Dental Anatomy: Tooth Forms, Occlusion, and Jaw Movements
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
mamelons
round eminences at the terminations of each labial lobe incisally
Haplodont class - single cone
Triconodont class - three cusps in line
Tritubercular class - three cusps in triangle
Quadritubercular class - four cusps in quadrangle
four phylogenetic classes of tooth forms
jaw movements and functions are governed by the forms of the teeth
jaw movements in relation to tooth forms
tubercle
an accessory projection of enamel, often considered an extra lobe
significance of the trapezoidal outline of a tooth crown
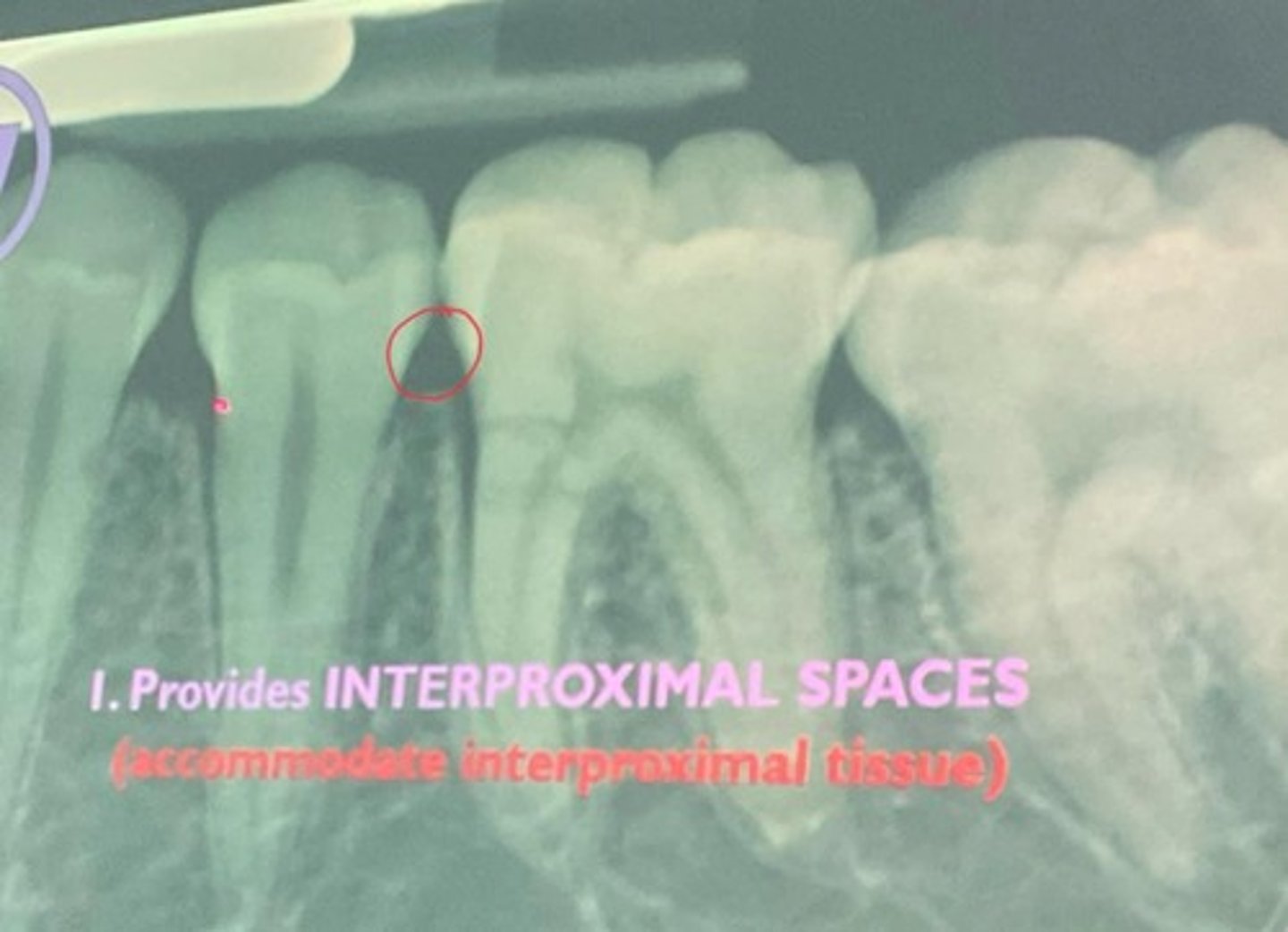
protects the periodontium, provides interproximal spaces, and allows for self-cleansing
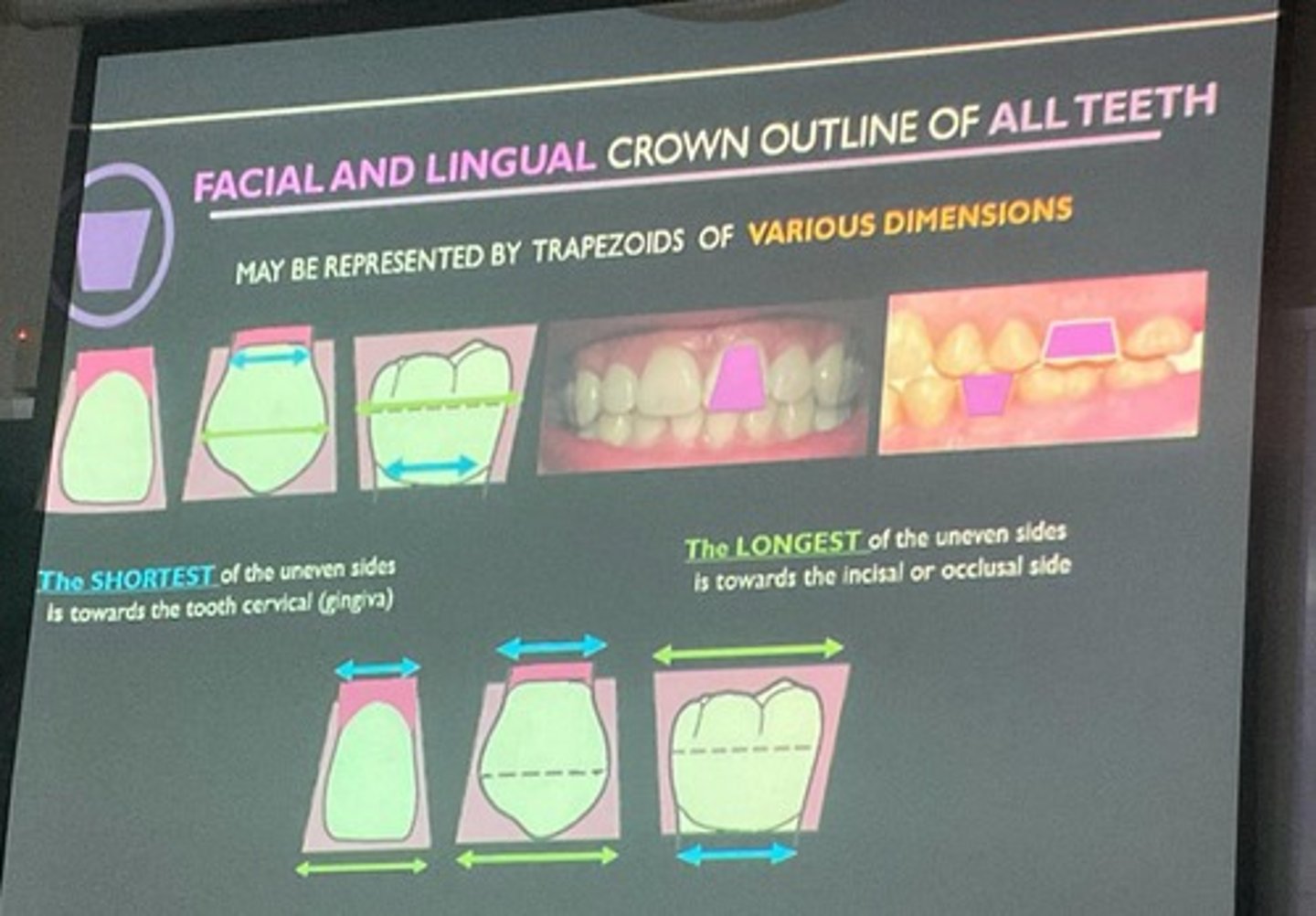
Trapezoid
Triangle
Rhomboid
three geometric figures used to describe tooth crown outlines
primary function of the permanent dentition
to prepare food for swallowing and facilitate digestion
malocclusion
deviations in intramaxillary and/or intermaxillary relations of the teeth and/or jaws
interdental papilla
it fills interproximal spaces and covers part of the cervical third of the tooth crowns
occlusion
the anatomical alignment of the teeth and their relationship to the masticatory system
cervical line
the stable anatomical demarcation of teeth defined as the cementoenamel junction
Length and shape of the root
Angle of the incisal and occlusal surfaces with respect to the root bases
two important points for occlusal stability
dehiscence
a cleft type partial absence of bone over the root area of a tooth
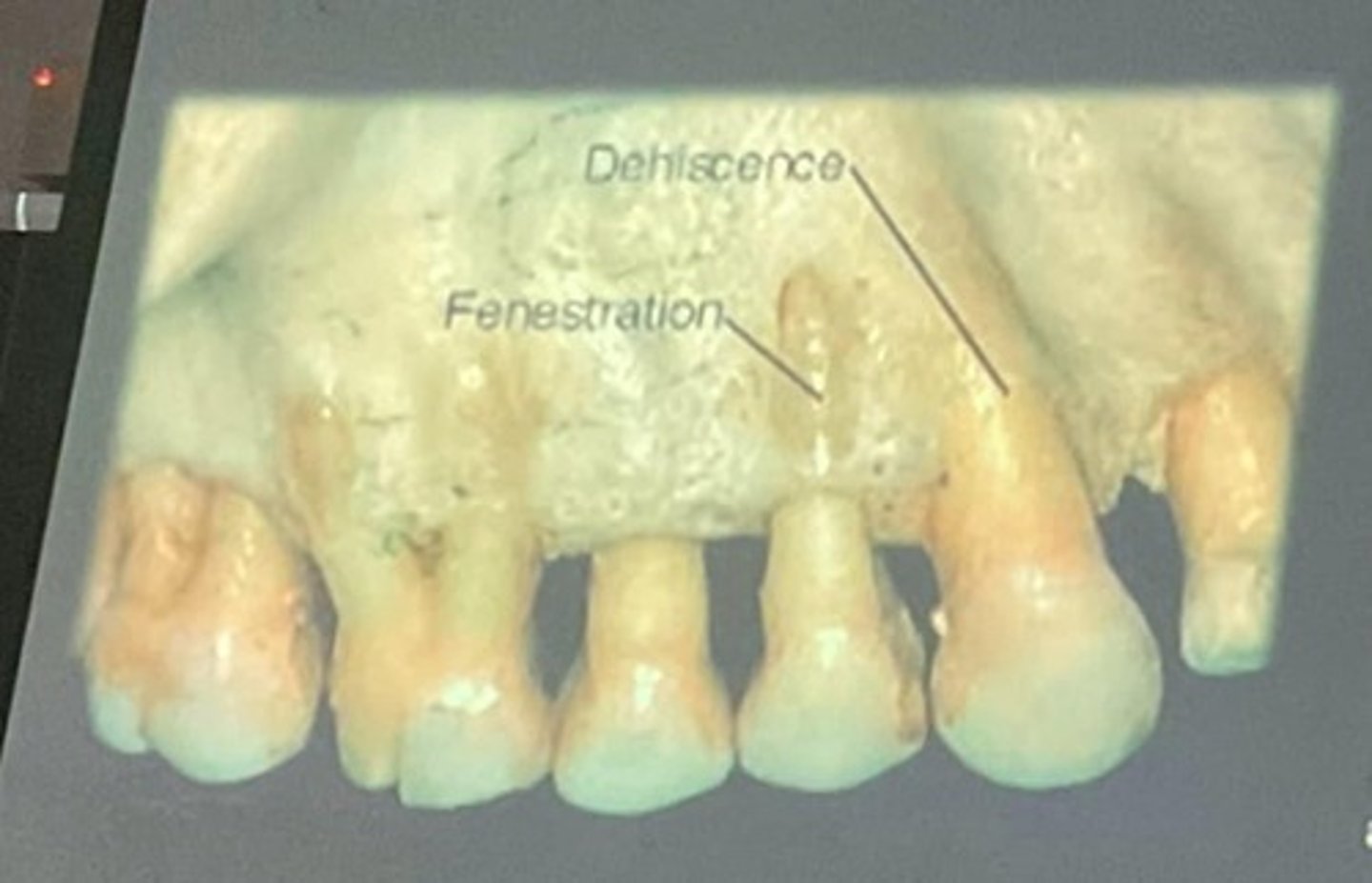
fenestration
a window type partial absence of bone over the root area of a tooth
Curve of Spee
a curvature that begins at the tip of the canine and follows the buccal cusp tips of premolars and molars posteriorly
Curve of Wilson
a curvature due to the lingual inclination of the mandibular molars, where the curvature of mandibular teeth is concave and maxillary teeth is convex
significance of the triangular outline of anterior teeth
it keeps the axis of crowns and roots parallel and ensures proper occlusion
primary lobes of anterior teeth
Mesial
Labial
Distal
Lingual
Mesial
Distal
Buccal
Lingual
primary lobes of premolars
Mesial
Distal
Buccal
Mesiolingual
Distolingual.
primary lobes of mandibular second premolars
significance of the rhomboid outline of mandibular posterior teeth
it protects the periodontium and maintains proper occlusion
importance of the trapezoidal outline of maxillary posterior teeth to dental function
it provides contact between teeth at proximal areas, protecting interproximal gingival tissue
interproximal spaces
pyramidal-like spaces that extend from the alveolar bone to and around the proximal contacts of the teeth
role of contact areas between adjacent teeth
ensure mutual support and occlusal stability
relationship between tooth form and food mastication
shapes of incisal and occlusal surfaces are related to the function they perform during chewing
effect of misalignment on the gingival line
abnormalities may change the gingival line, potentially harming tissue health
canines
arch form
jaw movement
primary difference in the dental anatomy of humans and anthropoid apes
purpose of the narrow occlusal surface in teeth
it facilitates the initial penetration of food materials and reduces masticatory force