Acids and Bases
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Define a Bronsted-Lowry
acid
Proton donor
Define a Bronsted-Lowry
base
Proton acceptor
What ion causes a solution
to be acidic? (2 answers)
Name and formula
H + (hydrogen ion) or, more accurately, H 3
O +
(oxonium ion), as protons react with H 2
O to form
it
What ion causes a solution
to be alkaline?
-
OH (hydroxide ion)
Write an equation for the
ionisation of water (2)
2H 2
O (l) ⇌ H 3
O + (aq) + -
OH (aq)
OR H 2
O (l) ⇌ H + (aq) + -
OH (aq)
Derive Kw using the
equation for ionisation of
water
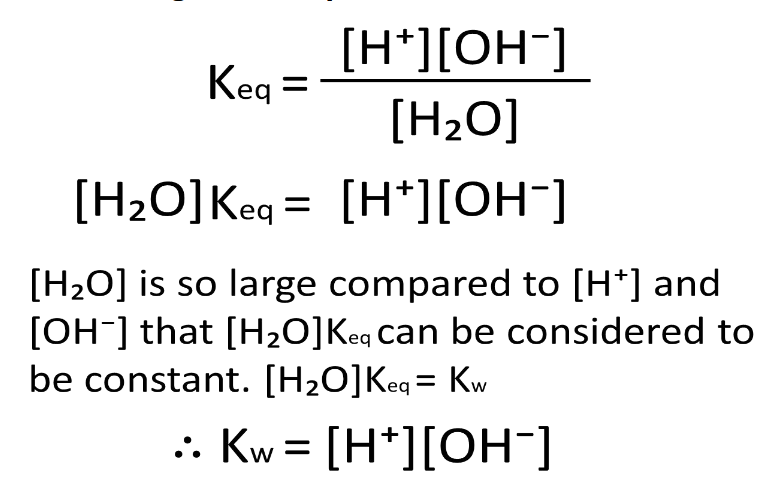
What is the value of K w at
298K?
1.0 x 10 -14
What physical factors affect
the value of K w ? How do
they affect it?
Temperature only - if temperature is increased,
the equilibrium moves to the right so K w
increases and the pH of pure water decreases
Why is pure water still
neutral, even if pH does not
equal 7?
[H + ] = [ - OH]
Give an expression for pH in
terms of H +
pH = -log 10 [H + ]
What is the relationship
between pH and
concentration of H + ?
Lower pH = higher concentration of H +
If two solutions have a pH
difference of 1, what is the
difference in [H + ]?
A factor of 10
How do you find [H + ] from
pH?
[H + ] = 10 -pH
How do you find [OH -
] from
pH? (at 298K)
Find [H + ], use K w
(equal to 1 x 10 -14 at 298K) to
calculate [ -
OH]
What is different when
finding [H + ] from the
concentration of diprotic and
triprotic acids?
Need to multiply the concentration of the acid by
the number of protons to find [H + ]
How do you calculate the
pH of a strong alkaline
solution?
Use Kw to calculate [H + ] from [OH -
]
Use pH=-log[H + ]
Define the term strong acid
One which fully dissociates in water ( HX → H + +
X -
)
Define the term strong base.
One which fully dissociates in water (XOH → X +
+ -
OH)
What is the difference
between concentrated and
strong?
Concentrated means many mol per dm 3
, strong
refers to amount of dissociation
What is a weak acid and a
weak base?
Weak acids and bases do not fully dissociate in
water. They only partially dissociate into their
ions.
Give some examples of
strong acids
HCl, H 2
SO 4
, H 3
PO
Give some examples of
strong bases
NaOH, CaCO 3
, Na 2
CO
Give some examples of
weak acids
CH 3
COOH (ethanoic), any organic acid
Give some examples of
weak bases
NH 3
What is K a ? (expression)
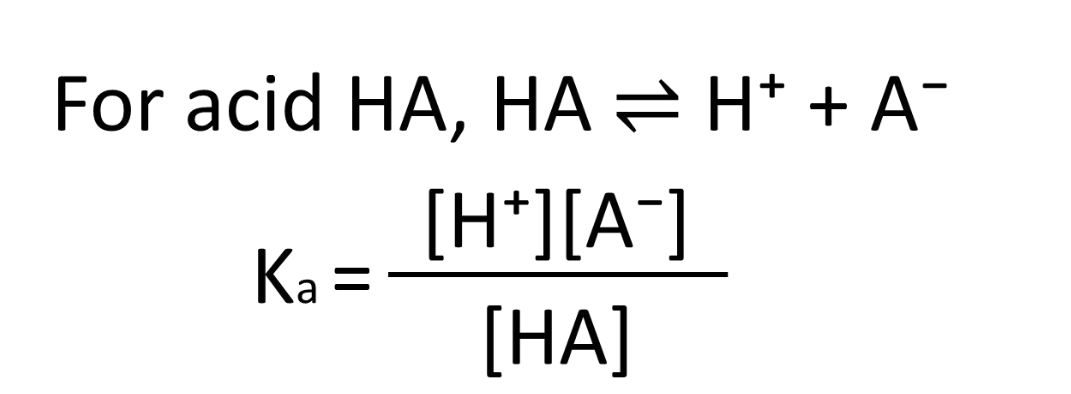
How would you work out the
pH of a weak acid?
Use the equation for K a
, subbing in values for [A -
]
and [HA].
Use pH=-log[H + ] equation to find pH
What is a titration?
The addition of an acid/base of know titration to a
base/acid of unknown titration to determine the
concentration. An indicator is used to show that
neutralization has occurred, as is a pH meter.
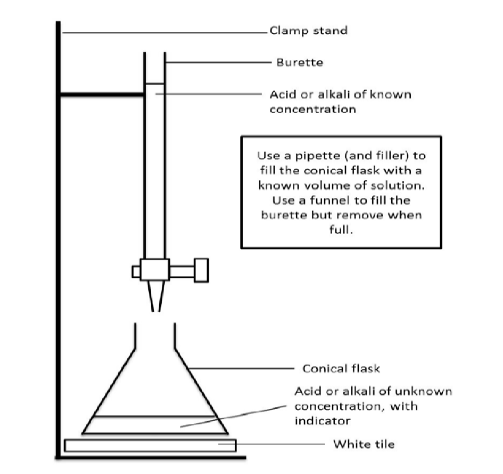
Draw a diagram of the
equipment that could be
used for a titration.
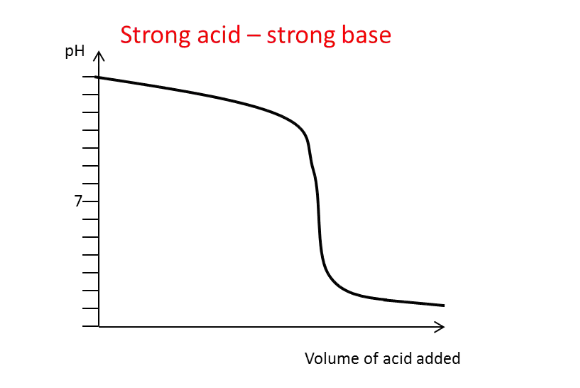
Draw the titration curve for a
strong acid with a strong
base added
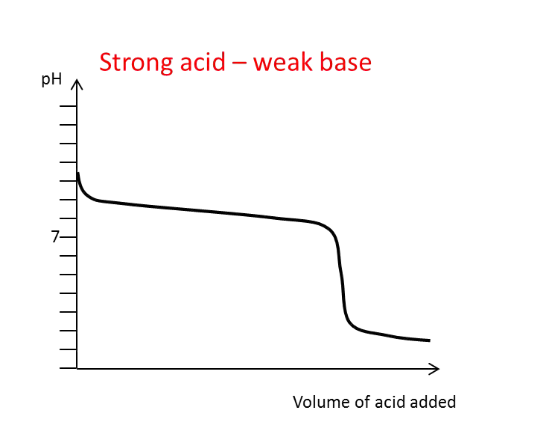
Draw the titration curve for a
strong acid with a weak
base added
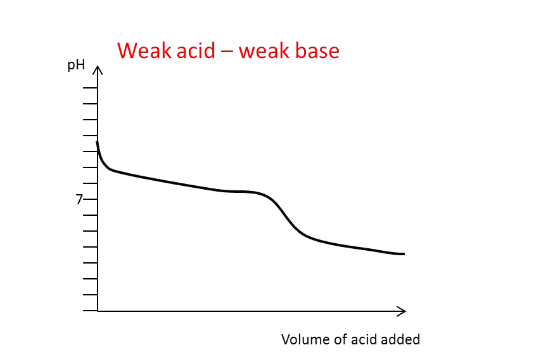
Draw the titration curve for a
weak acid with a weak base
added
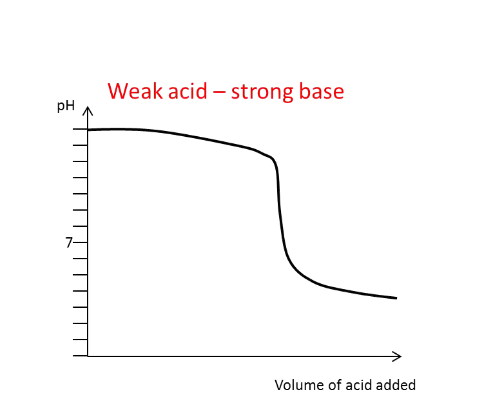
Draw the titration curve for a
weak acid with a strong
base added
Define the term equivalence
point.
The point at which the exact volume of base has
been added to just neutralise the acid, or
vice-versa.
What generally happens to
the pH of the solution
around the equivalence
point?
There is a large and rapid change in pH, except
in the weak-weak titration.
How would you calculate the
concentration of a reactant if
you know the volume and
conc of the other reactant and
the volume of that reactant
added
Calculate mols of one reactant
use balanced equation to work out mols of the
other
Use conc = mol/vol to calculate concentration
What is the end point?
The volume of acid or alkali added when the
indicator just changes colour. If the right indicator
is chosen, equivalence point = end point.
What are the properties of a
good indicator for a
reaction? (3)
Sharp colour change (not gradual) - no more than one drop of
acid/alkali needed for colour change
End point must be the same as the equivalence point, or
titration gives wrong answer.
Distinct colour change so it is obvious when the end point has
been reached.
What indicator would you
use for a strong acid-strong
base titration?
Phenolphthalein or methyl orange, but
phenolphthalein is usually used as clearer colour
change.
What indicator would you
use for a strong acid-weak
base titration?
Methyl orange
What indicator would you
use for a strong base-weak
acid titration?
Phenolphthalein
What indicator would you
use from a weak acid-weak
base titration?
Neither methyl orange or phenolphthalein is
suitable, as neither give a sharp change at the
end point.
What colour is methyl
orange in acid? In alkali? At
what pH does it change?
Red in acid; yellow in alkali. Changes at about
pH = 4-5. Approx same as pK a value
What colour is
phenolphthalein in acid? In
alkali? At what pH does it
change?
Colourless in acid; red in alkali. Changes at
about pH = 9-10. Approx same as pK a value
What is the
half-neutralisation point?
When volume = half the volume that has been
added at the equivalence point
Define a buffer solution
A solution that resist changes in pH when small
amount of acid/alkali are added.
What do acidic buffer
solutions contain in general
terms?
A weak acid and a soluble salt of that acid that
fully dissociates
Write a reaction for an
acidic buffer with added acid
A - + H + → HA, opposes addition of H +
Write a reaction for an
acidic buffer with added
alkali.
HA + OH - → H 2
O + A -
How else can you achieve
an acidic buffer solution
other than just mixing the
constituents?
Neutralise half of a weak acid (meaning the acid
must be in excess) with an alkali - this forms a
weak acid / soluble salt mixture.
What do basic buffer
solutions contain in general
terms?
Weak base and soluble salt of that weak base
How can you calculate the
pH of buffer solutions?
Use the K a of the weak acid, sub in [A - and [HA],
calculate [H + ] → pH
How can you calculate the
new pH of a buffer solution
when acid or base is
added?
Calculate number of moles of H + and A - and HA
before acid or base is added. Use equations to
work out new moles of A - and HA → find [H + ] →
pH
Which buffer system
maintains blood pH at 7.4?
What happens when
acid/alkali is added?
H + + HCO 3
-- ⇌ CO 2 + H 2
O
Add OH - → reacts with H + to form H 2
O, then
shifts equilibrium left to restore H + lost
Add H + → equilibrium shifts to the right, removing
excess H +
What products are buffers
found in?
Shampoos, detergents → important to keep pH
right to avoid damage to skin, hair, fabrics