Sem 1 ICA: Foundation Concepts
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
inspiratory capacity
all the air that can be inspired at rest
IC equation
VT + IRV
Functional residual capacity
air remaining in lungs after normal expiration
FRC equation
ERV + RV
vital capacity
all the air you're capable of moving
VC equation
TV + IRV + ERV
total lung capacity
all air in the lungs after maximal inspiration
TLC equation
TV + IRV + ERV + RV
Functions of the respiratory system
1) Gas exchange between atmosphere and blood
2)Homeostatic regulation of pH
3)Protection against inspired pathogens/irritating substances
4)Vocalization
5)Metabolic functions
Conducting zone function
Brings air in/out. Before it reaches gas exchange area, it's warmed, humidified & filtered
Respiratory zone function
Gas exchange
Respiratory zone
Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts & alveolar sacs
Ventilation requirements
1)Hollow conducting system
2)Pump (respiratory muscles)
3) Volume change
4)Pressure difference
5)Air flow
Boyle's Law
Pressure that a gas exerts in a container is inversely proportional to the volume of the container
What is Pb at sea level
760 mmHg
Tidal volume
1)Volume of air flowing into lungs during inspiration
2)Volume of air flowing into lungs during expiration in a normal resting respiratory cycle
Minute volume (total pulmonary ventilation)
Total volume of air that enters/exits the respiratory system per minute
Dalton's Law
Total pressure exerted by a mixture of non-reactive gases = sum of the partial pressures
Pressure gradient for oxygen
60 mmHg
Pressure gradient for carbon dioxide
6 mmHg
The driving force for diffusion in gas exchange
partial pressure difference
Parenchyma cells
responsible for the organ's specialized functions
Stroma cells
Cells that have a supporting role in the organ
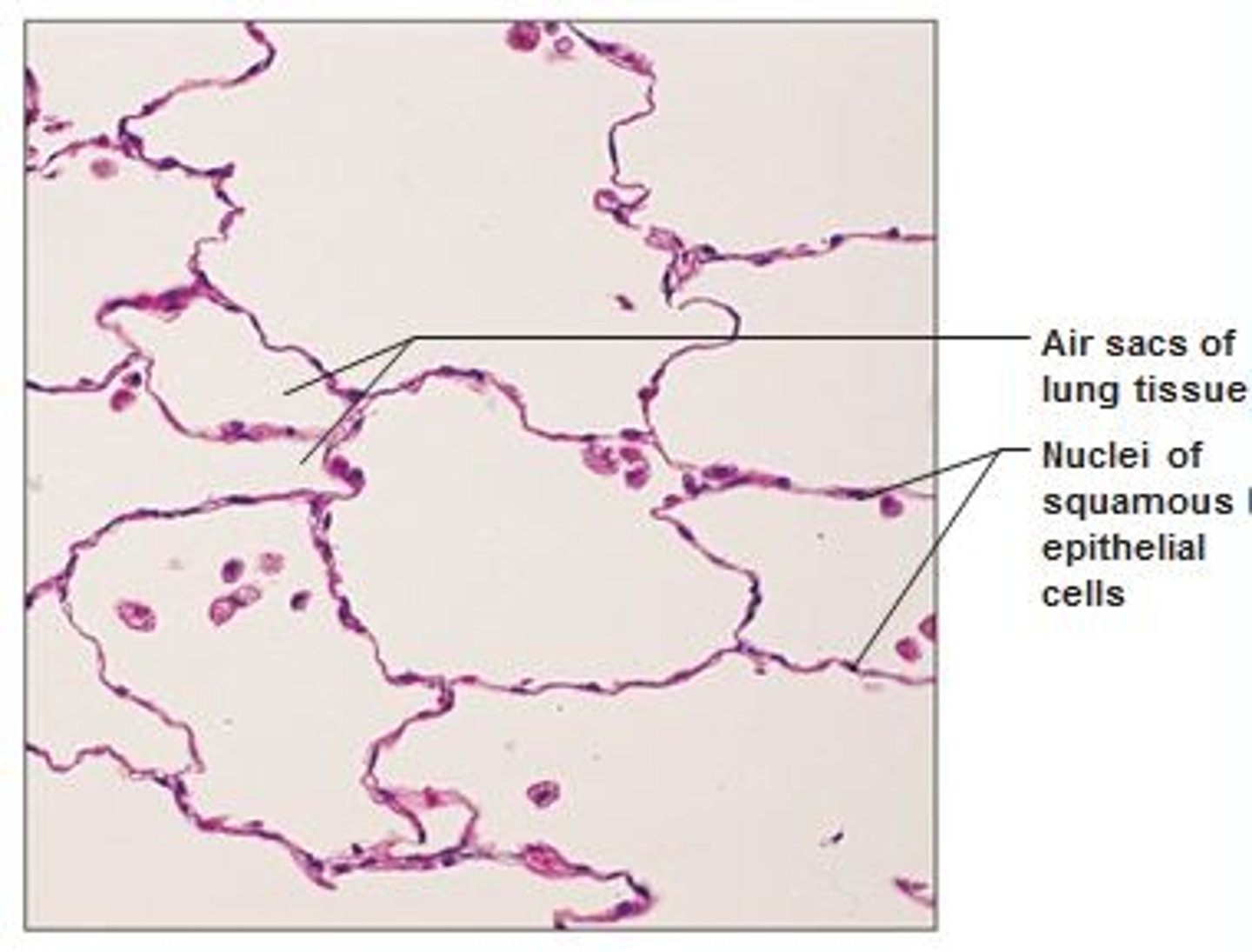
Where is simple squamous found
alveoli, endothelium and mesothelium
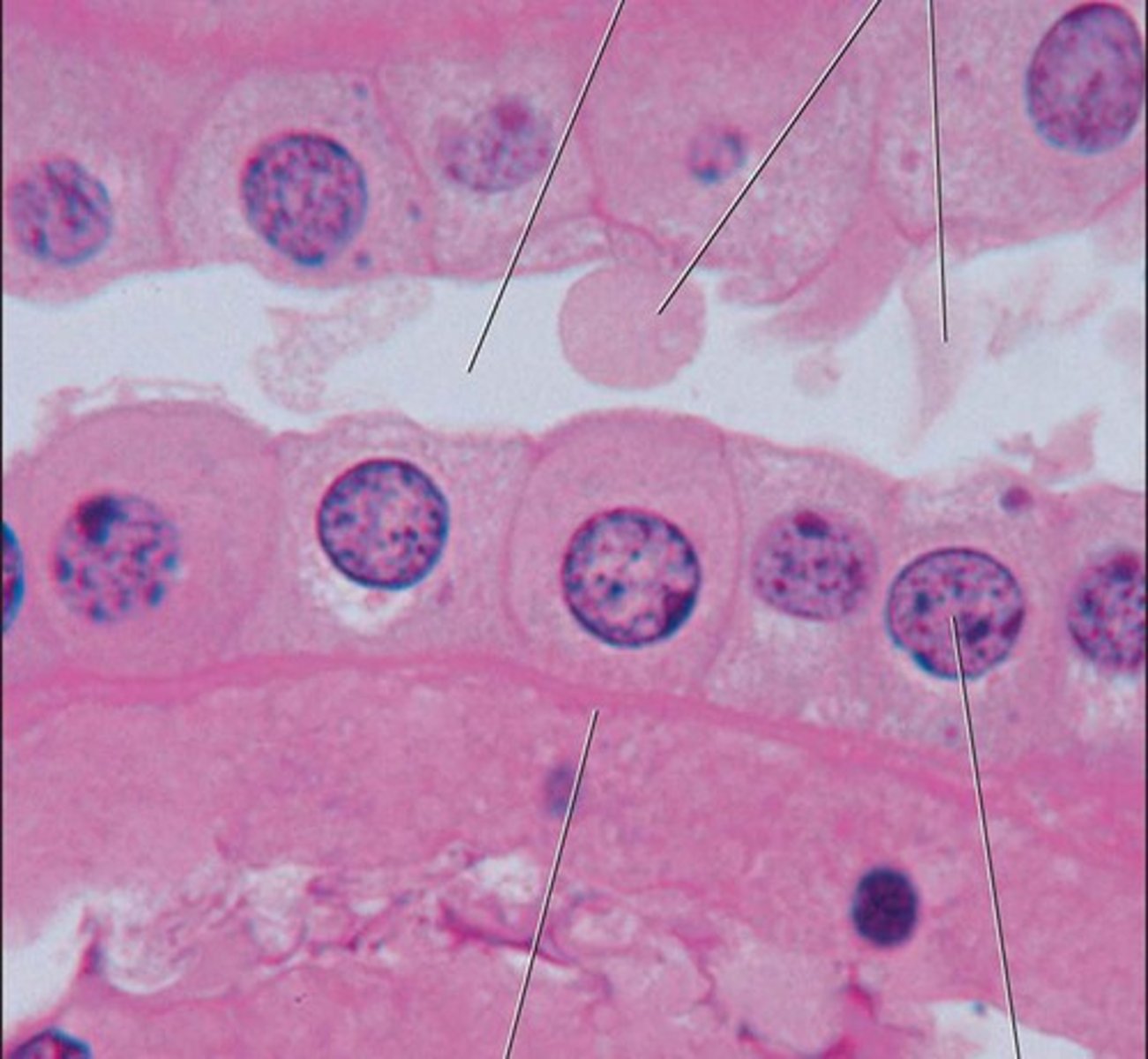
Where is simple cuboidal found
Tubules of kidney, ovary, bile duct and thyroid gland
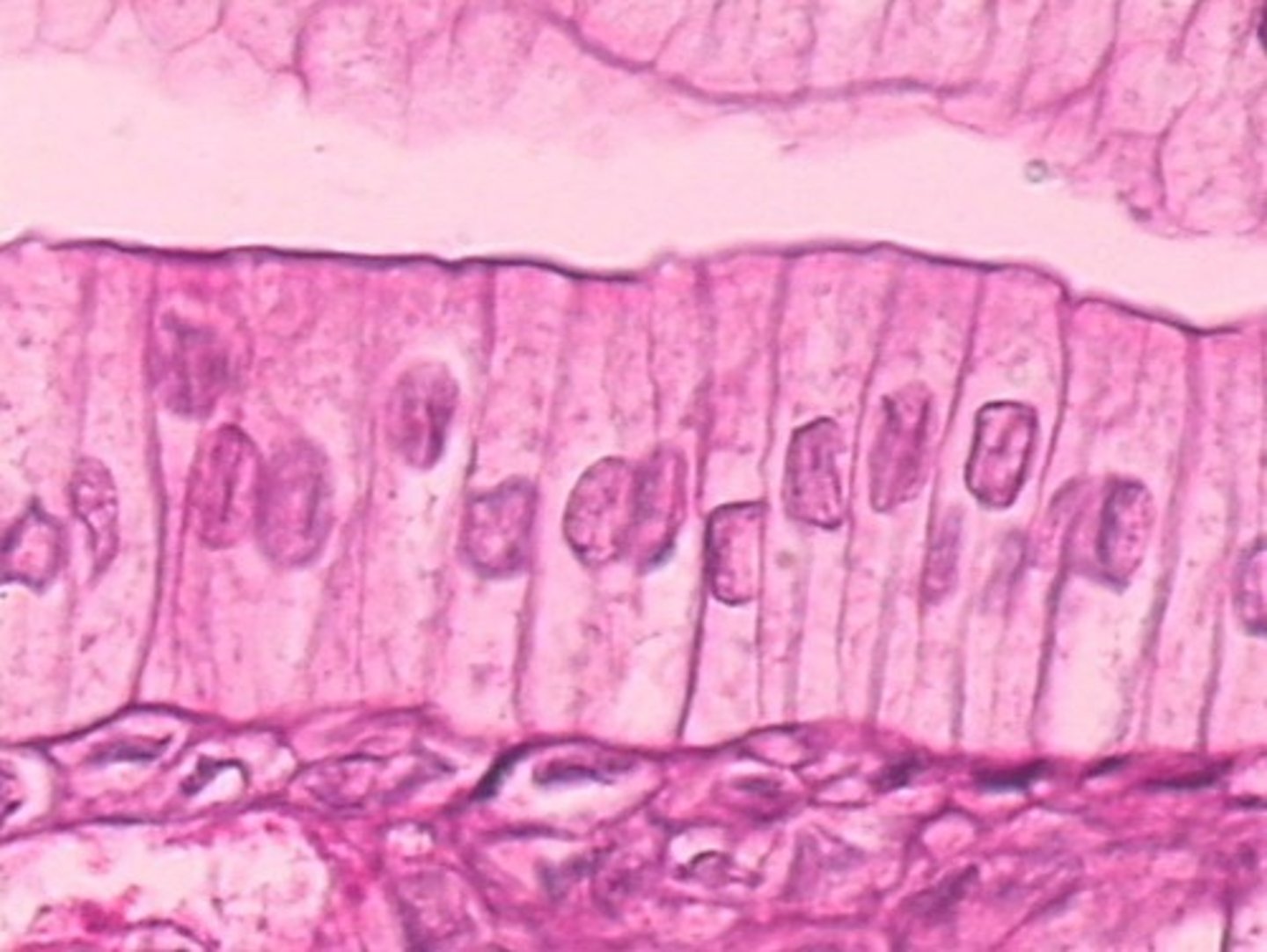
where is non-ciliated simple columnar found
digestive tract (stomach, gallbladder, collecting ducts of kidneys)
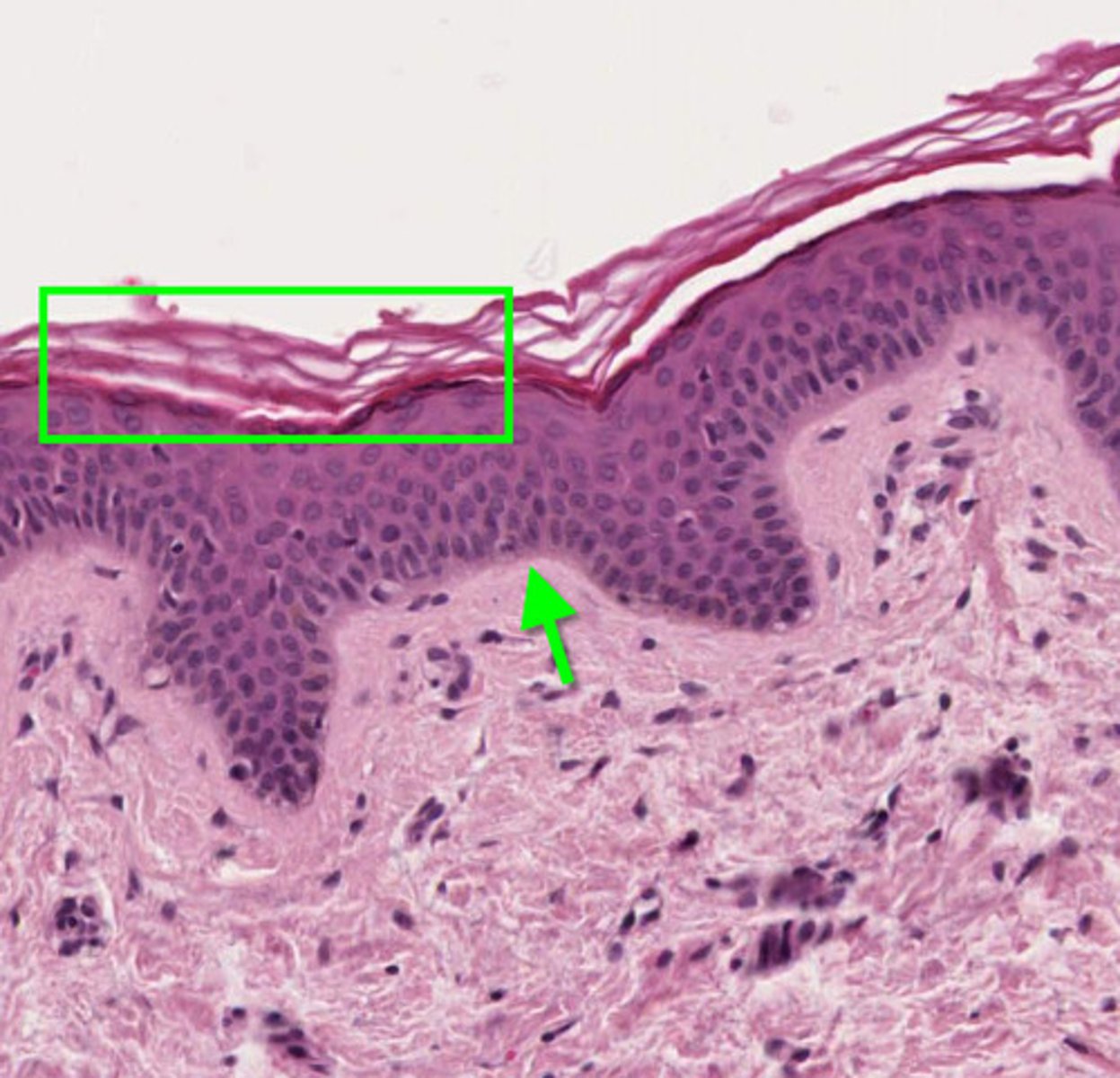
Where is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
epidermis and anal canal
Where is non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
oral cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, ectocervix, vagina, urethra, upper part of anal canal
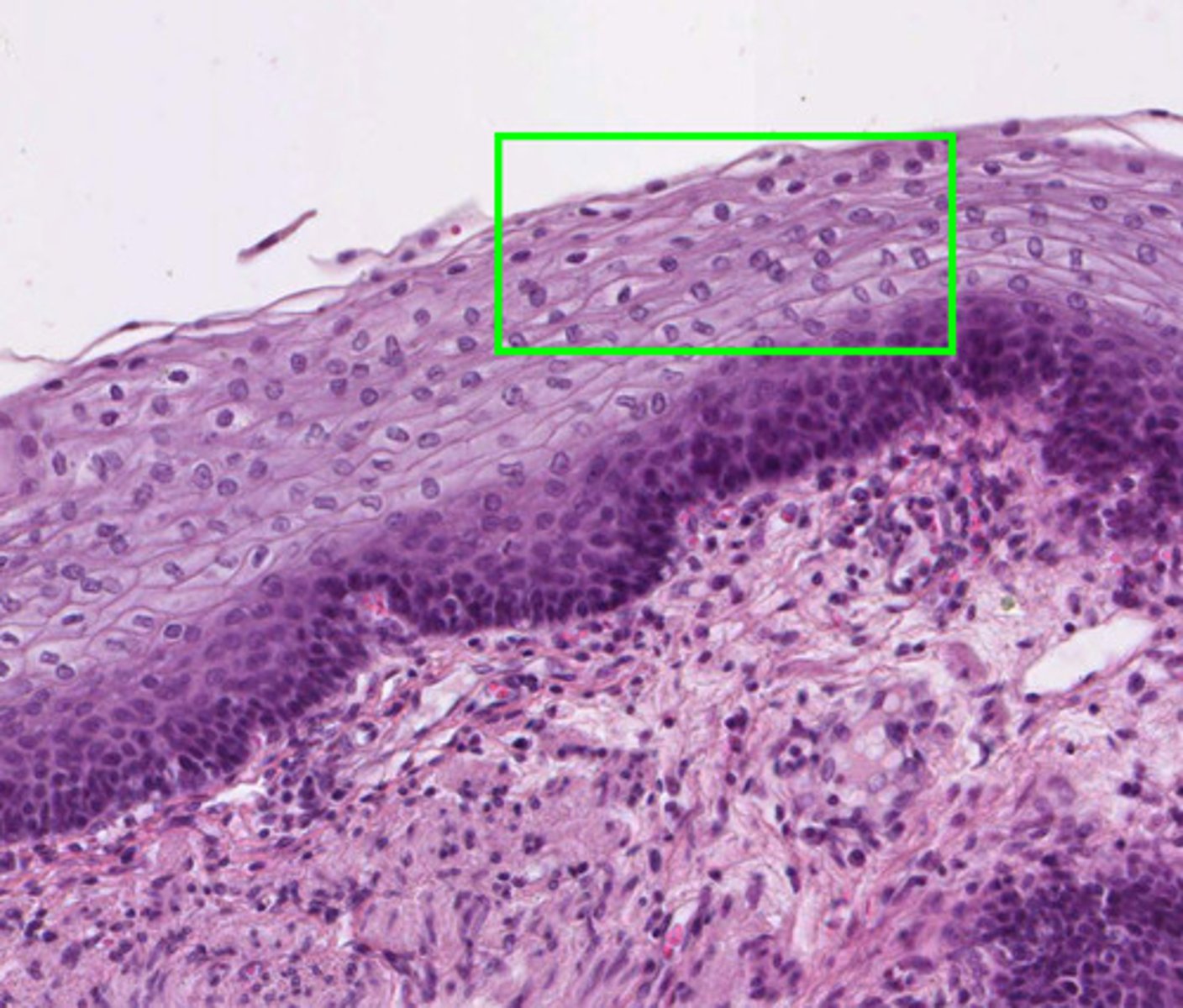
Where is stratified cuboidal found?
Ducts of salivary glands
What is the function of stratified columnar?
secretion and protection
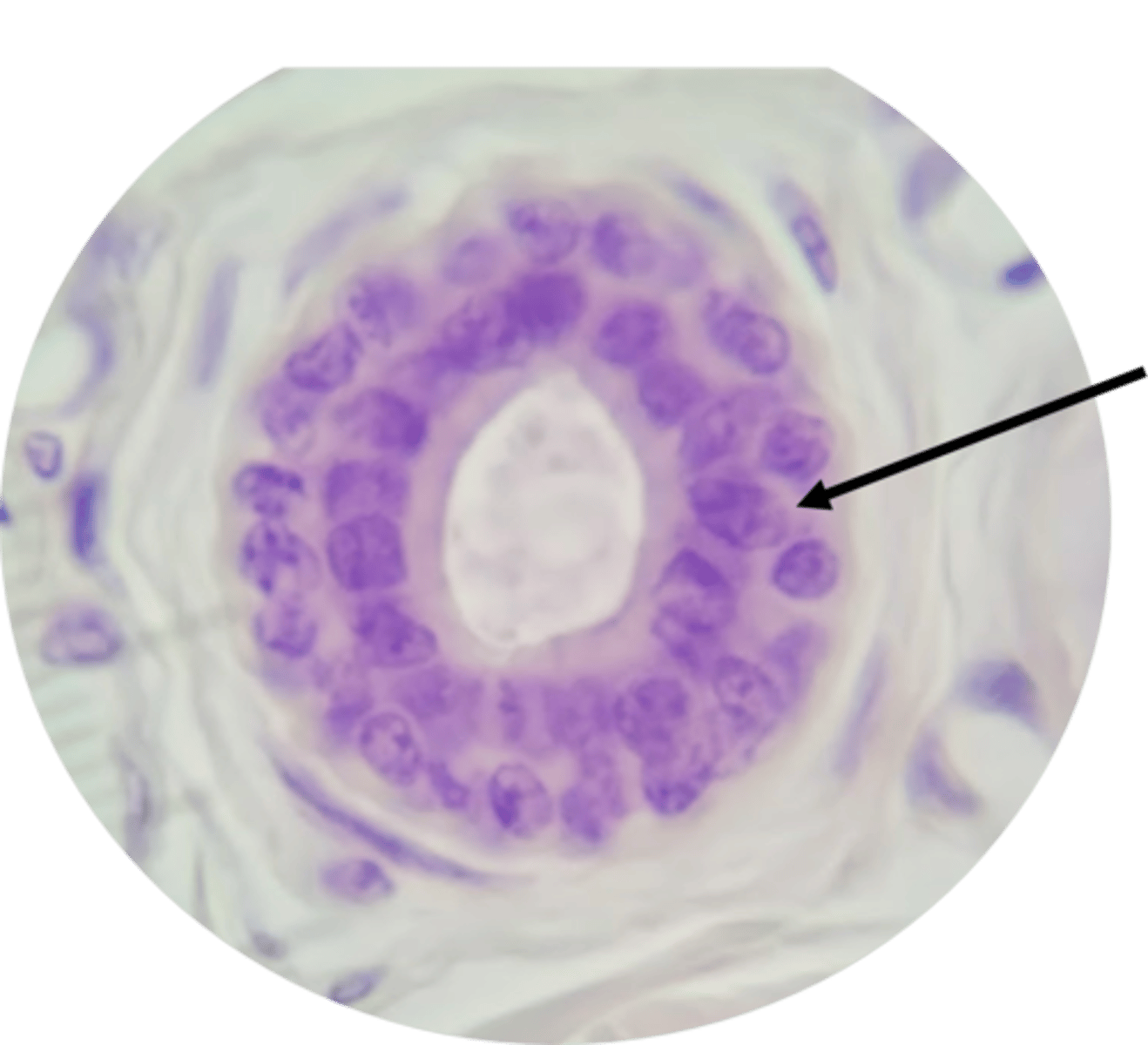
Where is non-ciliated pseudostratified columnar found?
In the male gonad
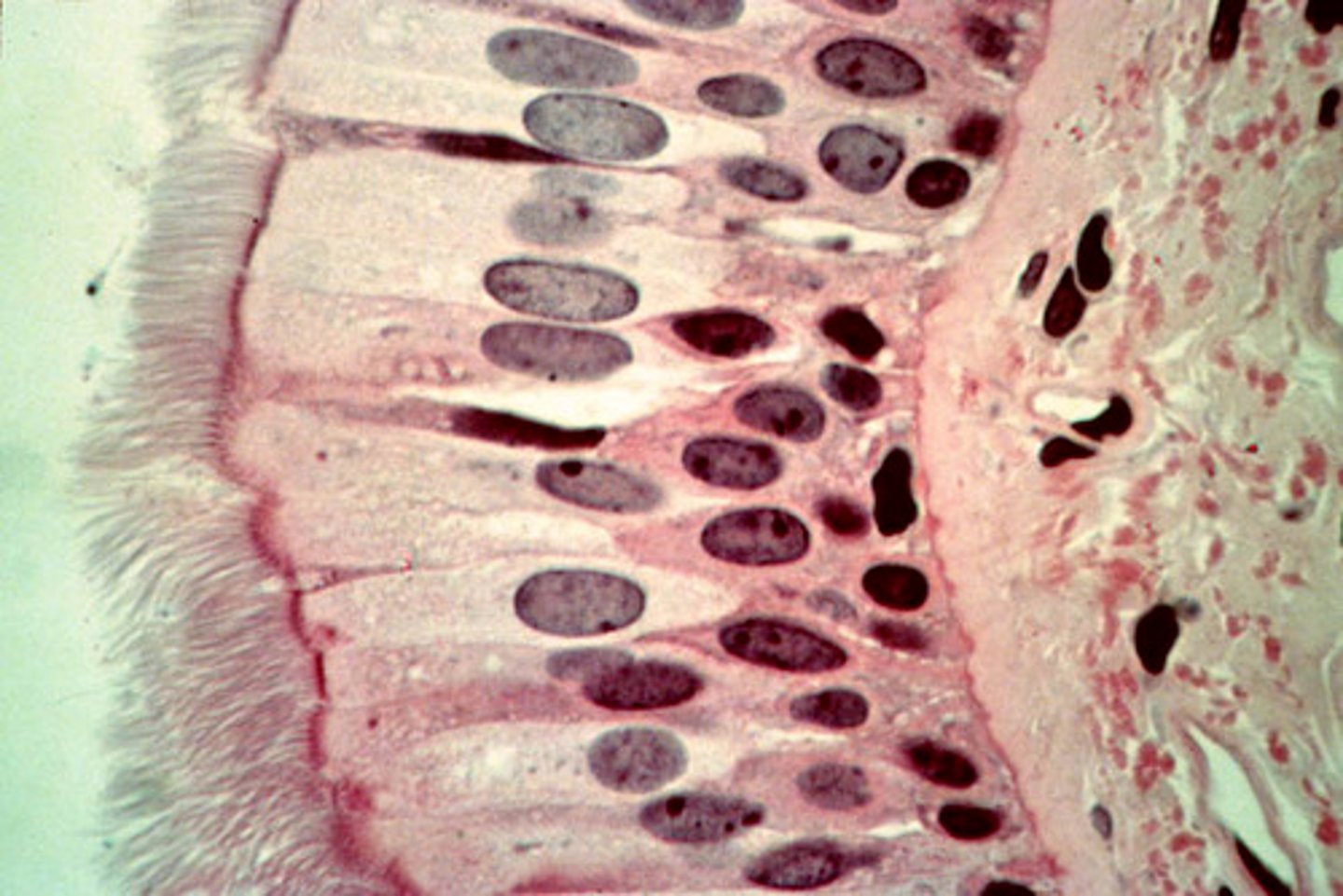
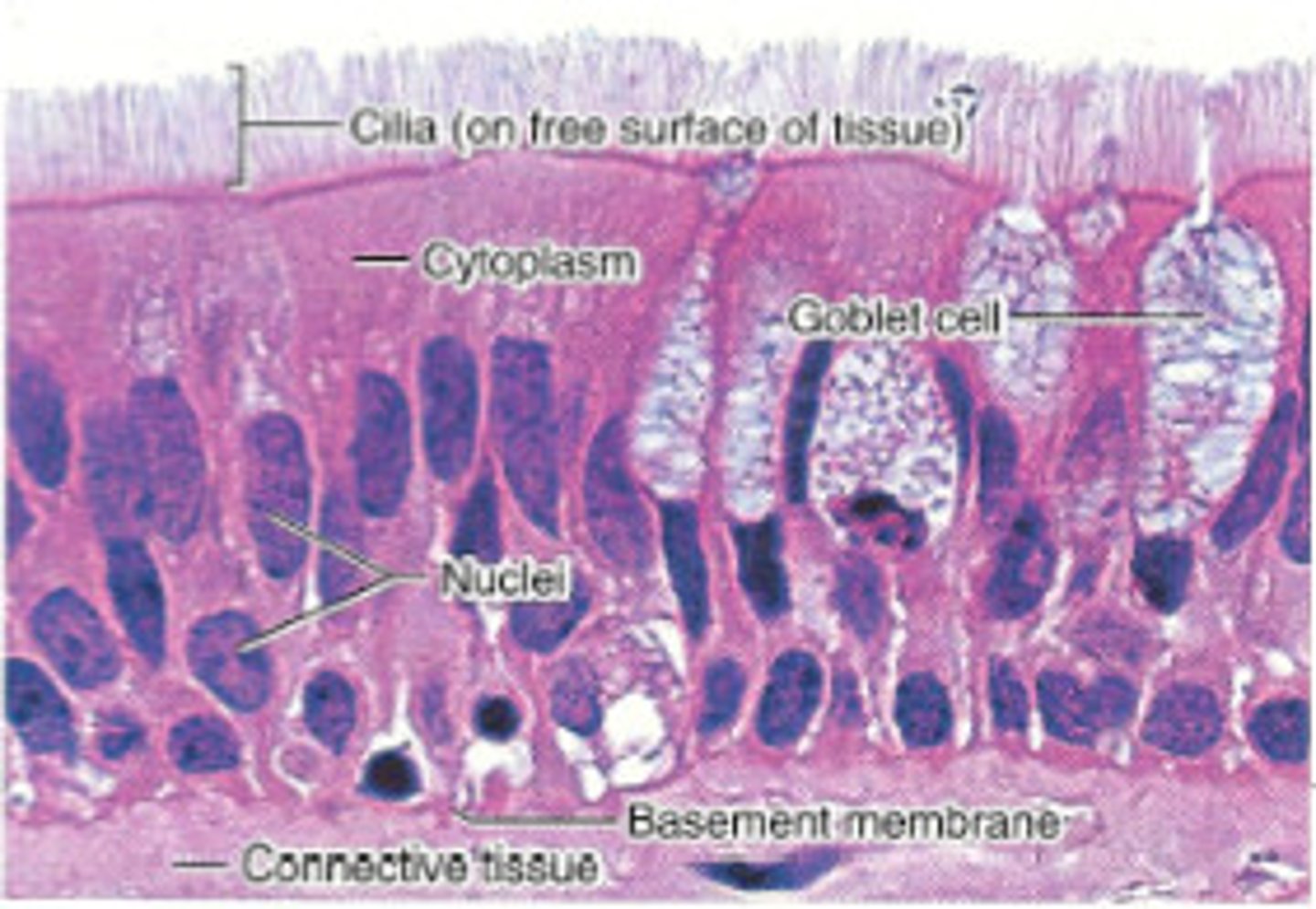
Where is ciliated pseudostratified columnar found?
In the trachea (mucociliary escalator)
What does the surface of distended/non-distended transitional look like?
Distended: scalloped. Non-distended: flattened
Epithelial metaplasia
Reversible conversion of one differentiated epithelial cell type to another differentiated epithelial cell type within the same tissue/organ
What are the stimuli of epithelial metaplasia?
Irritation/inflammation, environmental changes and nutritional
Barrett's oesophagus
Chronic GERD= inflammation
Distal oesophagus: Stratified squamous epithelia replaced by simple columnar with goblet cells
What are the 4 intercellular junctions found
1)gap junctions
2)hemidesmosomes
3) adhering junction (belt, desmosome)
4) tight junction
What junction is attacked in food poisoning and asthma attacks?
tight junction
What happens when viruses, bacteria, pathogens attack junctions?
Destruction of junctional complexes between epithelial cells =protective functions compromised
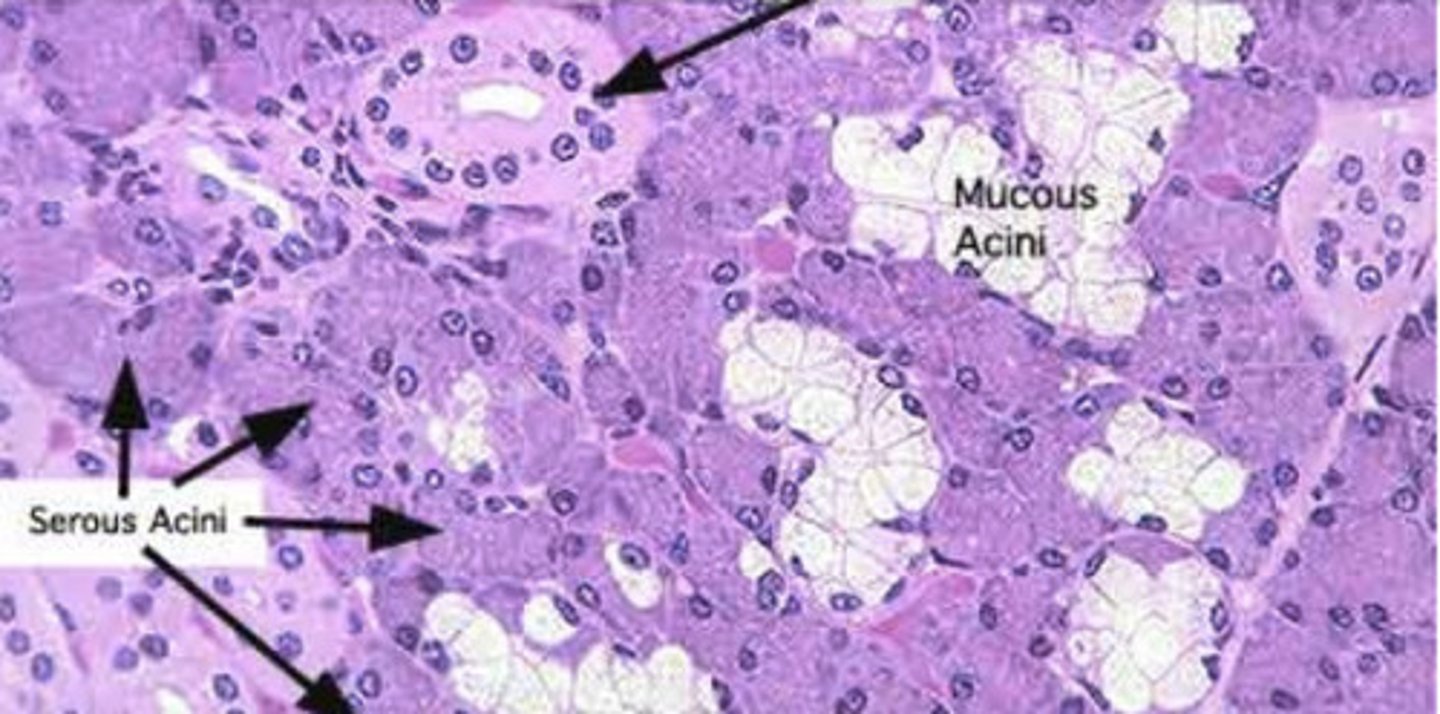
What is the function of serous cells?
enzymatic action
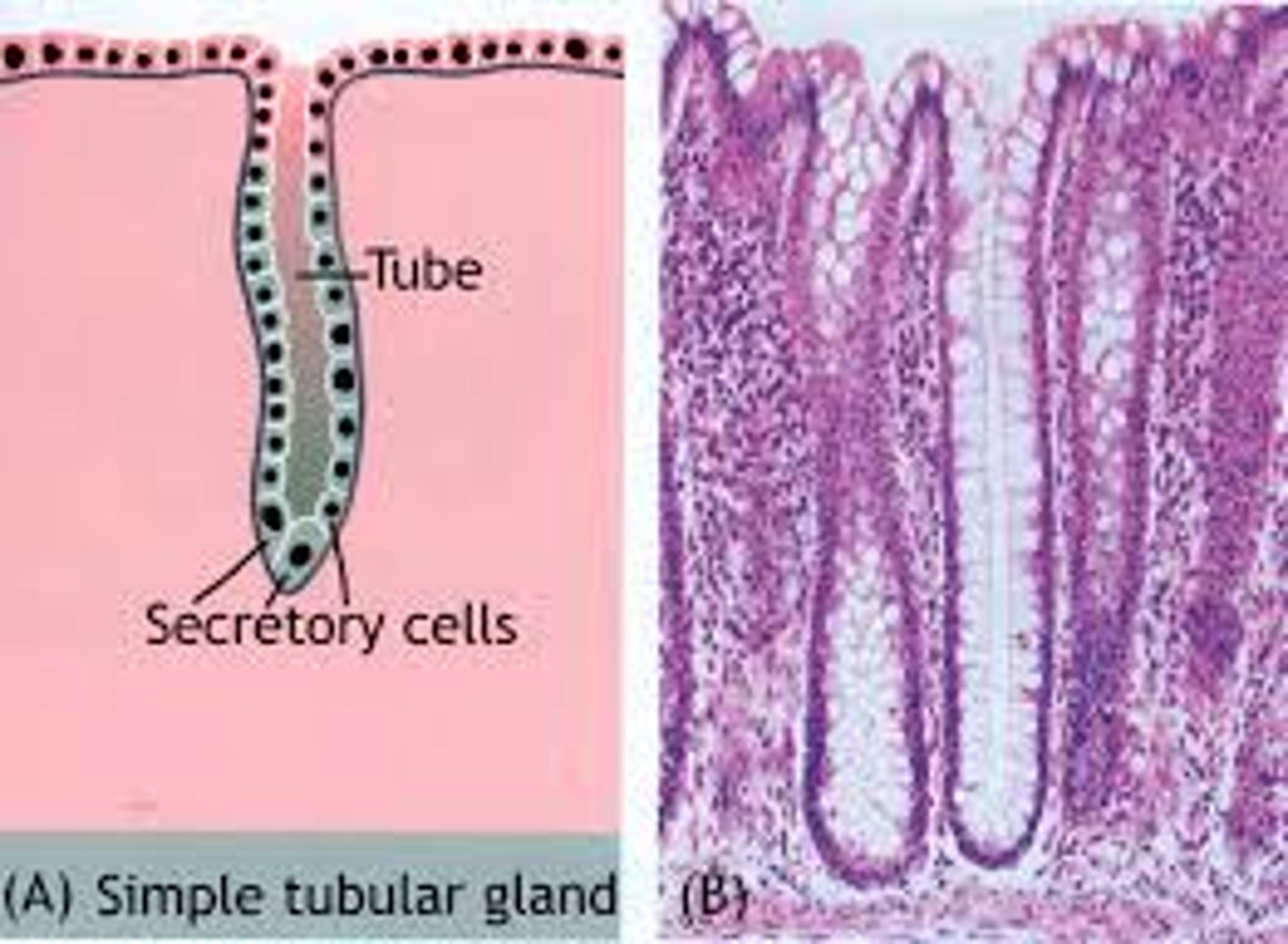
Where are simple tubular glands found?
small intestine and colon
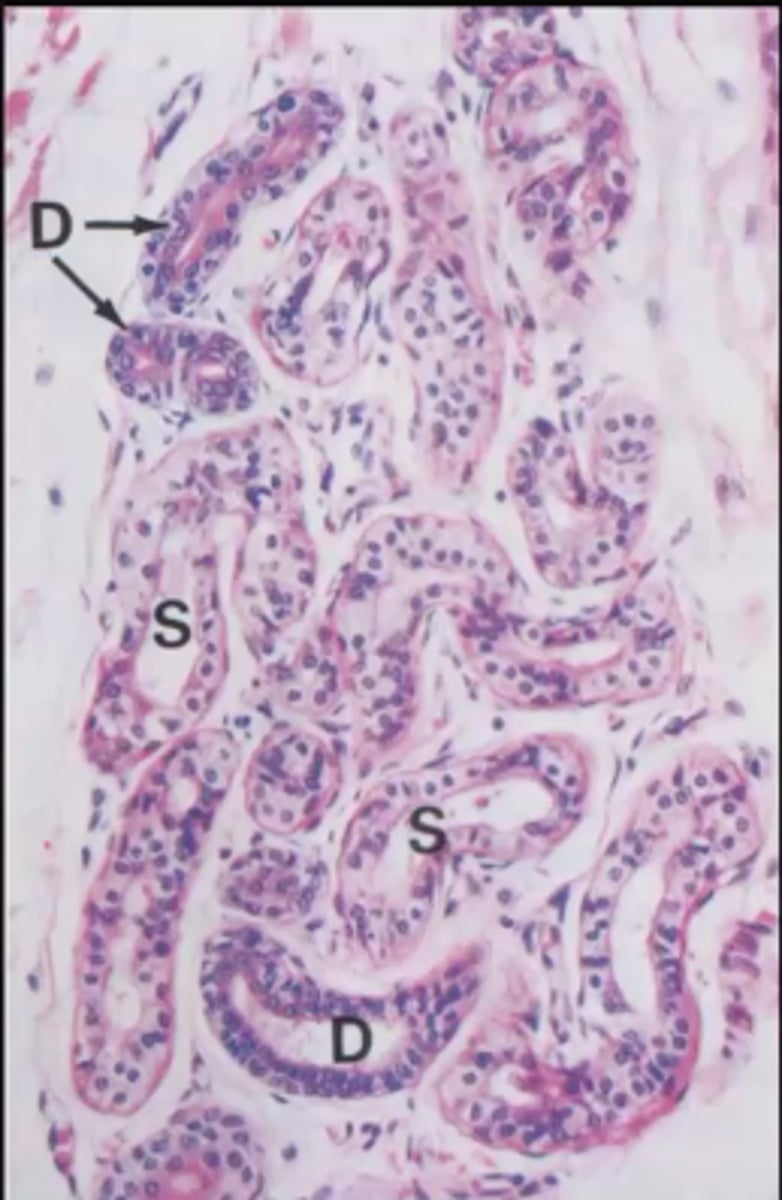
Where are simple coiled tubular glands found?
sweat glands
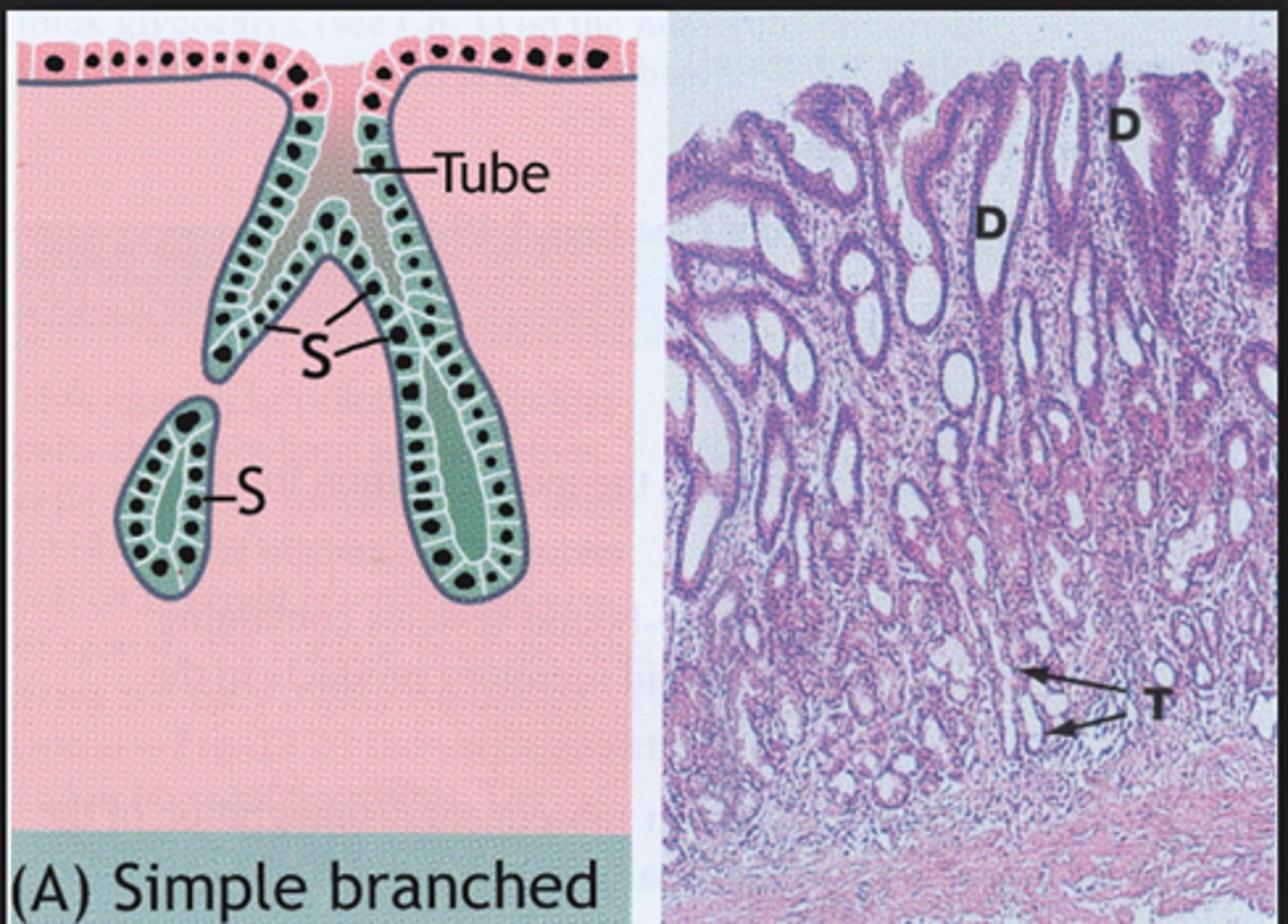
Where are simple branched tubular glands found?
stomach
Where are simple acinar glands found?
penile urethra
Where are simple branched acinar glands found?
sebaceous glands of the skin
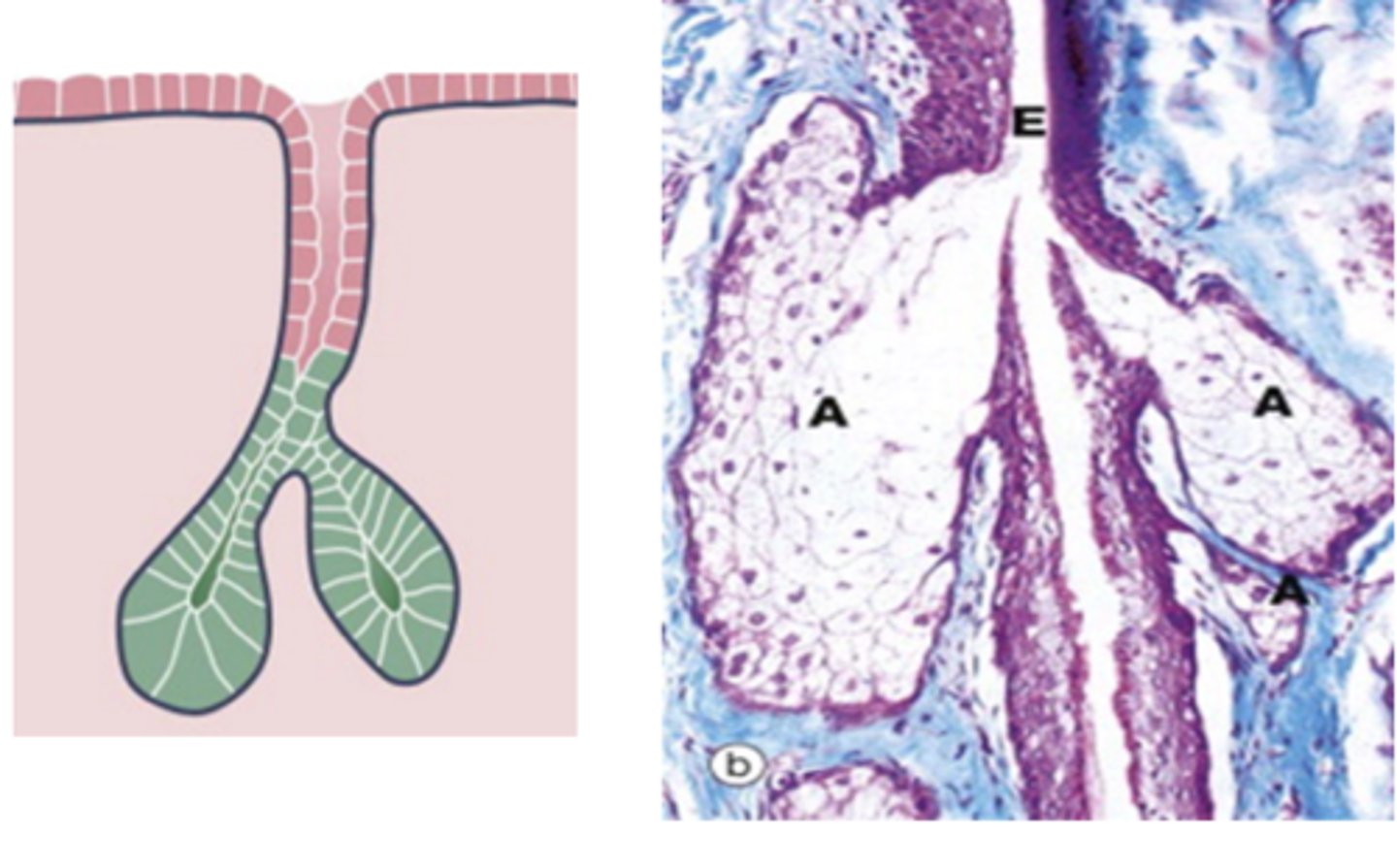
Which glands are involved with acne vulgaris?
simple branched acinar glands
Acne vulgaris
At puberty: upsurge of testosterone = excessive holocrine secretion of sebum & keratin = blockage of glandular ducts = localized inflammation
Where are compound branched tubular glands found?
Duodenum
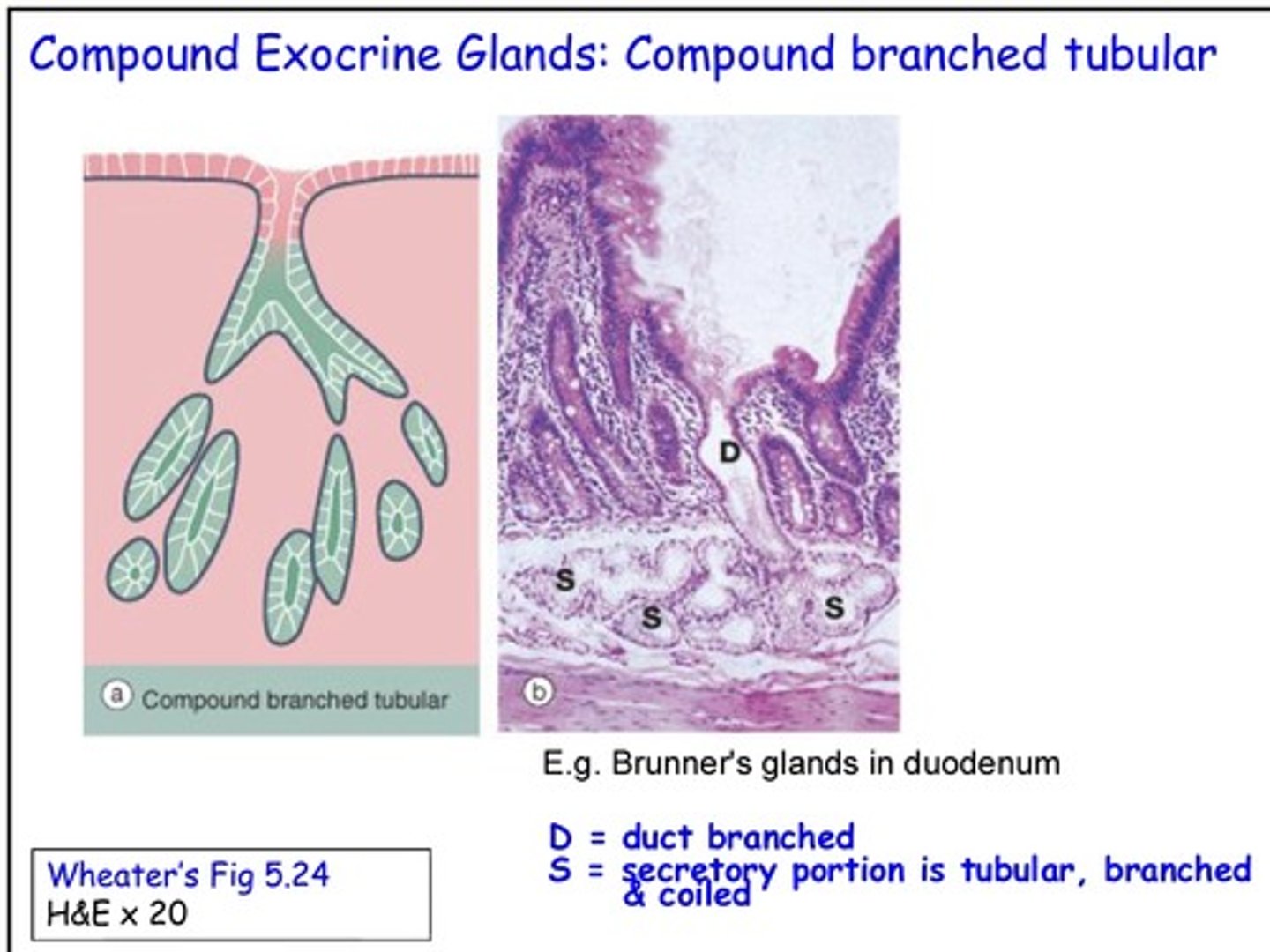
What is the function of compound exocrine glands?
Secretion
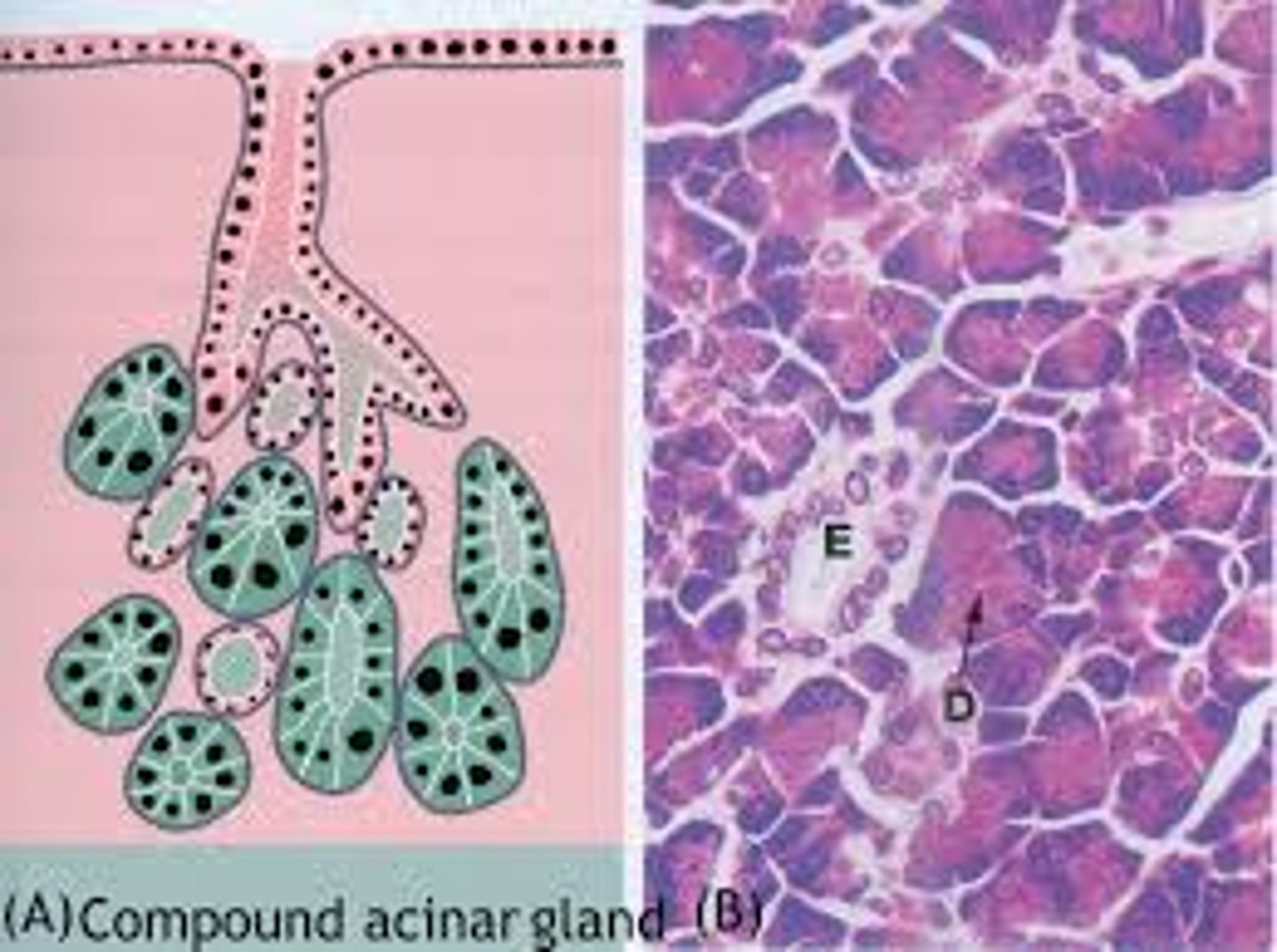
Where are compound acinar glands found?
Pancreas, mammary glands
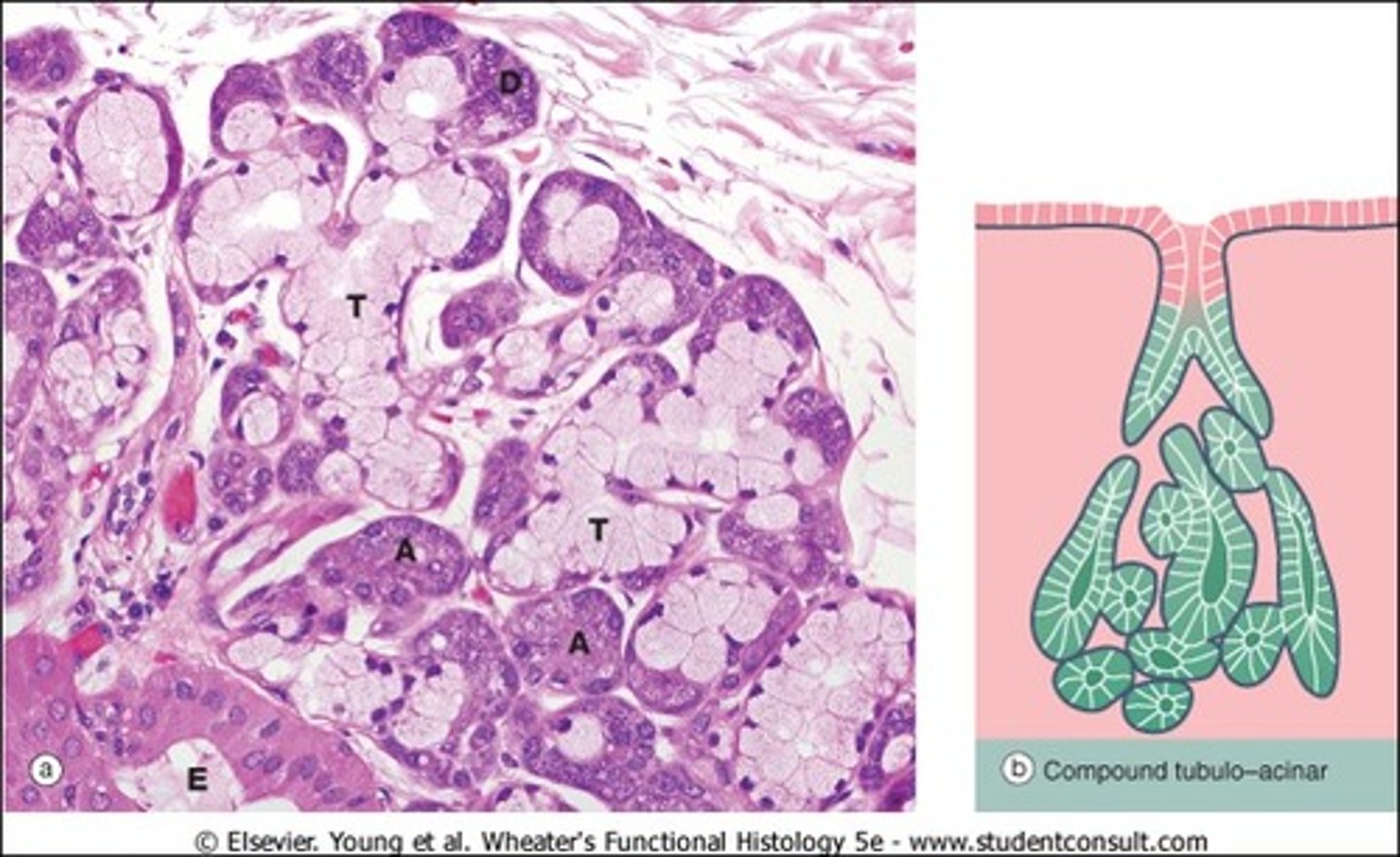
Where are compound tubulo-acinar glands found?
Salivary/prostate glands
Difference between FRC and RV
RV: # air that cannot be expelled from the lungs at the end of a forced expiration
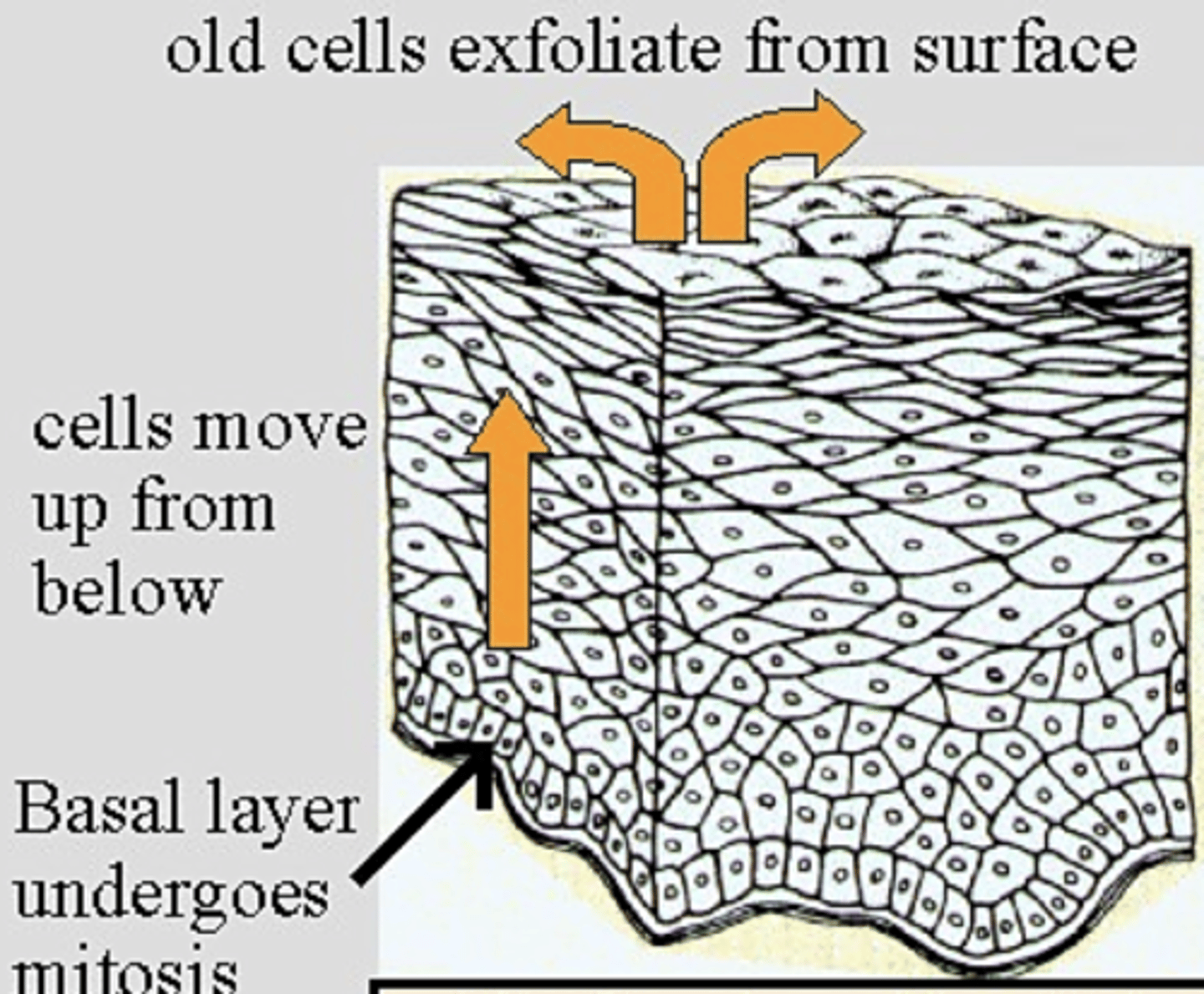
Where does cell exfoliation occur?
1)Skin epidermis & skin appendages
2)Surfaces of internal cavities & passages
3)Major exocrine glands & glandular ducts
Epimysium
surrounds all the fascicles in a muscle
Perimysium
surrounds a fascicle (a bundle of muscle cells/myocytes)
Endomysium
surrounds a myocyte
Myocytes
composed of longitudinally-arranged myofibrils
Myofibril
a sub-unit of myocytes. Composed of a bundle of myofilaments
What does a triad contain?
2 terminal cisternae and 1 T tubule
How many triads per sarcomere? (# of terminal cisterns)
2
Triad function
ECC
Myofibril structure
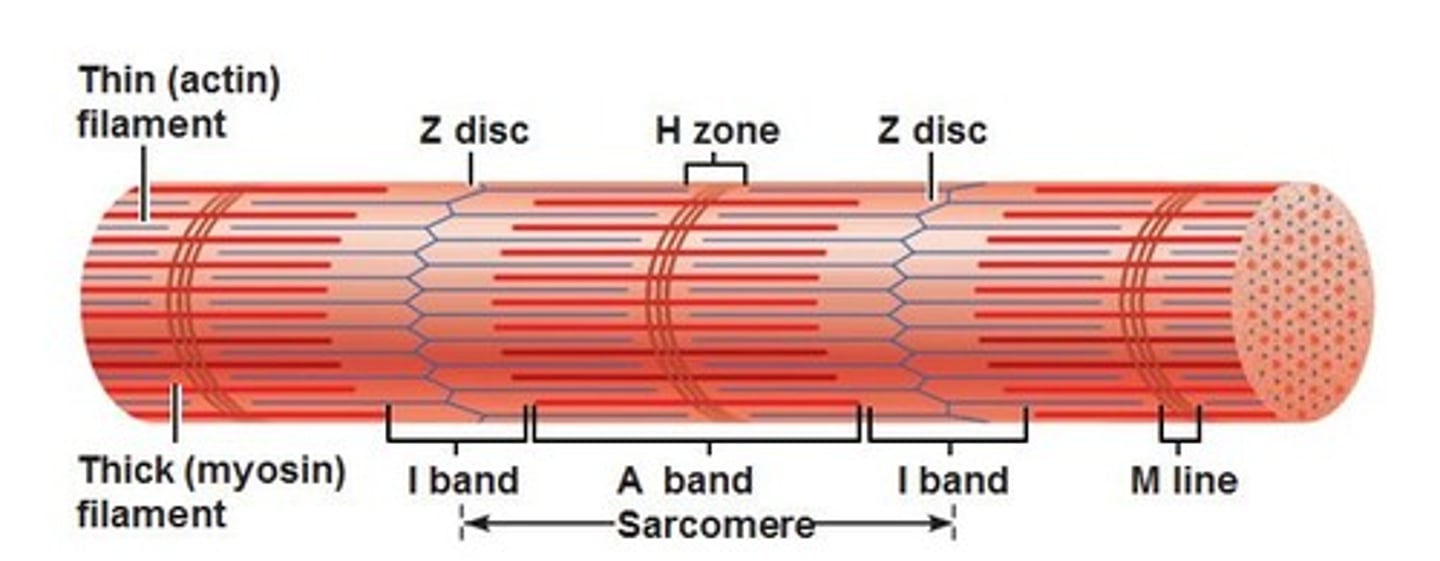
Why are myosin heads in opposite directions?
To form cross-bridges
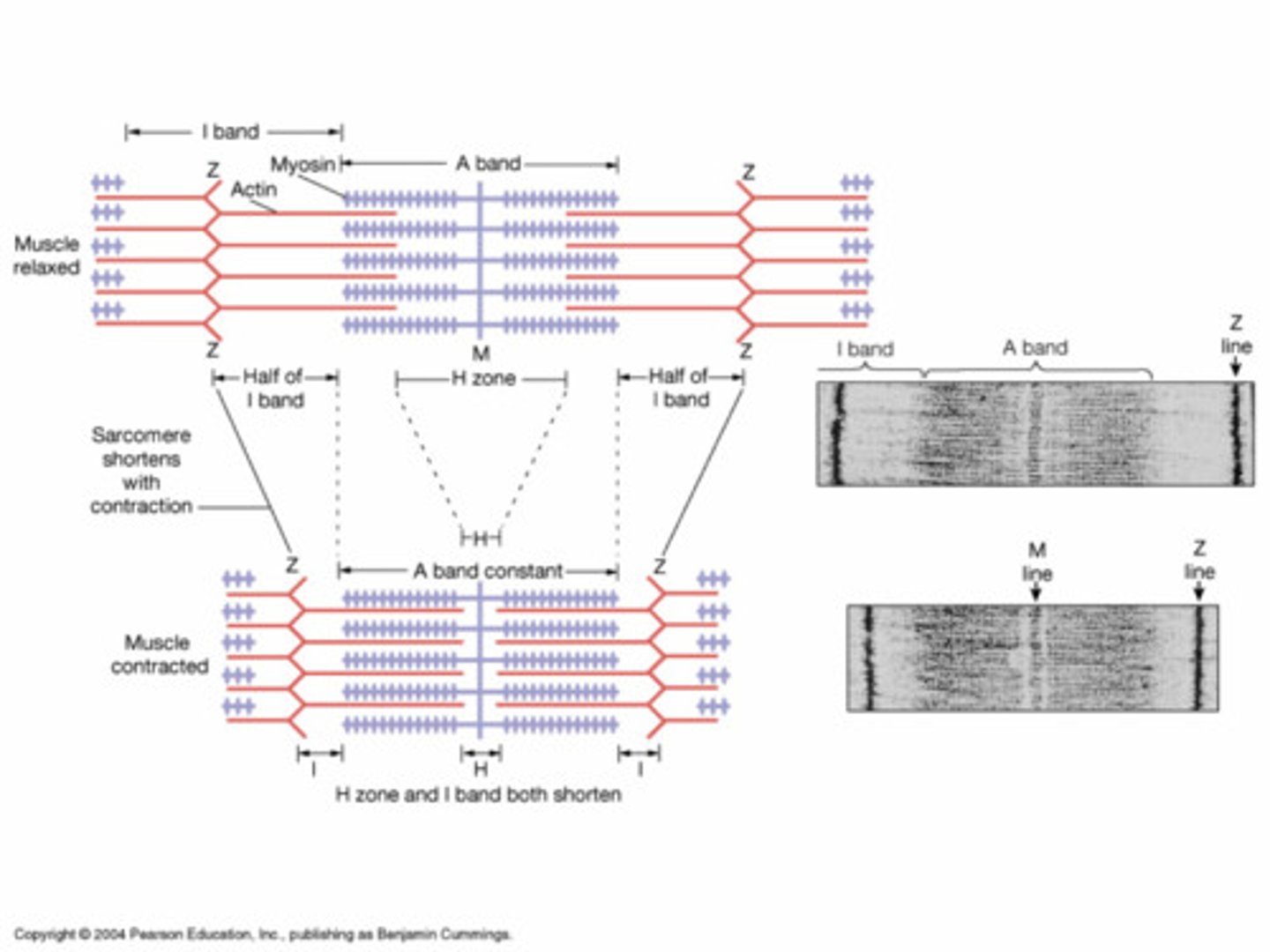
Relxed sarcomere
H zone and I band are relatively wide
Where is slow twitch type I found?
back
Where is fast twitch type IIA found?
major muscles of leg
Where is fast twitch type IIB found?
extra-ocular muscles, limb-digit muscles
Muscle atrophy
muscle mass decreases in size
How many diads per sarcomere? (# of terminal cisterns)
1
Transverse intercalated disc
Has desmosomes and fascia adherens
Lateral intercalated disc
Has gap junctions
What happens to cardiomyocytes in an MI?
They're replaced by scar tissue
SR in triads/diads
triad: complex,abundant
Location of T tubules in triads/diads
Triads: A-I junction
Diads: Z disk
Smooth muscle cell
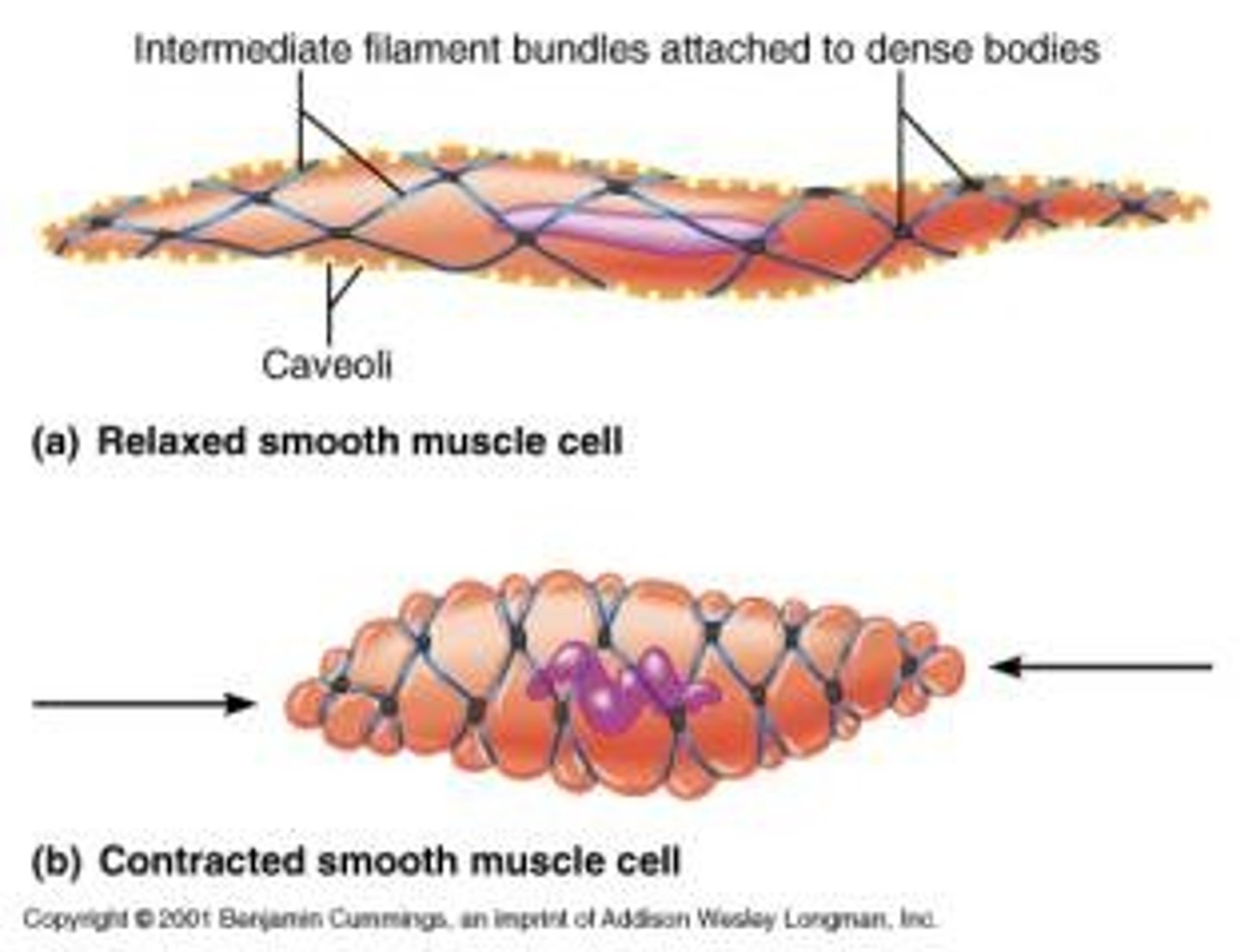
Calveolae
invaginations
Dense bodies
Allows smooth muscle to generate intracellular contractile tension; analogous to z-line
Contractile protein of smooth muscle
calmodulin
Multi-unit smooth muscle
Stimulated independently, but function as a single unit
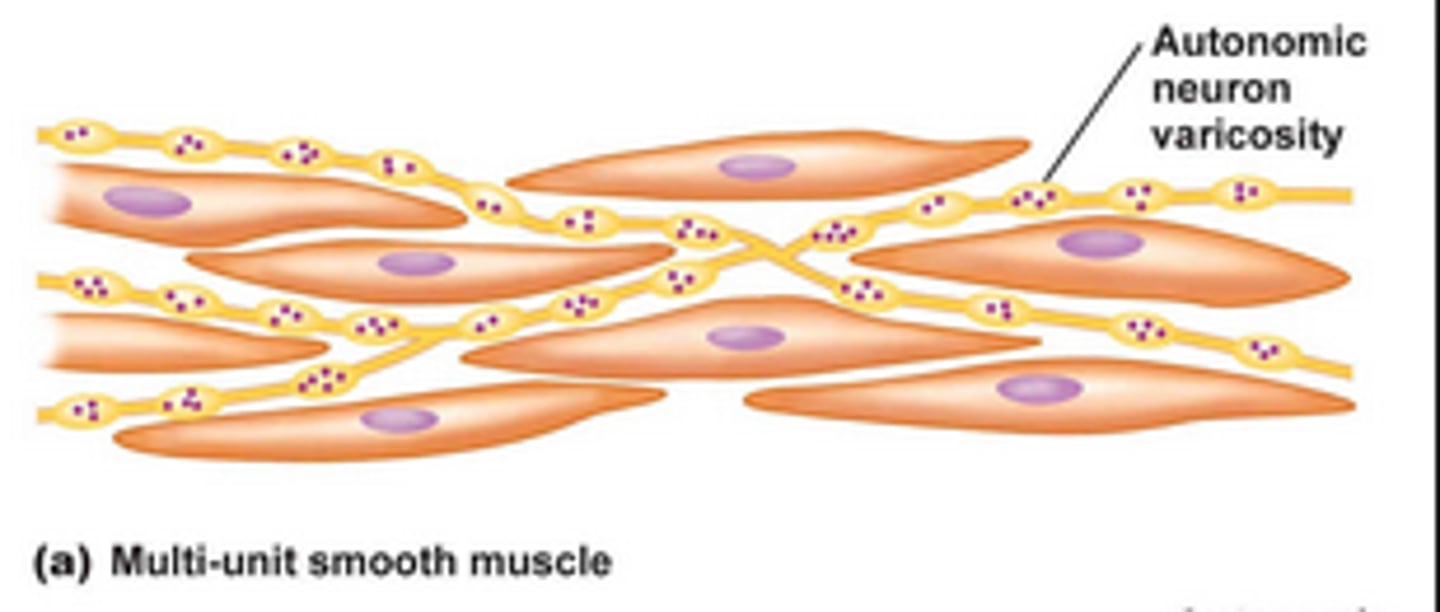
Where is multi unit smooth muscle tissue found?
iris and epididymis
Single-unit smooth muscle
Smooth muscle with gap junctions linking the cells together so they function as a unit
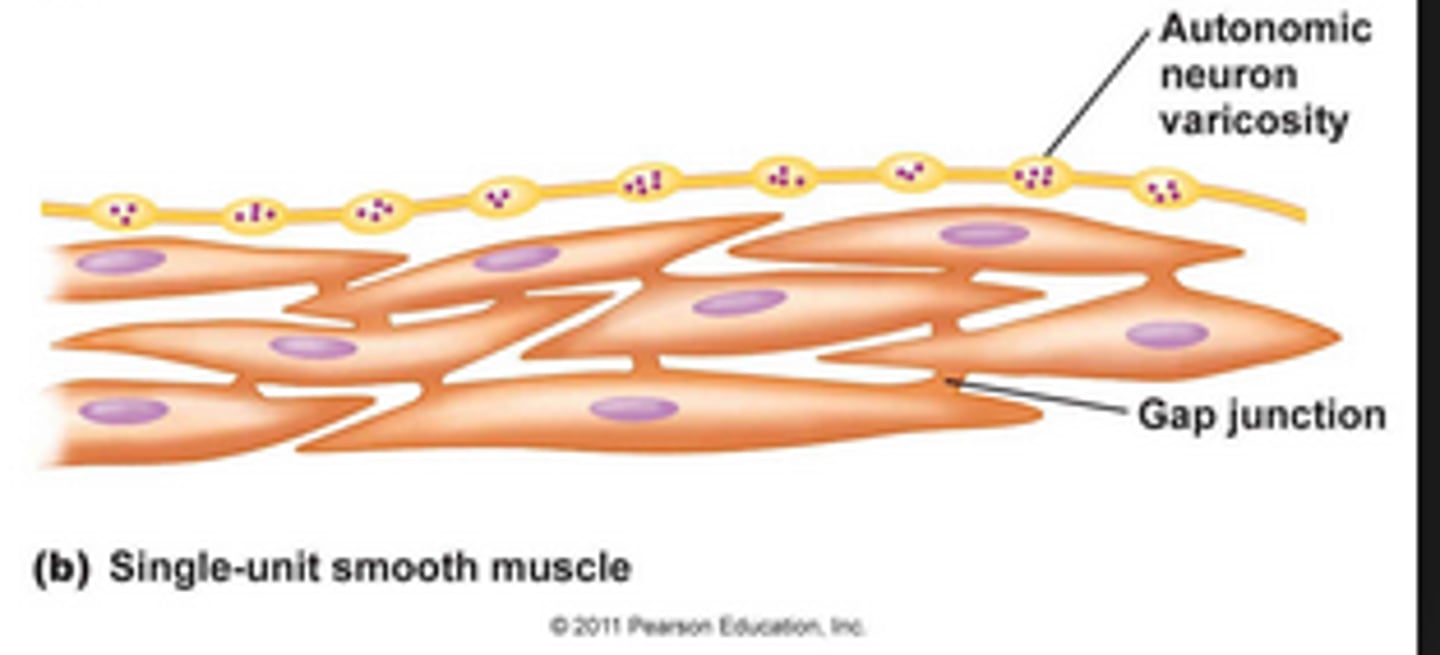
Where is single unit smooth muscle found?
hollow organs
Leiomyomas
Benign tumors of smooth muscle fibers.
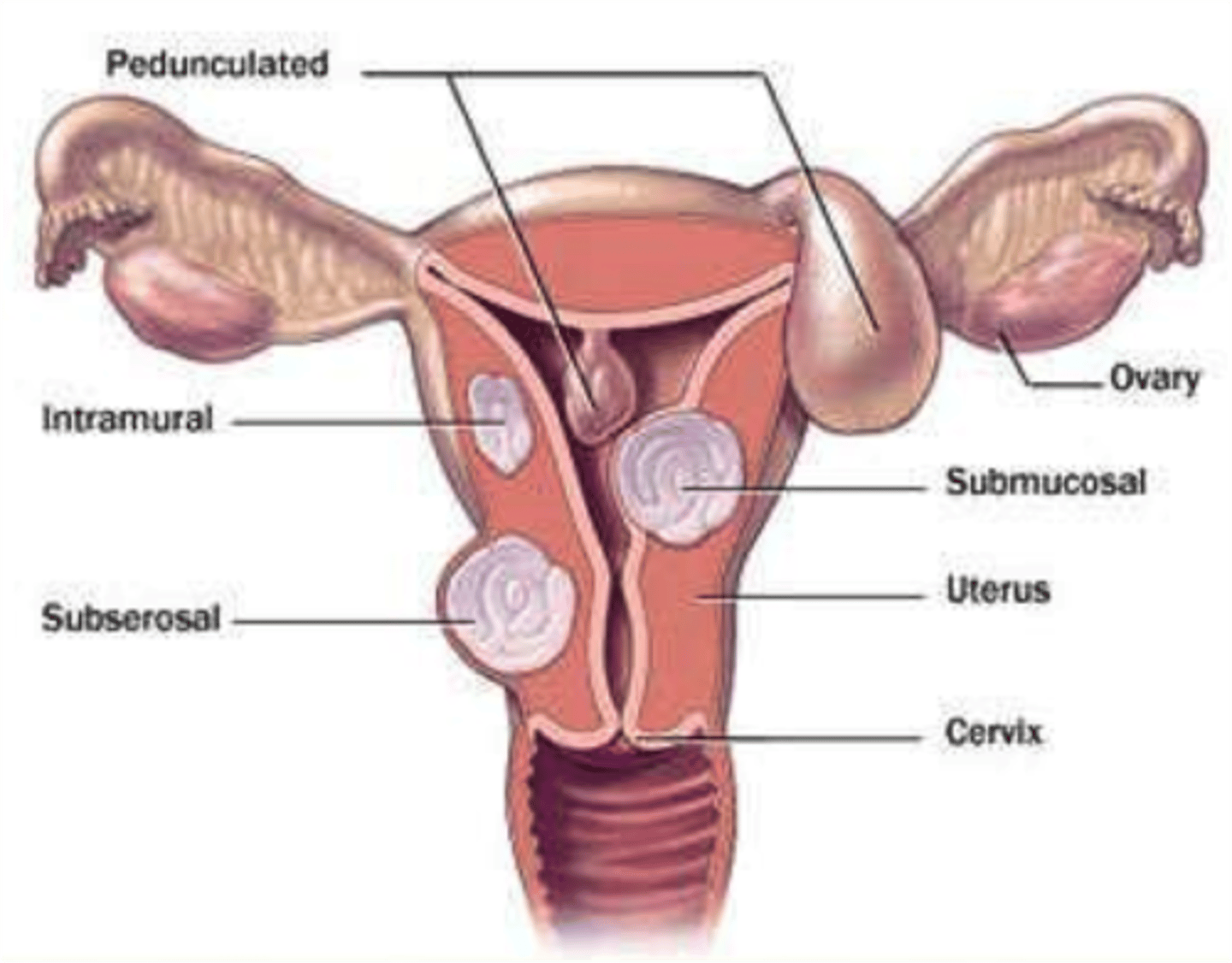
Possible causes of leiomyomas
1) Pregnancy
2) Family history
3) Hormonal changes
primary microcephaly
AR, missense mutation of CDK6
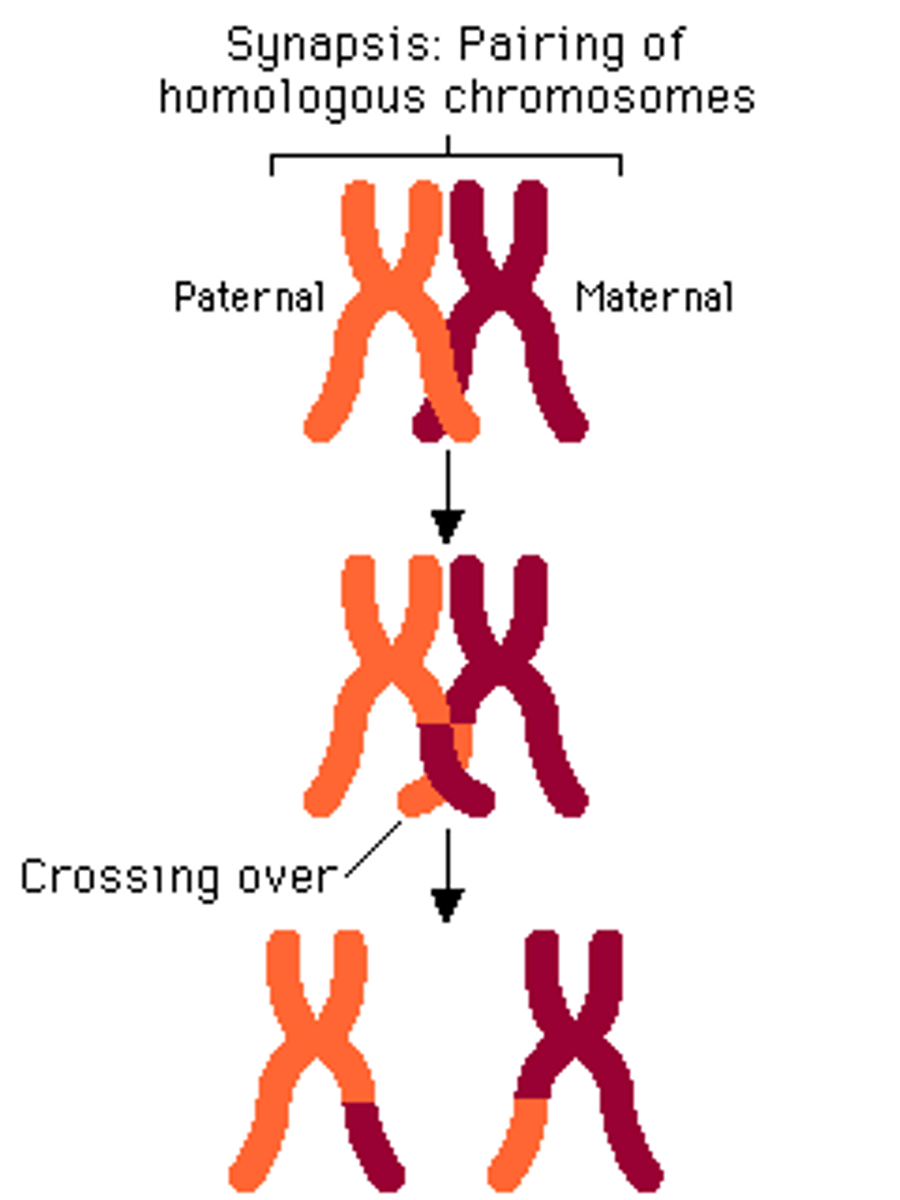
Synapsis
Pairing of homologous chromosomes
Cell loss disorders
AIDS, MI
Cell accumulation disorders
Cancer, viral infections
Necrosis
inable to maintain homeostasis. Membrane not maintained.
Apoptosis
normal physiological condition. Cell membrane maintained.
Embryonic stem cell
totipotent
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein
a channel across the membrane. Helps maintain the balance of salt and water on surface.
Significance of membranes
compartmentalization, increase efficiency
Non-membranous organelles
cytoskeleton, proteasome, ribosomes, inclusions
Cytoskeleton function
stability & movement
Alzheimer's disease
Changes in neurofilaments. Produces neurofibrillary tangles & aggregations
Acidic cytokeratin (intermediate filament involved with AlZheimers)
Epithelial. Skin-blistering disorders
Basic cytokeratin (intermediate filament involved with AlZheimers)
Epithelial. Keratoderma, corneal dystrophy
Lamins (intermediate filament involved with AlZheimers)
Cardiomyopathy, muscular dystrophies, progeria
Heterochromatin staining
dark