Breathing and Gas exchange
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is respiration?
chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy
Why do we need energy?
for life processes
active transport
cell division
protein synthesis
muscle contraction
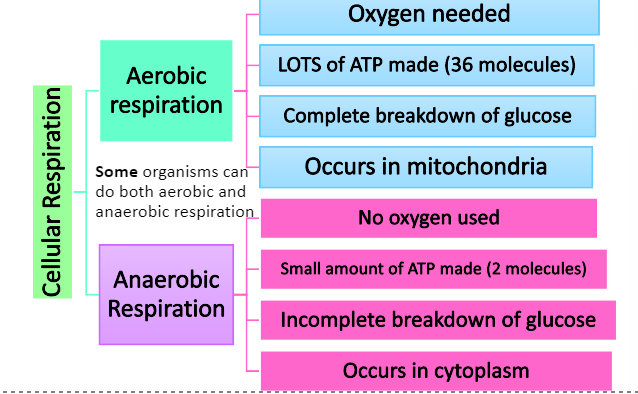
Where does respiration occur?
MITOCHONDRIA
release of energy from food
occurs in every living cell
in eukaryotic cells the main reactions occur in the mitochondria
What does respiration produce and where is it stored?
produces energy stored in glucose
stores it in ATP
Energy in ATP used by the cell to carry out all its activities
What are the products of respiration?
Carbon dioxide
limewater turns cloudy in presence of CO2
heat
its an exothermic reaction
rise in temperature
Water
energy
What is the equation for aerobic respiration
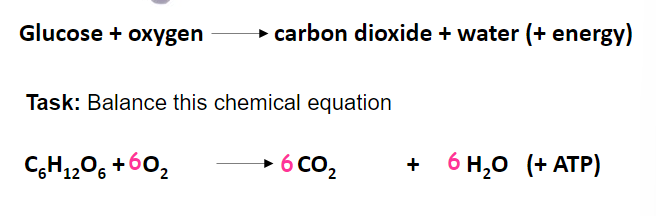
What are examples of anaerobic respiration?
yeast causes bread to rise
yeast producing ethanol in beer production
animals carrying out short bursts of exercise
plant roots in waterlogged soils
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration in animals

What are the disadvantages of anaerobic respiration?
less ATP is produced for every molecule of glucose
lactic acid is toxic + can result in fatigue and muscle cramps
Oxygen debt
after anaerobic respiration has taken place
lactic acid must be broken down
which requires extra oxygen
What is the anaerobic respiration equation in plants + yeast
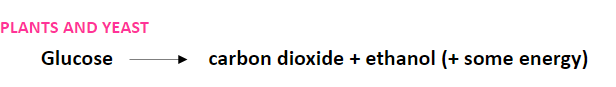
Compare aerobic + anaerobic respiration
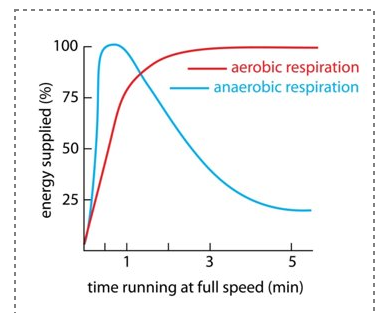
compare energy supplied for aerobic + anaerobic on a graph
How can CO2 be detected?
using limewater
turns cloudy in presence of CO2
using hydrogen carbonate indicator
changes color depending on level of CO2 in surrounding air
What is the scale of hydrogen carbonate indicator?
yellow = high level
red = normal/atmospheric levels
purple = low levels
what is a respirometer?
a setup which allows us to investigate respiration
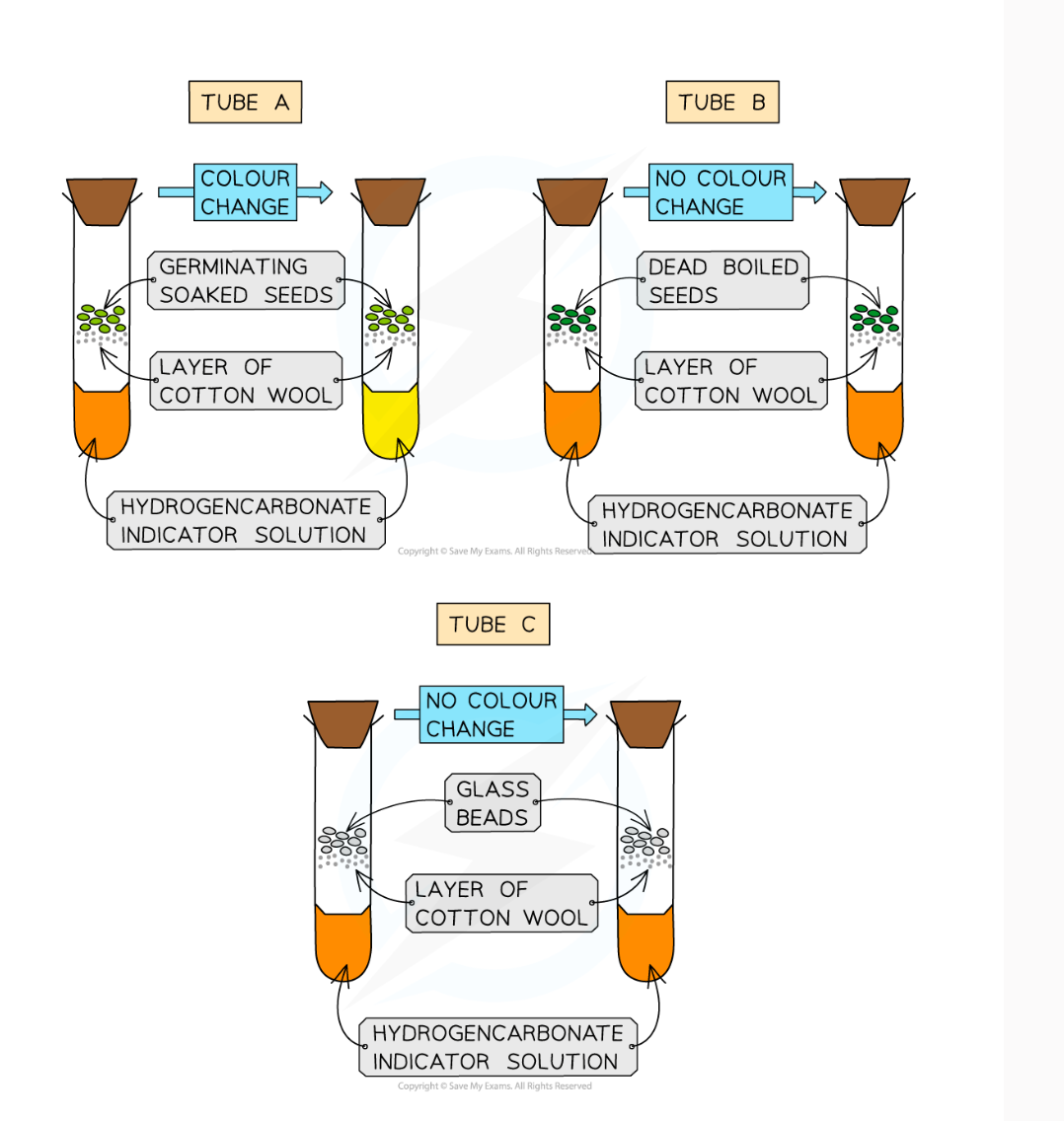
What is the method for investigating respiration
Measure out 10 cm3 of hydrogencarbonate indicator into 3 boiling tubes
Put in a layer of cotton wool
Place 10 germinating seeds in tube A
Place 10 boiled/dead seeds in tube B
Place 10 glass beads in tube C
Seal each tube with a rubber bung
After 3 hours, observe the colour of the indicator
What are the results?
What is breathing?
movement of gases in and out of the lungs
muscles are involved
aka ventilation
inhalation = breathing in
exhalation = breathing out
NOT respiration
What is the link between respiration + breathing?
organisms breathe to obtain oxygen so their cells can aerobically respire
Label
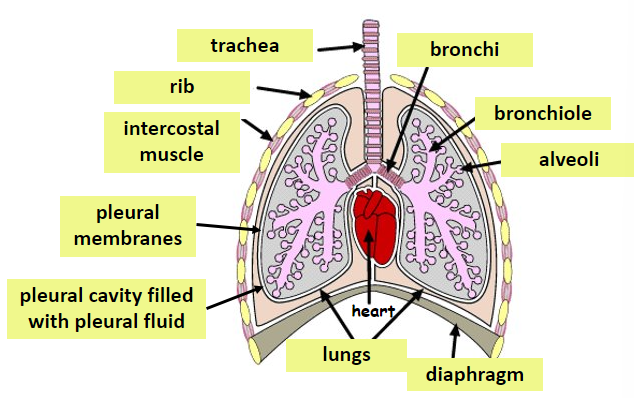
what is the purpose of alveoli?
air sacs where gas exchange occurs
what are bronchi?
2 tubes that trachea splits into
contains rings of cartilage to keep airways open while breathing
What are bronchioles?
smaller tubes bronchi split into
lead into alveoli
what is the diaphragm?
muscular sheet at bottom of the thorax
involved in ventilation
what are the intercostal muscles?
muscles used to move the ribs during ventilation
2 sets - internal + external
what is pleural membranes?
moist membranes between the inside of the thorax + lungs
provides lubrication to prevent the lungs from sticking
what are the ribs
bones that surround the lungs
act as protection + involved in ventilation
what is the trachea?
windpipe
passage of air from outside to inside
contains rings of cartilidge
what is the pleural fluid?
fills the gap between the pleural membranes (pleural cavity)
What is ventilation?
breathing in and
breathing out
involved:
internal + external intercostal muscles
diaphragm
What is the process of inhalation?
external intercostal muscles contract - moving ribs up + out
diaphragm contracts - flattens
increases volume of chest
decreases pressure below atmospheric pressure
air enters lungs
What is the process of exhalation?
external intercostal muscles relax
intercostal muscles contract - move ribs down + in
diaphragm relaxes - dome
decreases volume of chest
increases pressure below atmospheric pressure
air forced out of lungs
What is gas exchange?
process of oxygen + carbon dioxide moving between the lungs + the blood
oxygen - diffuses from air → blood
carbon dioxide - diffuses from blood → air
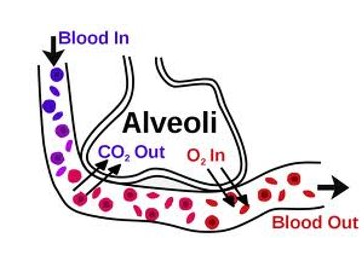
What is the process of gas exchange throughout the body?
oxygenated blood is picked up by RBC - oxygenated blood
oxygenated blood is pumped around the body to the cells in our tissues
cells of the tissues use the oxygen- blood is now deoxygenated
tissues produces waste carbon dioxide
carbon dioxide is removed from the blood in the lungs
why can small unicellular organisms such as bacteria simply diffuse resources?
small organisms have a large surface area to volume ratio
diffusion of resources such as oxygen is therefore very efficient
how do large multicellular organisms with small SA:V get sufficient resources such as oxygen?
large organisms with small SA:V need specialised exchange surfaces such as lungs to obtain the resources they need
where does gas exchange take place?
takes place in alveoli
oxygen diffuses into the blood + carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood
What makes alveoli efficient for gas exchange?
short diffusion path
one cell thick alveoli + one cell thick capillaries
surface across diffusion occurs is thing → rate is high
Large surface area
alveoli increase the surface area immensely
Large difference in concentration
maintained by breathing + a continuous blood flow
increase rate of diffusion
moist surface
moist surfaces allow gases to dissolve + diffuse across the wall more effectively
Many of them
large surface area
well ventilated
maintains large concentration gradient - increase rate of diffusion
why does breathing rate increase during exercise?
during exercise muscle cells respire more to produce ATP for muscle contraction
oxygen - must be delivered to them more quickly
waste carbon dioxide must be removed more quickly
achieved by increasing breathing rate
what is the method of effect of exercise on breathing rate?
Work out student A's breathing rate at rest
Count their number breaths for 15 seconds and multiply by 4
Repeat several times to calculate an average
Student A should then exercise for a set time (at least 4 minutes)
Immediately after exercising, count the breaths taken in 15 seconds and multiply by 4 to obtain the breathing rate per minute
Compare the result to the breathing rate at rest in order to work out the change in breathing rate as a result of exercise
Repeat this last step every minute after exercise for 5 minutes
Repeat the process for student B
Finally, repeat the whole investigation for each student after a period of rest
what are the results?
Frequency of breathing increases when exercising
This is because muscles are working harder and aerobically respiring more and they need more oxygen to be delivered to them (and carbon dioxide removed) to keep up with the energy demand
If they cannot meet the energy demand they will also respire anaerobically, producing lactic acid
After exercise has finished, the breathing rate remained elevated for a period of time
This is because the lactic acid that has built up in muscles needs to be removed as it lowers the pH of cells and can denature enzymes catalysing cell reactions
It can only be removed by combining it with oxygen - this is known as ‘repaying the oxygen debt’
This can be tested by seeing how long it takes after exercise for the breathing rate to return to normal
The longer it takes, the more lactic acid produced during exercise and the greater the oxygen debt that needs to be repaid
Why do people smoke?
it helps them think
it relieves stress
to break the ice when socialising
to calm down after a fight
to have a break from work
to pass time or relieve boredom
What is in cigarettes?
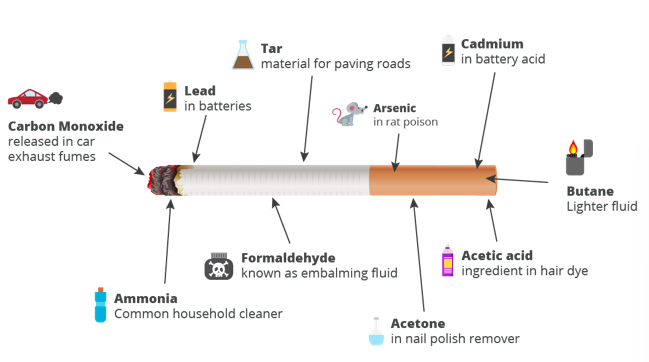
What is nicotine + its effect?
addictive drug
affects central nervous system
increases the heart rate + narrow blood vessels
causing high blood pressure
can lead to heart disease
What is carbon monoxide + its effect?
a poisonous gas that reduces the amount of oxygen that RBC carry around the body
combines with haemoglobin in RBC preenting oxygen from combining with it
also causes an increases in heart rate to compensate for the reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood
can lead to heart disease
What is cilia and mucus purpose?
cells in the lining of the respiratory tract
produce sticky mucus to trap dirt + microbes
cells with tiny hair like parts - cilia
normally move the mucus out of the lungs
What is tar + its effect?
brown sticky substance consisting of tiny particles
formed when tobacco smoke condenses
deposited in the lungs + coats the surface of the cilia - making them non-funcitonal
leads to build up of mucus with trapped pathogens
pathogens in warm + moist airways - leading to infection such as bronchitis
carcinogenic
causes cells to mutate + divide uncontrollably - leading to a tumour
what types of cancer does tar lead to?
lung
tongue
bladder
kidney
liver
How does smoking affect the skin?
premature aging + wrinkles
poor wound healing
how does smoking affect the respiratory system?
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
increased risk of viral + bacterial infection
increased risk of active tuberculosis
increased risk of asthma
how does smoking affect the cardiovascular system?
increased risk of heart failure + stroke
peripheral vascular disease
how does smoking affect the immune system?
weakens it
how does smoking affect the teeth?
gum disease
how does smoking affect reproduction?
infertility in men + women
paternal germline DNA mutation
increased risk of sexually transmitted diseases
how does smoking cause diabetes?
non-insulin dependent diabetes melitus
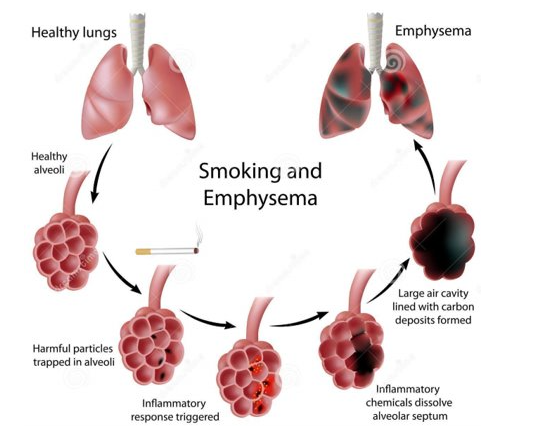
What is emphysema?
smoke damages the delicate alveoli
they lose elasticity
and the walls break down + fuse back togehter forming large irregular air spaces
this reduces surface area for gas exchange
gas exchange becomes very inefficient
sufferers struggle to carry out even light activities
How does smoking effect pregnancy?
underweight baby
heart defects
decrease lung function
brain function affected
death