HRM Exam #1 (Ch 1-3)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
human resource management
the process of managing human talent to achieve an org’s objective
involves a wide variety of activities including:
analyzing a company’s competitive environment
designing jobs and teams
human capital
the knowledge, skills, and capabilities of individuals who have economic value to an org (KSAOs)
it is intangible
managers need to develop knowledge, skills, experiences
organizational culture
the shared values, beliefs, and assumptions ppl in an org have
affects how ppl in an org work and treat each other and their customers
negative culture: stifles employees and leads to lower productivity and morale
positive culture: helps employees acquire knowledge and skills; allows employees to grow and thrive
human capital and organizational culture chart
strategic planning
procedures for making decisions about the org’s long-term goals and strategies
human resource planning (HRP)
process of anticipating and providing for the movement of people into, within, and out of an org
strategic human resource management
human resources deployments and activities that enable an org to achieve its strategic goals
step 1
mission, vision, values
mission
basic purpose of the org as well as its scope of operations
strategic vision
statement about where the company is going and what it intends to become in the future
compared to mission, the vision ideally clarifies the long-term direction of the company and its strategic intent
core values
strong and enduring beliefs and principles that guide a firm’s decisions and are the foundation of its corporate culture
forecasting
three factors seem to have influenced the growth of EEO legislation
changing attitudes toward employment discrimination
published reports highlighting the economic problems and injustices experienced by underrepresented workers
growing body of disparate discrimination laws and regulations at diff levels of gov that legislators feel should be standardized
it is illegal to discriminate in any aspect of employment, including:
hiring and firing
compensation, assignment, or classification of employees
transfer promotion, layoff, or recall
job advertisements
recruitment
testing
use of company facilities
training and apprenticeship programs
fringe benefits
pay, retirement plans, and disability leave
other terms and conditions of employment
discriminatory practices under these laws also include:
harassment on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, disability, genetic info, or age
retaliation against an individual for filing a change of discrimination, participating in an investigation, or opposing discriminatory practices
employment decisions based on stereotypes, or assumptions about the abilities, traits, or performance of individuals of a certain sex, race, age, religion, or ethnic group, or individuals with disabilities, or based on myths or assumptions about an individual’s genetic info
denying employment opportunities to a person bc of marriage to, or assoc w, an individual or a particular race, religion, nation origin, or individual w a disability. Title 7 also prohibits discrimination bc of participation in schools or places of worship assoc w a particular racial, ethnic, or religious group
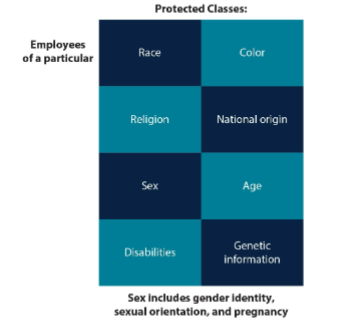
protected classes
individuals of underrepresented races, women, older people, and individuals with disabilities who are covered by federal laws on equal employment opportunity
Civil Rights Act of 1964
landmark law that addresses discrimination in society
Title VII of the act specifically bars employment discrimination in all HR activities
created the EEOC to administer the law and thereby promote equal employment opportunity
sexual harassment
unwelcome advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature in the working environment
EEOC recognizes two forms of sexual harassment as illegal under Title VII
quid pro quo
hostile environment
quid pro quo
submission to or rejection of sexual conduct is used as a basis for employment decisions
hostile environment
unwelcome sexual conduct “unreasonably interfer[es] with an individual’s work performance” or creates an “intimidating, hostile, or offensive working environment”
EEOC considers an employer guilty of sexual harassment when
they know or should have known about the unlawful conduct and failed to remedy it or to take corrective action
they allow nonemployees (customers or salespeople) to sexually harass employees
#MeToo
uniform guidelines on employee selection procedures
a procedural document published in the Federal Register to help employers comply w federal regulations against discriminatory actions
validity
employers must be able to prove that the selection instrument bears a direct relationship to success on the job
adverse impact
a concept that refers to the rejection of a significantly higher percentage of a protected class for employment, placement, or promotion when compared with the successful, nonprotected class
disparate treatment
a situation in which protected class members receive unequal treatment or are evaluated by diff standards
charge form
a discrimination complaint filed w the EEOC by employees or job applicants
must be filed w in 180 days of the alleged unlawful practice occurring
notifies the employer that a charge has been filed
retaliation
managers must not retaliate against individuals who invoke their legal rights to file charges or to support other employees during EEOC proceedings
can include any punitive action taken against employees who elect to exercise their legal rights before any EEO agency
affirmative action
a policy that goes beyond EEO by requiring orgs to comply w the law and correct any past discriminatory practices by increasing the #s of underrepresented groups in specific positions
specifically, employers must:
provide an org profile that graphically illustrates their workforce demographics
establish goals and timetables for employee of underutilized protected classes
linking strategic planning and human resources
step 1: mission, vision, and values
step 2: external analysis
step 3: internal analysis
step 4: formulating a strategy
step 5: executing a firm’s strategy
step 6: evaluation
quantitative approaches
forecasting approaches involve the use of statistical or mathematical techniques
trend analysis: forecasting labor demand based on a factor, such as sales
more advanced methods combine several factors, such as interest rates, gross domestic product, the disposable income of consumers, and sales
qualitative approaches
management forecasts: the opinions (judgments) of supervisors, department managers, experts, or others knowledgeable about the org’s future employment needs
delphi technique: decreases the subjectivity by soliciting and summarizing the judgments of a preselected group of individuals
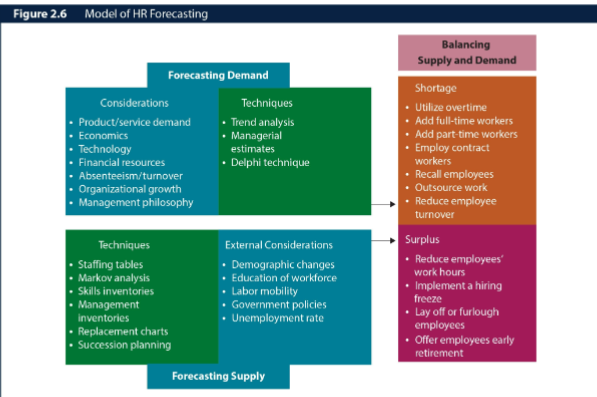
forecasting a firm’s demand for employees
quantitative approach
qualitative approach
forecasting the supply of employees
staffing table: shows a firm’s jobs, along w the #s of employees currently occupying those jobs and future of employment requirements
Markov analysis: tracks the pattern of employee movements through various jobs in a firm
Quality of fill: measures how well new hires who fill positions are performing on the job
skill inventories: files of personnel education, experience, interests, skills, and so on that allow managers to quickly match job openings w employee backgrounds
management inventories: when data are gathered on managers
replacement charts: listings of current jobholders and ppl who are potential replacements if an opening occurs
succession planning: process of identifying, developing, and tracking key individuals for executive positions
talent reviews: strategic meetings to determine if a company has the HR it needs to compete in the future
Bona Fide Occupational Qualification (BFOQ)
suitable defense against a discrimination charge only when age, religion, sex, or national origin is an actual qualification for performing the job
business necessity: work-related practice that is necessary to the safe and efficient operation of an org
religious preference
employers need only make a reasonable accommodation for a current employee’s or job applicant’s religious observance or practice without incurring undue hardship in the conduct of the business
reasonable accommodation
attempt by employers to adjust, without undue hardship, the working conditions or schedules of employees w disabilities or religious preferences
amendments to the ADA:
broadened definition of what constitutes a disability
made it less likely that a person will be denied protection bc their condition doesn’t seem severe enough or bc the person’s symptoms are minimized by drugs, prosthetic devices, and so forth
emerging employment discrimination issues
weight discrimination
attractiveness and discrimination
natural hair discrimination
caregivers and discrimination
SWOT analysis
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
a simple way to summarize the major facts and forecasts derived from external and internal analyses
environmental scanning
systematic monitoring of the major external forces influencing the org
includes forces in the business environment and the competitive environment
business environment
factors in the external environment that a firm cannot directly control but that can affect its strategy and performance
firms can only adapt to these changes rather than influence them
economic changes
during good economic times, firms can more easily expand; during bad times, they often contract
ecological changes
conditions in the natural environment like climate change, wildfires, etc
technological changes
while some firms adapt their strategies to take advantage of technological changes like the internet, others are slower to react and may fall victim to the change and faster-moving competitors
demographic and social changes
changes in the labor supply can limit the strategies available to firms and societal attitudes are constantly changing the business landscape for firms in all industries
legal and regulatory changes
any one change in laws and admin rulings can require firms and entire industries to dramatically adjust their strategic directions
competitive environment
a firm’s specific industry, including:
customers
rival firms
new entrants
substitutes
suppliers
stakeholders
benchmarking
the process of reviewing your practices and performance in a given area and comparing them w those of other companies
the HR benchmarks, or metrics, a firm collects fall into two basic categories:
human capital metrics assess aspects of the workforce
HR metrics assess the performance of the HR function itself
HR managers can’t simply rely on the benchmarks and strategies of other firms but instead must develop their own
internal analysis
core capabilities: integrated knowledge sets w in an org that distinguish it from its competitors and that deliver value to customers (processes, systems, ppl)
value creation: what a firm adds to a product or service by virtue of their making it; the amount of benefits provided by the product or service once the costs of making it are subtracted
cultural audits
sustaining a competitive advantage through ppl
orgs can achieve a sustained competitive advantage if their resources meet the following criteria:
the resources must be valuable
the resources must be rare
the resources must be difficult to imitate
the resources must be organized
types of talent and their composition in the workforce
strategic knowledge workers
core employees
supporting workers
complementary (external) partners
formulating a strategy
growth and diversification
mergers and acquisitions
strategic alliances and joint ventures
low cost
differentiation