Prokaryotes and Protists
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Cell Morphology
Coccus
Bacillus
Helical

Spherical
Coccus
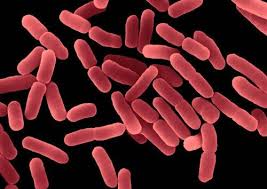
Rod-shapped
Bacillus

spirilloid
helical
Purple Stained
Gram (+)
Pink Stained
Gram (-)
Cyanobacteria
Anabaena
Rivularia
Nonstoc
Oscillatoria
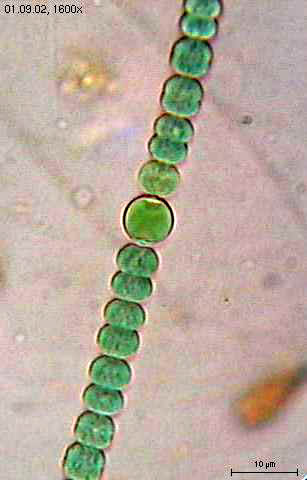
Anabaena (heterocyst)
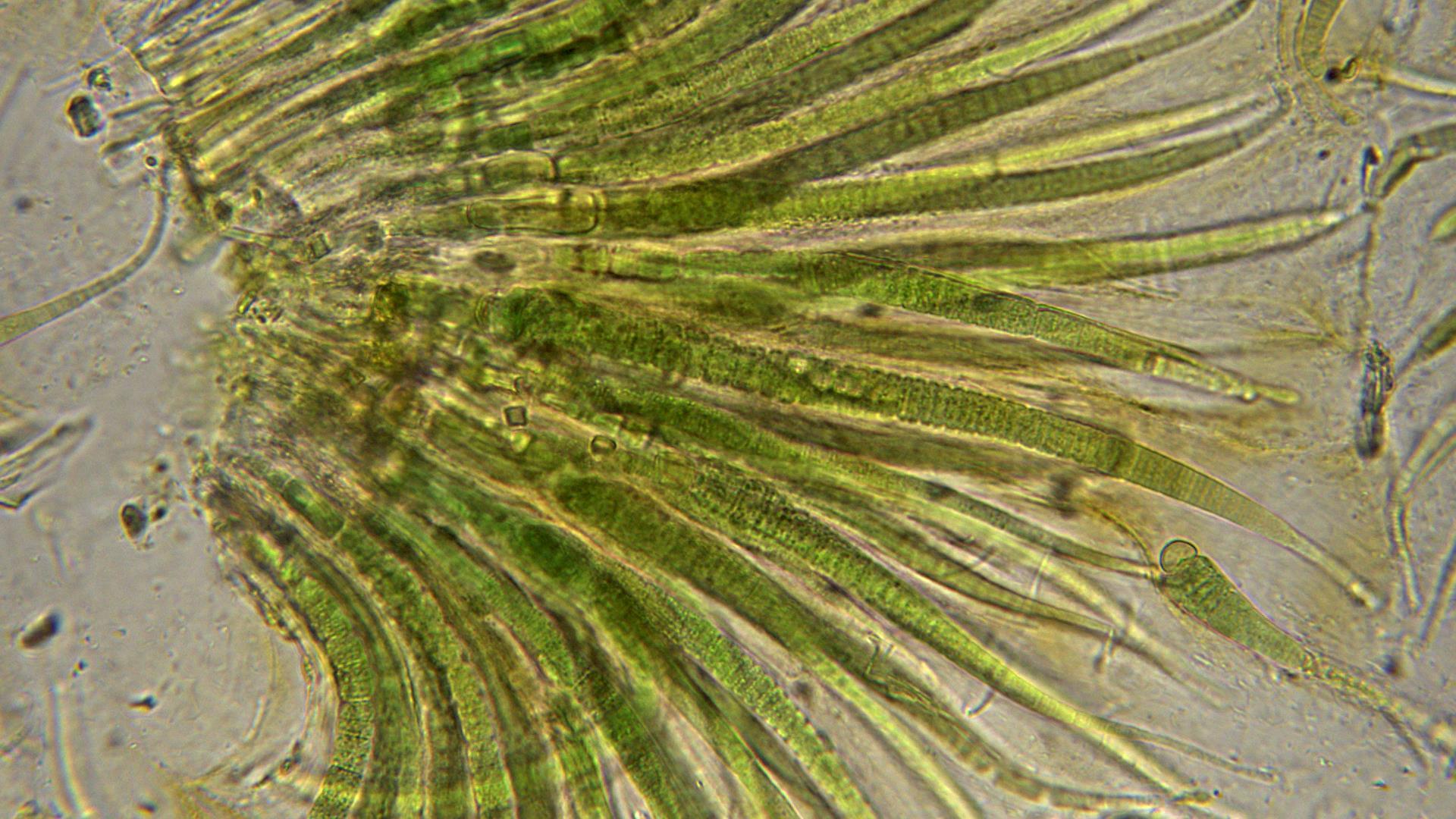
Rivularia (heterocyst)
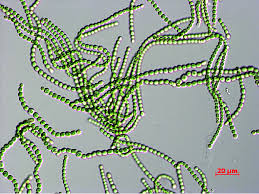
Nostoc (heterocyst)
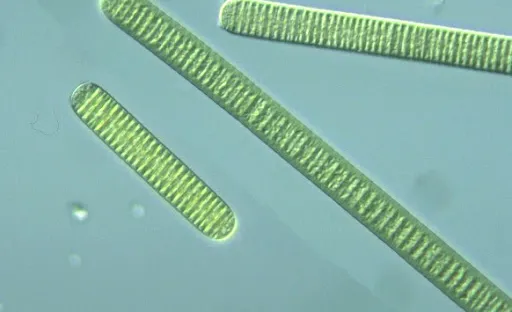
Oscillatoria
convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to biologically accessible compounds
Heterocysts
swellings on plant roots where bacteria convert nitrogen into usable forms for plants, in exchange for sugars.
Root Nodules
Amoeba proteus
Physarum slime mold
Supergroup Amoeboza
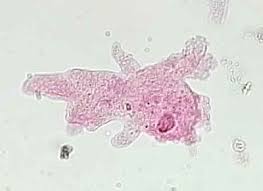
single-celled eukaryotes that can alter their shape, primarily by extending pseudopods.
Amoeba proteus
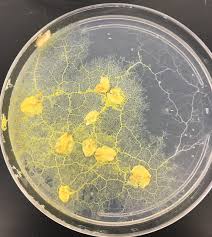
Not fungi, begin life as amoeba-like cells but may eventually form slimy yellow plasmodial strands
Physarum slime mold
Supergroup Excavata
Euglena
Giardia intestinalis
Trichomonas vaginalis
Tripanosoma sp.
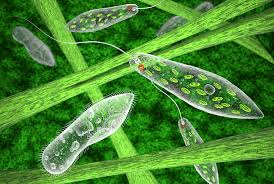
Flagellated Cells
Red stigma
Euglena
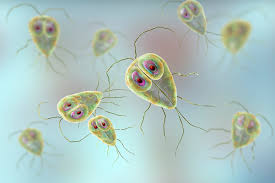
infects the digestive system
Giardia intestinalis
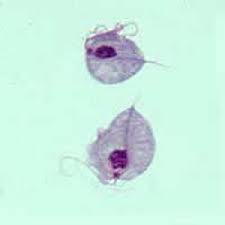
vaginalis infects the lining of the lower reproductive system and urinary tract
Trichomonas vaginalis
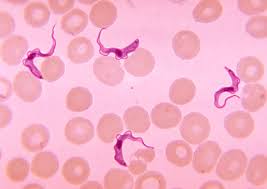
Causes sleeping sickness and Chagas disease.
Tripanosoma sp.
Multicellular brown algae
Kelp
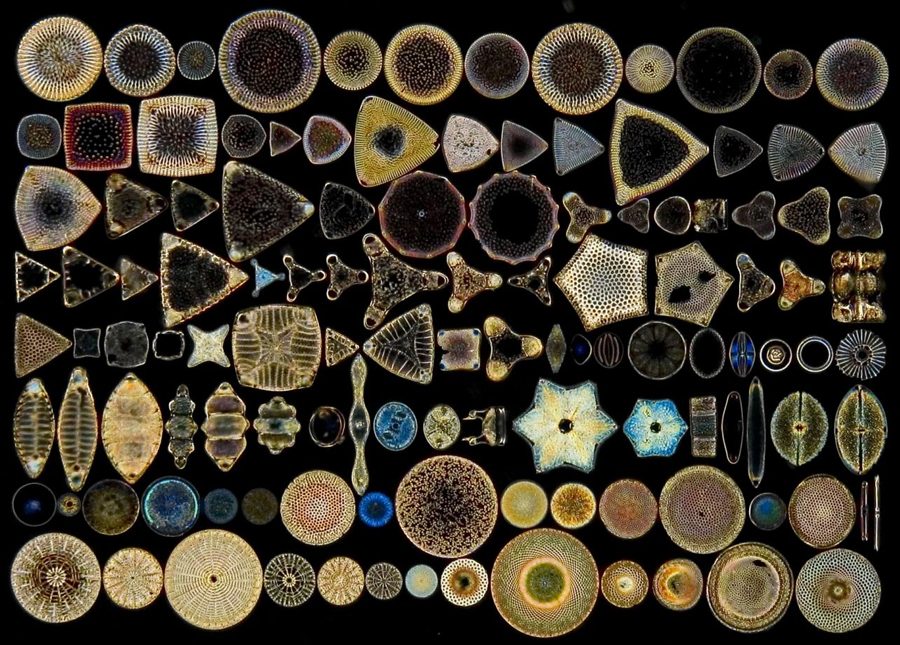
single celled and create “shells” made of
organic glass (silica) that protect them.
Diatoms
Supergroup Alveolata
Paramecium
Stentor
Dinoflagellates
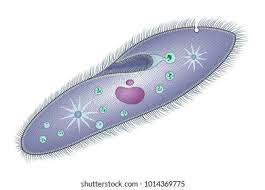
Has cilia, gullet, oral groove, and vacuoles
Paramecium
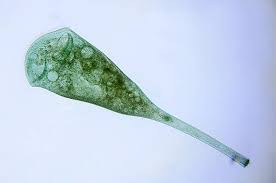
A ciliate - single-celled organisms, possess cilia, short hairlike organelles
Stentor
photosynthetic “algae” with two flagella located in grooves in cellulose “armor”.
Dinoflagellates
Supergroup Rhizaria
Radiolarians
Foraminiferans

typically made of silica that is deposited within the outer layer of their cells.
Radiolarians

possess a test (shell-like hardened structure outside the cell) made of calcium carbonate.
Foraminiferans