ANSCI 201--Meat
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
:(
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
What are the types of red meat?
Beef, pork, veal, lamb/mutton, horse

What is the leading meat produced in the world?
Chicken (140 million tons/year)
Which muscle type makes up the walls of the digestive tract and capillaries?
Smooth
Which muscle type makes up the heart?
Involuntary striated
Which muscle type has alternating dark and white bands?
Voluntary striated (skeletal)

Which muscle type is meat?
Skeletal
What are the structural units of muscle?
Myofibers
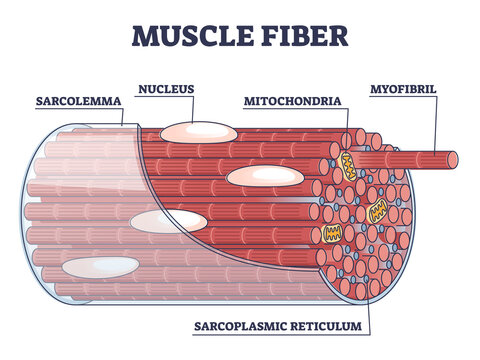
What is the excitable outer cell membrane of muscle cells?
Sarcolemma
How many nuclei do voluntary striated muscles have?
Multiple
How many nuclei do smooth and involuntary striated muscles have?
One
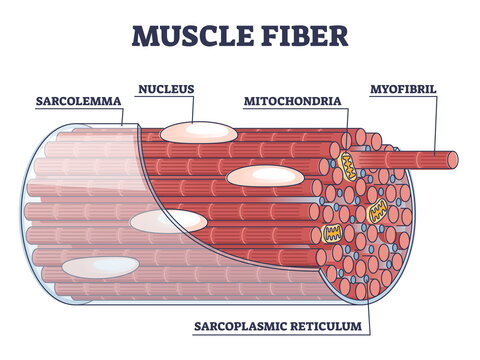
What are the long fibers of contractile filaments in myofibers?
Myofibrils
What is the liquid portion of a muscle cell?
Sarcoplasm
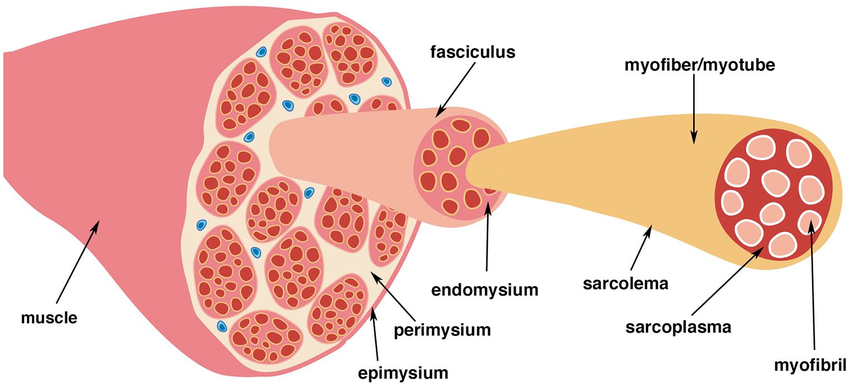
What is the thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds each muscle cell?
Endomysium

What is the layer that wraps around several muscle cells and forms a bundle?
Perimysium
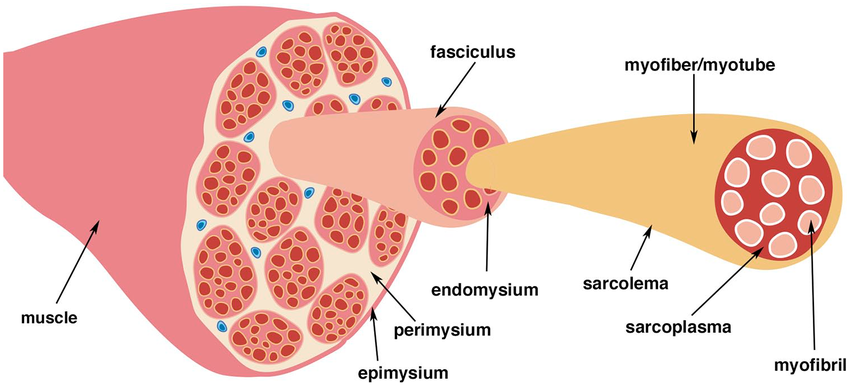
What is the layer that surrounds the entire muscle?
Epimysium
What is the smallest functional contracticle unit of muscles?
Sarcomere
Where are sarcomeres located?
Between two Z bands
What are the two types of myofibrils?
Actin and myosin

What is the function of myofibrils?
Permit each cell to do work
Which myofibril is the thin/light band?
Actin
Which myofibril is the thick/dark band?
Myosin
According to the sliding filament theory, muscle contraction is regulated by the concentration of which ion?
Calcium
Where is calcium held in muscles?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounding muscles
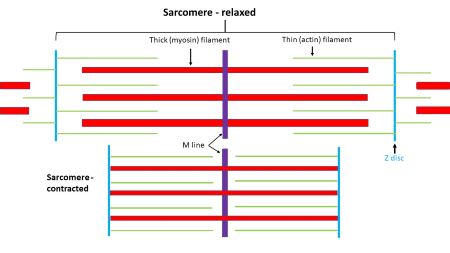
During muscle contraction, what shortens? What stays the same length?
Sarcomere shortens
Actin/myosin stay the same length

What is the role of ATP during relaxation?
Keeps actin and myosin separated

What is the role of ATP during contraction?
Provide energy

Do anaeorbic or aerobic reactions produce more energy?
Aerobic
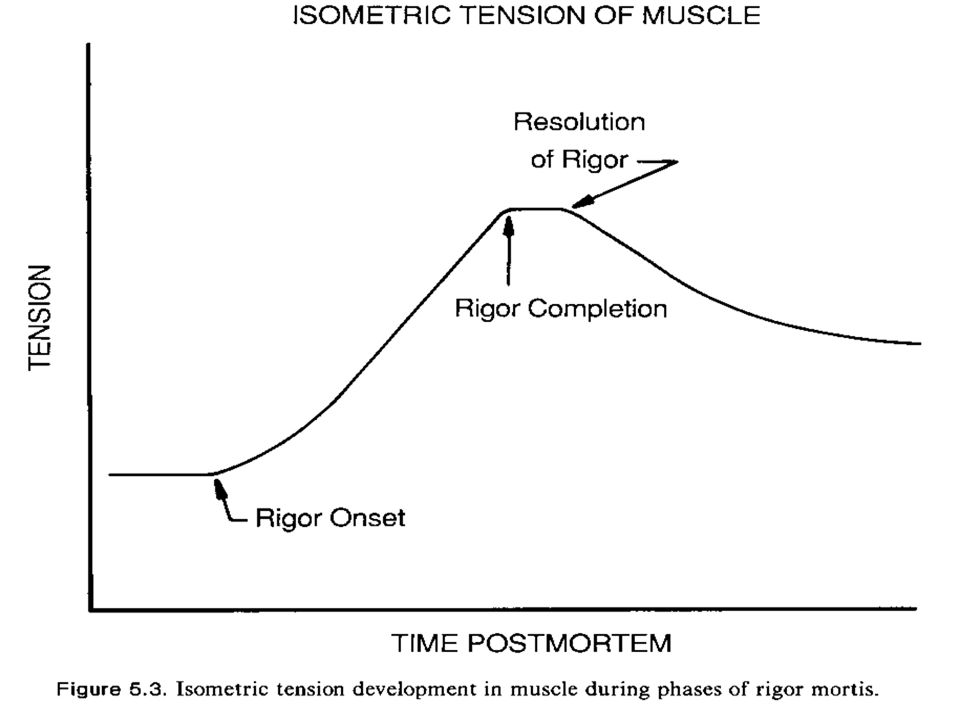
During what phase of the rigor curve is the muscle most relaxed and tender?
Rigor onset
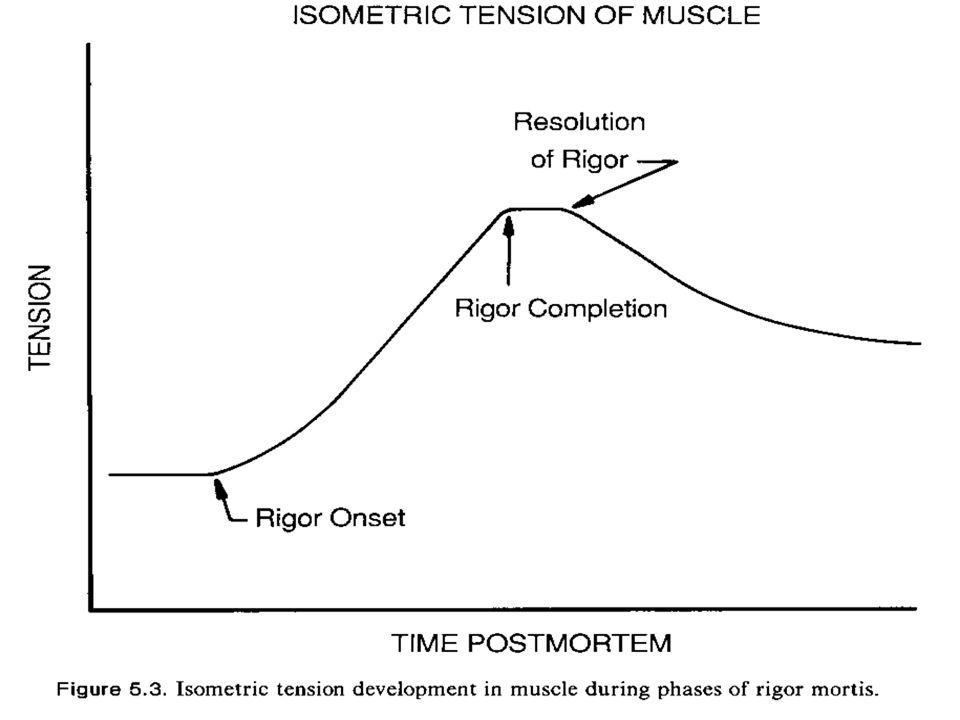
During what phase of the rigor curve is the muscle most contracted and tough?
Rigor completion
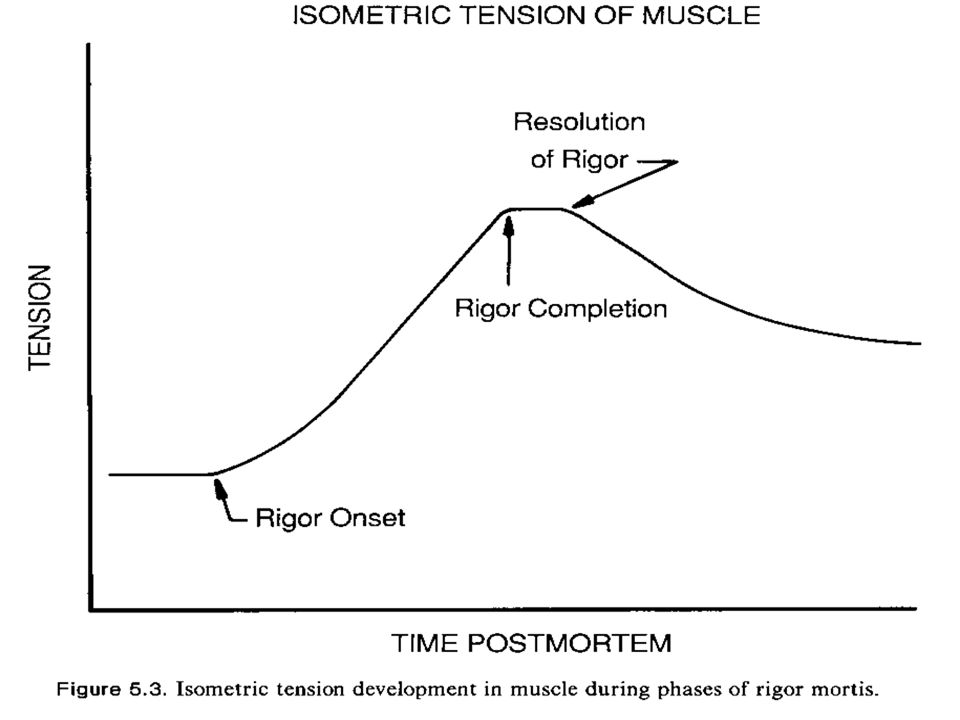
During what phase of the rigor curve is the muscle tender due to enzymes breaking down the protein?
Resolution
What is the stiffening of the carcass by intense shortening of muscle fibers?
Rigor mortis
What is the self breakdown of muscles during rigor resolution?
Autolysis

Which enzymes contribute to autolysis?
Cathepsins and calpains
At which pH does autolysis occur?
5.6
What causes the low pH of autolysis?
Buildup of lactic acid
What activates the cathepsins and calpains of rigor resolution?
Low pH

Why is old meat watery?
Water binding capacity drops as pH drops
Meat can be aged for 7-14 days at what temp?
35°F
Meat can be aged for 2-3 days at what temp plus UV lights?
60-68°F

Meat can be aged with what enzyme?
Papain

What is the meat aging method where meat is retained in its own fluid?
Wet aging
Meat is what % water?
75%

Meat is what % protein?
19%
Meat is what % lipids?
4%

Meat is what % carbs?
1%
Meat is what % minerals?
1%
Fatty acids of which animals reflect their diet?
Monogastrics
Fatty acids of which animals are uniform?
Ruminants
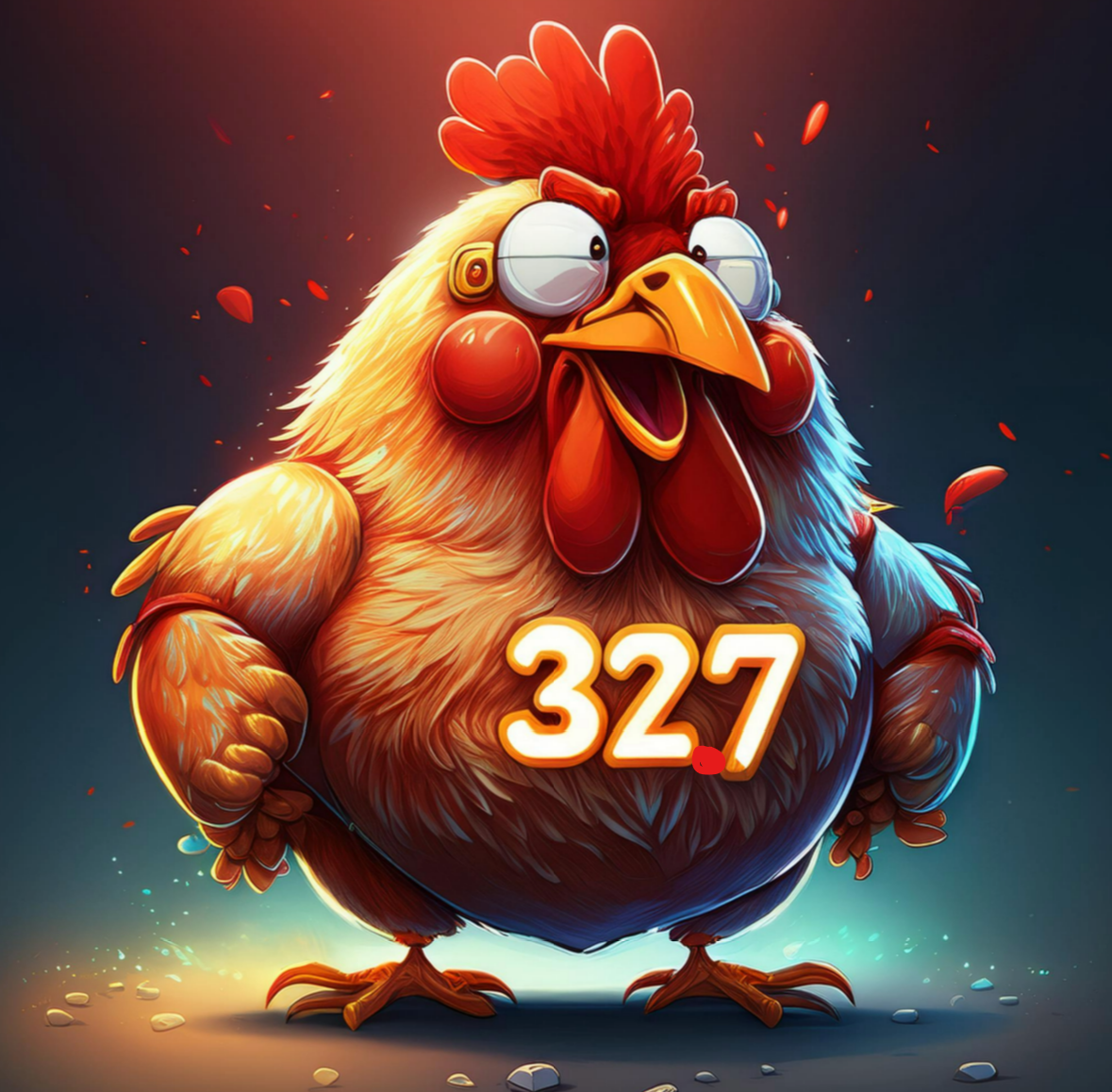
Chicken fatty acids are what % saturated?
32.7%

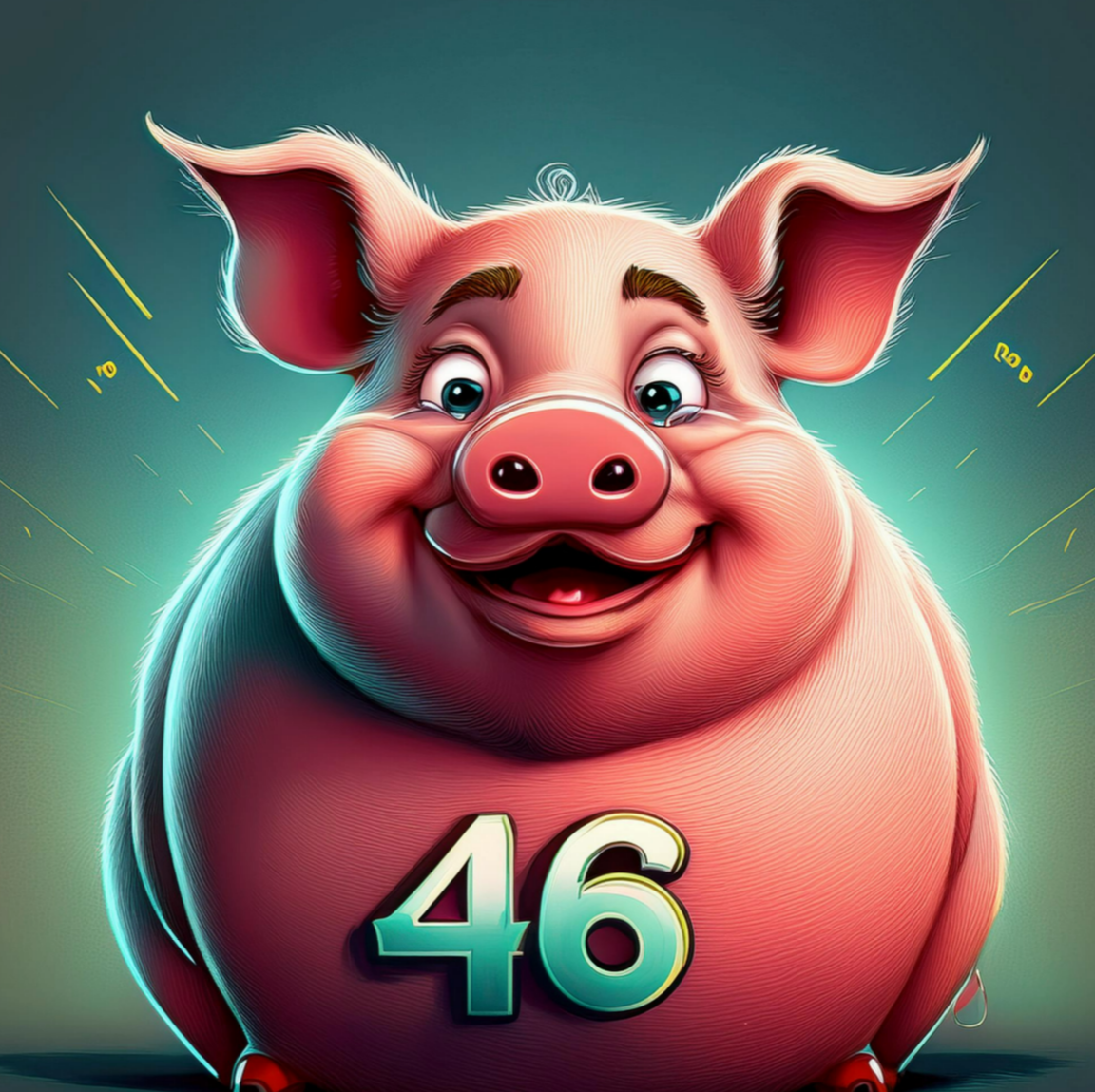
Pig fatty acids are what % saturated?
46.0%

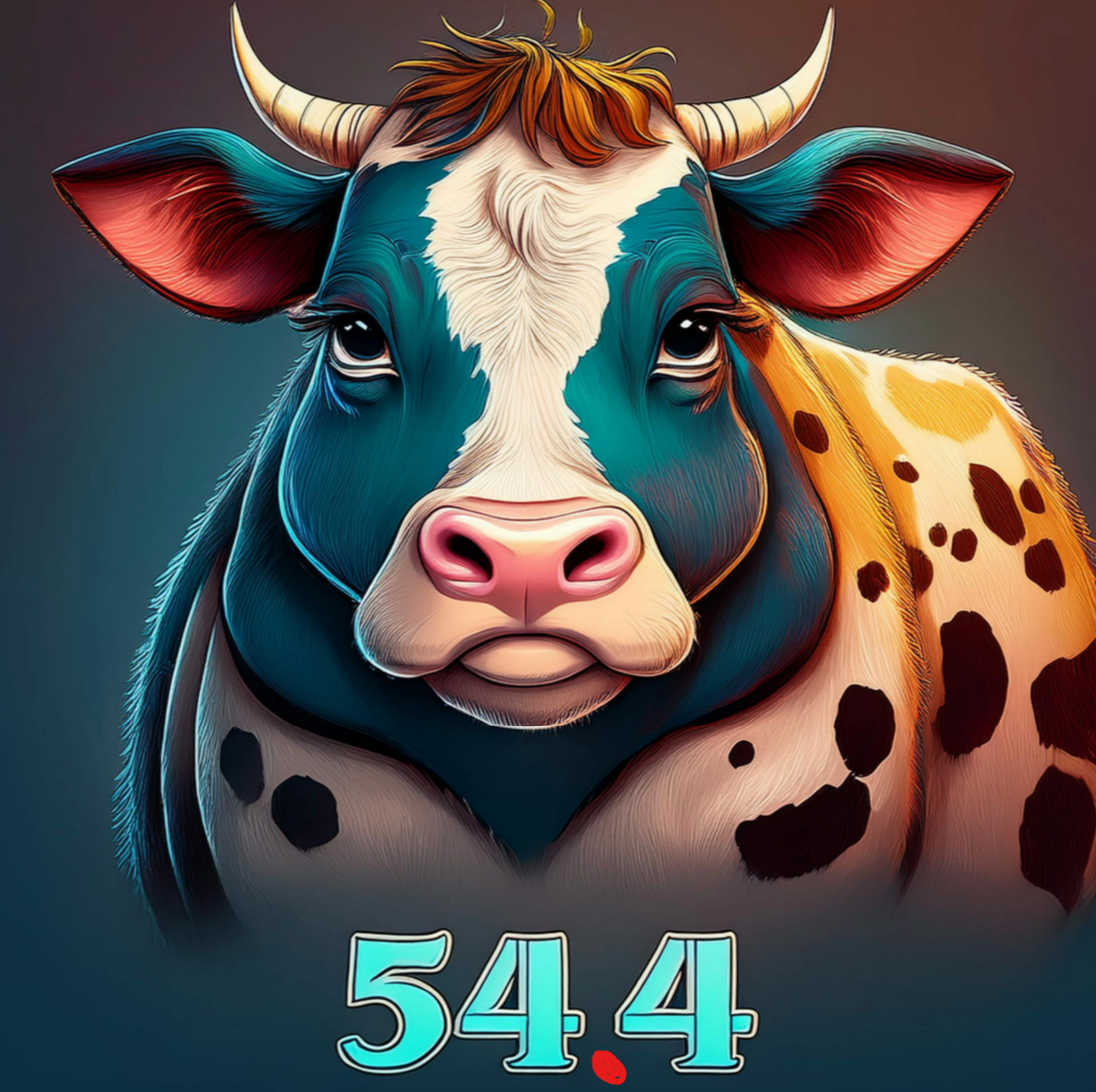
Cattle fatty acids are what % saturated?
54.4%

Shoop fatty acids are what % saturated?
58.6%


What unsaturated fatty acid makes up the highest % in all meat?
Oleic
Meat protein ranks in which place for nutritional value?
Third
Are different types of meat more nutritious than others?
No
What is the major protein in meat?
Actomyosin
What protein transports oxygen and carbon dioxide within muscle tissue?
Myoglobin
What are the three inedible meat proteins (connective tissue)?
Collagen, elastin, keratin
What is the major carb in meat before rigor mortis?
Glycogen
What is the major carb in meat after rigor mortis?
Lactic acid
What are the four vitamins in meat?
B12
Niacin
Riboflavin
B6
Which meat is high in vitamin B12?
Beef
Which meat is high in thiamine?
Pork
What are the minerals present in meat?
Fe, Zn, K, S, Na, Cl, Mg, Ca, P

Which meat minerals are present in bone?
Mg, Ca, P

Used muscles produce ________ myoglobin, so they are ________ in color.
More; darker

Unused muscles produce ________ myoglobin, so they are ________ in color.
Less; lighter
As the pH of meat increases, what happens to the color of meat?
Darkens
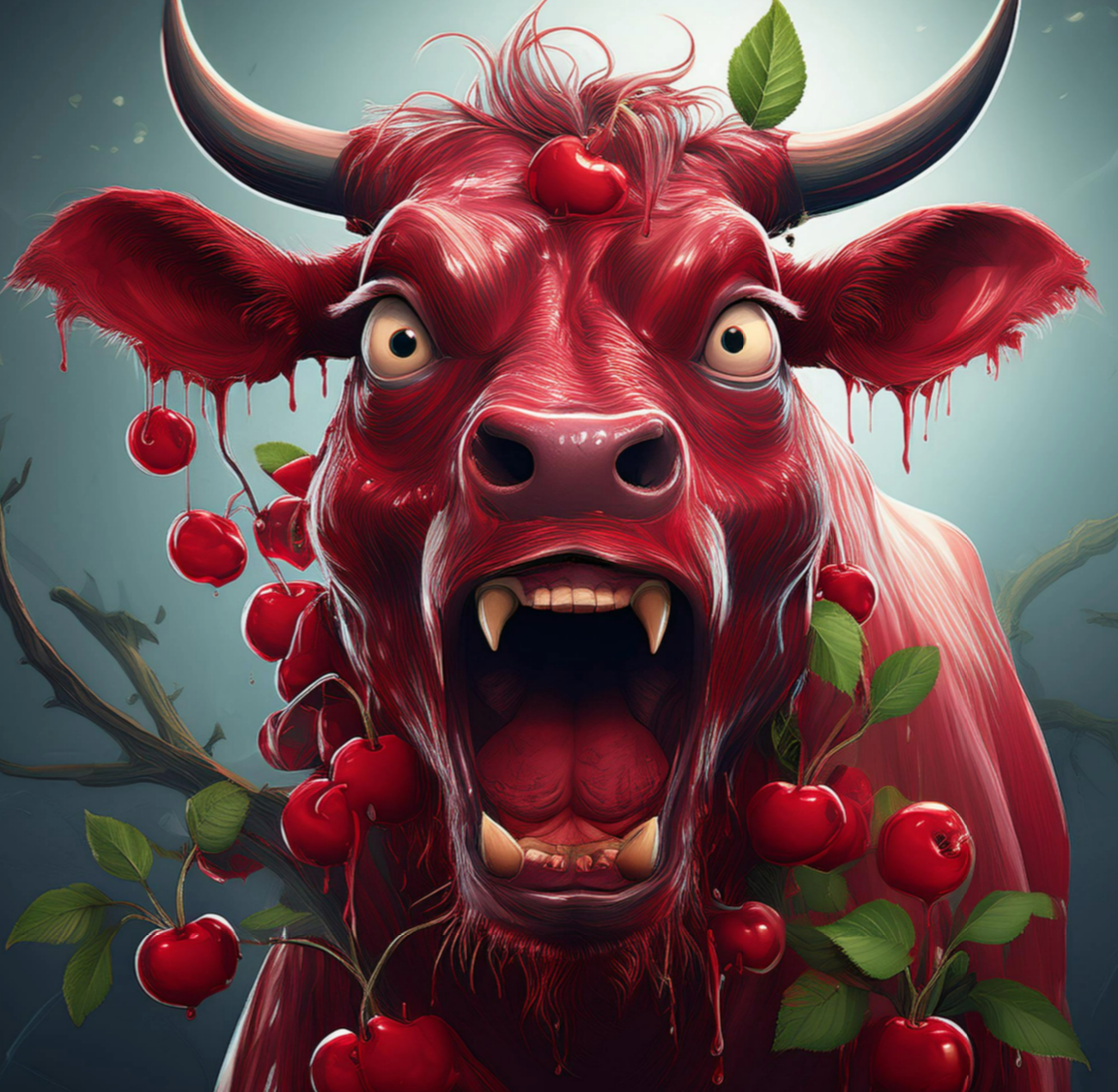

What is the desirable color of beef?
Bright cherry red

What is the desirable color of pork?
Grayish pink

What is the desirable color of muton?
Light pink
What is the desirable color of veal?
Pinkish brown

What is the desirable color of poultry?
Yellowish
Volatile compounds that contribute to meat’s flavor are liberated by what?
Heating
Do water or fat soluble compounds have more effect on meat’s flavor?
Fat
What is the wetness produced by release of meat fluids?
Juiciness
What is the #1 palatability factor for meat?
Tenderness
Does more or less marbling produce a juicier meat?
More
What is the measurement of how easily meat can be cut or chewed (or resistance to shear force)?
Tenderness
More connective tissue makes for ________ tender meat.
Less
Myofibrils become __________ (tougher/softer) with heat, so we should cook them __________ (slowly/quickly).
Tougher; quickly
Connective tissue becomes __________ (tougher/softer) with heat, so we should cook them __________ (slowly/quickly).
Softer; slowly

How does tenderness change as an animal ages?
Decreases
Are small or large fibers more tender?
Small
Is tenderness heritable?
Yes
Hormal balance in meat has more effect in _______ (young/old) animals.
Old
Less stress during slaughter is good for meat quality because it allows for the storage of what chemical?
Glycogen
Aging generally improves tenderness, but for monogastrics, it may cause what flavor due to increased unsaturated fatty acids?
Oxidized
What effect does electrical stimulation have on meat quality?
Makes rigor more uniform by contracting muscles at the same time
What is the term for the amount of meat we get from an animal?
Dressing percentage
What is the formula for dressing percentage?
carcass weight/live weight x 100
Which animal has the highest dressing percentage?
Swine
What is the dressing % for sheep?
50%
What is the dressing % for cattle?
60%
What is the dressing % for swine?
72%
Which 1967 act made it so that every slaughtered animal must be inspected?
Wholesome Meat Act
Which federal organization conducts meat inspections?
Food Safety and Inspection Servivce (FSIS)
Who pays for meat grading?
Meat packers
Which federal organization regulates meat grades?
USDA
What are the four quality grades for beef?
Prime, choice, select, standard