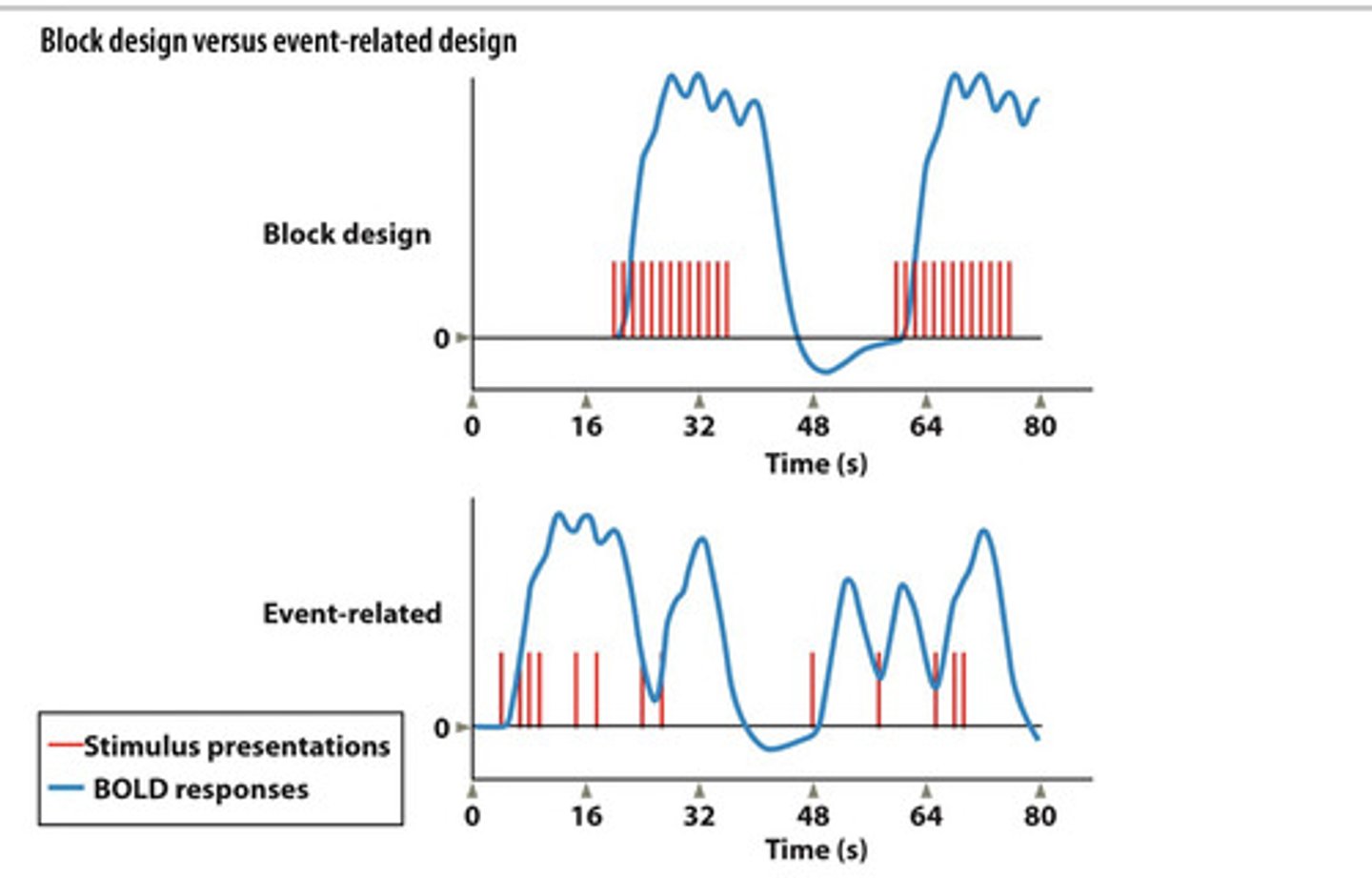
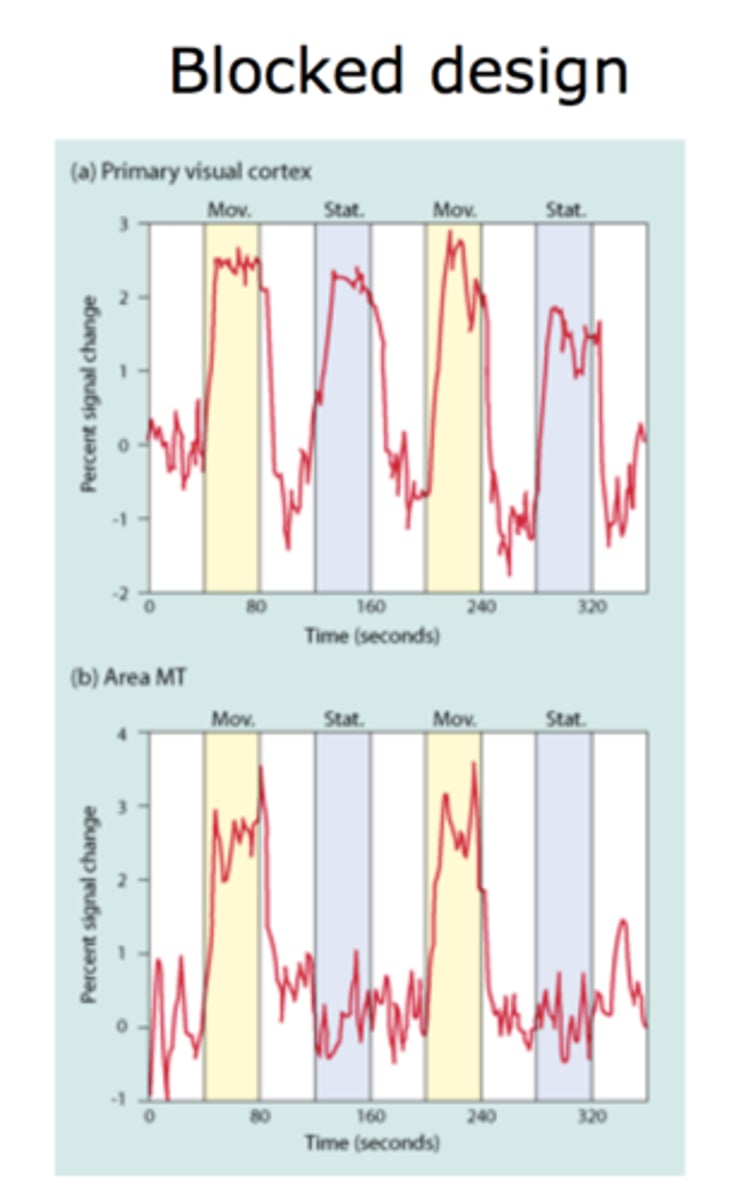
What is Block Design? (This won't be on midterm 1)
Stimuli are presented in blocks
*Example: moving vs static dots.
note how different areas (PV1 vs MT) BOLD signal changes in response to stimuli
What is Event Related Design? (This won't be on midterm 1)
Stimuli from two or more conditions are presented at various time points.
Pros:
- shows responses to individual events
- allows for more complex experimental designs
Cons:
-requires more trials