other pulmonary diseases
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
cystic fibrosis
-autosomal recessive disease
-chronic sinopulmonary infections, malabsorption, and nutritional abnormalities
-most common lethal disease
-lung disease= major cause of morbidity
cystic fibrosis patho
-single gene defect on chromosome 7 encodes for CTRF protein > absence of this protein leads to altering salt and water across cell membrane > thick secretions altering host defense lungs
cystic fibrosis etiology/RF
-genetic >2000 CF mutations
-deleted chromosome 7
-caucasians
-family hx
-jewish
cystic fibrosis sx
-neonatal: meconium ileus, failure to thrive
-HEENT/pulm: chronic productive cough, recurrent respiratory infection, crackles/wheeze, digital clubbing
-GI: steatorrhea (fat in stool), abdominal pain, constipation, rectal prolapse
-poor weight gain, delayed puberty
-salty tasting skin, nasal polyps, infertility, poor weight gain
-hepatomegaly, distension, palpable fecal mass
cystic fibrosis exacerbations
-acute worsening of respiratory sx
-leading cause of mortality
-sx: increased cough, change in sputum, increased dyspnea, new hemoptysis, fever, fatigue, malaise, dullness of percussion
cystic fibrosis dx
-prenatal screening
-sweat chloride test= confirmatory
-genetic testing: CTRF gene
fecal elastase testing: <200 indicates pancreatic insufficiency
-CXR: eventually shows progressive bronchiectasis hyperinflation
-high resolution chest CT: better detection of ling
-PFT: decline in FEV1
cystic fibrosis tx
-referral to a regional cystic fibrosis center
-airway clearance: chest physiotherapy, chest oscillation, posititive expiratory pressure device
-nutritional: high calorie, fat diet, fat soluble vitamins
-lung transplant= only definitive tx
-CFTR modulations, mucolytics
-must be up to date on vaccinations
-abx for exacerbations: MRSA and pseudomonas empiric tx and then narrow down based on sputum culture
cystic fibrosis complications
-pseudomonas aeruginosa infection becomes most predominant pathogen
bronchiectasis
-abnormal and PERMANENT, widening and thickening of airways due to infection and inflammation
-women and elderly
bronchiectasis patho
-initial injury > impaired clearance > infection > inflammation > structural damage and pathologic changes including bronchial wall thickening, loss of bronchial tapering, cystic changes leading to
-progressive airway dilation
-loss of ciliary function
-chronic bacterial colonization (pseudomonas aeruginosa)
-airway hyperresponsiveness and airflow obstruction
bronchiectasis etiology/RF
-post infectious
-genetic
-immunodeficiency
-inflammatory
-aspiration
-women
bronchiectasis sx
-daily productive cough, dyspnea, fatigue
-sputum: purulent often large volume
-recurrent respiratory infection
-persistant wet crackles= hallmark
-digital clubbing
-cyanosis, use of accessory muscles
bronchiectasis dx
-high resolution chest CT: dilated, tortus airways, tram tracks, signet ring sign, tree in bid pattern, cystic damage
-bronchoscopy: elvaulate hemoptysis, remove secretions, rule out
bronchiectasis tx
-manage underlying condition
-airwary clearance, pulmonary rehab, nutritional support, vaccination
-surgery: lobectomy for localized disease
-exacerbation: augmentin
-chronic suppresive therapy: macrolide
-mucolytics: hypertonic saline, dornase alfa
-bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteriods
obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
-most common sleep related disorder
-50-70 yo
-male
OSA patho
repetitive complete apnea or partial upper airway collapse during sleep > hypoxemia, hypercapnia and arousal from sleep > sympathetic nervous system activation ``
OSA etiology/RF
-obesity BMI >30
-anatomical factors
- >40
-male
-postmenopausal
-family hx
-smoking, alcohol use, sedative mediaction
-large neck circumference >17in in men and 16 in women
OSA sx
-loud, habitual snoring with witnesses apneic episodes
-excessive daytime sleepiness
-unrefreshing sleep
-morning headache
-obesity, large neck circumference
-hypertension in 50-60% of pt
-mallampati score III-IV
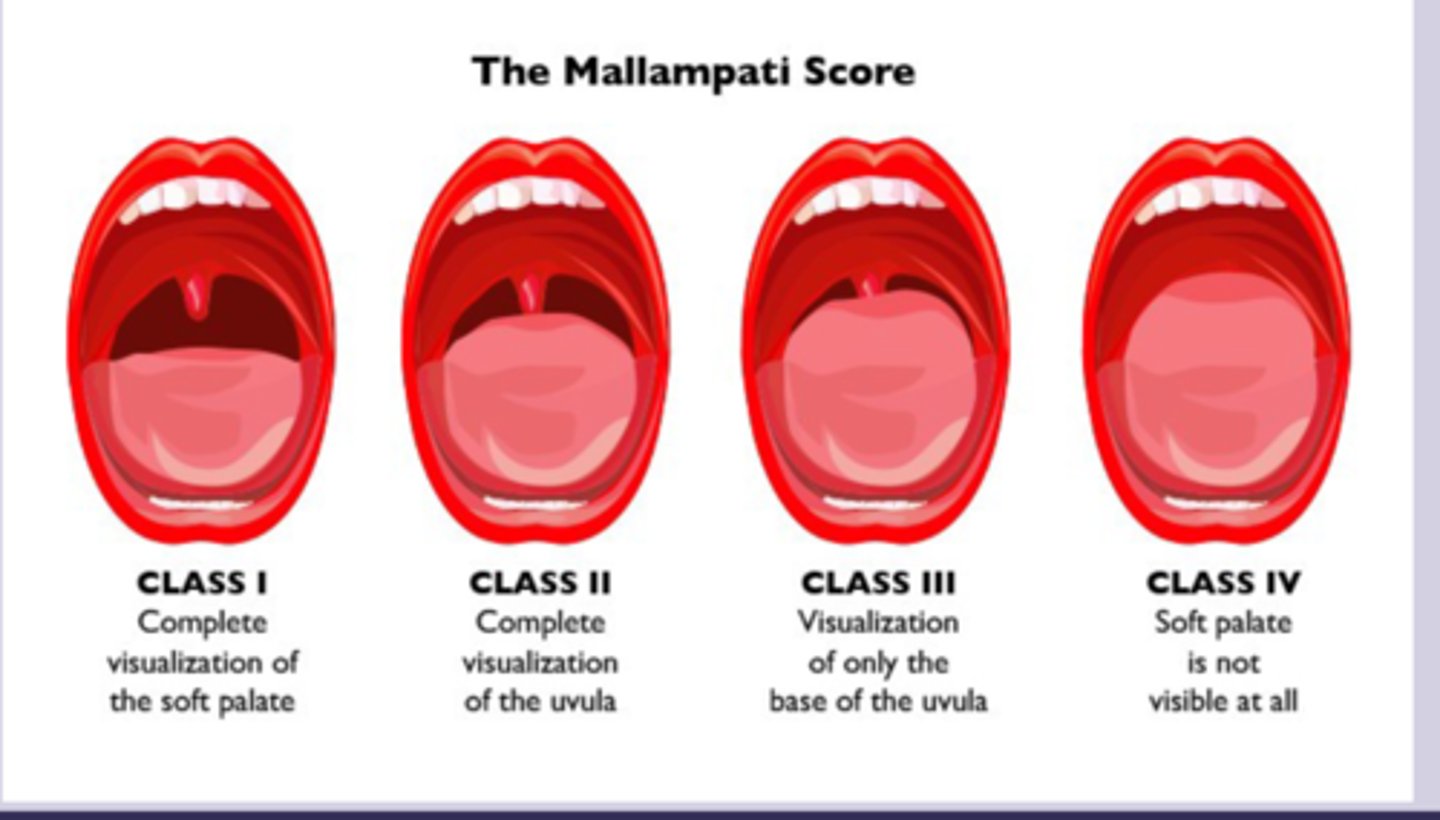
OSA dx
-screening questionnaires: STOP-BANG
-snoring, tired, observed apnea, pressure, BMI >35, age >50, neck size, gender
-gold standard= overnight polysomnography (PSG) in sleep laboratory
-AHI (number of apneas and hypopnea per hour): mild, mod, severe
-if abnormal most pt undergo pap titration
OSA tx
-weight loss
-first line: CPAP for >4hrs (reduced risk of heart disease and stoke
-avoid sedating medications and agents like alcohol
-Surgical interventions: uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, genioglossus
advancement, maxillomandibular advancement
-treat underlying conditions
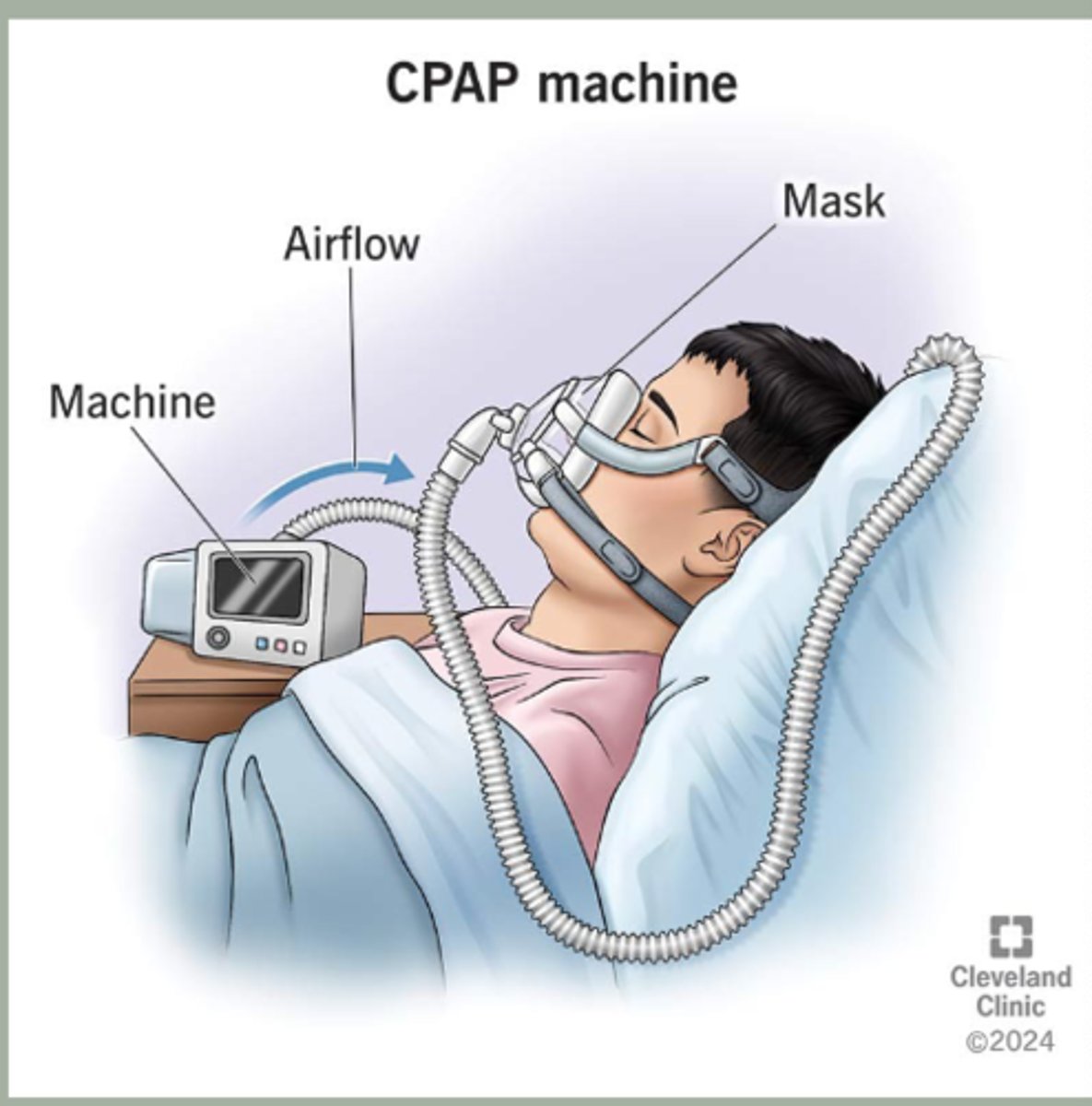
obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS)
-chronic hypercapnic respiratory failure in obese pt
-present in most pt with OSA
-aka pickwickian syndrome
OHS patho
-obesity induced restrictive lung disease with decreased lung volume + impaired central respiratory drive and blunt hypercapnic response > chronic hypoventilation leading to compensated acidosis
-pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale
OHS etiology/RF
-severe obesity (BMI >30)
-upper airway obstruction
-male
-advanced age
-hypothyroidism
-sedative use
OHS sx
-exessive daytime sleeping, morning headache, dysonea, orthopnea
-sx of OSA
-morbid obesity
-cyanosis
-signs of right heart faulure
-more respiratory sx than OSA
OHS dx
-BMI >30
-SpO2 <94%
-sx of pulmonary hypertension
-facial plethora
-diagnostic criteria: awake hypoventilation in obese pt in absence of other alveolar hypoventilation
-ABG: PaCO2 >40 while awake and stable
-CXR: cardiomegaly
-PFT: restrictive pattern
OHS tx
-weight loss= gold standard
=CPAP is OHS present, BiPAP is hypoventilation
-sleep positioning
-pulmonary rehab
-oxygen therapy
-avoid sedating meds
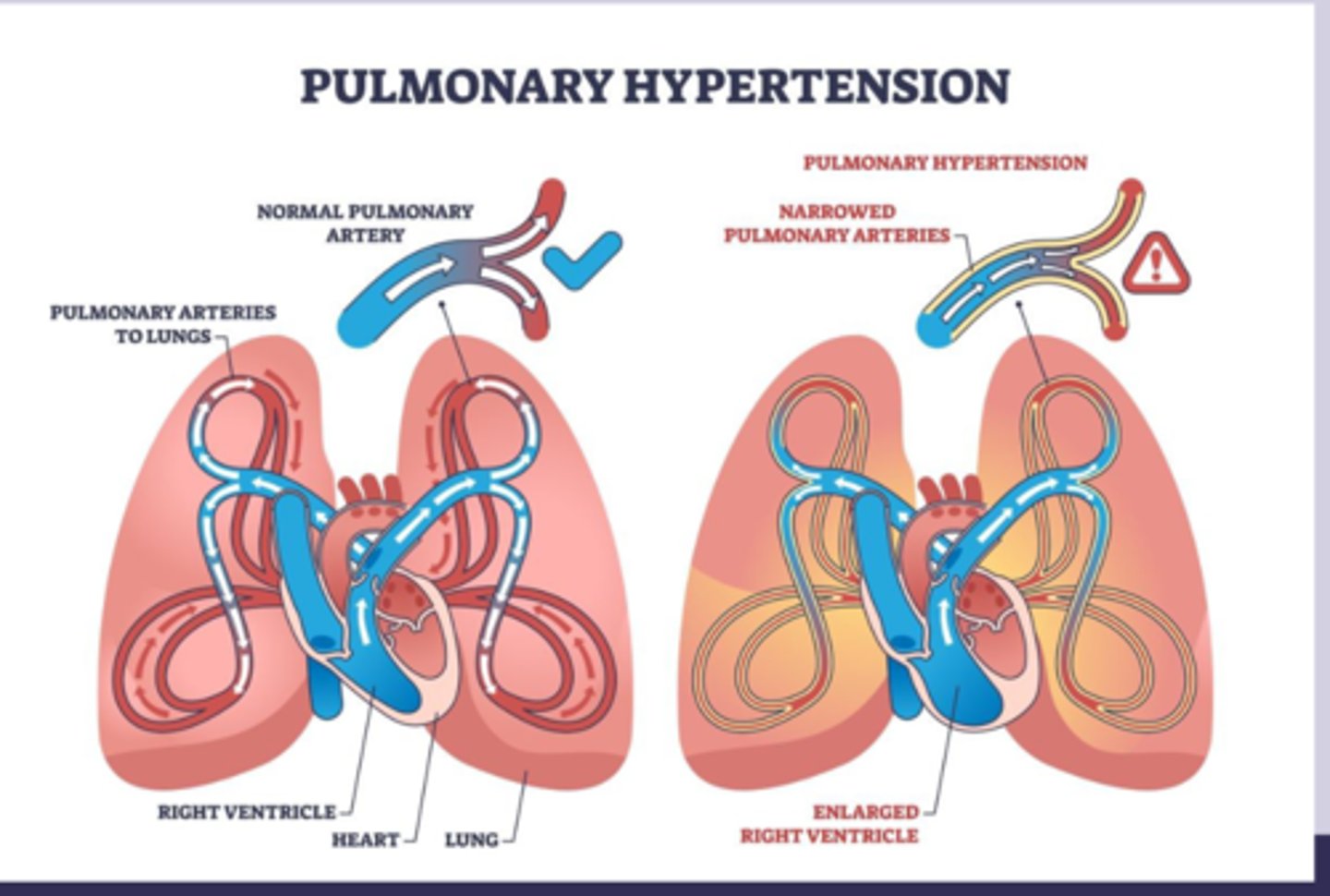
pulmonary hypertension
-hypertension in pulmonary arteries
-mPAP >20
-progressive disease
pulmonary hypertension patho
-increased pulmonary vascular resistance due to vasocontriction, remodeling, thrombosis > endothelial dysfunction with impaired vasodilation > vascular remodeling with smooth muscle proliferation
-results in por pulmonale
pulmonary hypertension etiology/RF
-group 3: lung disease/hypoxia
-female
-family hx
-connective tissue disease
-portal hypertension
-HIV infection
-chronic lung disease
-chronic hypertension
pulmonary hypertension sx
-progressice dyspnea on exertion (most common)
-fatigue, weakness, exercise intolerance
-chest pain
-dry cough
-loud foxed S2 with prominent S2 component
-right ventricular heave
-jugular venous distension, hepatojular reflux, peripheral edema
-cyanosis, clubbing
pulmonary hypertension > cor pulmonale
-when right sided heart failure is caused by lung condition
-long term high BP in the arteries of the lung and right ventricle of heart can lead to cor pulmonale
pulmonary hypertension dx
-echocardiogram: right ventricular systolic pressure
-gold standard: right heart catheterization, mean arterial pressure >20= diagnostic
-chest CT, VQ scan, seriology, genetic testing
pulmonary hypertension tx
-treat underlying lung disease
-diuretics and salt restriction
-pulm rehab
-lung transplant
-group 1: phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor= sildenafil, tadalafil
foreign body (airway)
-leading cause of death <4yo
-less common in adults, usually with altered mental status
-nuts, seeds, small toys, food, dental appliances (adults)
foreign body sx
-even may or may not be witnesses
-acute: chocking, gagging, stridor, unilateral wheeze, cant speak or cry, cyanosis
-chronic: persistant cough, reccurent pneumonia, unilateral wheeze, decreased exercise tolerance, chest pain
foreign body dx
-witness choking episode, sudden onset sx
-unilateral wheeze
-CXR: object is visible, hyperinflation, left mediastinal shift, atelectasis, air trapping
-CT chest: more sensitive
-flexical bronchoscope= diagnostic
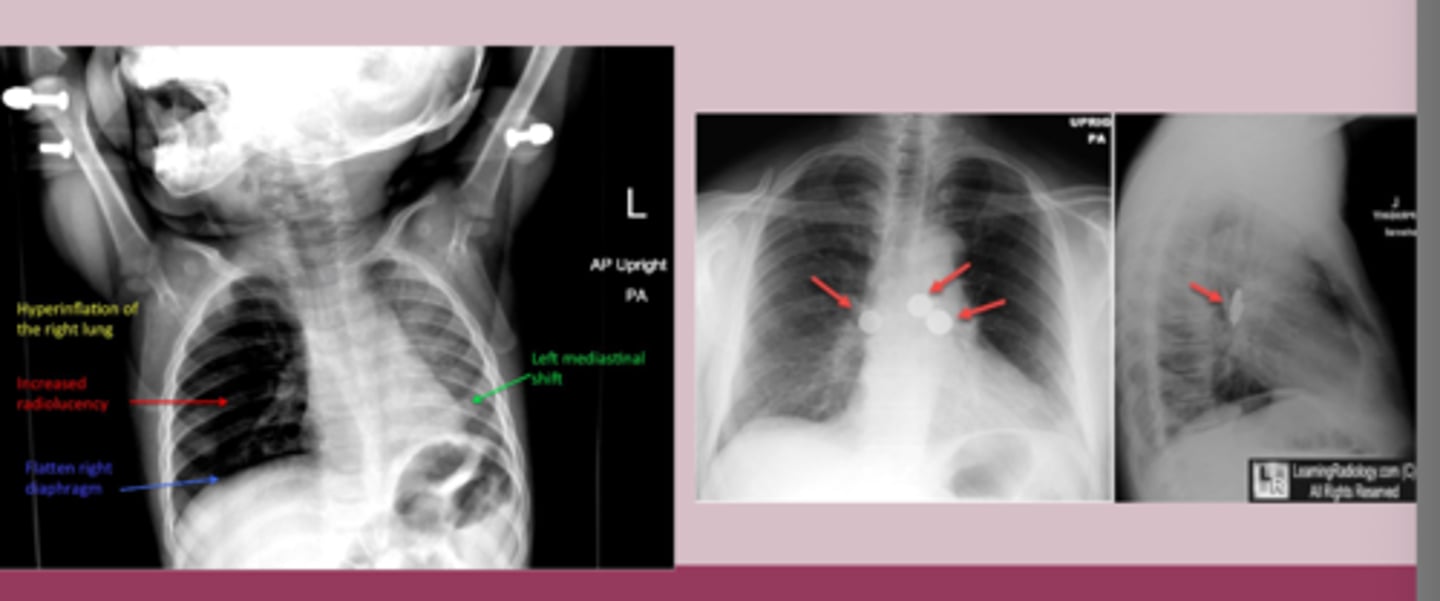
foreign body tx
-must be removed, urgency depends on location and presentation
-mainstay= flexible bronchoscopy
-complete obstruction: immediate intervention
-partial obstruction: avoid blind finger sweeps
-rigid bronchoscopy: larger objects
-surgical intervention: thoractomy, lobectomy
-post removal care: abc if secondary infection, bronchodilators