new uworld incorrect
1/431
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
432 Terms
difficult conversations about prognosis should
express empathy using "wish and worry" framework
-avoid promoting false hope and offer constructive suggestions
in patients with peripheral artery disease "atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries" there is a risk of
thrombosis and acute on chronic limb ischemia which presents with mottling, coolness, prolonged capillary refill, paresis
simple renal cysts present as
thin, smooth, unilocular with no septae, asymptomatic require no follow up
->work up if features irregular walls, thickened septae, contrast enhanced, multilocular mass
as disease prevalence increases the NPV and PPV will
NPV decrease
PPV increase
AMS with COPD raise suspicion for
hypercapnic encephalopathy
->next step arterial blood gas due to prone CO2 retention
hypercapnia
excessive carbon dioxide in the blood
-presents with HA, somnolence, asterixis, profound CNS dysfunction
somatic symptom disorder involves
excessive anxiety and behaviors related to >1 symptom
-these pts have high health care use and undergo multiple tests with negative results
calcium stone reoccurrence from hypercalciuria tx with
increased fluid intake, dietary measures and if fails->add thiazide (increase renal Ca2+ absorption)
thiazide moa
increase calcium reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule and produce a relative hypovolemia that results in compensatory increase in sodium reabsorption
->decrease calcium urinary excretion!!!
-CALCIUM SPARING DIURETIC
cirrhosis of liver presentation
hypogonadism HPA dysfunction with elevated estradiol due to increased conversion from androgens
->ED, testicular atrophy, gynecomastia, low total T3/T4, weight loss
primary CNS lymphoma
AIDS defining malignancy associated with expression of EBV oncogenes
->MRI of brain shows solitary irregular nonhomogeneous ring enhancing mass
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
AIDs defining illness presents with confusion, lethargy, seizures
->brain imaging shows numerous Non enhancing lesions that do not cause mass effect
-reactivation of JC virus
EBV cancer associations
non Hodgkin lymphoma and primary CNS lymphoma
acute lymphoblastic leukemia(ALL) presents with
bruising, petechiae, bleeding due to impaired platelets production in bone marrow
-non tender lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly
hypospadias characterized by
ventrally displaced urethral opening and dorsal hooded foreskin
-failure of urethral folds to fuse
->needs urologic evaluation
open globe injury
laceration typically caused by small high velocity particles sent airborne
-may presents with peaked or teardrop pupil, asymmetric anterior chamber depth, loss of visual acuity, afferent pupillary response, reduced intraocular pressure
Sydenham chorea
a sequela of group A streptococcus(GAS) infection is the primary cause of chorea (abnormal, jerky movements that disappear during sleep) in children
-hypotonia and behavioral changes commonly seen
-work up: GAS testing with throat culture and Anti streptolysin O and Anti deoxyribonuclease(anti-DNAase) titers
->eval for RF with echo, ECG, inflamm markers
meconium ileus
inspissated stool causing obstruction at terminal ileum, strongly associated with CF
->fails to pass meconium within 24 hours, abd distention with or without perf, no stool in vault
->CF places pt at increased risk for chronic sinopulmonary disease
Meconium ileus is associated with which of the following disorders?
cystic fibrosis
Hirschsprung disease associated with
down syndrome
->increased rectal tone with squirt sign, stool in vault vs meconium ileus has no stool in vault
in clinical trials randomization is said to be successful when
a similarity of baseline characteristics of the patients in the treatment and placebo groups are seen
heat stroke
characterized by core temperature >104, with CNS dysfunction (ex: AMS), most commonly to those exposed in hot/humid environments while performing extreme activities
->complications include rhabdomyolysis, DIC, endo organ dysfunction
pts need to undergo pre0op CV risk assessments prior to noncardiac surgery ->6 risk predictors are
-high risk surgery(vascular, intrathoracic)
-ischemic heart disease
-hx of CHF
-hx of cerebrovascular disease9stroke or TIA)
-DM tx with insulin
-pre op Cr>2
low risk: 0-1 factor->no further eval
elevated risk >2 factors->further eval cardiac stress test
chronic osteomyelitis in setting of fracture can lead to
nonunion
->symptoms include intermittent pain and swelling and sinus tract formation
-must treat infection before fixing fracture or hardware will be infected!!!
->open bone biopsy is recommended for microbio assessment
->tx: surgical debridement of infected and necrotic bone
iron def anemia work up
GI blood loss m/c cause->endoscopy needed
->regardless of symptomatology work up with endoscopy do not need symptoms
still murmur
occurs in active, healthy children between 3-7 years old.
caused by vigorous expulsion of blood from left ventricle into aorta, increases with activity and diminishes when child is quiet.
->systolic vibratory murmur best heard of LLSB increasing in intensity when supine
carotid artery dissection or thrombus presents
with penetrating trauma (fall with object in mouth, neck manipulation)
->gradual onset hemiplegia, aphasia, neck pain, "thunderclap" HA
->can cause stroke which partial horner syndrome, unilateral HA and neck pain with cerebral ischemia
->dx: CT or MR angiography
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy physical exam shows
crescendo-decrescendo murmur that increases in intensity with decreased left ventricular blood volume, audible S4, brisk carotid pulses
->many patients have asymmetric hypertrophy of interventricular septum
aortic stenosis physical exam findings
crescendo-decrescendo murmur that decreases with Valsalva
-presents with S4, ejection click
-soft and delayed carotid pulses
secondary amyloidosis is a complication of a
chronic inflammatory condition (RA, psoriasis, IBD) resulting in extracellular tissue deposition of protein fibrils into tissues and organs
->pts develop multiorgan dysfunction (kidney, liver)
->tx; manage underlying disease
patients with burn injuries susceptible to
sepsis
->first sign acute enteral feeding intolerance
scleroderma renal crisis is characterized by
acute onset of HTN and AKI in patients with systemic sclerosis (thickened shiny skin)
->mainstay of treatment is ACE inhibitors which produce RAAs hyperactivity, improve renal function and normal BP
alcoholic cerebellar degeneration is
caused by damage to purkinje cells of cerebellar vermis
->manifests as slowly progressive onset of ambulation difficulties, wide based gait, postural instability, impaired truncal coordination (tandem gait) but limb coordination intact (finger to nose)
breast cyst management
Asymptomatic Simple
-Observe
Symptomatic (Tender) Simple
-FNA
--> Nonbloody or Bloody
->bloody needs biopsy
->nonbloddy and resolves no work up, if recurrent biopsy
Complex
-Biopsy
gastric cancer
common in those from eastern Asia/Europe, south america
->presents with progressive epigastric pain and weight loss
->iron def anemia
->metastasis to liver result in hepatomegaly, elevated transaminases, alkaline phosphatase
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) treatment
small clinically stable pts->observe and supplemental oxygen
->occurs inpatients without hx of lung disease and is m/c in tall thin men in early 20s
Parkinson tremor
-basal ganglia dysfunction
->resting pill rolling tremor that asymmetrically affects the hands
-improves with involuntary actions(reaching for something), worsens when patients are distracted(doing math) and is not impacted by caffeine or alcohol
amiodarone adr
causes thyroid dysfunction due to iodine content and effect on thyroid metabolism->impairs synthesis of thyroid hormone and decreases conversion of T4->T3
-hepatocellular injury
a lesion impacting medulla can cause
motor weakness with UMN signs and lower CN dysfunction (CN12)
->tongue deviation
neurosyphilis
early manifestations are meningitis with ischemic stroke, uveitis, optic neuritis, hearing loss
->rash that is symmetric maculopapular involving extremities(palms, soles) and trunk
meningovascular syphilis presents with
subacute meningeal manifestations(HA, N/V, dizziness, neck stiffness) followed by signs of ischemic stroke
->m/c MCA affected, arteriography shows focal segmental arterial narrowing
->dx: LP with CSF analysis showing +VDRL
the most specific diagnostic test in osteomyelitis is
bone biopsy and culture
cyanide is a lethal toxin released in
house fires, mining, sodium nitroprusside
->features: reddish skin, lactic acidosis, elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis, HA, confusion, HTN, tahcycardia
->tx: hydroxocobalmin
methemoglobinemia
a blood disorder in which an abnormal amount of methemoglobin, a form of hemoglobin, is produced
-can also be due to exposure to oxidizing agents(dapsone, nitrates, topical/local anesthetics)
-pts cyanotic/dusky colored skin that does not resolve with supplemental oxygen
diaper dermititis-irritant
skin breakdown from exposure to stool/urine
-m/c type, confined to area in diaper
->erythematous papules, plaques that spare skin folds(vs candida does not spare)
-tx: topical barrier
atopic dermatitis can lead to
infectious complications(impetigo)
-consider when topical corticosteroids for flare is ineffective
->impetigo presents with golden crusts weeping, purulence, tx: topical mupirocin
anogenital warts(condyloma acuminata) in children
HPV infection(direct genital contact)
->due to sexual abuse, prenatal or perinatal, autoinoculation from other sites
-features: pink/flesh colored, verrucous papules and plaques, asymptomatic, pruritic friable lesions
-tx: self resolving, if symptomatic surgery or topical podophyllotoxin
diagnostics for idiopathic intracranial HTN
Lumbar puncture: elevated opening pressure, after looking for mass lesion
MRI/CT: for mass lesions and hydrocephalus
MR venography rule out thrombosis
->tx: acetazolamide
Rocky mountain spotted fever presents
in 3-4 days with nonspecific fever, HA, myalgia, arthralgia, macular and petechial rash on wrist/ankle->palms/soles->then spread centrally
-Labs: low platelets, hyponatremia, increased AST/ALT
tx: empiric doxycycline while awaiting serology
SCFE
commonly seen in obese adolescents
->dull hip pain, referred knee pain, altered gait, limited internal rotation of hip
-tx: surgical pinning
iliopsoas bursitis
inflammation in bursa posterior to iliopsoas muscle due to overuse or trauma
->pt have hip pain and limited ROM, with palpable click with manipulation of the hip present
anterior cord syndrome
loss of most function below the site of injury to the anterior portion of the spinal cord, usually due to trauma
->characterized by b/l motor function loss at and below level of the injury with diminished pain and temperature and crude touch sensation b/l that begins 1-2 levels below injury
->bilateral loss motor, pain, temp, crude touch
->proprioception, vibratory sensation and light touch unaffected
anticholinergics can cause
acute urinary retention by preventing detrusor muscle contraction and urinary sphincter relaxation
->tx with urinary catheterization and d/c medication
-ex: amitriptyline(TCA)
hyperventilation syndrome presents with
acute onset of deep breathing and/or tachypnea often with neurologic symptoms(tingling, numbness)
-nl lung exam
-similar to panic disorders but panic attacks characterized by intense fear that does not always have to include respiratory symptoms
tx: reassurance with breathing training
in children with HIV notice
immunocompromised at higher CD4 T cell counts
->PJP is often initial AID defining illness presenting at 3-6 months
-manifests as low grade fever, tachypnea, poor feeding, progressive dyspnea
->tx: TMP-SMX with corticosteroids if PaO2<70 or A-a >35
risk factors for osteoarthritis
advanced age
female
family hx
abnormal joint alignment
prior joint trauma or surgery
Secondary causes: infection, inflamm, bony deformities, neuromuscular weakness
ankylosing spondylitis complications
Osteoporosis/vertebral fractures
Aortic regurgitation(laterally displaced PMI due to compensatory hypertrophy)
Cauda equina syndrome
cocaine associated chest pain should be tx with
IV benzodiazepines (diazepam)
->then treat with aspirin, nitroglycerine, calcium channels blockers
CI: beta blockers
myasthenic crisis
an acute exacerbation of myasthenia gravis caused by inadequate amount of meds, infection fatigue or stress.
->characterized by severe respiratory muscle weakness->respiratory failure
->tx: intubations, plasmapheresis, IVIG
m/c cause of nonreactive stress test
quiet fetal sleep cycle, no accelerations
-can last as long as 40 minutes, extend to ensure fetal activity outside of sleep is captures
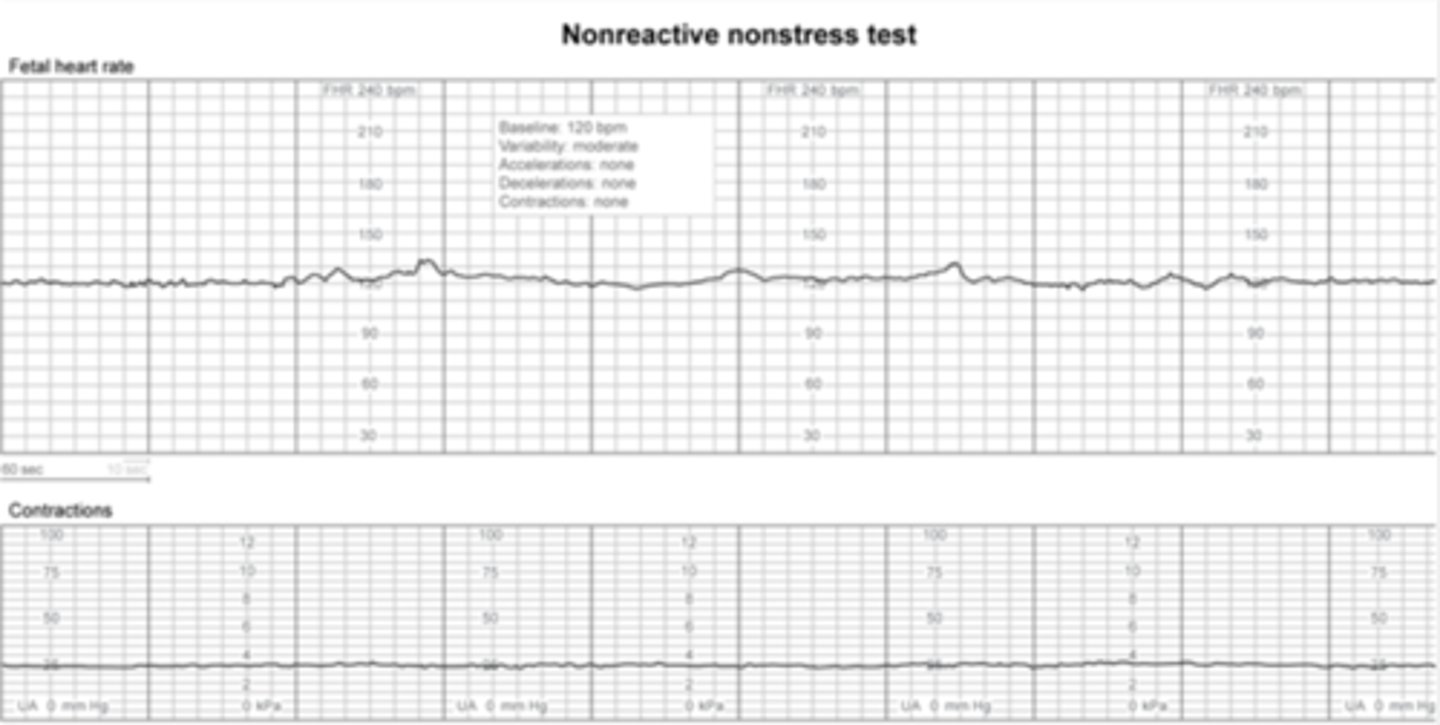
congenital fetal heart block on NST
fetal bradycardia (<110/min)
symmetric polyarticular arthritis with brief self limited course->
viral arthritis due m/c to parvo
-think with exposure to children
guillian barre syndrome is a
acute or subacute ascending flaccid paralysis
->CSF shows elevated protein level with normal cell count
->tx: IVIG, plasmapheresis
craniopharyngiomas are
benign suprasellar tumors that present with visual defects, HA, symptoms of pituitary hormonal deficiencies (mass effect, decreased libido due to hypogonadism)
-commonly occur in children age 5-14, with second peak in adults 50-75
generalized anxiety disorder characterized by
hx of feeling easily overwhelmed by anxiety and multiple worries accompanied by physical nonspecific symptoms
-commonly have perinatal GAD->tx: psychotherapy
acute vertebral compression fracture
caused by twisting, lifting, other minimal trauma and presents with back pain and vertebral point tenderness
->typically occurs in patients with osteoporosis and other conditions with decreased bone mineral density
-dx: plain x-ray of spine
complication of miliary Tb
primary adrenal insufficiency
-hypovolemia, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia
-combines with pulmonary airspace disease with lymphadenopathy prior residence in Tb endemic region
-infectious/tuberculosis adrenalitis is the second m/c caused or adrenal insufficiency
idiopathic intracranial HTN (pseudotumor cerebri)
m/c in obese women of childbearing age or are pregnant
->presents with headaches, pulsatile tinnitus, papilledema
-dx: MRI of brain followed by LP
initial treatment of choice in patients with persistent tachyarrhythmia causing hemodynamic instability is
immediate synchronized cardioversion
ex: A-fib with RVR
in patients with ventricular fibrillation of pulseless v-tachy treatment is
defibrillation
breast pain that is cyclical, b/l, diffuse->tx
reassurance and symptom management (supportive bra, NSAIDs)
inhibitor development
occurs in severe hemophilia patients with factor 8 deficiency
-consider in a patient bleeding refractory to replacement therapy or with increased bleeding frequency
suspect PE in any patients who presents with
sudden onset SOB and pleuritic CP
->commonly see tachycardia, hypoxemia, low grade fever, JVD
chemical pneumonitis:
look for patient who went under conscious sedation
-inhalation of gastric acid leads to direct chemical injury of bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells
-sudden onset within minutes to hour
-abrupt onset dyspnea, cough, hypoxemia
->tx: resolves spontaneously
effect modification
results when an extraneous variable(modifier) changes the direction or strength of an association between a risk factor and a disease
-a modifier is associated with the disease but not the RF
-distinguished from confounding by stratified analysis, will show significant difference in each strata while confounding will not
Chiari I malformation is characterized by
inferior displacement of cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum
->commonly associated with syringomyelia(cyst in spinal cord)
-occipital HA exacerbated by activity and Valsalva
complication of celiac disease
vit D deficiency->osteoporosis
-bone pain, muscle weakness, impaired ambulation
principles of prescribing in elderly
limit the number of prescribers
consider time to benefit for each drug
tailor regimen to patients goals and life expectency
myasthenia gravis presentation
fluctuating and fatigable proximal muscle weakness, worsens with activity, improves with rest
-ocular(diplopia, ptosis)
-bulbar(dysphagia, dysarthria)
-respiratory(myasethnic crisis)
tx: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors(pyridostigmine), thymectomy
ARP (attributable risk percent)=
(RR-1)/RR x 100
rectus abdominis diastasis
not a true hernia, not palpable while supine
pericardial effusion
accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity
->can be purulent from hematogenous or direct intrathoracic spread (staph)
-fevers, chills, CP
EKG: tachycardia, diffuse ST segment elevation, low voltage QRS complex
CXR: enlarged cardiac silhouette and clear lung fields
->dx via ECHO: pericardial effusion
but if purulent pericardiocentesis needed for dx and tx
hydrocephalus
suspect in young child or infant with rapidly enlarging head circumference crossing multiple growth percentiles
->signs of increased ICP see once anterior fontanelle closes, irritable, developmental delay, HTN/bradycardia, papilledema
patellofemoral pain syndrome
common cause of anterior knee pain in young women, seen in runners from chronic overuse or malalignment
-pain provoked by maneuvers that involve contraction of quadriceps with the knee in flexion
-tx: activity modification, NSAIDs, strengthening and stretching exercises(quads)
tuberous sclerosis
autosomal dominant
-ash leaf spots, periungual fibromas, shagreen patch, seizures, cardiac rhabdomyomas, renal angiomyolipoma's
vitreous hemorrhage
Sudden loss of vision with floaters, usually secondary to diabetic retinopathy
->hazy vision, red hue, vision loss, floaters with a decreased or absent red reflex
predictors of severe acute pancreatitis includes
SIRS criteria with elevated bun and hematocrit with intravascular volume depletion
->patients have increased risk of morbidity and mortality
=acute pancreatitis with organ failure persistent over 48 hours
unilateral lower extremity edema with hx of recurrent cellulitis->
chronic lymphedema
-since chronic now non pitting edema with firm thickened skin
pulmonary edema causes
hypoxemia due to R->L intrapulmonary shunting, an extreme V/Q mismatch
-when the edema is diffuse, alveolar ventilation is zero throughout much of the lungs and hypoxemia does not correct with supplemental O2
-with V/Q mismatch->increased A-a gradient
increased A-a gradient in
diffusion limitations, V/Q mismatch, large intrapulmonary shunt, large dead space ventilation
renal colic secondary to nephrolithiasis in preg will present as
presents with abdominal pain, flank tenderness, hematuria, irregular uterine contractions
dx: US
disseminated gonococcal infection presents as
purulent monoarthritic or triad of tenosynovitis, dermatitis, migratory polyarthralgia
CGD
recurrent cutaneous and pulmonary infections with catalase positive organisms(staph, Serratia)
-abnormal oxidative burst is consistent with diagnosis
-prophylaxis: TMP-SMX, itraconazole
posterior hip dislocation:
commonly occurs in head on MVA
-leg appears shortened and IR, hip held in flexion and adduction
m/c than anterior
-also in SCFE
tibial stress fractures
Overuse injuries that seem like shin splints except that the pain is in a specific location. (point tenderness)
-common in athletes or others who increase activity level
antiphospholipid antibody syndrome should be suspect
patients with still birth and multiple prior pregnancy loss
-stillbirth from uteroplacental artery thrombosis which leads to uteroplacental insufficiency and asymmetric growth restriction
ulnar injury at elbow presents as
numbness in medial hand, decreased grip strength, weaker wrist flexion
->if at wrist just numbness and paresthesia
ventilator associated pneumonia
suspect when intubated patient develops new pulmonary infiltrates on chest x-ray, worsened respiratory status(increased oxygen requirement), clinical signs of infection
hypokalemic, hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis
in patients with NG suctioning, vomiting, loop or thiazide diuretic use
->tx: saline to correct alkalosis
medication induced hyperkalemia with
ACE/ARBs
NSAID
amiloride, spirinolactone
heparin
TMP
cyclosporine
digoxin
succinylcholine