Tooth Anatomy
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
maxilla
upper jaw
made up of many bones
mandible
lower jaw
connected to maxilla by the temporomandibular joint TMJ
roof of the mouth consists of what
hard and soft palate
pulp
located at center of tooth, consists of connective tissue, nerves and blood vessels
most of these nerves and blood vessels enter through the apex
cells lining the pulp are called odontoblasts which form dentin
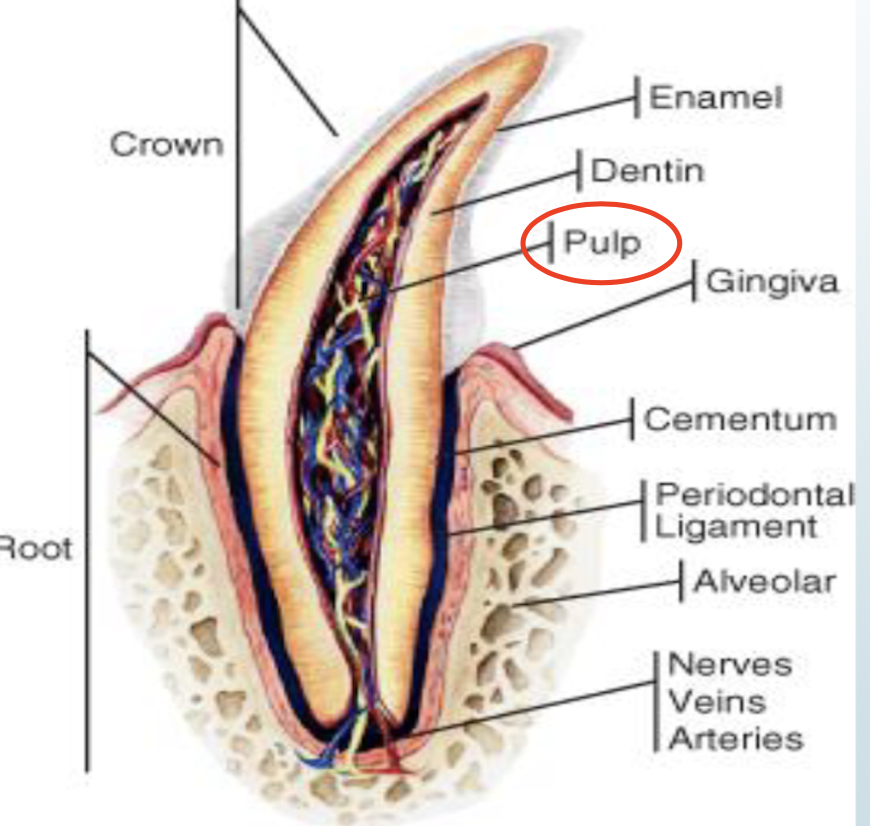
dentin
bulk of the tooth
surrounds the pulp
hard as bone, softer than enamel
can detect heat, touch, and cold
what is the difference between primary and secondary dentin
primary: formed before tooth eruption
secondary: continually formed throughout the life of the tooth
what happens to the pulp chamber as the secondary dentin forms
it reduces in size
what is the dentin of the crown encased in
enamel
what is the dentin of the root covered by
cementum
what is enamel
hardest tissue
formed before tooth eruption
susceptible to chipping
what happens to the enamel just before a tooth erupts through the gums
the formation of enamel stops is lost gradually over the life of the tooth
what is the alveolar bone
forms the jaw and the sockets into which the roots of the teeth extend
what are periodontal ligaments
tough tissue that helps hold the tooth in the socket
attaches to the cementum of the tooth and alveolar bone
what is gingiva
the gums
covers rest of the peridontum
directed attached to the tooth which is why it can withstand the forces of chewing
what is the sulcus
the area between the free gingiva and the tooth
what is a pocket
the space between the free gingiva and the tooth
lateral canal
very small channel that connects the root pulp to the periodontal tissue through which small blood vessels run
what is cementum
hard calcified tissue that covers the dentin of the root
slowly foirmed throughout the life of the tooth
assists in supporting the tooth in the jaw and in root repair
coronal
towards the crown
apical
towards the apex
buccal
towards the cheek
labial
towards the lips
lingual
towards the tongue
palatal
towards the palate
mesial
towards midline
distal
away from midlines
supragingival
above gingiva
subgingival
below gingiva