Urinary System
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is the function of the urinary system?
maintaining osmotic balances in the body, such as filtering the blood / removing metabolic waste, maintaining pH and fluid balances, regulating blood pressure, and producing hormones
Where does urine production occur?
In the kidney’s nephron
Name the overall journey of urine?
Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Bladder 4. Urethra
How does urine travel through the kidney?
Bowman’s capsule → Proximal convoluted tubule → Descending Loop of Henle → Ascending Loop of Henle
What delivers urine from the kidneys to the bladder for storage?
Ureters
What is the outer portion of the kidney called?
Renal cortex
What is the inner portion of the kidney called?
Adrenal medulla
What is the function of the kidney’s?
filtering blood, regulating fluid volume in the body, and producing urine to remove the waste materials from the body
What is the function of the urethra?
carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body during urination
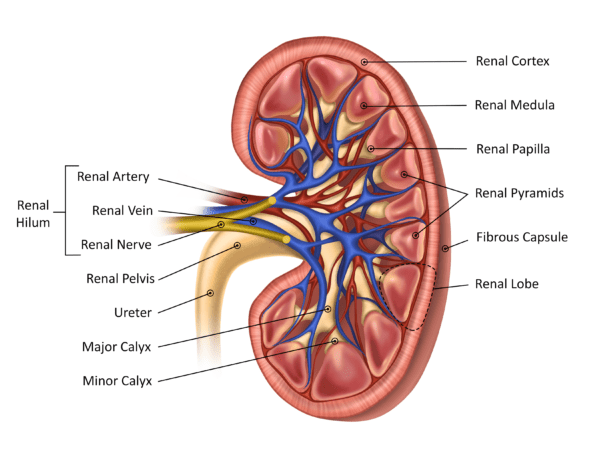
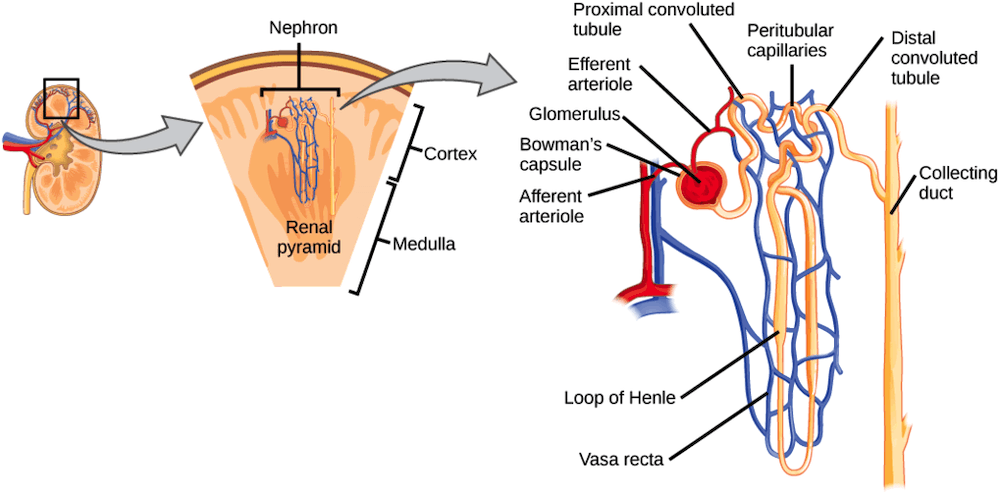
what is the urinary system composed of?
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
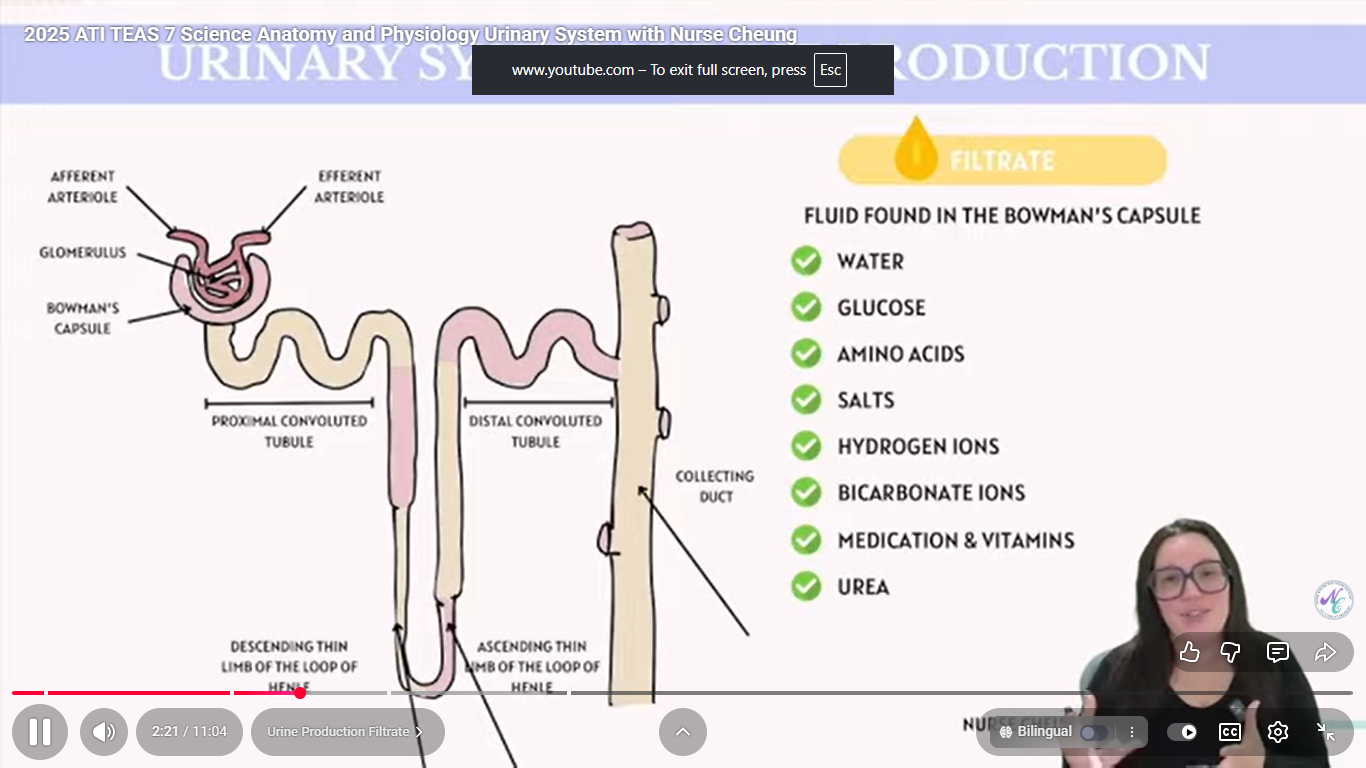
What is renin?
a hormone that regulates blood pressure by retaining or removing water and salt, controls volume of the blood
What does liver convert ammonia into?
Urea
What is passive transport vs active transport?
Passive transport: does not require energy, moves high → low
types: diffusion (moving small particles), facilitated diffusion (moving large particles), and osmosis (moving of water)
Active transport: requires energy, low → high
If you are dehydrated what will your urine look like?
More concentrated urine and less water due to reabsorption due to dehydration
If you overhydrated what will your urine look like?
Less concentrated urine and more water in the pee