Chem- Ch 4: Atoms and elements
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
groups
each vertical column
periods
each horizontal row
metals
solids at room temp except mercury, shiny, conduct electricity, are ductile and malleable, form alloys
in chemical reactions, they tend to give up electrons
nonmetals
lie on right side of periodic table, except hydrogen
metalloids
have some properties metals and some of nonmetals, for example, they are shiny like metals, but do not conduct electricity
6 metalloids: boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium
atoms
all elements of the periodic table are made up of atoms, smallest subunit
dalton’s atomic theory
atoms of the same element have the same properties and different elements have different properties
compounds
formed by chemical combos of 2 or more of the same or different kinds of atoms
molecules
tightly bound combo of 2 or more atoms that act as a single unit
law of conservation of matter
matter can neither be created nor destroyed
makeup of an atom
proton- p or p + , 1+, nucleus
neutron- n, 0, nucleus
electron- e- , 1- , outside nucleus
mass #
the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom (protons + neutrons = mass #)
atomic #
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, provides the exact identity of an atom (# of protons)
Isotopes
atoms with the same # of protons but a different number of neutrons
atomic weight
the weighted average of the masses (in amu) of the naturally occurring isotopes
electromagnetic radiation
radio we listen to, light waves, microwaves, x rays
Bohrs model
since atoms can only absorb or emit photons at certain energy levels, the levels can be fixed.
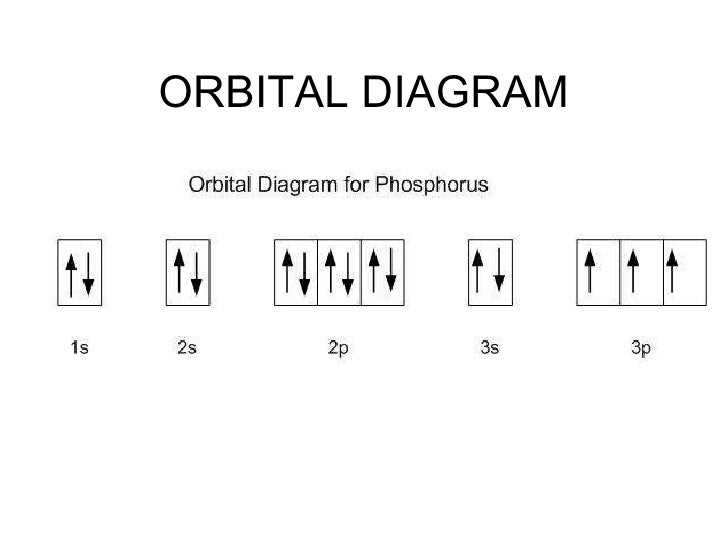
electron configuration
describes the “map of an electron arrangement around the nucleus, in each level only certain energies are allowed (1s2 , 2s2 , 2p6 , 3s2 , 3p6 )
orbital box diagrams
arrows represent electrons
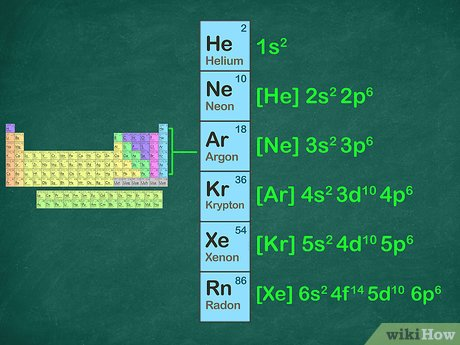
noble gas notation
s orbitals
spheres
p orbitals
shaped like doorknobs, called lobes (2)
d orbitals
shaped like 4 lobes, 1 d orbital is shaped like a donut and a set of lobes
atomic size
the size (radius) of an atom is determined by the radius of its outermost occupied orbitals
Ionization energy
the energy required to remove the most-loosely held electron from an atom in the gaseous state ( increases from left to right and and going up vertically.)