HSCI 333 final
1/260
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
261 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintenance of stable internal conditions despite external changes.
- depend on constant energy input from external environment to reduce entropy and maintain order of internal environment
regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP)
baroreceptor system: baroreceptor cells sense pressure found in aortic arch and carotid arteries → stimulated by stretch of arterial wall when ABP is high → impulses inhibit vasomotor center in CNS → diminishes heart activity & drives dilation of peripheral blood vessels → reduce ABP
Negative Feedback for blood glucose
High blood glucose → pancreas secretes insulin into blood → insulin helps liver stores glycogen, muscle cells store glycogen & build proteins, adipose tissue uses glucose from blood for fat → lower glucose level
negative feed back for blood calcium
Blood calcium level high → thyroid gland releases calcitonin → stimulates CA2+ deposition in bones, reduce CA2+ uptake in kidneys → lower blood CA2+ level
Parturition
Process of childbirth involving positive feedback.
positive feedback for blood calcium
Blood calcium level low - parathyroid glands release PTH → inc Ca2+ uptake in intestines & kidneys, stimulates Ca2+ release from bones → inc blood Ca2+ level
Core Body Temperature Regulation
lower/ higher than set point → sensor → hypothalamus → (lower) shivering to generate heat, (higher) constriction of blood vessels in skin
Explain the 60-40-20 rule
- total body water: 60% of adult weight is fluid (42L)
- intracellular fluid (ICF): 40% of body weight; 28L within cells.
- extracellular fluid (ECF): 20% of body weight (plasma 20%, interstitial fluid 80%), 14L outside cells
how are materials exchange (CO2, O2)
waste:: cell produce CO2 --> diffuse to ECF --> plasma --> exit from lungs
nutrients: blood pick up O2 from alveoli by diffusion, cardiovascular system delivers oxygenated blood to cells
blood composition
formed elements 45%: RBC, WBC, platelets
plasma 55%: water (95%), electrolytes, proteins, hormones, gases, nutrients, wastes
leukocytes
WBC, Defend against infections and foreign invaders/ abnormal cells
enthrocytes
RBC, transport O2 to cells, CO2 away from tissues (99% of formed element)
electrolytes
ions that control cell function and volume and electrical charge across cells, maintain homeostasis
proteins in plasma
albumins maintain blood volume, transport electrolyes, hormones, wastes & globolins as antibodies, transport substance
arteries, capillaries, venules structure
Arteries (withstand high pressure), 3 layer wall (thin inner epithelium/ intima, thick smooth muscle/ media, outer connective tissues/ adventitia)
Capillaries: made of one cell layer of endothelial tissue, large SA
veins: 3 layer wall (thin inner epithelium, thin smooth muscle layer, thinner outer connective tissues), valves, lower pressure, larger volume than artery
Cardiac Cycle
systole (atria → ventricle contraction), diastole (chambers relax, atria fill with blood)
Phlebotomy
Practice of drawing blood for clinical purposes, found in Egyptian history
idea of the four humors (blood element)
1. blood (RED, hot, wet, air)
2. yellow bile (YELLOW, fire, hot, dry)
3. black bile (black, earth, dry, cold)
4. phlegm (blue, water, cold, wet)
- found in greek history, introduced by hippocrates
role of spleen in blood production
Filters and recycles blood cells
transubstatiation
blood to wine/ wine to blood
what blood is bright red
oxygenated blood
transmutation
lead to gold
congealing process
factors promote and inhibit coagulable lymph (not just cold temp)
hirudin
anticoagulant secreted to prevent blood clotting
what is the first ever blood transfusion experiment
dog to dog by richard lower
Parabiosis
experimental technique where model organisms have shared blood supplies by connecting their circulatory system
Plasma-rich treatment
Accelerates injury repair in sports.
- found to improves people's appearance memory, strength
- suggest that factors in plasma can help restore brain function (can be used to treat neurodegenerative disease)
3 main problems on blood transfusion historically
clotting, infection, immune reaction
why is it called Rh
antisera produced in rabbits/ guinea pigs reacted to rhesus monkey blood and caucasian popn
how was clotting problem solved
- sodium citrate showed to prevent blood clotting (also used oxalate, sulfate)
- Glucose-citrate combination extend storage for weeks
optimum citrate conc
0.2%
functions of plasma fraction
helpful for victims of blood loss
Glycerol addition
Enables long-term storage of blood products.
Blood substitutes
- manufacturing blood
- saline/ other balanced salt solution
- albumin
- coconut milk
- synthetic forms
splenic anemia
- spleen dysfunction, produce "black bile", swell up in many situation
splenectomy
cutting the spleen to cure splenic anemia
Perfluorochemicals
Synthetic hemoglobin substitutes for oxygen transport.
Hematocrit
Tool measuring blood cell levels, stain cells to judge quality
Aplastic anemia
Condition with insufficient red blood cell production, fatty appearance of the bone marrow
Pernicious anemia
Low RBC counts, megaloblastic appearance (large RBC)
Erythropoiesis
Production of red blood cells.
what are the extrinsic and intrinsic factor to prevent pernicious anemia
extrinsic: meat consumption
intrinsic: body/ stomach component
Vitamin B12
- extrinsic factor that we absorb from intestine (made by bacteria in GI tract)
- Essential for generating folic acid --> Vitamin B12 and folic acid is crucial for thymine synthesis, DNA replication, cell replication, hemoglobin synthesis
glycoprotein
intrinsic factor, made by gastric parietal cells to aid VB12 absorption
Emergent properties
When simple parts come together, they create something more complex and unique that you cannot see in the parts alone.
- ex: water shows unique traits such as universal solvent, but H and O itself does not show this property
Diffusion
Passive movement from high to low concentration that follow the 2nd law of thermodynamics
Osmosis
Water movement across semi-permeable membranes from high to low water potential
Oncotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure due to proteins in blood.
fluid exchange at capillary beds due to osmotic & blood (hydrostatic) pressure forces
- high conc of proteins (albumin) in blood create high osmotic forces
At arteriole: blood pressure (32 mmHg), osmotic pressure (25 mmHg) → net pressure out (water, O2, amino acid)
At venule: blood pressure (15mmHg), osmotic pressure (25 mmHg), net pressure in (water, wastes, CO2)
lymph fluid collection (2 phases)
lymph retrieves ECF and bring it back to blood (one way) at subclavian veins
- expansion phase: hydrostatic pressure in intersititium Pif > initial lymphatic pressure Pl --> open microvalves --> fluid enter vessels outside
- compression phase: Pl inc --> closing microvalves --> open secondary lymph valves --> fluid flow downstream
Continuous Capillary
- most common, allows selective diffusion of small molecules with small vesicles assist in transport across capillary wall (outermost basement membrane)
Fenestrated Capillary
- found in kidney, small intestine
- Contains small fenestration (pores) for faster exchange of larger molecules. (nutrients, wastes, hormones)
Sinusoidal Capillary
Large fenestration between endothelial and basement membrane for passage of proteins and cells.
- found in liver
blood pH buffer
- bicarbonate (HCO3-)
- HCO3- + H+ <--> H2CO3 <--> CO2 + H2O
what will happen if blood pH is too low/ high
low: acidemia/ acidosis
high: alkalemia/ alkalosis
what do we need O2 as e-aste acceptor
Essential for accept electrons stripped away during aerobic respiration and oxidation
Hemoglobin structure
Protein + prosthetic group --> heme group (contains iron that bind single O2)
- 4 protein subunits: 2 alpha (α)-globin proteins, 2 beta (β)-globin proteins --> assemble to a tetramer
origin of hemoglobin
evolved from ancestral protein similar to myoglobin (an oxygen-binding protein found in muscle tissue)
what is heme
a type of porphyrin
- excellent shape for coordinating metals and absorbing e- and energy
2 redox state of iron atom in heme group
LEO: losing electrons in oxidation, GER: gaining electrons is reduction
- Fe3+/ ferric form is oxidised (methemoglobin form), Fe2+/ ferrous form is reduced
- The reduced form (Fe2+) binds O2 and oxidizes Hb → release of O2 reverses this and go back to reduced state
coorperativity of O2 binding
- it is an emergent property of hemoglobin, binding O2 increase affinity for additional binding
Allostery
- drive binding of O2
- Shape change in proteins enhancing ability for O2--Fe2+ interaction
does Hb still bind with O2 even when O2 pressure is low
yes, Hb is good at binding O2, is saturated even at low pressure
function of hemoglobin polypeptides
to ensure heme/ Fe binding to O2 is not too tight and is reversible
why is CO bad for us
CO irreversibly binds heme, makes blood bright
Bohr Effect
O2 release due to increased CO2 and temp and decreased pH. (reduce affinity)
Hemostasis
Process to prevent blood loss through clotting. (aka thrombosis, coagulation)
- thrombus = clot
key clot formers
platelets, fibrinogen, thrombin, coagulation factors (vitamin K produce thrombin), Ca2+ (binds with citrate)
thrombocytopenia
lack of platelets
Clotting Factors
Proteins necessary for blood coagulation.
- Lack of these can produce deficiencies in blood clotting (hemophilia)
key clot inhibitors
antithrombin, heparin
Key clot dissolvers
fibrinolysis (tPA, plasminogen)
factors of evolution
recombination, mutation, environment, mating
Mutation
Source of genetic variation in organisms.
- include insertion, deletion, substitution, duplication, rearrangement
3 types of hemoglobin mutation
- at protein coding region, altering protein sequence (HbS, HbC, HbE)
- at mRNA splicing region (affect mRNA maturation and stability)
- at gene regulatory region (affect mRNA production)
- can occur tgt
Recombination
Process of genetic material exchange during meiosis. (independent assortment)
HbS Variant
HbS variant caused by a single nucleotide mutation (GAG → GTG), leading to difference in protein sequence
relative fitness of genotypes of Hb allele
1. HbA/HbA: reduced fitness due to malaria susceptibility
- Fitness coefficient (Waa)=0.9
2. HbS/HbS: reduced fitness due to RBC sickle cell anemia
- Wss=0.2
3. HbA/HbS: increased fitness due to protection against malaria and no anemia
- Wss=1.0
Sickle Cell Anemia
- Molecular disease affecting red blood cell shape
- causing capillary blockade --> higher risk for ishchemia/ infraction/ hemorrhage
- causing overgrowth of bones (naturopathy) to support erythropoiesis
first test for sickle cell anemia
emmel's test: show sickling under reduced oxygen conditions
electrophoresis
find that there are 2 forms and designate the sickling associated allele (HbS)
X-ray Crystallography
Technique revealing 3D structure of hemoglobin.
what happen to HbS in deoxygenated state
HbS stick to each other and form tactoids that deform RBC
Thalassemia
Anemic condition linked to decreased expression level and amount of beta-globin gene variants.
both sickle cell anemia and thalassemias were categorized under...
hemoglobinopathies
- variation in sequence, structure, stability, expression of Hb
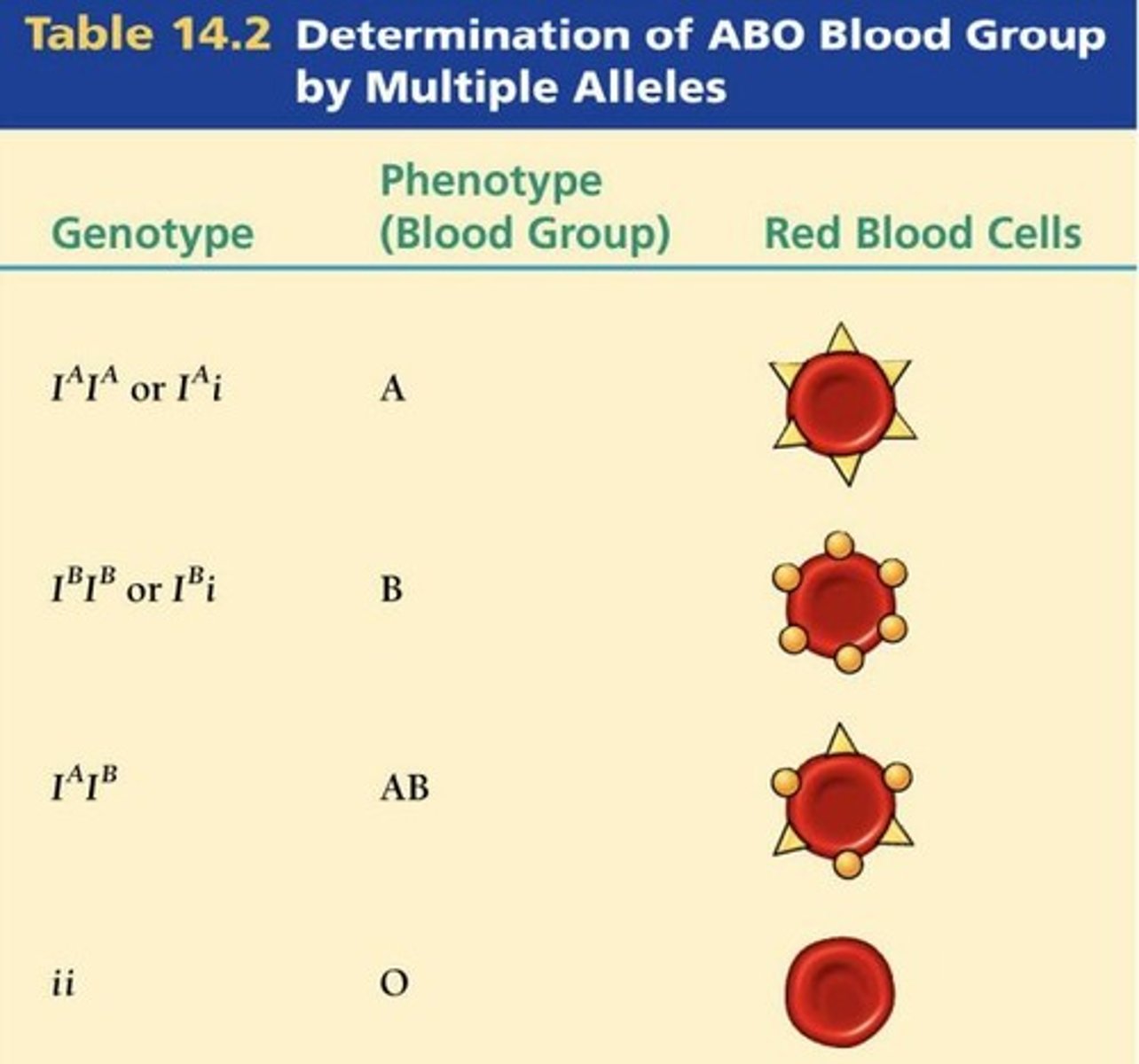
Codominance
Both alleles expressed equally in phenotype.
ABO gene encodes...
glycosylation enzyme and ceates glycoproteins and glycolipids on the surface of RBC (antigen)
benefit of sickle cell anemia and thalassemia
- RBC are host cells for part of malaria parasitic life cycle --> but with HbS they are poor host (alter cytoskeleton) --> prevent parasitic proteins from working properly and completing their life cycle
- thalassemia reduce infectivity of RBC and inc clearance of infected cells
Blood quantum
Measure of heritage/ ancestry is counted
Hypodescent
Classification of mixed heritage as inferior (lower status)
One drop rule
1/32 black legally defines black identity.
Second-generation cut-off rule
Non-identity with only ¼ Indian blood.
Blood purity
Concept of inherent superiority of bloodlines.
Eugenics movement
Defined racial purity to justify oppression, reinforce existing hierarchy, promote superior races
Genotype
Specific DNA sequence for a trait.
Phenotype
Physical expression of genotype influenced by environment.
Gene
DNA sequence that codes for proteins.
Allele
Specific version of a gene.
Ploidy
Number of chromosome sets in a cell.
- Haploid: one copy (1n), Diploid (2n), aneuploid: uneven copy sets
Homozygous vs heterozygous
homozygous: Two identical alleles at a gene locus.
heterozygous: 2 diff allele at a gene